Abstract
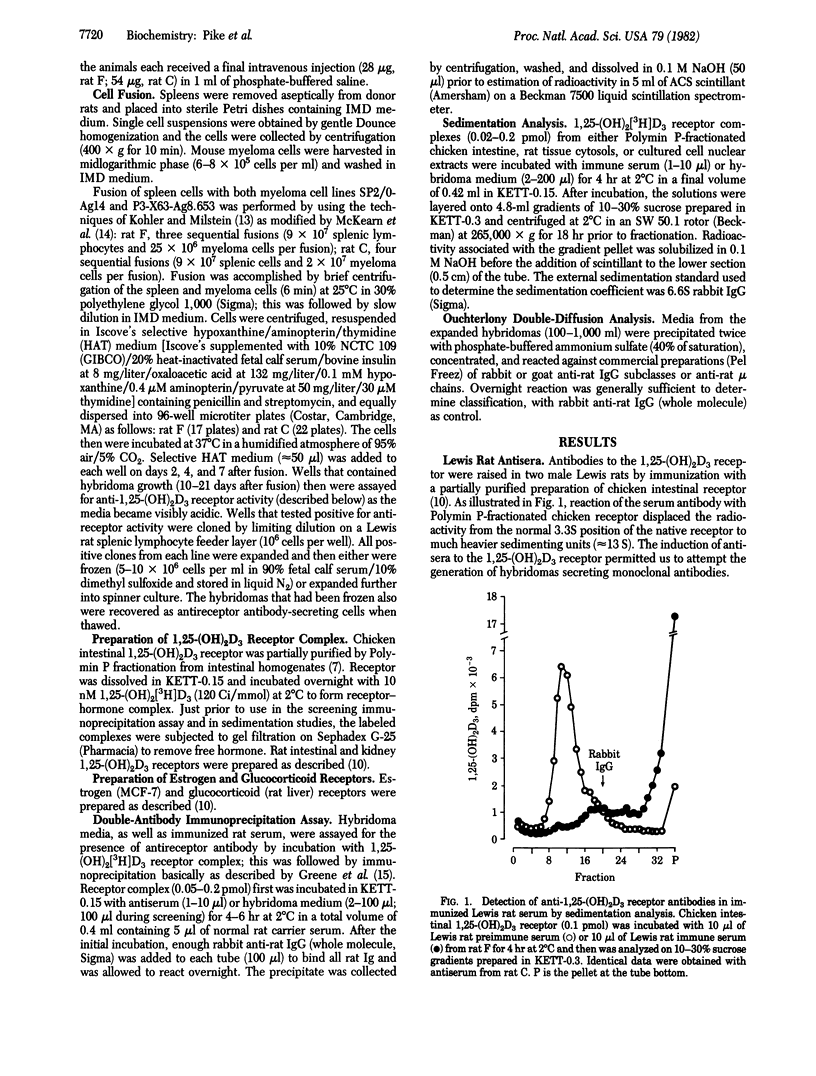
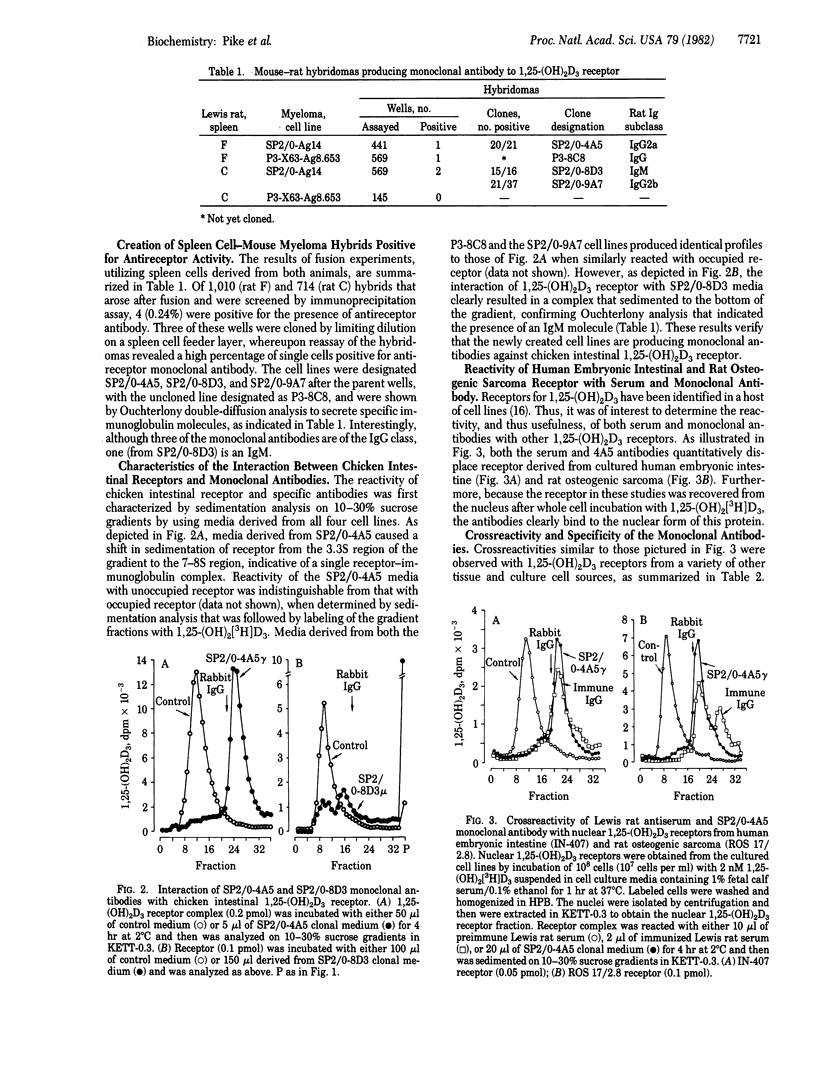
Four hybridomas that secrete monoclonal antibodies to the chicken intestinal cytoplasmic 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 [1,25-(OH)2D3] receptor have been obtained. Splenic lymphocytes, derived from two male Lewis rats expressing serum antireceptor activity after repeated immunization with a partially purified preparation of this protein, were fused with two nonsecreting murine myeloma cell lines, SP2/0-Ag14 and P3-X63-Ag8.653. Viable hybrids were screened for anti-chicken intestinal 1,25-(OH)2D3 receptor activity by incubation of hybrid media with receptor-hormone complex; this was followed by immunoprecipitation with rabbit anti-rat IgG. Of 1,724 hybridomas assayed by this technique, 4 were positive (2 derived from each animal) for the secretion of an antireceptor immunoglobulin molecule. After cloning by limiting dilution, the cell lines (designated SP2/0-4A5, P3-8C8, SP2/0-8D3, and SP2/0-9A7) were expanded into suspension culture. Antibody-induced alterations in the sedimentation pattern of the native 1,25-(OH)2D3 receptor, coupled with Ouchterlony double-diffusion techniques, indicate that SP2/0-4A5 secretes an IgG2a, SP2/0-9A7 produces an IgG2b, and P3-8C8 secretes an IgG. In contrast, SP2/0-8D3 was found to synthesize an IgM. The monoclonal antibodies react with both occupied and unoccupied chicken intestinal receptor and nuclear receptors, and they crossreact with 1,25-(OH)2D3 receptors from a wide variety of tissue and cultured cell types, including human 1,25-(OH)2D3 receptors. These immunological reagents should prove valuable in the elucidation of the molecular action of 1,25-(OH)2D3.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brumbaugh P. F., Haussler M. R. 1 Alpha,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol receptors in intestine. I. Association of 1 alpha,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol with intestinal mucosa chromatin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 25;249(4):1251–1257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brumbaugh P. F., Haussler M. R. Specific binding of 1alpha,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol to nuclear components of chick intestine. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1588–1594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler J. S., Pike J. W., Haussler M. R. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptors in rat kidney cytosol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Oct 12;90(3):1057–1063. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91933-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eil C., Liberman U. A., Rosen J. F., Marx S. J. A cellular defect in hereditary vitamin-D-dependent rickets type II: defective nuclear uptake of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D in cultured skin fibroblasts. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jun 25;304(26):1588–1591. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198106253042608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen H. J. An antiserum to the rat liver glucocorticoid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3893–3897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene G. L., Closs L. E., DeSombre E. R., Jensen E. V. Antibodies to estrophilin: comparison between rabbit and goat antisera. J Steroid Biochem. 1979 Jul;11(1A):333–341. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(79)90316-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene G. L., Fitch F. W., Jensen E. V. Monoclonal antibodies to estrophilin: probes for the study of estrogen receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):157–161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene G. L., Nolan C., Engler J. P., Jensen E. V. Monoclonal antibodies to human estrogen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5115–5119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haussler M. R., Chandler J. S., Hagan L. A., Pike J. W. Use of chick kidney to enzymatically generate radiolabeled 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D and other vitamin D metabolites. Methods Enzymol. 1980;67:529–542. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)67066-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haussler M. R., McCain T. A. Basic and clinical concepts related to vitamin D metabolism and action (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1977 Nov 3;297(18):974–983. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197711032971804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haussler M. R., McCain T. A. Basic and clinical concepts related to vitamin D metabolism and action (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1977 Nov 10;297(19):1041–1050. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197711102971906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haussler M. R., Pike J. W., Chandler J. S., Manolagas S. C., Deftos L. J. Molecular action of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3: new cultured cell models. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;372:502–517. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb15501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kream B. E., Jose M., Yamada S., DeLuca H. F. A specific high-affinity binding macromolecule for 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in fetal bone. Science. 1977 Sep 9;197(4308):1086–1088. doi: 10.1126/science.887939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logeat F., Hai M. T., Milgrom E. Antibodies to rabbit progesterone receptor: crossreaction with human receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1426–1430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKearn T. J., Fitch F. W., Smilek D. E., Sarmiento M., Stuart F. P. Properties of rat anti-MHC antibodies produced by cloned rat-mouse hybridomas. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:91–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00290.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNutt K. W., Haussler M. R. Nutritional effectiveness of 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol in preventing rickets in chicks. J Nutr. 1973 May;103(5):681–689. doi: 10.1093/jn/103.5.681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike J. W., Haussler M. R. Purification of chicken intestinal receptor for 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5485–5489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. U., DeLuca H. F. Purification of chicken intestinal receptor for 1 alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 to apparent homogeneity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):16–20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer R., Charman M., Lawson D. E., Emtage J. S. Production and properties of vitamin-D-induced mRNA for chick calcium-binding protein. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Dec 11;71(2):399–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11127.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



