Abstract
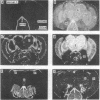
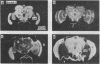
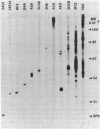
A panel of 148 monoclonal antibodies directed against Drosophila neural antigens has been prepared by using mice immunized with homogenates of Drosophila tissue. Antibodies were screened immunohistochemically on cryostat sections of fly heads. A large diversity of staining patterns was observed. Some antigens were broadly distributed among tissues; others were highly specific to nerve fibers, neuropil, muscle, the tracheal system, cell nuclei, photoreceptors, or other structures. The antigens for many of the antibodies have been identified on immunoblots. Monoclonal antibodies that identify specific molecules within the nervous system should prove useful in the study of the molecular genetics of neural development.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braitenberg V. Patterns of projection in the visual system of the fly. I. Retina-lamina projections. Exp Brain Res. 1967;3(3):271–298. doi: 10.1007/BF00235589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Niday E., Matus A. Monoclonal antibodies identify novel neural antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2410–2414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matus A., Pehling G., Ackermann M., Maeder J. Brain postsynaptic densities: the relationship to glial and neuronal filaments. J Cell Biol. 1980 Nov;87(2 Pt 1):346–359. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.2.346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ready D. F., Hanson T. E., Benzer S. Development of the Drosophila retina, a neurocrystalline lattice. Dev Biol. 1976 Oct 15;53(2):217–240. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90225-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trisler G. D., Schneider M. D., Nirenberg M. A topographic gradient of molecules in retina can be used to identify neuron position. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2145–2149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trujillo-Cenóz O., Melamed J. Compound eye of dipterans: anatomical basis for integration--an electron microscope study. J Ultrastruct Res. 1966 Oct;16(3):395–398. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(66)80071-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox M., Brower D. L., Smith R. J. A position-specific cell surface antigen in the drosophila wing imaginal disc. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90240-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zipser B., McKay R. Monoclonal antibodies distinguish identifiable neurones in the leech. Nature. 1981 Feb 12;289(5798):549–554. doi: 10.1038/289549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]