Abstract
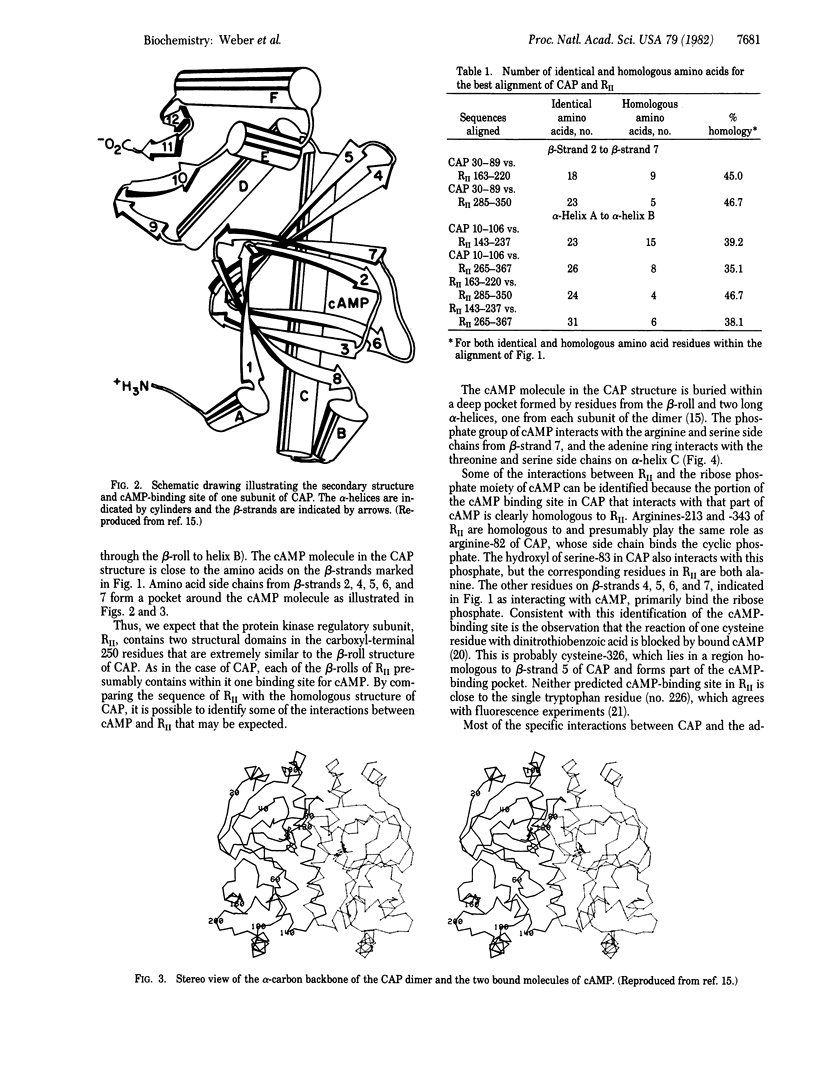
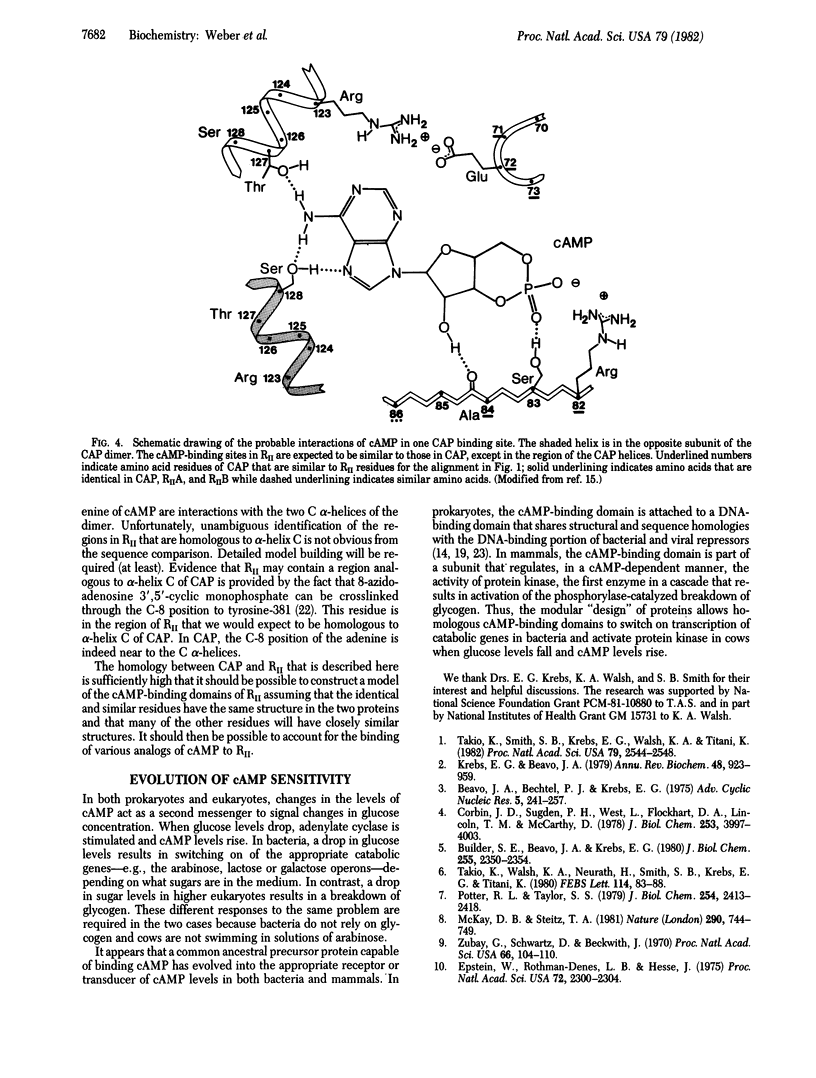
Comparison of the recently determined amino acid sequences of the regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (RII) from bovine cardiac muscle and the Escherichia coli catabolite gene activator protein (CAP) shows significant homology. This homology extends over most of the amino-terminal domain in CAP and is particularly good for the region of the beta-roll structure. The RII sequence contains two adjacent and internally homologous regions, both of which have high resemblance to the cAMP-binding domain in CAP. This suggests that the protein kinase regulatory subunit contains two cAMP-binding domains in the carboxyl-terminal region, each having a beta-roll structure similar to that in CAP. The cAMP molecule is expected to bind to the RII within a pocket formed by residues from the beta-roll, as is the case with CAP. One cAMP molecule would interact with residues from about 163 to 220, and the other cAMP would interact with amino acids in the stretch 285-350 of the RII protein kinase sequence. As the carboxyl-terminal domain of CAP shows homologies to the DNA-binding domains of other regulatory proteins, the protein appears to be of modular construction: a DNA-binding domain joined to a cAMP-binding domain.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiba H., Fujimoto S., Ozaki N. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequencing of the gene for E. coli cAMP receptor protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 25;10(4):1345–1361. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.4.1345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong R. N., Kaiser E. T. Sulfhydryl group reactivity of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate dependent protein kinase from bovine heart: a probe of holoenzyme structure. Biochemistry. 1978 Jul 11;17(14):2840–2845. doi: 10.1021/bi00607a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Builder S. E., Beavo J. A., Krebs E. G. Stoichiometry of cAMP and 1,N6-etheno-cAMP binding to protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2350–2354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Sugden P. H., West L., Flockhart D. A., Lincoln T. M., McCarthy D. Studies on the properties and mode of action of the purified regulatory subunit of bovine heart adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3997–4003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossart P., Gicquel-Sanzey B. Cloning and sequence of the crp gene of Escherichia coli K 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 25;10(4):1363–1378. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.4.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Crombrugghe B., Chen B., Anderson W., Nissley P., Gottesman M., Pastan I., Perlman R. Lac DNA, RNA polymerase and cyclic AMP receptor protein, cyclic AMP, lac repressor and inducer are the essential elements for controlled lac transcription. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 2;231(22):139–142. doi: 10.1038/newbio231139a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W., Rothman-Denes L. B., Hesse J. Adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate as mediator of catabolite repression in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2300–2304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerlavage A. R., Taylor S. S. Covalent modification of an adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate binding site of the regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase II with 8-azidoadenosine 3':5'-monophosphate. Identification of a single modified tyrosine residue. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8483–8488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Beavo J. A. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:923–959. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaPorte D. C., Builder S. E., Storm D. R. Spectroscopic studies of the cAMP binding sites of the regulatory subunits of types I and II protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2343–2349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. B., Steitz T. A. Structure of catabolite gene activator protein at 2.9 A resolution suggests binding to left-handed B-DNA. Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):744–749. doi: 10.1038/290744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. B., Weber I. T., Steitz T. A. Structure of catabolite gene activator protein at 2.9-A resolution. Incorporation of amino acid sequence and interactions with cyclic AMP. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9518–9524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D. Tests for comparing related amino-acid sequences. Cytochrome c and cytochrome c 551 . J Mol Biol. 1971 Oct 28;61(2):409–424. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90390-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musso R. E., Di Lauro R., Adhya S., de Crombrugghe B. Dual control for transcription of the galactose operon by cyclic AMP and its receptor protein at two interspersed promoters. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):847–854. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90283-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden S., Haggerty D., Stoner C. M., Kolodrubetz D., Schleif R. The Escherichia coli L-arabinose operon: binding sites of the regulatory proteins and a mechanism of positive and negative regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3346–3350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter R. L., Taylor S. S. Relationships between structural domains and function in the regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinases I and II from porcine skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2413–2418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz T. A., Ohlendorf D. H., McKay D. B., Anderson W. F., Matthews B. W. Structural similarity in the DNA-binding domains of catabolite gene activator and cro repressor proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3097–3100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takio K., Smith S. B., Krebs E. G., Walsh K. A., Titani K. Primary structure of the regulatory subunit of type II cAMP-dependent protein kinase from bovine cardiac muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2544–2548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takio K., Walsh K. A., Neurath H., Smith S. B., Krebs E. G., Titani K. The amino acid sequence of a hinge region in the regulatory subunit of bovine cardiac muscle cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase II. FEBS Lett. 1980 May 19;114(1):83–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80865-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber I. T., McKay D. B., Steitz T. A. Two helix DNA binding motif of CAP found in lac repressor and gal repressor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 25;10(16):5085–5102. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.16.5085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubay G., Schwartz D., Beckwith J. Mechanism of activation of catabolite-sensitive genes: a positive control system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 May;66(1):104–110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.1.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


