Abstract
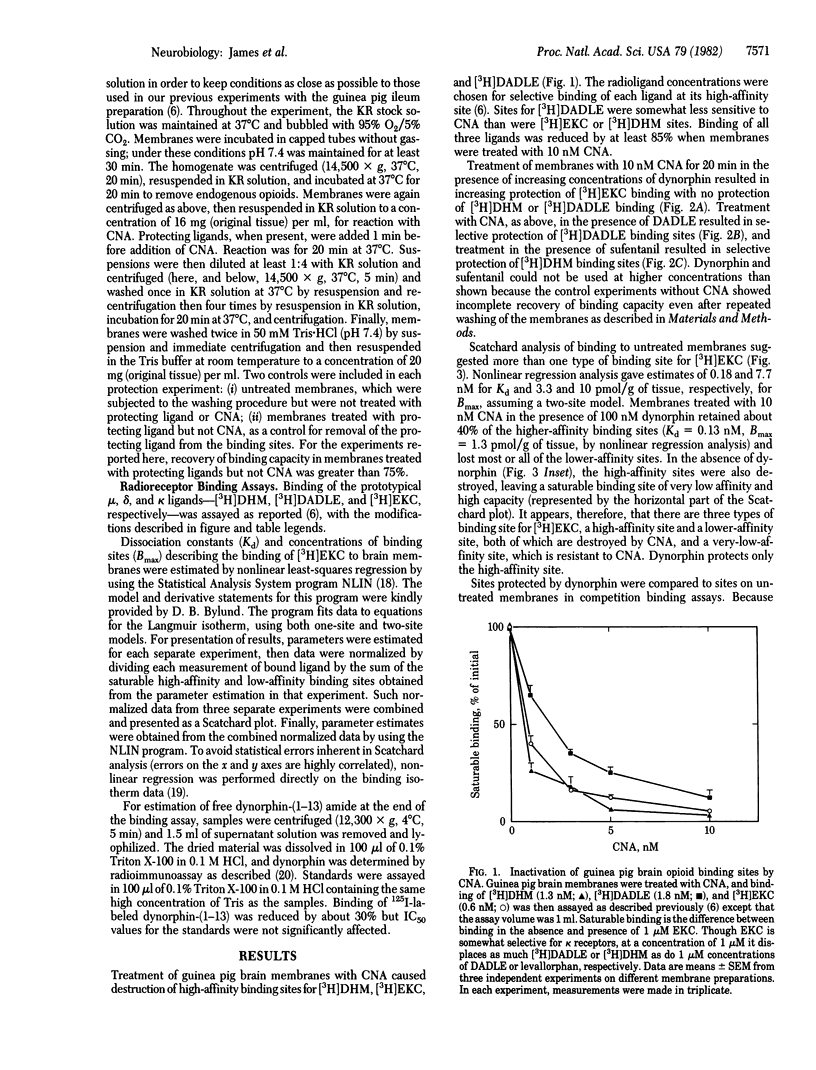
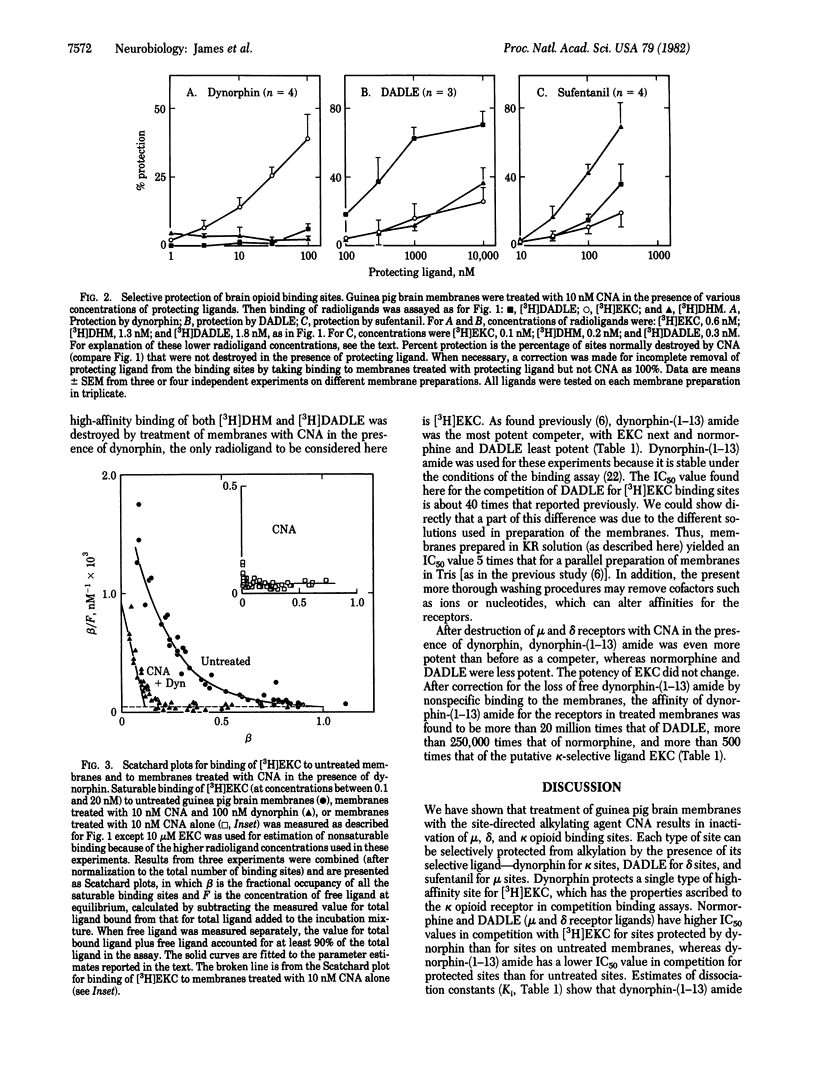
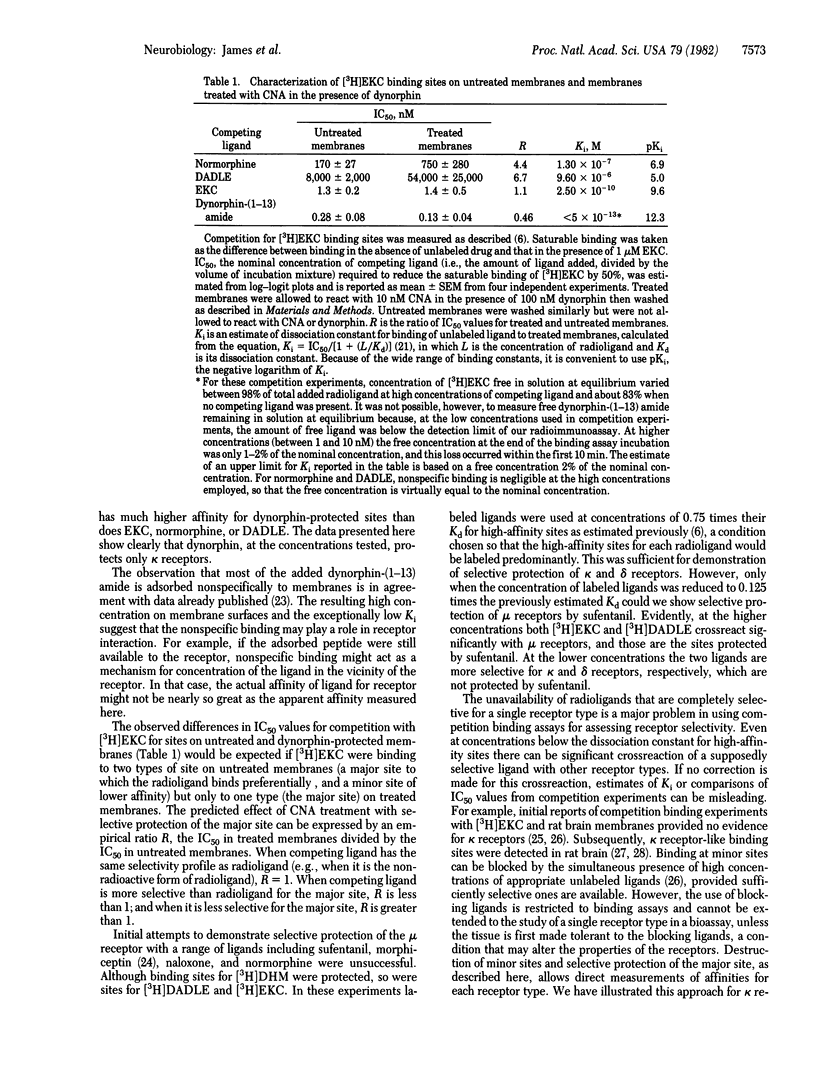
Opioid receptors on guinea pig brain membranes were alkylated by the naltrexone analogue beta-chlornaltrexamine. Binding of the prototypical mu and kappa ligands, [3H]dihydromorphine and [3H]ethylketocyclazocine, was more readily affected by the reagent than was binding of the delta ligand, 3H-labeled [D-Ala2, D-Leu5]enkephalin. Treatment of membranes with beta-chlornaltrexamine in the presence of dynorphin resulted in significant protection of [3H]ethylketocyclazocine binding sites, without protection of [3H]dihydromorphine or 3H-labeled [D-Ala2, D-Leu5]enkephalin sites. Similarly, [D-Ala2, D-Leu5]enkephalin and sufentanil selectively protected binding sites for 3H-labeled [D-Ala2, D-Leu5]enkephalin and [3H]dihydromorphine, respectively. Scatchard analysis of [3H]ethylketocyclazocine binding to untreated membranes suggested two types of binding site with 40-fold difference in affinities. Membranes treated with beta-chlornaltrexamine in the presence of dynorphin retained about 40% of the high-affinity sites and lost the low-affinity sites. Selective protection of sites with high affinity for dynorphin and ethylketocyclazocine was confirmed in competition binding assays. These results strongly suggest that the three types of opioid receptor are not interconvertible and provide further evidence that the endogenous peptide dynorphin is a highly selective ligand of the kappa opioid receptor.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowen W. D., Gentleman S., Herkenham M., Pert C. B. Interconverting mu and delta forms of the opiate receptor in rat striatal patches. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4818–4822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caruso T. P., Larson D. L., Portoghese P. S., Takemori A. E. Pharmacological studies with an alkylating narcotic agonist, chloroxymorphamine, and antagonist, chlornaltrexamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Jun;213(3):539–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Cuatrecasas P. Multiple opiate receptors. Enkephalins and morphine bind to receptors of different specificity. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2610–2618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Hazum E., Cuatrecasas P. Novel opiate binding sites selective for benzomorphan drugs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4141–4145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Hazum E., Cuatrecasas P. Possible role of distinct morphine and enkephalin receptors in mediating actins of benzomorphan drugs (putative kappa and sigma agonists). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4469–4473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Lillian A., Hazum E., Cuatrecasas P., Chang J. K. Morphiceptin (NH4-tyr-pro-phe-pro-COHN2): a potent and specific agonist for morphine (mu) receptors. Science. 1981 Apr 3;212(4490):75–77. doi: 10.1126/science.6259732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Miller R. J., Cuatrecasas P. Interaction of enkephalin with opiate receptors in intact cultured cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1978 Nov;14(6):961–970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavkin C., Goldstein A. Demonstration of a specific dynorphin receptor in guinea pig ileum myenteric plexus. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):591–593. doi: 10.1038/291591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavkin C., James I. F., Goldstein A. Dynorphin is a specific endogenous ligand of the kappa opioid receptor. Science. 1982 Jan 22;215(4531):413–415. doi: 10.1126/science.6120570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazarossian V. E., Chavkin C., Goldstein A. A specific radioimmunoassay for the novel opioid peptide dynorphin. Life Sci. 1980 Jul 7;27(1):75–86. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert P. E., Martin W. R. The effects of morphine and nalorphine-like drugs in the nondependent, morphine-dependent and cyclazocine-dependent chronic spinal dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Jul;198(1):66–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman R. R., Snyder S. H., Kuhar M. J., Young W. S., 3rd Differentiation of delta and mu opiate receptor localizations by light microscopic autoradiography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6239–6243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiller J. M., Simon E. J. Specific, high affinity [3H]ethylketocyclazocine binding in rat central nervous system: lack of evidence for kappa receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Sep;214(3):516–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen L. L., Iversen S. D., Bloom F. E. Opiate receptors influence vasopressin release from nerve terminals in rat neurohypophysis. Nature. 1980 Mar 27;284(5754):350–351. doi: 10.1038/284350a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James I. F., Chavkin C., Goldstein A. Selectivity of dynorphin for kappa opioid receptors. Life Sci. 1982 Sep 20;31(12-13):1331–1334. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90374-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Paterson S. J., Robson L. E. Characterization of the kappa-subtype of the opiate receptor in the guinea-pig brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Aug;73(4):939–949. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb08749.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law P. Y., Wu J., Koehler J. E., Loh H. H. Demonstration and characterization of opiate inhibition of the striatal adenylate cyclase. J Neurochem. 1981 May;36(5):1834–1846. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb00438.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire S., Magnan J., Regoli D. Rat vas deferens: a specific bioassay for endogenous opioid peptides. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Nov;64(3):327–329. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb08653.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. A., Waterfield A. A., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):495–499. doi: 10.1038/267495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. R., Eades C. G., Thompson J. A., Huppler R. E., Gilbert P. E. The effects of morphine- and nalorphine- like drugs in the nondependent and morphine-dependent chronic spinal dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Jun;197(3):517–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka T., Negishi K., Suda M., Sawa A., Fujino M., Wakimasu M. Evidence that dynorphin-(1-13) acts as an agonist on opioid kappa-receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Jan 22;77(2-3):137–141. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumbridge T. W., Aarons L. J., Brown J. R. Problems associated with analysis and interpretation of small molecule/macromolecule binding data. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1978 Feb;30(2):69–74. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1978.tb13164.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portoghese P. S., Larson D. L., Jiang J. B., Caruso T. P., Takemori A. E. Synthesis and pharmacologic characterization of an alkylating analogue (chlornaltrexamine) of naltrexone with ultralong-lasting narcotic antagonist properties. J Med Chem. 1979 Feb;22(2):168–173. doi: 10.1021/jm00188a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson L. E., Kosterlitz H. W. Specific protection of the binding sites of D-Ala2-D-Leu5-enkephalin (delta-receptors) and dihydromorphine (mu-receptors). Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1979 Aug 31;205(1160):425–432. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1979.0076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz R., Wüster M., Krenss H., Herz A. Lack of cross-tolerance on multiple opiate receptors in the mouse vas deferens. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Nov;18(3):395–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. R., Simon E. J. Selective protection of stereospecific enkephalin and opiate binding against inactivation by N-ethylmaleimide: evidence for two classes of opiate receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):281–284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. J., Akil H., Fischli W., Goldstein A., Zimmerman E., Nilaver G., van wimersma Griedanus T. B. Dynorphin and vasopressin: common localization in magnocellular neurons. Science. 1982 Apr 2;216(4541):85–87. doi: 10.1126/science.6121376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. J., Akil H., Ghazarossian V. E., Goldstein A. Dynorphin immunocytochemical localization in brain and peripheral nervous system: preliminary studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1260–1263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Roth K. A., Barchas J. D. Immunohistochemical distribution of alpha-neo-endorphin/dynorphin neuronal systems in rat brain: evidence for colocalization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):3062–3066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.3062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood P. L., Charleson S. E., Lane D., Hudgin R. L. Multiple opiate receptors: differential binding of mu, kappa and delta agonists. Neuropharmacology. 1981 Dec;20(12A):1215–1220. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(81)90067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood P. L., Charleson S. High affinity [3H]ethylketazocine binding: evidence for specific kappa receptors. Neuropharmacology. 1982 Mar;21(3):215–219. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(82)90190-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüster M., Rubini P., Schulz R. The preference of putative pro-enkephalins for different types of opiate receptors. Life Sci. 1981 Sep 21;29(12):1219–1227. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90226-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



