Abstract
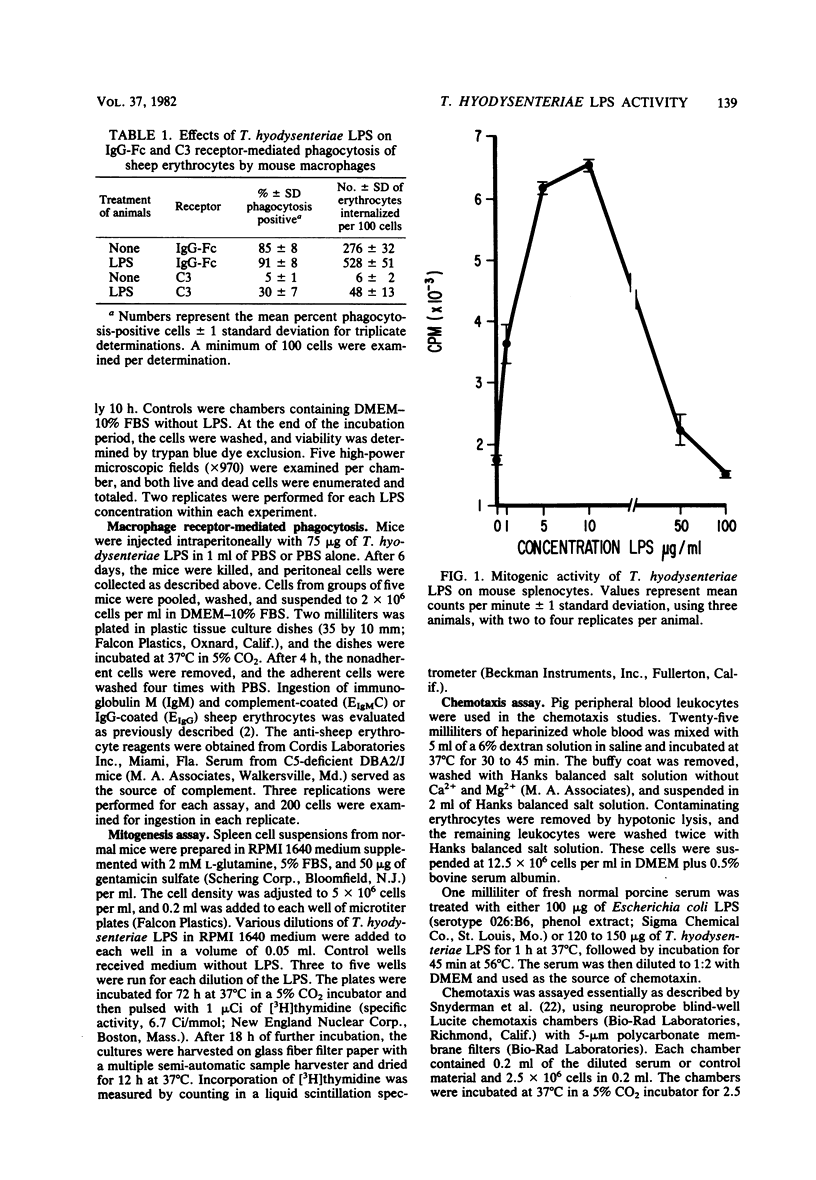
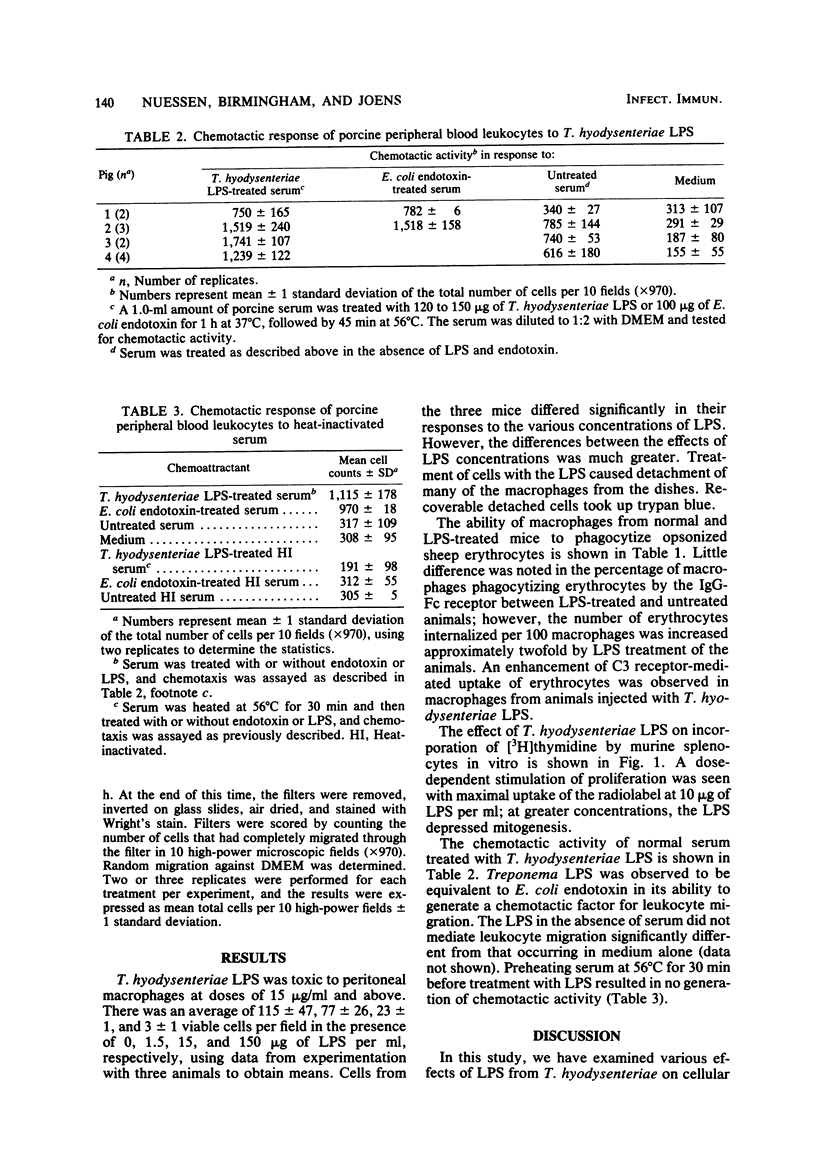
A lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was obtained from pathogenic Treponema hyodysenteriae by hot phenol-water extraction. Various effects of the LPS on host cells were examined in vitro. Toxicity for mouse peritoneal macrophages was observed after 10 h of incubation at concentrations as low as 15 micrograms of the LPS per ml. Marked enhancement of both complement (C3) and immunoglobulin G-Fc receptor-mediated internalization was noted in macrophages obtained from mice injected 6 days previously with 75 micrograms of the material. Incorporation of [3H]thymidine into murine splenocytes was elevated approximately fourfold when splenocytes were treated with 5 to 10 micrograms of LPS per ml. Incubation of the LPS with normal porcine serum resulted in the generation of a factor(s) that stimulated the migration of porcine leukocytes. Generation of the chemotactic activity was inhibited by heating the serum at 56 degrees C for 30 min before treatment with LPS. The results suggest that T. hyodysenteriae contains an LPS that is biologically active.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baum D. H., Joens L. A. Serotypes of beta-hemolytic Treponema hyodysenteriae. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):792–796. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.792-796.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birmingham J. R., Jeska E. L. Characterization of macrophage functions in mice infected with Brucella abortus. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1079–1083. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1079-1083.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bladen H. A., Hampp E. G. Ultrastructure of Treponema microdentium and Borrelia vincentii. J Bacteriol. 1964 May;87(5):1180–1191. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.5.1180-1191.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryceson A. D., Cooper K. E., Warrell D. A., Perine P. L., Parry E. H. Studies of the mechanism of the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction in louse-borne relapsing fever: evidence for the presence of circulating Borrelia endotoxin. Clin Sci. 1972 Sep;43(3):343–354. doi: 10.1042/cs0430343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIANSEN A. H. Studies on the antigenic structure of Treponema pallidum. 2. Isolation and purification of polysaccharides from Reiter's apathogenic strain. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1962;56:166–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'ALESSANDRO G., DEL CARPIO C. A lipopolysaccharide antigen of the Treponema. Nature. 1958 Apr 5;181(4614):991–992. doi: 10.1038/181991b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finco D. R., Low D. G. Endotoxin properties of Leptospira canicola. Am J Vet Res. 1967 Nov;28(127):1863–1872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand J. A., Elin R. J., Berry F. W., Jr, Frank M. M. Endotoxemia associated with the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction. N Engl J Med. 1976 Jul 22;295(4):211–213. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197607222950409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glode L. M., Jacques A., Mergenhagen S. E., Rosenstreich D. L. Resistance of macrophages from C3H/HeJ mice to the in vitro cytotoxic effects of endotoxin. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):162–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEYMAN A., SHELDON W. H., EVANS L. D. Pathogenesis of the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction; a review of clinical and experimental observations. Br J Vener Dis. 1952 Jun;28(2):50–60. doi: 10.1136/sti.28.2.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C. Anatomy and chemistry of spirochetes. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):114–160. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.114-160.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S. W., Zey P. N. Ultrastructure of lipopolysaccharide isolated from Treponema pallidum. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):838–844. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.838-844.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joens L. A., Nord N. A., Kinyon J. M., Egan I. T. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibody to Treponema hyodysenteriae antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):249–252. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.249-252.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LISTGARTEN M. A., SOCRANSKY S. S. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF AXIAL FIBRILS, OUTER ENVELOPE, AND CELL DIVISION OF CERTAIN ORAL SPIROCHETES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1087–1103. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1087-1103.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERGENHAGEN S. E., HAMPP E. G., SCHERP H. W. Preparation and biological activities of endotoxins from oral bacteria. J Infect Dis. 1961 May-Jun;108:304–310. doi: 10.1093/infdis/108.3.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayberry W. R. Hydroxy fatty acids in Bacteroides species: D-(--)-3-hydroxy-15-methylhexadecanoate and its homologs. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):582–587. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.582-587.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ryan J. L. Bacterial endotoxins and host immune responses. Adv Immunol. 1979;28:293–450. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60802-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ulevitch R. J. The effects of bacterial endotoxins on host mediation systems. A review. Am J Pathol. 1978 Nov;93(2):526–618. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman R., Altman L. C., Hausman M. S., Mergenhagen S. E. Human mononuclear leukocyte chemotaxis: a quantitative assay for humoral and cellular chemotactic factors. J Immunol. 1972 Mar;108(3):857–860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



