Abstract
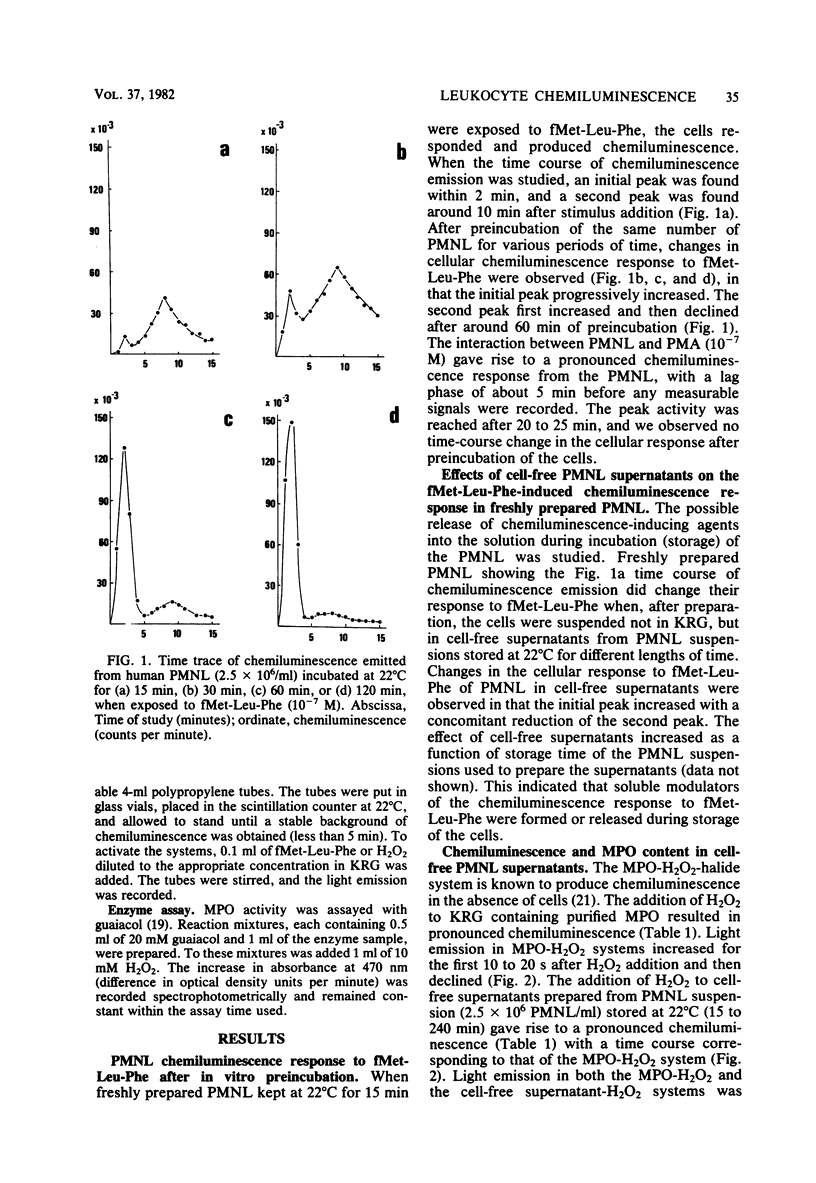
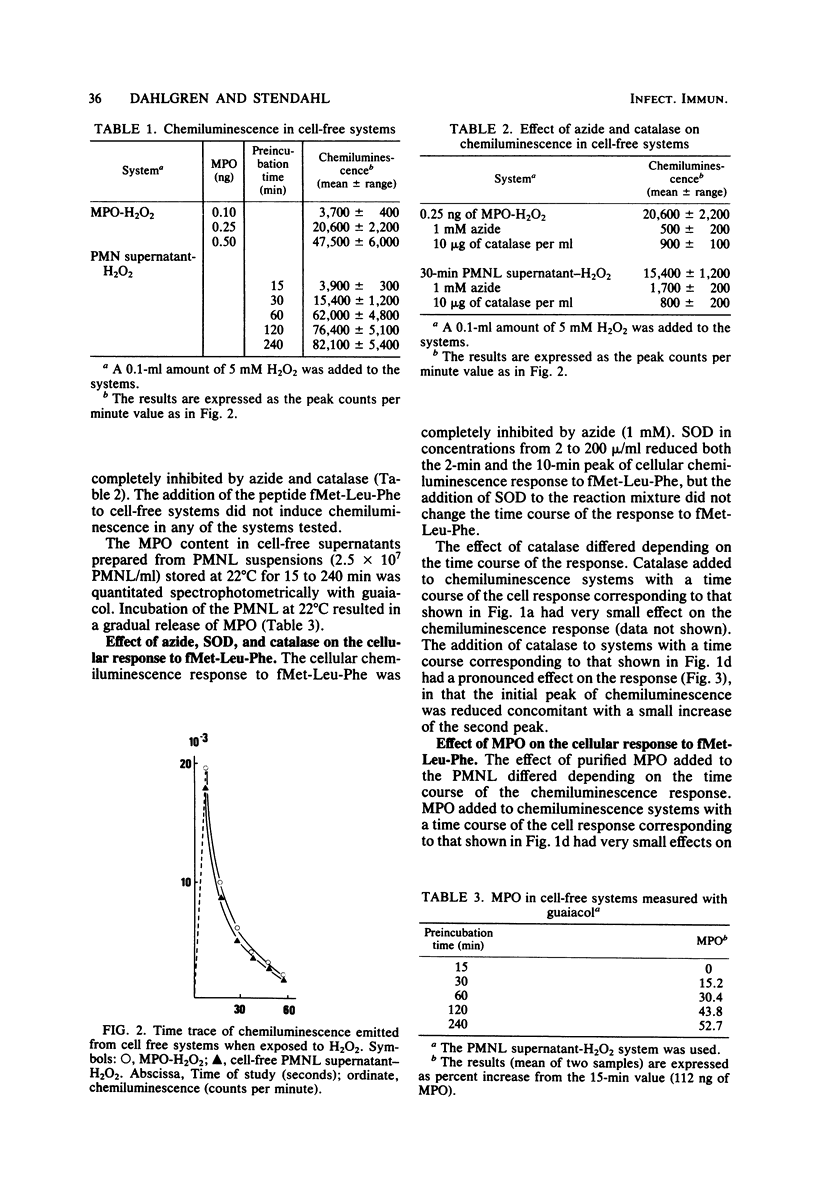
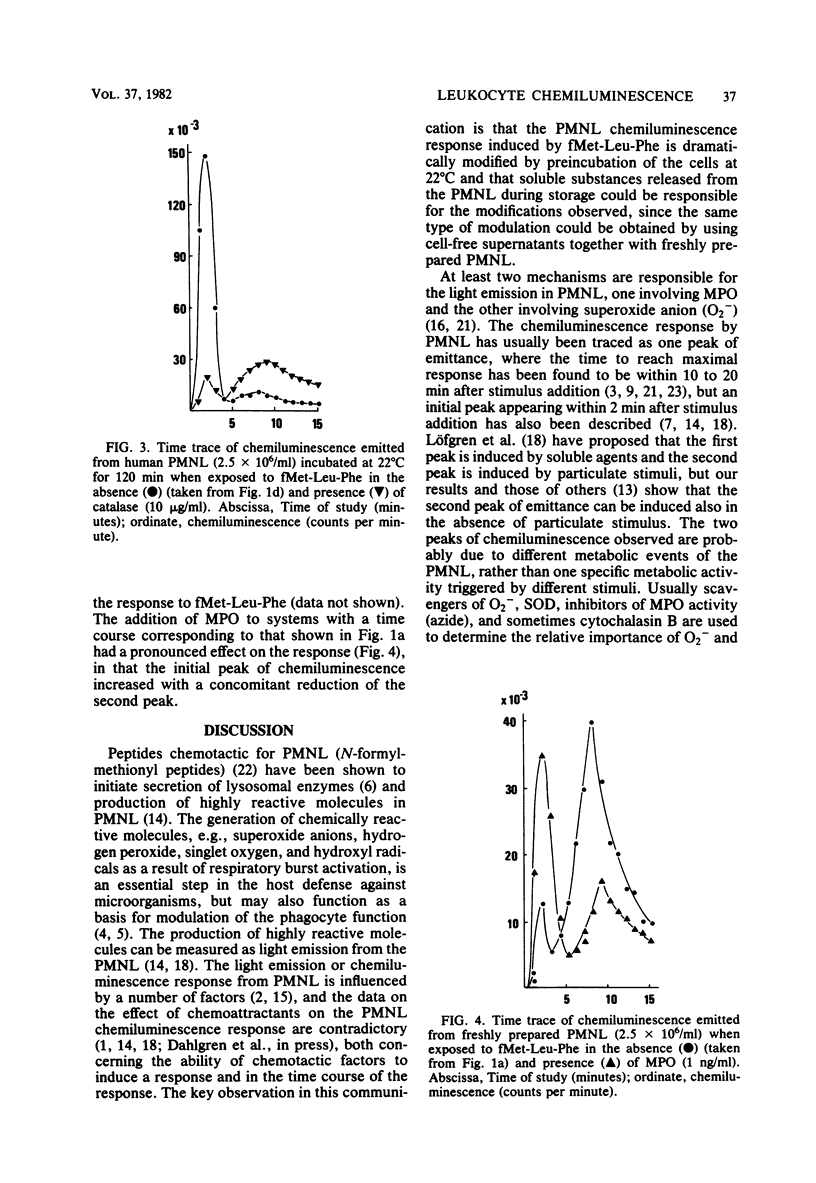
When polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNL) and soluble or particulate matter interact, the cells produce chemiluminescence. The chemotactic peptide formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine induced a two-peak chemiluminescence response in PMNL. The response was modified, both in magnitude and in the time course of the response, when PMNL were incubated at 22 degrees C for 15 to 120 min before the addition of stimulus. The cellular response to formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine was also changed by the addition of cell-free supernatants from stored PMNL suspensions to freshly prepared PMNL before the addition of formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine. This indicated that PMNL during storage released substances that changed the chemiluminescence response. A similar change could be obtained by addition of purified myeloperoxidase to freshly prepared PMNL before the addition of stimulus, indicating that the myeloperoxidase-hydrogen peroxide system can function as a modulator of the cellular response to chemotactic factors.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allred C. D., Hill H. R. Effect of chemoattractants on chemiluminescence. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):833–838. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.833-838.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen B. R., Amirault H. J. Important variables in granulocyte chemiluminescence. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Oct;162(1):139–145. doi: 10.3181/00379727-162-40633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen B. R., Brendzel A. M., Lint T. F. Chemiluminescence spectra of human myeloperoxidase and polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):62–66. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.62-66.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R., Gatner E. M., van Rensburg C. E., Grabow G., Imkamp F. M., Kok S. K., van Rensburg A. J. In vitro and in vivo effects of dapsone on neutrophil and lymphocyte functions in normal individuals and patients with lepromatous leprosy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Apr;19(4):495–503. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.4.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baehner R. L., Boxer L. A., Allen J. M., Davis J. Autooxidation as a basis for altered function by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Blood. 1977 Aug;50(2):327–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker E. L. A multifunctional receptor on the neutrophil for synthetic chemotactic oligopeptides. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1979 Dec;26(Suppl):701–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beswick P. H., Kay A. B. The effects of an ECF-A and formyl methionyl chemotactic peptides on oxidative metabolism of human eosinophils and neutrophils. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Feb;43(2):399–407. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheson B. D., Christensen R. L., Sperling R., Kohler B. E., Babior B. M. The origin of the chemiluminescence of phagocytosing granulocytes. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):789–796. doi: 10.1172/JCI108530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Szot S., Venkatasubramanian K., Schiffmann E. Chemotactic factor inactivation by myeloperoxidase-mediated oxidation of methionine. J Immunol. 1980 Apr;124(4):2020–2026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- English D., Roloff J. S., Lukens J. N. Regulation of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte superoxide release by cellular responses to chemotactic peptides. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):165–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher M. P., Gallin J. I. Degranulating stimuli increase the availability of receptors on human neutrophils for the chemoattractant f-met-leu-phe. J Immunol. 1980 Apr;124(4):1585–1588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvath L., Amirault H. J., Andersen B. R. Chemiluminescence of human and canine polymorphonuclear leukocytes in the absence of phagocytosis. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1145–1154. doi: 10.1172/JCI109029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch G. E., Gardner D. E., Menzel D. B. Chemiluminescence of phagocytic cells caused by N-formylmethionyl peptides. J Exp Med. 1978 Jan 1;147(1):182–195. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.1.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato T., Wokalek H., Schöpf E., Eggert H., Ernst M., Rietschel E. T., Fischer H. Measurement of chemiluminescence in freshly drawn human blood. I. Role of granulocytes, platelets, and plasma factors in zymosan-induced chemiluminescence. Klin Wochenschr. 1981 Mar 2;59(5):203–221. doi: 10.1007/BF01476577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao C. S., Freer R. J. Cryptic receptors for chemotactic peptides in rabbit neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Mar 28;93(2):566–571. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91114-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löfgren S., Tärnvik A., Carlsson J. Influence of complement on the chemiluminescent response of human leukocytes to immune complex. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):335–341. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.335-341.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRipley R. J., Sbarra A. J. Role of the phagocyte in host-parasite interactions. XII. Hydrogen peroxide-myeloperoxidase bactericidal system in the phagocyte. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1425–1430. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1425-1430.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root R. K., Cohen M. S. The microbicidal mechanisms of human neutrophils and eosinophils. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 May-Jun;3(3):565–598. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.3.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen H., Klebanoff S. J. Chemiluminescence and superoxide production by myeloperoxidase-deficient leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):50–60. doi: 10.1172/JCI108458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann E., Corcoran B. A., Wahl S. M. N-formylmethionyl peptides as chemoattractants for leucocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1059–1062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb L. S., Keele B. B., Jr, Johnston R. B., Jr Inhibition of phagocytosis-associated chemiluminescence by superoxide dismutase. Infect Immun. 1974 Jun;9(6):1051–1056. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.6.1051-1056.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. J., Cole P. J. The onset of polymorphonuclear leucocyte membrane-stimulated metabolic activity. Immunology. 1981 Aug;43(4):733–739. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrogemann K., Weidemann M. J., Ketelsen U. P., Wekerle H., Fischer H. Chemiluminescence and immune cell activation. II. Enhancement of concanavalin A-induced chemiluminescence following in vitro preincubation of rat thymocytes; dependency on macrophage-lymphocyte interaction. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Jan;10(1):36–40. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



