Abstract
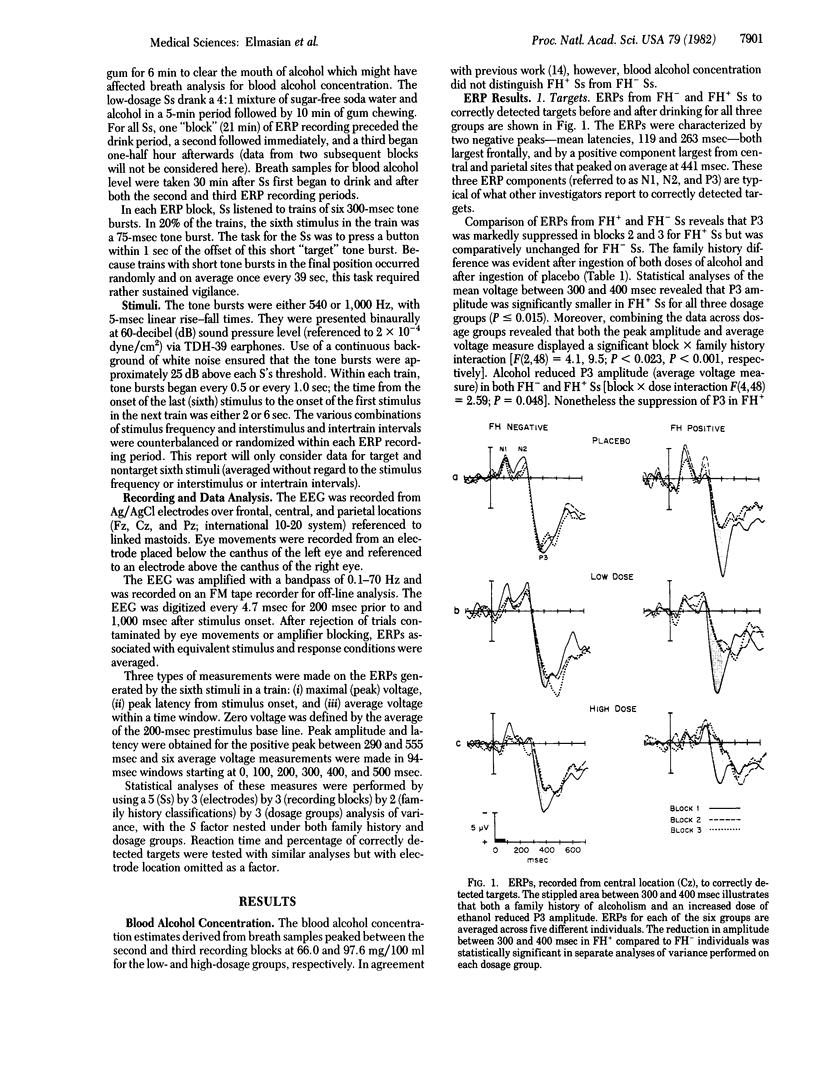
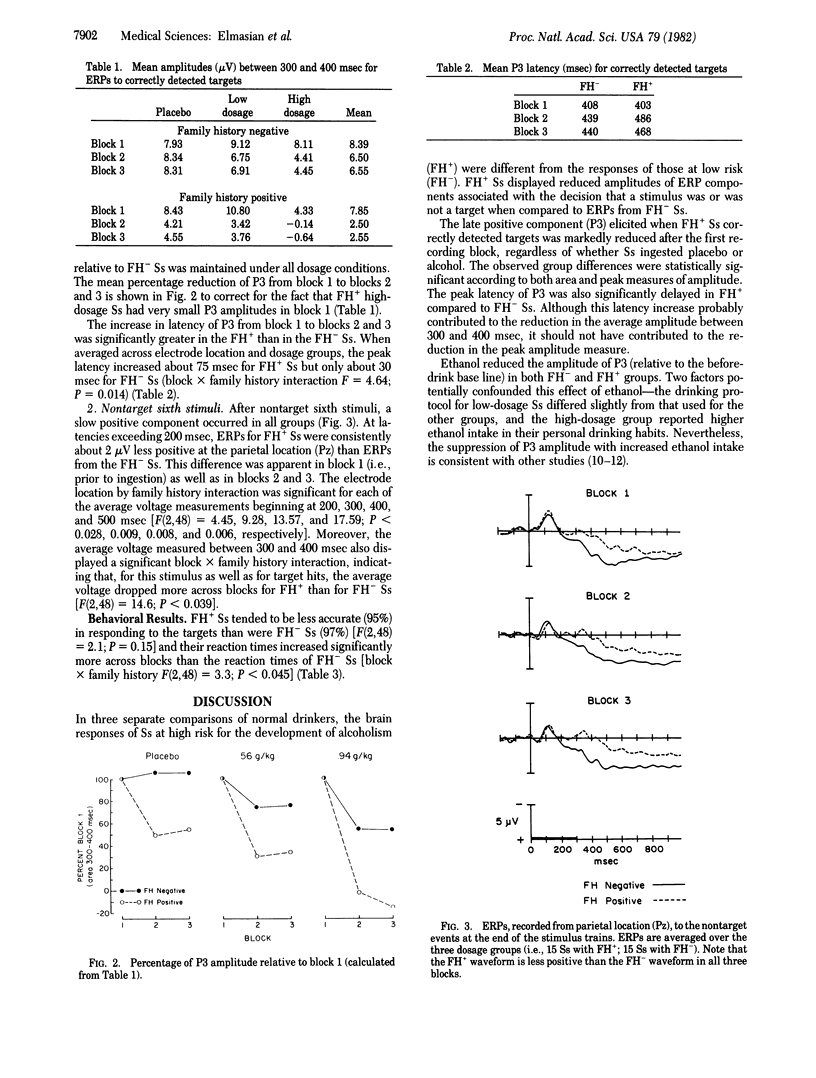
Event-related brain potentials (ERPs) from normal drinkers with and without a family history of alcoholism were compared. Three separate groups of 10 subjects each (5 with and 5 without a family history of alcoholism) ingested either a placebo or ethanol at 0.56 or 0.94 g/kg. In each comparison, ERP components elicited in conjunction with subjects' decisions about task-relevant stimuli were of significantly reduced amplitude in individuals with a family history of alcoholism. Additionally, both the latency of the positive component and reaction times to correctly detected targets were significantly later in individuals with a positive history of alcoholism than in those without such a history. These group differences were apparent both with and without a challenge of alcohol. The data suggest that brain functions are different in individuals at high and low risk for the development of alcoholism (i.e., those with and without a family history of alcoholism, respectively).
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cadoret R. J., Cain C. A., Grove W. M. Development of alcoholism in adoptees raised apart from alcoholic biologic relatives. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1980 May;37(5):561–563. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1980.01780180075008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloninger C. R., Bohman M., Sigvardsson S. Inheritance of alcohol abuse. Cross-fostering analysis of adopted men. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1981 Aug;38(8):861–868. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1981.01780330019001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotton N. S. The familial incidence of alcoholism: a review. J Stud Alcohol. 1979;40(1):89–116. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1979.40.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitrich R. A., McClearn G. E. Neurobiological and genetic aspects of the etiology of alcoholism. Fed Proc. 1981 May 15;40(7):2051–2055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan-Johnson C. C. Young Psychophysiologist Award address, 1980. P300 latency: a new metric of information processing. Psychophysiology. 1981 May;18(3):207–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.1981.tb03020.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielli W. F., Jr, Mednick S. A., Volavka J., Pollock V. E., Schulsinger F., Itil T. M. Electroencephalograms in children of alcoholic fathers. Psychophysiology. 1982 Jul;19(4):404–407. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.1982.tb02495.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin D. W. Alcoholism and heredity. A review and hypothesis. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1979 Jan;36(1):57–61. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1979.01780010063006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halgren E., Squires N. K., Wilson C. L., Rohrbaugh J. W., Babb T. L., Crandall P. H. Endogenous potentials generated in the human hippocampal formation and amygdala by infrequent events. Science. 1980 Nov 14;210(4471):803–805. doi: 10.1126/science.7434000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hari R., Sams M., Järvilehto T. Auditory evoked transient and sustained potentials in the human EEG: II. Effects of small doses of ethanol. Psychiatry Res. 1979 Dec;1(3):307–312. doi: 10.1016/0165-1781(79)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hrubec Z., Omenn G. S. Evidence of genetic predisposition to alcoholic cirrhosis and psychosis: twin concordances for alcoholism and its biological end points by zygosity among male veterans. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1981 Spring;5(2):207–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1981.tb04890.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isreal J. B., Chesney G. L., Wickens C. D., Donchin E. P300 and tracking difficulty: evidence for multiple resources in dual-task performance. Psychophysiology. 1980 May;17(3):259–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.1980.tb00146.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutas M., McCarthy G., Donchin E. Augmenting mental chronometry: the P300 as a measure of stimulus evaluation time. Science. 1977 Aug 19;197(4305):792–795. doi: 10.1126/science.887923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parasuraman R., Richer F., Beatty J. Detection and recognition: Concurrent processes in perception. Percept Psychophys. 1982 Jan;31(1):1–12. doi: 10.3758/bf03206196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferbaum A., Horvath T. B., Roth W. T., Kopell B. S. Event-related potential changes in chronic alcoholics. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1979 Dec;47(6):637–647. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(79)90292-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard W. S. Psychophysiology of P300. Psychol Bull. 1981 May;89(3):506–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth W. T., Tinklenberg J. R., Kopell B. S. Ethanol and marihuana effects on event-related potentials in a memory retrieval paradigm. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1977 Mar;42(3):381–388. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(77)90174-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuckit M. A. Peak blood alcohol levels in men at high risk for the future development of alcoholism. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1981 Jan;5(1):64–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1981.tb04866.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen S., Palmer M., Dunwiddie T., Hoffer B. Electrophysiological correlates of ethanol-induced sedation in differentially sensitive lines of mice. Science. 1980 Dec 5;210(4474):1143–1145. doi: 10.1126/science.7444444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarter R. E., McBride H., Buonpane N., Schneider D. U. Differentiation of alcoholics. Childhood history of minimal brain dysfunction, family history, and drinking pattern. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1977 Jul;34(7):761–768. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1977.01770190023002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]