Abstract
Background
Anthrax lethal toxin (LT), produced by the Gram-positive bacterium Bacillus anthracis, is a highly effective zinc dependent metalloprotease that cleaves the N-terminus of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases (MAPKK or MEKs) and is known to play a role in impairing the host immune system during an inhalation anthrax infection. Here, we present the transcriptional responses of LT treated human monocytes in order to further elucidate the mechanisms of LT inhibition on the host immune system.
Results
Western Blot analysis demonstrated cleavage of endogenous MEK1 and MEK3 when human monocytes were treated with 500 ng/mL LT for four hours, proving their susceptibility to anthrax lethal toxin. Furthermore, staining with annexin V and propidium iodide revealed that LT treatment did not induce human peripheral monocyte apoptosis or necrosis. Using Affymetrix Human Genome U133 Plus 2.0 Arrays, we identified over 820 probe sets differentially regulated after LT treatment at the p <0.001 significance level, interrupting the normal transduction of over 60 known pathways. As expected, the MAPKK signaling pathway was most drastically affected by LT, but numerous genes outside the well-recognized pathways were also influenced by LT including the IL-18 signaling pathway, Toll-like receptor pathway and the IFN alpha signaling pathway. Multiple genes involved in actin regulation, signal transduction, transcriptional regulation and cytokine signaling were identified after treatment with anthrax LT.
Conclusion
We conclude LT directly targets human peripheral monocytes and causes multiple aberrant gene responses that would be expected to be associated with defects in human monocyte’s normal signaling transduction pathways and function. This study provides further insights into the mechanisms associated with the host immune system collapse during an anthrax infection, and suggests that anthrax LT may have additional downstream targets outside the well-known MAPK pathway.
Background
Bacillus anthracis, the causative agent of anthrax, is a gram-positive bacterium that is naturally found in the soil, and rarely affects the human population. Unfortunately, deliberate dissemination of anthrax spores is capable of delivering a highly potent and lethal air-borne bioterrorist agent, as documented in the 2001 U.S. anthrax attacks. Inhalation anthrax is a highly fatal, acute disease characterized by a rapid onset of systemic shock and ultimately death [1].
The most virulent strains of B. anthracis contain two plasmids, pXO2 and pXO1, encoding an antiphagocytic poly-D-glutamic acid capsule and three exotoxins: lethal factor, edema factor and protective antigen [2]. Protective antigen is an 83 kDa protein that is known to bind to two host cell receptors, TEM-8 and CMG-2, facilitating the entry of edema and/or lethal factor into host cells [3]. Lethal factor is a 90 kDa zinc-dependent metalloprotease that cleaves the N-terminus of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases (MAPKKs or MEKs) [4,5]. Edema factor is an 89 kDa adenylate cyclase that increases intracellular cAMP levels [6].
Previous studies using anthrax animal models have documented resistance to anthrax lethal toxin (LT) through depletion of host macrophages, suggesting that these cells play a critical role in anthrax LT induced lethality [7,8]. LT has also been shown to suppress cytokine responses by peripheral blood mononuclear cells, induce macrophage apoptosis, and prevent monocyte proliferation and differentiation [1,9,10]. Inhalation anthrax cases present clinical manifestations indicative of host immune collapse in humans and in nonhuman primate studies [11-13]. However, more recent studies investigating human monocytes and macrophages have suggested human alveolar macrophages are resistant to LT, and undifferentiated human monocytic cell lines are resistant to LT-induced death [10,14]. LT’s targeting of human monocytes/macrophages could help to explain the rapid onset of fatal symptoms and host demise during an inhalation anthrax infection, but the exact effects LT exerts on human peripheral monocytes, along with the mechanisms underlying the impairment of the host immune cell’s responses, have yet to be fully determined.
Previous studies investigating LT treated murine macrophages have shown a broad range in transcriptional effects induced by LT. These studies concluded LT-induced changes in macrophage inflammation, signaling, and transcription factors, along with changes in the immune response by macrophages. This study discovered the down regulation of CD-137 after LT treatment, shown to play a role in monocyte proliferation in response to LPS, and up regulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor type I, which results in fibrin deposits, massive imbalances in coagulation, and, in some instances, multi-organ failure [15,16]. Another study has measured the transcriptional responses of THP-1 cells after B. anthracis spore exposure, finding toxigenic B. anthracis strains suppress the cell signaling responses to infection [17].
Blood monocytes are mononuclear cells that play a major role in the host immune response through regulation of inflammatory responses, secretion of cytokine and antimicrobial factors, and direct pathogen clearance [18]. Monocytes are derived from monoblasts in the bone marrow, and circulate in the blood for 1-2 days before they migrate into tissues where they replenish the macrophage and dendritic pools [19-21]. Here, we determined human monocyte susceptibility to LT by demonstrating cleavage of MEKs, and utilized Affymetrix GeneChip® Human Genome U133 Plus 2.0 Arrays in order to identify additional mechanisms of LT impairment on the transcriptional responses of human peripheral monocytes. The arrays contained 54,675 probe sets representing over 22,000 of the best characterized human genes, providing extensive insights into the mechanisms behind LT induced dysfunction of human peripheral monocytes.
This study is the first to determine direct human monocyte susceptibility via cleavage of MEKs, along with the analysis of the transcriptional responses, to anthrax LT. The mechanisms of LT impairment on human peripheral monocytes will help elucidate the roles monocytes contribute during the host immune system collapse documented during an anthrax infection. The transcriptional analysis will serve to not only unravel the mechanisms behind the rapid onset of death in anthrax victims, but will also potentially provide new targets for controlling inflammation and enhancing host defense.
Results and discussion
Monocyte purity, apoptosis and susceptibility to anthrax LT
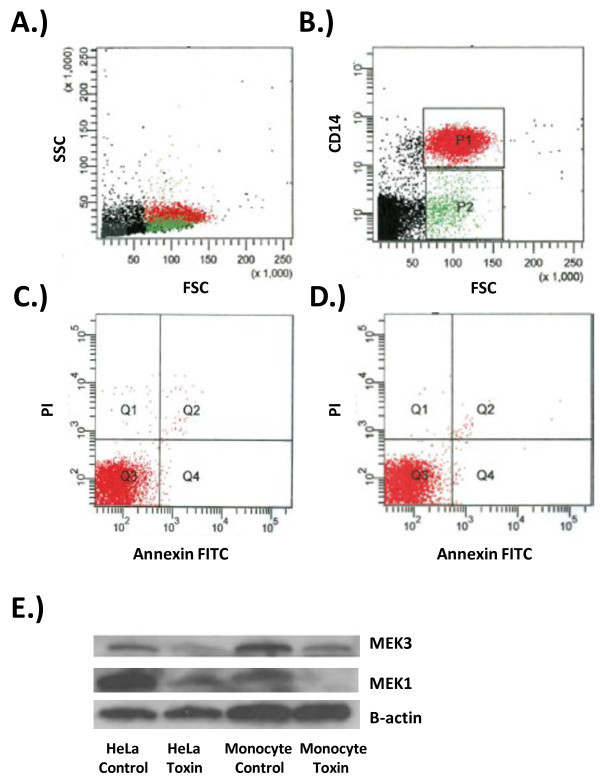
In order to first determine monocyte cell purity, isolated cells were analyzed using flow cytometry and gated using forward and side scatter, along with the monocytic marker, CD14. It was found that monocytes were isolated with a >85% purity (Figure 1A and 1B). Because previous reports have documented LT induced cell apoptosis, it was important to assure the transcriptional response of LT treated monocytes were independent of apoptosis. This was assured by the analysis of the necrosis and apoptosis markers, propidium iodide (PI) and annexin V, on human peripheral monocytes. Nearly all (99%) human peripheral monocytes showed no evidence of necrosis or apoptosis after a 4 h treatment of LT (Figure 1C and 1D). There has been some conflicting data suggesting monocytes, along with monocyte-derived cells, are not susceptible to the actions of anthrax LT. One study utilized human monocytic cell lines and found that undifferentiated monocytic cells did not undergo LT-induced cytotoxicity, while the differentiated cells were susceptible [10]. Another study investigating human alveolar macrophages (AM) found that these cells were relatively resistant to the actions of LT. It was ascertained that LT failed to suppress human AM cytokine responses, cleave MEKs, and induce apoptosis [14].
Figure 1.
Monocyte purity, apoptosis, and susceptibility to LT. Red = CD14+ monocytes. Green = CD14-lymphocytes. A.) Forward and side scatter analysis of purified fixed human monocytes showing the monocyte population as compared to total population. B.) CD14 Pacific Blue and forward scatter analysis of fixed purified human monocytes showing >85% monocytes. C.) PI and annexin-FITC analysis of CD14 + monocytes after a 4 h incubation showing 99.0% viable cells indicated in quadrant 3. D.) PI and annexin-FITC analysis of CD14 + monocytes after a 4 h LT treatment showing 99.1% viable cells indicated in quadrant 3. HeLa cells or human monocytes were left untreated or treated with 500 ng/mL LT for 4 h at 37°C. Samples were lysed, run on SDS-PAGE, transferred to PVDF membrane, and probed with indicated antibodies. Both MEK3 and MEK1 were cleaved by LT while control cells showed no MEK cleavage. β-actin loading controls show equivalent loading of both control and LT treated cells.
In order to explore the actions of LT on human peripheral monocytes, a Western Blot analysis was performed and MEK1, along with MEK3, cleavage was determined after a 4-hour treatment with LT. Human peripheral monocytes were found to be susceptible to the actions of LT as evidenced by cleavage of MEK1 and MEK3 (Figure 1E). HeLa cells were used as a positive control and β-actin was used to assure equal loading controls. We conclude that human peripheral monocytes are a direct target of anthrax LT.
Microarray analysis and results
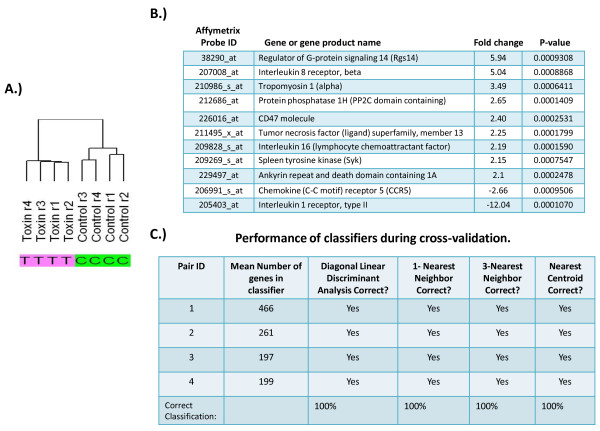
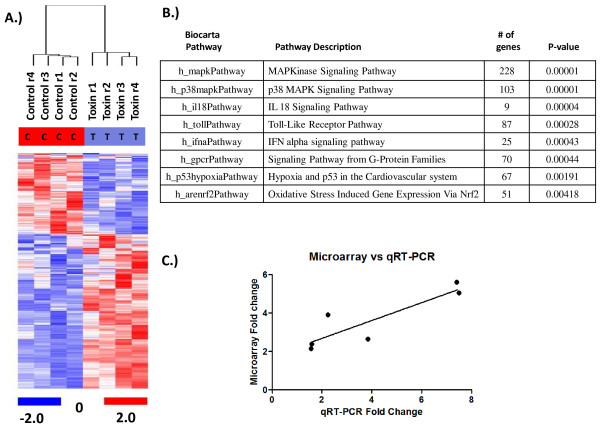
Human peripheral monocytes were treated with LT or media alone, and microarray analysis was performed using four biological replicates from healthy volunteers. A total of 8 microarray hybridizations were employed and analyzed on Affymetrix Gene Chips®(HG U133 plus 2.0). The chips contained 54,675 probe sets and identified multiple differentially regulated pathways and genes by human peripheral monocytes after LT treatment. Unsupervised hierarchical analysis was used to assess the noise in the array experiments. First, probe sets whose signal intensity varied most in the data set were selected by applying a variation filter. Probes sets that displayed a coefficient of variation of greater than 0.5 were subjected to hierarchical analysis. The clustering dendrogram showed the major node of separation between control and LT treated samples (Figure 2A).
Figure 2.
Unsupervised microarray analysis. A.) Hierarchical clustering dendrogram showing similarities between expression patterns within each condition. Specimens were paired based on donor, using 4 separate donors as indicated in replica r1 through r4. B.) Significant genes (p < 0.001) up or down regulated after LT treatment, along with their fold change, p-value and probe ID. C.) Leave-one-out-cross validation was used to calculate mis-classification rate that yielded a 100% correct classification between pairs.
To identify specific genes responsive to LT treatment, a paired t-test (by donor) was performed at a significance threshold of p < 0.001. Genes specified by 820 probe sets were found to be significant among the treatment groups (Table 1). The hierarchical cluster pattern of the significant probe sets is shown (Figure 3A). Of these probe sets, multiple gene products known to play a role in monocyte function were discovered (Figure 2B). The ability of probe sets significant at p < 0.001 to function as a classifier between treatment groups (LT treated vs. control) was established by leave-one-out-cross-validation and Monte Carlo simulations. Using 4 different prediction models, the classifier performed flawlessly. Of the significant genes identified, many are known to play a role in monocyte function (Figure 2C).
Table 1.
Control vs Toxin corresponding P-value p<0.001
| Paramet. p-value | Geometric mean of intensities | Probe set | Gene symbol | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
2.80E-006 |
1.78 |
222001_x_at |
FAM91A2 |
family with sequence similarity 91, member A2 |
| 2 |
2.90E-006 |
1.25 |
218734_at |
NAT11 |
N-acetyltransferase 11 |
| 3 |
3.40E-006 |
1.6 |
230350_at |
NA |
NA |
| 4 |
7.80E-006 |
1.56 |
228930_at |
NA |
NA |
| 5 |
8.70E-006 |
1.58 |
208661_s_at |
TTC3 |
tetratricopeptide repeat domain 3 |
| 6 |
9.80E-006 |
1.16 |
218716_x_at |
MTO1 |
mitochondrial translation optimization 1 homolog (S. cerevisiae) |
| 7 |
1.07E-005 |
1.15 |
238538_at |
ANKRD11 |
ankyrin repeat domain 11 |
| 8 |
1.22E-005 |
2.92 |
225896_at |
NA |
NA |
| 9 |
1.41E-005 |
3.87 |
227450_at |
ERP27 |
endoplasmic reticulum protein 27 kDa |
| 10 |
1.49E-005 |
1.23 |
226602_s_at |
BCR |
breakpoint cluster region |
| 11 |
1.60E-005 |
1.65 |
209123_at |
QDPR |
quinoid dihydropteridine reductase |
| 12 |
1.66E-005 |
1.73 |
213934_s_at |
ZNF23 |
zinc finger protein 23 (KOX 16) |
| 13 |
1.66E-005 |
1.56 |
226419_s_at |
SFRS1 |
splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich 1 |
| 14 |
1.84E-005 |
2.91 |
227946_at |
OSBPL7 |
oxysterol binding protein-like 7 |
| 15 |
2.04E-005 |
1.84 |
242989_at |
NA |
NA |
| 16 |
2.18E-005 |
1.92 |
242590_at |
NA |
NA |
| 17 |
2.29E-005 |
1.36 |
204559_s_at |
LSM7 |
LSM7 homolog, U6 small nuclear RNA associated (S. cerevisiae) |
| 18 |
2.35E-005 |
1.68 |
225902_at |
NA |
NA |
| 19 |
2.44E-005 |
1.29 |
220939_s_at |
DPP8 |
dipeptidyl-peptidase 8 |
| 20 |
2.63E-005 |
1.2 |
218682_s_at |
SLC4A1AP |
solute carrier family 4 (anion exchanger), member 1, adaptor protein |
| 21 |
2.72E-005 |
2.21 |
212056_at |
KIAA0182 |
KIAA0182 |
| 22 |
2.91E-005 |
2.87 |
222477_s_at |
TM7SF3 |
transmembrane 7 superfamily member 3 |
| 23 |
3.01E-005 |
2.01 |
202512_s_at |
ATG5 |
ATG5 autophagy related 5 homolog (S. cerevisiae) |
| 24 |
3.07E-005 |
1.52 |
209042_s_at |
UBE2G2 |
ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2G 2 (UBC7 homolog, yeast) |
| 25 |
3.10E-005 |
5.25 |
232181_at |
LOC153346 |
hypothetical protein LOC153346 |
| 26 |
3.13E-005 |
1.79 |
1554452_a_at |
HIG2 |
hypoxia-inducible protein 2 |
| 27 |
3.36E-005 |
2.11 |
228772_at |
HNMT |
histamine N-methyltransferase |
| 28 |
3.37E-005 |
1.3 |
221501_x_at |
LOC339047 |
hypothetical protein LOC339047 |
| 29 |
3.39E-005 |
1.81 |
239038_at |
C1orf52 |
chromosome 1 open reading frame 52 |
| 30 |
3.46E-005 |
1.95 |
203839_s_at |
TNK2 |
tyrosine kinase, non-receptor, 2 |
| 31 |
3.89E-005 |
1.89 |
227558_at |
CBX4 |
chromobox homolog 4 (Pc class homolog, Drosophila) |
| 32 |
3.90E-005 |
1.4 |
214691_x_at |
FAM63B |
family with sequence similarity 63, member B |
| 33 |
3.91E-005 |
1.32 |
228301_x_at |
NDUFB10 |
NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 beta subcomplex, 10, 22kDa |
| 34 |
4.05E-005 |
1.8 |
1556306_at |
NA |
NA |
| 35 |
4.22E-005 |
3.27 |
229016_s_at |
TRERF1 |
transcriptional regulating factor 1 |
| 36 |
4.47E-005 |
3.85 |
223741_s_at |
TTYH2 |
tweety homolog 2 (Drosophila) |
| 37 |
4.48E-005 |
5.6 |
49306_at |
RASSF4 |
Ras association (RalGDS/AF-6) domain family member 4 |
| 38 |
4.63E-005 |
1.49 |
32209_at |
FAM89B |
family with sequence similarity 89, member B |
| 39 |
4.75E-005 |
2.83 |
225298_at |
PNKD |
paroxysmal nonkinesigenic dyskinesia |
| 40 |
5.00E-005 |
1.59 |
228726_at |
NA |
NA |
| 41 |
5.36E-005 |
1.17 |
1562984_at |
NA |
NA |
| 42 |
5.39E-005 |
1.6 |
201639_s_at |
CPSF1 |
cleavage and polyadenylation specific factor 1, 160kDa |
| 43 |
5.66E-005 |
1.47 |
221649_s_at |
PPAN |
peter pan homolog (Drosophila) |
| 44 |
5.88E-005 |
1.94 |
225360_at |
TRABD |
TraB domain containing |
| 45 |
6.23E-005 |
1.27 |
221005_s_at |
PTDSS2 |
phosphatidylserine synthase 2 |
| 46 |
6.35E-005 |
2.13 |
228914_at |
NA |
NA |
| 47 |
6.47E-005 |
1.65 |
208206_s_at |
RASGRP2 |
RAS guanyl releasing protein 2 (calcium and DAG-regulated) |
| 48 |
6.49E-005 |
1.64 |
209198_s_at |
SYT11 |
synaptotagmin XI |
| 49 |
6.55E-005 |
1.7 |
221575_at |
SCLY |
selenocysteine lyase |
| 50 |
6.74E-005 |
1.82 |
229969_at |
NA |
NA |
| 51 |
6.76E-005 |
2.22 |
235513_at |
NA |
NA |
| 52 |
6.77E-005 |
1.93 |
236922_at |
NA |
NA |
| 53 |
6.78E-005 |
1.14 |
204364_s_at |
REEP1 |
receptor accessory protein 1 |
| 54 |
6.87E-005 |
1.55 |
227025_at |
PPHLN1 |
periphilin 1 |
| 55 |
7.02E-005 |
1.78 |
227288_at |
SFRS12IP1 |
SFRS12-interacting protein 1 |
| 56 |
7.13E-005 |
2.55 |
205075_at |
SERPINF2 |
serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade F (alpha-2 antiplasmin, pigment epithelium derived factor), member 2 |
| 57 |
7.16E-005 |
2.29 |
222988_s_at |
TMEM9 |
transmembrane protein 9 |
| 58 |
7.35E-005 |
1.39 |
231831_at |
COX19 |
COX19 cytochrome c oxidase assembly homolog (S. cerevisiae) |
| 59 |
7.37E-005 |
1.88 |
221788_at |
NA |
NA |
| 60 |
7.66E-005 |
1.61 |
236004_at |
NA |
NA |
| 61 |
7.68E-005 |
1.85 |
219751_at |
SETD6 |
SET domain containing 6 |
| 62 |
7.92E-005 |
1.74 |
227273_at |
NA |
NA |
| 63 |
8.67E-005 |
1.56 |
235787_at |
NA |
NA |
| 64 |
8.91E-005 |
1.42 |
212888_at |
DICER1 |
dicer 1, ribonuclease type III |
| 65 |
8.93E-005 |
1.93 |
1568593_a_at |
NUDT16P |
nudix (nucleoside diphosphate linked moiety X)-type motif 16 pseudogene |
| 66 |
9.00E-005 |
1.92 |
226721_at |
DPY19L4 |
dpy-19-like 4 (C. elegans) |
| 67 |
9.02E-005 |
1.39 |
227159_at |
GHDC |
GH3 domain containing |
| 68 |
9.14E-005 |
2.36 |
225982_at |
UBTF |
upstream binding transcription factor, RNA polymerase I |
| 69 |
9.25E-005 |
1.62 |
220341_s_at |
C5orf45 |
chromosome 5 open reading frame 45 |
| 70 |
9.51E-005 |
1.36 |
214501_s_at |
H2AFY |
H2A histone family, member Y |
| 71 |
9.96E-005 |
7.6 |
226186_at |
NA |
NA |
| 72 |
0.0001001 |
2.59 |
224946_s_at |
CCDC115 |
coiled-coil domain containing 115 |
| 73 |
0.0001056 |
1.66 |
237059_at |
NA |
NA |
| 74 |
0.0001076 |
3.11 |
38671_at |
PLXND1 |
plexin D1 |
| 75 |
0.0001083 |
1.92 |
231912_s_at |
DKFZP434B0335 |
DKFZP434B0335 protein |
| 76 |
0.0001087 |
1.55 |
238492_at |
NA |
NA |
| 77 |
0.0001088 |
2.05 |
228548_at |
NA |
NA |
| 78 |
0.0001089 |
1.9 |
225757_s_at |
CLMN |
calmin (calponin-like, transmembrane) |
| 79 |
0.0001093 |
1.15 |
203926_x_at |
ATP5D |
ATP synthase, H+ transporting, mitochondrial F1 complex, delta subunit |
| 80 |
0.0001100 |
1.41 |
232520_s_at |
NSFL1C |
NSFL1 (p97) cofactor (p47) |
| 81 |
0.0001101 |
2.06 |
238012_at |
DPP7 |
dipeptidyl-peptidase 7 |
| 82 |
0.0001101 |
1.38 |
211101_x_at |
LILRA2 |
leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor, subfamily A (with TM domain), member 2 |
| 83 |
0.0001109 |
1.35 |
210128_s_at |
LTB4R |
leukotriene B4 receptor |
| 84 |
0.0001115 |
1.34 |
223393_s_at |
TSHZ3 |
teashirt zinc finger homeobox 3 |
| 85 |
0.0001123 |
1.46 |
213628_at |
CLCC1 |
chloride channel CLIC-like 1 |
| 86 |
0.0001152 |
1.27 |
214870_x_at |
LOC100132540 |
similar to LOC339047 protein |
| 87 |
0.0001171 |
2.41 |
221756_at |
PIK3IP1 |
phosphoinositide-3-kinase interacting protein 1 |
| 88 |
0.0001171 |
1.62 |
222478_at |
VPS36 |
vacuolar protein sorting 36 homolog (S. cerevisiae) |
| 89 |
0.0001192 |
1.99 |
225719_s_at |
MRPL55 |
mitochondrial ribosomal protein L55 |
| 90 |
0.0001206 |
1.87 |
212959_s_at |
GNPTAB |
N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate transferase, alpha and beta subunits |
| 91 |
0.0001210 |
7.64 |
238520_at |
TRERF1 |
transcriptional regulating factor 1 |
| 92 |
0.0001235 |
3.04 |
226974_at |
NA |
NA |
| 93 |
0.0001269 |
2.06 |
225851_at |
FNTB |
farnesyltransferase, CAAX box, beta |
| 94 |
0.0001288 |
2.04 |
224452_s_at |
MGC12966 |
hypothetical protein LOC84792 |
| 95 |
0.0001306 |
1.46 |
226092_at |
MPP5 |
membrane protein, palmitoylated 5 (MAGUK p55 subfamily member 5) |
| 96 |
0.0001312 |
1.5 |
1558693_s_at |
C1orf85 |
chromosome 1 open reading frame 85 |
| 97 |
0.0001336 |
1.19 |
204020_at |
PURA |
purine-rich element binding protein A |
| 98 |
0.0001350 |
1.73 |
1555882_at |
SPIN3 |
spindlin family, member 3 |
| 99 |
0.0001354 |
1.8 |
235532_at |
PIGM |
phosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis, class M |
| 100 |
0.0001371 |
2.61 |
1553111_a_at |
KBTBD6 |
kelch repeat and BTB (POZ) domain containing 6 |
| 101 |
0.0001408 |
1.44 |
227868_at |
LOC154761 |
hypothetical LOC154761 |
| 102 |
0.0001408 |
3.15 |
214058_at |
MYCL1 |
v-myc myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog 1, lung carcinoma derived (avian) |
| 103 |
0.0001409 |
2.65 |
212686_at |
PPM1H |
protein phosphatase 1H (PP2C domain containing) |
| 104 |
0.0001414 |
1.61 |
218971_s_at |
WDR91 |
WD repeat domain 91 |
| 105 |
0.0001418 |
2.07 |
225777_at |
C9orf140 |
chromosome 9 open reading frame 140 |
| 106 |
0.0001426 |
1.92 |
225366_at |
PGM2 |
phosphoglucomutase 2 |
| 107 |
0.0001451 |
1.74 |
238768_at |
C2orf68 |
chromosome 2 open reading frame 68 |
| 108 |
0.0001454 |
1.49 |
218674_at |
C5orf44 |
chromosome 5 open reading frame 44 |
| 109 |
0.0001462 |
1.26 |
218490_s_at |
ZNF302 |
zinc finger protein 302 |
| 110 |
0.0001537 |
1.17 |
202704_at |
TOB1 |
transducer of ERBB2, 1 |
| 111 |
0.0001561 |
1.69 |
218361_at |
GOLPH3L |
golgi phosphoprotein 3-like |
| 112 |
0.0001565 |
1.32 |
222994_at |
PRDX5 |
peroxiredoxin 5 |
| 113 |
0.0001590 |
2.19 |
209828_s_at |
IL16 |
interleukin 16 (lymphocyte chemoattractant factor) |
| 114 |
0.0001593 |
1.47 |
204611_s_at |
PPP2R5B |
protein phosphatase 2, regulatory subunit B@#$%&, beta isoform |
| 115 |
0.0001593 |
1.48 |
227730_at |
NA |
NA |
| 116 |
0.0001599 |
1.14 |
228605_at |
NA |
NA |
| 117 |
0.0001646 |
1.54 |
202135_s_at |
ACTR1B |
ARP1 actin-related protein 1 homolog B, centractin beta (yeast) |
| 118 |
0.0001669 |
1.73 |
226183_at |
NA |
NA |
| 119 |
0.0001709 |
1.88 |
65472_at |
C2orf68 |
chromosome 2 open reading frame 68 |
| 120 |
0.0001738 |
1.57 |
200098_s_at |
ANAPC5 |
anaphase promoting complex subunit 5 |
| 121 |
0.0001748 |
1.37 |
218181_s_at |
MAP4K4 |
mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase 4 |
| 122 |
0.0001762 |
2.81 |
238135_at |
AGTRAP |
angiotensin II receptor-associated protein |
| 123 |
0.0001767 |
3.66 |
203386_at |
TBC1D4 |
TBC1 domain family, member 4 |
| 124 |
0.0001784 |
2.06 |
213670_x_at |
NSUN5B |
NOL1/NOP2/Sun domain family, member 5B |
| 125 |
0.0001787 |
1.69 |
212109_at |
HN1L |
hematological and neurological expressed 1-like |
| 126 |
0.0001789 |
1.85 |
219968_at |
ZNF589 |
zinc finger protein 589 |
| 127 |
0.0001799 |
2.25 |
211495_x_at |
TNFSF13 |
tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 13 |
| 128 |
0.0001836 |
2.07 |
214177_s_at |
PBXIP1 |
pre-B-cell leukemia homeobox interacting protein 1 |
| 129 |
0.0001843 |
1.64 |
1554085_at |
DDX51 |
DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 51 |
| 130 |
0.0001852 |
1.99 |
203271_s_at |
UNC119 |
unc-119 homolog (C. elegans) |
| 131 |
0.0001878 |
1.43 |
226072_at |
FUK |
fucokinase |
| 132 |
0.0001878 |
3.32 |
212235_at |
PLXND1 |
plexin D1 |
| 133 |
0.0001902 |
1.67 |
205658_s_at |
SNAPC4 |
small nuclear RNA activating complex, polypeptide 4, 190kDa |
| 134 |
0.0001983 |
1.84 |
218021_at |
DHRS4 |
dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR family) member 4 |
| 135 |
0.0001987 |
1.76 |
229429_x_at |
FAM91A2 |
family with sequence similarity 91, member A2 |
| 136 |
0.0001990 |
1.27 |
212429_s_at |
GTF3C2 |
general transcription factor IIIC, polypeptide 2, beta 110kDa |
| 137 |
0.0002007 |
1.81 |
226873_at |
NA |
NA |
| 138 |
0.0002010 |
1.31 |
227801_at |
TRIM59 |
tripartite motif-containing 59 |
| 139 |
0.0002032 |
1.36 |
227679_at |
NA |
NA |
| 140 |
0.0002081 |
4.03 |
218326_s_at |
LGR4 |
leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled receptor 4 |
| 141 |
0.0002087 |
1.93 |
235252_at |
KSR1 |
kinase suppressor of ras 1 |
| 142 |
0.0002093 |
1.45 |
1558522_at |
NA |
NA |
| 143 |
0.0002165 |
1.57 |
225396_at |
NA |
NA |
| 144 |
0.0002167 |
1.4 |
206469_x_at |
AKR7A3 |
aldo-keto reductase family 7, member A3 (aflatoxin aldehyde reductase) |
| 145 |
0.0002197 |
1.79 |
1563549_a_at |
ANO8 |
anoctamin 8 |
| 146 |
0.0002219 |
1.79 |
211576_s_at |
SLC19A1 |
solute carrier family 19 (folate transporter), member 1 |
| 147 |
0.0002234 |
1.35 |
202846_s_at |
PIGC |
phosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis, class C |
| 148 |
0.0002246 |
2.17 |
232231_at |
RUNX2 |
runt-related transcription factor 2 |
| 149 |
0.0002301 |
1.24 |
213480_at |
VAMP4 |
vesicle-associated membrane protein 4 |
| 150 |
0.0002335 |
1.57 |
1558755_x_at |
ZNF763 |
zinc finger protein 763 |
| 151 |
0.0002348 |
1.87 |
1557667_at |
NA |
NA |
| 152 |
0.0002362 |
1.53 |
211036_x_at |
ANAPC5 |
anaphase promoting complex subunit 5 |
| 153 |
0.0002367 |
2.73 |
203387_s_at |
TBC1D4 |
TBC1 domain family, member 4 |
| 154 |
0.0002416 |
1.35 |
217896_s_at |
NIP30 |
NEFA-interacting nuclear protein NIP30 |
| 155 |
0.0002420 |
2.35 |
212136_at |
ATP2B4 |
ATPase, Ca++ transporting, plasma membrane 4 |
| 156 |
0.0002425 |
1.4 |
207618_s_at |
BCS1L |
BCS1-like (yeast) |
| 157 |
0.0002450 |
1.85 |
239300_at |
NA |
NA |
| 158 |
0.0002478 |
2.1 |
229497_at |
ANKDD1A |
ankyrin repeat and death domain containing 1A |
| 159 |
0.0002509 |
1.29 |
214035_x_at |
LOC399491 |
LOC399491 protein |
| 160 |
0.0002517 |
1.66 |
229874_x_at |
NA |
NA |
| 161 |
0.0002521 |
1.74 |
221264_s_at |
LOC100128223 |
hypothetical protein LOC100128223 |
| 162 |
0.0002522 |
1.54 |
227630_at |
NA |
NA |
| 163 |
0.0002531 |
2.4 |
226016_at |
CD47 |
CD47 molecule |
| 164 |
0.0002559 |
1.53 |
1558947_at |
NA |
NA |
| 165 |
0.0002582 |
2.08 |
222664_at |
KCTD15 |
potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 15 |
| 166 |
0.0002606 |
4.49 |
207843_x_at |
CYB5A |
cytochrome b5 type A (microsomal) |
| 167 |
0.0002633 |
2.1 |
218394_at |
ROGDI |
rogdi homolog (Drosophila) |
| 168 |
0.0002634 |
1.86 |
214100_x_at |
NSUN5B |
NOL1/NOP2/Sun domain family, member 5B |
| 169 |
0.0002641 |
1.4 |
212895_s_at |
ABR |
active BCR-related gene |
| 170 |
0.0002648 |
2.01 |
227580_s_at |
DKFZP434B0335 |
DKFZP434B0335 protein |
| 171 |
0.0002678 |
2.59 |
227253_at |
CP |
ceruloplasmin (ferroxidase) |
| 172 |
0.0002679 |
1.78 |
230917_at |
NA |
NA |
| 173 |
0.0002686 |
1.69 |
200843_s_at |
EPRS |
glutamyl-prolyl-tRNA synthetase |
| 174 |
0.0002686 |
2.67 |
227346_at |
IKZF1 |
IKAROS family zinc finger 1 (Ikaros) |
| 175 |
0.0002715 |
1.44 |
219095_at |
LOC100137047-PLA2G4B |
hypothetical protein LOC8681 |
| 176 |
0.0002762 |
1.68 |
229776_at |
SLCO3A1 |
solute carrier organic anion transporter family, member 3A1 |
| 177 |
0.0002768 |
4.48 |
226436_at |
RASSF4 |
Ras association (RalGDS/AF-6) domain family member 4 |
| 178 |
0.0002796 |
1.37 |
221951_at |
TMEM80 |
transmembrane protein 80 |
| 179 |
0.0002809 |
1.49 |
228606_at |
TM4SF19 |
transmembrane 4 L six family member 19 |
| 180 |
0.0002817 |
1.66 |
232535_at |
NA |
NA |
| 181 |
0.0002826 |
1.28 |
1569597_at |
NA |
NA |
| 182 |
0.0002831 |
1.77 |
1555845_at |
NA |
NA |
| 183 |
0.0002835 |
2.77 |
205955_at |
NA |
NA |
| 184 |
0.0002839 |
2.47 |
220137_at |
FLJ20674 |
hypothetical protein FLJ20674 |
| 185 |
0.0002845 |
2.56 |
218459_at |
TOR3A |
torsin family 3, member A |
| 186 |
0.0002870 |
1.73 |
238929_at |
SFRS2B |
splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich 2B |
| 187 |
0.0002872 |
2.1 |
203317_at |
PSD4 |
pleckstrin and Sec7 domain containing 4 |
| 188 |
0.0002969 |
1.32 |
238263_at |
LOC285965 |
hypothetical protein LOC285965 |
| 189 |
0.0003005 |
2.64 |
235159_at |
NA |
NA |
| 190 |
0.0003043 |
1.24 |
218388_at |
PGLS |
6-phosphogluconolactonase |
| 191 |
0.0003057 |
1.3 |
206729_at |
TNFRSF8 |
tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 8 |
| 192 |
0.0003121 |
1.28 |
231130_at |
NA |
NA |
| 193 |
0.0003123 |
1.4 |
1552257_a_at |
TTLL12 |
tubulin tyrosine ligase-like family, member 12 |
| 194 |
0.0003129 |
1.29 |
219175_s_at |
SLC41A3 |
solute carrier family 41, member 3 |
| 195 |
0.0003162 |
1.41 |
204786_s_at |
IFNAR2 |
interferon (alpha, beta and omega) receptor 2 |
| 196 |
0.0003176 |
1.47 |
225391_at |
LOC93622 |
hypothetical LOC93622 |
| 197 |
0.0003216 |
1.35 |
227127_at |
TMEM110 |
transmembrane protein 110 |
| 198 |
0.0003219 |
3.64 |
202341_s_at |
TRIM2 |
tripartite motif-containing 2 |
| 199 |
0.0003243 |
2.09 |
210731_s_at |
LGALS8 |
lectin, galactoside-binding, soluble, 8 |
| 200 |
0.0003251 |
1.77 |
213374_x_at |
HIBCH |
3-hydroxyisobutyryl-Coenzyme A hydrolase |
| 201 |
0.0003260 |
1.38 |
200931_s_at |
VCL |
vinculin |
| 202 |
0.0003264 |
1.45 |
230304_at |
NA |
NA |
| 203 |
0.0003271 |
2.03 |
235195_at |
FBXW2 |
F-box and WD repeat domain containing 2 |
| 204 |
0.0003290 |
4.23 |
215726_s_at |
CYB5A |
cytochrome b5 type A (microsomal) |
| 205 |
0.0003300 |
2.01 |
242794_at |
MAML3 |
mastermind-like 3 (Drosophila) |
| 206 |
0.0003304 |
2.18 |
225961_at |
KLHDC5 |
kelch domain containing 5 |
| 207 |
0.0003309 |
1.48 |
212556_at |
SCRIB |
scribbled homolog (Drosophila) |
| 208 |
0.0003322 |
2.66 |
220494_s_at |
NA |
NA |
| 209 |
0.0003337 |
2.38 |
242297_at |
RREB1 |
ras responsive element binding protein 1 |
| 210 |
0.0003349 |
1.9 |
228771_at |
ADRBK2 |
adrenergic, beta, receptor kinase 2 |
| 211 |
0.0003390 |
1.19 |
227465_at |
KIAA0892 |
KIAA0892 |
| 212 |
0.0003390 |
1.37 |
228667_at |
AGPAT4 |
1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase 4 (lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase, delta) |
| 213 |
0.0003408 |
1.72 |
202161_at |
PKN1 |
protein kinase N1 |
| 214 |
0.0003417 |
1.32 |
AFFX-LysX-M_at |
NA |
NA |
| 215 |
0.0003429 |
1.57 |
223314_at |
TSPAN14 |
tetraspanin 14 |
| 216 |
0.0003438 |
2.51 |
204610_s_at |
CCDC85B |
coiled-coil domain containing 85B |
| 217 |
0.0003438 |
2.03 |
218027_at |
MRPL15 |
mitochondrial ribosomal protein L15 |
| 218 |
0.0003450 |
2.45 |
204718_at |
EPHB6 |
EPH receptor B6 |
| 219 |
0.0003454 |
2.06 |
227313_at |
CNPY4 |
canopy 4 homolog (zebrafish) |
| 220 |
0.0003454 |
1.52 |
228600_x_at |
C7orf46 |
chromosome 7 open reading frame 46 |
| 221 |
0.0003472 |
1.28 |
226335_at |
RPS6KA3 |
ribosomal protein S6 kinase, 90kDa, polypeptide 3 |
| 222 |
0.0003481 |
1.48 |
219147_s_at |
C9orf95 |
chromosome 9 open reading frame 95 |
| 223 |
0.0003492 |
1.41 |
219801_at |
ZNF34 |
zinc finger protein 34 |
| 224 |
0.0003534 |
1.37 |
224865_at |
FAR1 |
fatty acyl CoA reductase 1 |
| 225 |
0.0003534 |
1.25 |
209450_at |
OSGEP |
O-sialoglycoprotein endopeptidase |
| 226 |
0.0003535 |
1.8 |
239016_at |
NA |
NA |
| 227 |
0.0003567 |
1.44 |
228670_at |
TEP1 |
telomerase-associated protein 1 |
| 228 |
0.0003600 |
1.87 |
210580_x_at |
SULT1A3 |
sulfotransferase family, cytosolic, 1A, phenol-preferring, member 3 |
| 229 |
0.0003607 |
1.38 |
213945_s_at |
NUP210 |
nucleoporin 210kDa |
| 230 |
0.0003644 |
1.32 |
218505_at |
WDR59 |
WD repeat domain 59 |
| 231 |
0.0003661 |
2.32 |
230343_at |
NA |
NA |
| 232 |
0.0003663 |
2.08 |
230888_at |
WDR91 |
WD repeat domain 91 |
| 233 |
0.0003691 |
1.87 |
226368_at |
CHST11 |
carbohydrate (chondroitin 4) sulfotransferase 11 |
| 234 |
0.0003691 |
1.67 |
213364_s_at |
SNX1 |
sorting nexin 1 |
| 235 |
0.0003706 |
2.17 |
213626_at |
CBR4 |
carbonyl reductase 4 |
| 236 |
0.0003712 |
1.45 |
AFFX-PheX-3_at |
NA |
NA |
| 237 |
0.0003730 |
1.59 |
206567_s_at |
PHF20 |
PHD finger protein 20 |
| 238 |
0.0003737 |
1.49 |
221090_s_at |
OGFOD1 |
2-oxoglutarate and iron-dependent oxygenase domain containing 1 |
| 239 |
0.0003762 |
1.33 |
44040_at |
FBXO41 |
F-box protein 41 |
| 240 |
0.0003796 |
2.03 |
226238_at |
MCEE |
methylmalonyl CoA epimerase |
| 241 |
0.0003812 |
1.45 |
204562_at |
IRF4 |
interferon regulatory factor 4 |
| 242 |
0.0003827 |
1.46 |
226241_s_at |
MRPL52 |
mitochondrial ribosomal protein L52 |
| 243 |
0.0003831 |
1.46 |
220178_at |
C19orf28 |
chromosome 19 open reading frame 28 |
| 244 |
0.0003841 |
1.31 |
209263_x_at |
TSPAN4 |
tetraspanin 4 |
| 245 |
0.0003893 |
1.45 |
232228_at |
ZNF530 |
zinc finger protein 530 |
| 246 |
0.0003907 |
2.04 |
208760_at |
UBE2I |
ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2I (UBC9 homolog, yeast) |
| 247 |
0.0003909 |
1.18 |
224562_at |
WASF2 |
WAS protein family, member 2 |
| 248 |
0.0003923 |
1.63 |
213485_s_at |
ABCC10 |
ATP-binding cassette, sub-family C (CFTR/MRP), member 10 |
| 249 |
0.0003984 |
1.13 |
202942_at |
ETFB |
electron-transfer-flavoprotein, beta polypeptide |
| 250 |
0.0004011 |
1.54 |
AFFX-LysX-3_at |
NA |
NA |
| 251 |
0.0004028 |
1.79 |
212135_s_at |
ATP2B4 |
ATPase, Ca++ transporting, plasma membrane 4 |
| 252 |
0.0004062 |
1.24 |
217828_at |
SLTM |
SAFB-like, transcription modulator |
| 253 |
0.0004150 |
2.05 |
212875_s_at |
C2CD2 |
C2 calcium-dependent domain containing 2 |
| 254 |
0.0004182 |
2.92 |
1557411_s_at |
SLC25A43 |
solute carrier family 25, member 43 |
| 255 |
0.0004259 |
2.11 |
227117_at |
NA |
NA |
| 256 |
0.0004308 |
1.57 |
207124_s_at |
GNB5 |
guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), beta 5 |
| 257 |
0.0004325 |
1.6 |
227607_at |
STAMBPL1 |
STAM binding protein-like 1 |
| 258 |
0.0004326 |
1.25 |
204538_x_at |
NPIP |
nuclear pore complex interacting protein |
| 259 |
0.0004339 |
2.03 |
244619_at |
BCL10 |
B-cell CLL/lymphoma 10 |
| 260 |
0.0004343 |
1.38 |
223239_at |
C14orf129 |
chromosome 14 open reading frame 129 |
| 261 |
0.0004347 |
1.58 |
201087_at |
PXN |
paxillin |
| 262 |
0.0004367 |
1.8 |
219149_x_at |
DBR1 |
debranching enzyme homolog 1 (S. cerevisiae) |
| 263 |
0.0004371 |
1.88 |
229905_at |
RAP1GDS1 |
RAP1, GTP-GDP dissociation stimulator 1 |
| 264 |
0.0004382 |
1.61 |
222111_at |
NA |
NA |
| 265 |
0.0004389 |
2.71 |
235052_at |
ZNF792 |
zinc finger protein 792 |
| 266 |
0.0004422 |
1.62 |
225748_at |
LTV1 |
LTV1 homolog (S. cerevisiae) |
| 267 |
0.0004451 |
1.37 |
241741_at |
CRLS1 |
cardiolipin synthase 1 |
| 268 |
0.0004463 |
1.46 |
221504_s_at |
ATP6V1H |
ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 50/57kDa, V1 subunit H |
| 269 |
0.0004468 |
1.98 |
213448_at |
NA |
NA |
| 270 |
0.0004483 |
1.15 |
201949_x_at |
CAPZB |
capping protein (actin filament) muscle Z-line, beta |
| 271 |
0.0004501 |
2.15 |
234295_at |
DBR1 |
debranching enzyme homolog 1 (S. cerevisiae) |
| 272 |
0.0004505 |
1.72 |
217608_at |
SFRS12IP1 |
SFRS12-interacting protein 1 |
| 273 |
0.0004518 |
1.34 |
215737_x_at |
USF2 |
upstream transcription factor 2, c-fos interacting |
| 274 |
0.0004529 |
1.47 |
215873_x_at |
ABCC10 |
ATP-binding cassette, sub-family C (CFTR/MRP), member 10 |
| 275 |
0.0004530 |
2.34 |
1552256_a_at |
SCARB1 |
scavenger receptor class B, member 1 |
| 276 |
0.0004546 |
2.47 |
208657_s_at |
9-Sep |
septin 9 |
| 277 |
0.0004555 |
2.08 |
228096_at |
C1orf151 |
chromosome 1 open reading frame 151 |
| 278 |
0.0004560 |
1.75 |
222471_s_at |
KCMF1 |
potassium channel modulatory factor 1 |
| 279 |
0.0004590 |
1.55 |
48808_at |
DHFR |
dihydrofolate reductase |
| 280 |
0.0004608 |
3.5 |
227228_s_at |
CCDC88C |
coiled-coil domain containing 88C |
| 281 |
0.0004636 |
1.94 |
1558445_at |
NA |
NA |
| 282 |
0.0004641 |
1.13 |
205540_s_at |
RRAGB |
Ras-related GTP binding B |
| 283 |
0.0004670 |
1.48 |
227239_at |
FAM126A |
family with sequence similarity 126, member A |
| 284 |
0.0004673 |
1.72 |
220246_at |
CAMK1D |
calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase ID |
| 285 |
0.0004677 |
3.38 |
226478_at |
NA |
NA |
| 286 |
0.0004700 |
1.41 |
230235_at |
NA |
NA |
| 287 |
0.0004709 |
1.22 |
220750_s_at |
LEPRE1 |
leucine proline-enriched proteoglycan (leprecan) 1 |
| 288 |
0.0004727 |
2.69 |
223455_at |
TCHP |
trichoplein, keratin filament binding |
| 289 |
0.0004736 |
1.31 |
238552_at |
NA |
NA |
| 290 |
0.0004739 |
1.47 |
200827_at |
PLOD1 |
procollagen-lysine 1, 2-oxoglutarate 5-dioxygenase 1 |
| 291 |
0.0004751 |
1.28 |
227710_s_at |
NA |
NA |
| 292 |
0.0004785 |
4.77 |
236798_at |
NA |
NA |
| 293 |
0.0004788 |
1.88 |
242824_at |
NA |
NA |
| 294 |
0.0004793 |
1.08 |
215846_at |
NA |
NA |
| 295 |
0.0004795 |
1.92 |
211385_x_at |
SULT1A2 |
sulfotransferase family, cytosolic, 1A, phenol-preferring, member 2 |
| 296 |
0.0004800 |
1.38 |
226358_at |
LOC145842 |
hypothetical protein LOC145842 |
| 297 |
0.0004832 |
1.95 |
213534_s_at |
PASK |
PAS domain containing serine/threonine kinase |
| 298 |
0.0004841 |
5.65 |
205698_s_at |
MAP2K6 |
mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 6 |
| 299 |
0.0004850 |
1.53 |
222661_at |
AGGF1 |
angiogenic factor with G patch and FHA domains 1 |
| 300 |
0.0004855 |
1.43 |
212036_s_at |
PNN |
pinin, desmosome associated protein |
| 301 |
0.0004858 |
1.6 |
244534_at |
NA |
NA |
| 302 |
0.0004876 |
1.58 |
1555751_a_at |
GEMIN7 |
gem (nuclear organelle) associated protein 7 |
| 303 |
0.0004879 |
1.87 |
203063_at |
PPM1F |
protein phosphatase 1F (PP2C domain containing) |
| 304 |
0.0004973 |
1.16 |
205922_at |
VNN2 |
vanin 2 |
| 305 |
0.0004975 |
1.23 |
202797_at |
SACM1L |
SAC1 suppressor of actin mutations 1-like (yeast) |
| 306 |
0.0005017 |
2.46 |
202826_at |
SPINT1 |
serine peptidase inhibitor, Kunitz type 1 |
| 307 |
0.0005059 |
1.73 |
226073_at |
TMEM218 |
transmembrane protein 218 |
| 308 |
0.0005077 |
1.55 |
238523_at |
KLHL36 |
kelch-like 36 (Drosophila) |
| 309 |
0.0005080 |
1.78 |
231843_at |
DDX55 |
DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 55 |
| 310 |
0.0005094 |
2.26 |
219714_s_at |
CACNA2D3 |
calcium channel, voltage-dependent, alpha 2/delta subunit 3 |
| 311 |
0.0005097 |
2.02 |
229202_at |
NA |
NA |
| 312 |
0.0005114 |
3.54 |
209048_s_at |
ZMYND8 |
zinc finger, MYND-type containing 8 |
| 313 |
0.0005132 |
1.64 |
218473_s_at |
GLT25D1 |
glycosyltransferase 25 domain containing 1 |
| 314 |
0.0005172 |
1.71 |
65493_at |
HEATR6 |
HEAT repeat containing 6 |
| 315 |
0.0005179 |
2.03 |
236194_at |
NA |
NA |
| 316 |
0.0005179 |
2.28 |
226531_at |
ORAI1 |
ORAI calcium release-activated calcium modulator 1 |
| 317 |
0.0005201 |
1.58 |
219351_at |
TRAPPC2 |
trafficking protein particle complex 2 |
| 318 |
0.0005244 |
1.26 |
220036_s_at |
LMBR1L |
limb region 1 homolog (mouse)-like |
| 319 |
0.0005321 |
4.22 |
217974_at |
TM7SF3 |
transmembrane 7 superfamily member 3 |
| 320 |
0.0005335 |
1.26 |
211759_x_at |
TBCB |
tubulin folding cofactor B |
| 321 |
0.0005359 |
1.4 |
242155_x_at |
NA |
NA |
| 322 |
0.0005397 |
2 |
209377_s_at |
HMGN3 |
high mobility group nucleosomal binding domain 3 |
| 323 |
0.0005401 |
2.12 |
230653_at |
LOC100132218 |
hypothetical protein LOC100132218 |
| 324 |
0.0005504 |
1.77 |
224708_at |
KIAA2013 |
KIAA2013 |
| 325 |
0.0005504 |
1.9 |
204000_at |
GNB5 |
guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), beta 5 |
| 326 |
0.0005559 |
1.32 |
244346_at |
NA |
NA |
| 327 |
0.0005568 |
1.9 |
225108_at |
AGPS |
alkylglycerone phosphate synthase |
| 328 |
0.0005599 |
1.85 |
236626_at |
NA |
NA |
| 329 |
0.0005615 |
1.85 |
228314_at |
LRRC8C |
leucine rich repeat containing 8 family, member C |
| 330 |
0.0005636 |
1.46 |
1558754_at |
ZNF763 |
zinc finger protein 763 |
| 331 |
0.0005650 |
1.42 |
226155_at |
FAM160B1 |
family with sequence similarity 160, member B1 |
| 332 |
0.0005679 |
1.72 |
229705_at |
NA |
NA |
| 333 |
0.0005686 |
4.21 |
228891_at |
C9orf164 |
chromosome 9 open reading frame 164 |
| 334 |
0.0005708 |
1.49 |
225146_at |
C9orf25 |
chromosome 9 open reading frame 25 |
| 335 |
0.0005724 |
1.86 |
219817_at |
C12orf47 |
chromosome 12 open reading frame 47 |
| 336 |
0.0005724 |
1.58 |
235610_at |
ALKBH8 |
alkB, alkylation repair homolog 8 (E. coli) |
| 337 |
0.0005728 |
1.59 |
217949_s_at |
VKORC1 |
vitamin K epoxide reductase complex, subunit 1 |
| 338 |
0.0005746 |
2.14 |
222858_s_at |
DAPP1 |
dual adaptor of phosphotyrosine and 3-phosphoinositides |
| 339 |
0.0005748 |
1.17 |
223049_at |
GRB2 |
growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 |
| 340 |
0.0005792 |
1.45 |
212987_at |
FBXO9 |
F-box protein 9 |
| 341 |
0.0005793 |
1.42 |
209903_s_at |
ATR |
ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3 related |
| 342 |
0.0005805 |
1.45 |
201067_at |
PSMC2 |
proteasome (prosome, macropain) 26S subunit, ATPase, 2 |
| 343 |
0.0005806 |
1.37 |
201076_at |
NHP2L1 |
NHP2 non-histone chromosome protein 2-like 1 (S. cerevisiae) |
| 344 |
0.0005811 |
1.28 |
236804_at |
NA |
NA |
| 345 |
0.0005820 |
1.27 |
234107_s_at |
DTD1 |
D-tyrosyl-tRNA deacylase 1 homolog (S. cerevisiae) |
| 346 |
0.0005858 |
2.04 |
1553987_at |
C12orf47 |
chromosome 12 open reading frame 47 |
| 347 |
0.0005877 |
1.42 |
226679_at |
SLC26A11 |
solute carrier family 26, member 11 |
| 348 |
0.0005893 |
1.7 |
1554608_at |
TGOLN2 |
trans-golgi network protein 2 |
| 349 |
0.0005911 |
1.65 |
219256_s_at |
SH3TC1 |
SH3 domain and tetratricopeptide repeats 1 |
| 350 |
0.0005950 |
1.46 |
232369_at |
NA |
NA |
| 351 |
0.0005992 |
1.39 |
243750_x_at |
C21orf70 |
chromosome 21 open reading frame 70 |
| 352 |
0.0006007 |
2.4 |
219759_at |
ERAP2 |
endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 2 |
| 353 |
0.0006025 |
1.24 |
203981_s_at |
ABCD4 |
ATP-binding cassette, sub-family D (ALD), member 4 |
| 354 |
0.0006028 |
1.43 |
202428_x_at |
DBI |
diazepam binding inhibitor (GABA receptor modulator, acyl-Coenzyme A binding protein) |
| 355 |
0.0006039 |
1.54 |
212886_at |
CCDC69 |
coiled-coil domain containing 69 |
| 356 |
0.0006041 |
2.12 |
221878_at |
C2orf68 |
chromosome 2 open reading frame 68 |
| 357 |
0.0006052 |
1.91 |
202039_at |
TIAF1 |
TGFB1-induced anti-apoptotic factor 1 |
| 358 |
0.0006058 |
2.8 |
40472_at |
LPCAT4 |
lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 4 |
| 359 |
0.0006135 |
1.48 |
217751_at |
GSTK1 |
glutathione S-transferase kappa 1 |
| 360 |
0.0006135 |
1.84 |
228303_at |
GALNT6 |
UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 6 (GalNAc-T6) |
| 361 |
0.0006147 |
1.44 |
202172_at |
VEZF1 |
vascular endothelial zinc finger 1 |
| 362 |
0.0006167 |
2.09 |
1558692_at |
C1orf85 |
chromosome 1 open reading frame 85 |
| 363 |
0.0006190 |
1.89 |
207122_x_at |
SULT1A2 |
sulfotransferase family, cytosolic, 1A, phenol-preferring, member 2 |
| 364 |
0.0006205 |
1.49 |
1560874_at |
FLJ33046 |
hypothetical gene supported by AK057608 |
| 365 |
0.0006228 |
1.97 |
212473_s_at |
MICAL2 |
microtubule associated monoxygenase, calponin and LIM domain containing 2 |
| 366 |
0.0006241 |
1.67 |
225409_at |
C2orf64 |
chromosome 2 open reading frame 64 |
| 367 |
0.0006246 |
1.97 |
203615_x_at |
SULT1A1 |
sulfotransferase family, cytosolic, 1A, phenol-preferring, member 1 |
| 368 |
0.0006275 |
1.4 |
224724_at |
SULF2 |
sulfatase 2 |
| 369 |
0.0006277 |
1.47 |
225022_at |
GOPC |
golgi associated PDZ and coiled-coil motif containing |
| 370 |
0.0006282 |
1.18 |
214879_x_at |
USF2 |
upstream transcription factor 2, c-fos interacting |
| 371 |
0.0006311 |
1.43 |
222843_at |
FIGNL1 |
fidgetin-like 1 |
| 372 |
0.0006313 |
2.06 |
210136_at |
MBP |
myelin basic protein |
| 373 |
0.0006322 |
2.27 |
229512_at |
FAM120C |
family with sequence similarity 120C |
| 374 |
0.0006326 |
1.2 |
209017_s_at |
LONP1 |
lon peptidase 1, mitochondrial |
| 375 |
0.0006333 |
1.69 |
237926_s_at |
NA |
NA |
| 376 |
0.0006351 |
1.44 |
222294_s_at |
RAB27A |
RAB27A, member RAS oncogene family |
| 377 |
0.0006411 |
3.49 |
210986_s_at |
TPM1 |
tropomyosin 1 (alpha) |
| 378 |
0.0006490 |
1.28 |
209932_s_at |
DUT |
deoxyuridine triphosphatase |
| 379 |
0.0006513 |
1.28 |
227656_at |
C6orf70 |
chromosome 6 open reading frame 70 |
| 380 |
0.0006514 |
1.63 |
228131_at |
ERCC1 |
excision repair cross-complementing rodent repair deficiency, complementation group 1 (includes overlapping antisense sequence) |
| 381 |
0.0006519 |
1.11 |
212848_s_at |
C9orf3 |
chromosome 9 open reading frame 3 |
| 382 |
0.0006526 |
2.3 |
1552540_s_at |
IQCD |
IQ motif containing D |
| 383 |
0.0006530 |
2.09 |
239698_at |
NA |
NA |
| 384 |
0.0006586 |
1.62 |
1553102_a_at |
CCDC69 |
coiled-coil domain containing 69 |
| 385 |
0.0006622 |
1.77 |
228542_at |
MRS2 |
MRS2 magnesium homeostasis factor homolog (S. cerevisiae) |
| 386 |
0.0006623 |
1.37 |
208956_x_at |
DUT |
deoxyuridine triphosphatase |
| 387 |
0.0006635 |
2.14 |
223528_s_at |
METT11D1 |
methyltransferase 11 domain containing 1 |
| 388 |
0.0006636 |
1.38 |
201234_at |
ILK |
integrin-linked kinase |
| 389 |
0.0006637 |
1.57 |
228694_at |
NA |
NA |
| 390 |
0.0006659 |
1.36 |
225136_at |
PLEKHA2 |
pleckstrin homology domain containing, family A (phosphoinositide binding specific) member 2 |
| 391 |
0.0006723 |
1.55 |
212567_s_at |
MAP4 |
microtubule-associated protein 4 |
| 392 |
0.0006726 |
1.52 |
219549_s_at |
RTN3 |
reticulon 3 |
| 393 |
0.0006730 |
1.89 |
232681_at |
NA |
NA |
| 394 |
0.0006742 |
2.21 |
219627_at |
ZNF767 |
zinc finger family member 767 |
| 395 |
0.0006762 |
2.7 |
231449_at |
NA |
NA |
| 396 |
0.0006771 |
1.58 |
239035_at |
MTHFR |
5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (NADPH) |
| 397 |
0.0006773 |
1.39 |
205256_at |
ZBTB39 |
zinc finger and BTB domain containing 39 |
| 398 |
0.0006786 |
1.51 |
205945_at |
IL6R |
interleukin 6 receptor |
| 399 |
0.0006802 |
4.26 |
230032_at |
OSGEPL1 |
O-sialoglycoprotein endopeptidase-like 1 |
| 400 |
0.0006837 |
1.56 |
225888_at |
C12orf30 |
chromosome 12 open reading frame 30 |
| 401 |
0.0006840 |
1.35 |
227767_at |
CSNK1G3 |
casein kinase 1, gamma 3 |
| 402 |
0.0006879 |
1.76 |
205060_at |
PARG |
poly (ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase |
| 403 |
0.0006921 |
1.37 |
239730_at |
DGCR14 |
DiGeorge syndrome critical region gene 14 |
| 404 |
0.0006924 |
1.58 |
201029_s_at |
CD99 |
CD99 molecule |
| 405 |
0.0006928 |
1.63 |
211709_s_at |
CLEC11A |
C-type lectin domain family 11, member A |
| 406 |
0.0006952 |
1.95 |
201985_at |
KIAA0196 |
KIAA0196 |
| 407 |
0.0006964 |
2.17 |
204995_at |
CDK5R1 |
cyclin-dependent kinase 5, regulatory subunit 1 (p35) |
| 408 |
0.0007029 |
1.52 |
217521_at |
NA |
NA |
| 409 |
0.0007045 |
1.35 |
1558184_s_at |
ZNF17 |
zinc finger protein 17 |
| 410 |
0.0007099 |
1.24 |
218167_at |
AMZ2 |
archaelysin family metallopeptidase 2 |
| 411 |
0.0007119 |
1.52 |
226712_at |
SSR1 |
signal sequence receptor, alpha |
| 412 |
0.0007129 |
1.22 |
238668_at |
NA |
NA |
| 413 |
0.0007138 |
1.16 |
221651_x_at |
IGKC |
immunoglobulin kappa constant |
| 414 |
0.0007143 |
1.85 |
64064_at |
GIMAP5 |
GTPase, IMAP family member 5 |
| 415 |
0.0007160 |
1.24 |
234734_s_at |
TNRC6A |
trinucleotide repeat containing 6A |
| 416 |
0.0007165 |
1.34 |
213582_at |
ATP11A |
ATPase, class VI, type 11A |
| 417 |
0.0007176 |
1.34 |
226165_at |
C8orf59 |
chromosome 8 open reading frame 59 |
| 418 |
0.0007186 |
2.61 |
205565_s_at |
FXN |
frataxin |
| 419 |
0.0007225 |
1.21 |
220251_at |
C1orf107 |
chromosome 1 open reading frame 107 |
| 420 |
0.0007231 |
2.16 |
225980_at |
C14orf43 |
chromosome 14 open reading frame 43 |
| 421 |
0.0007247 |
1.69 |
238379_x_at |
NA |
NA |
| 422 |
0.0007266 |
1.72 |
1559034_at |
SIRPB2 |
signal-regulatory protein beta 2 |
| 423 |
0.0007273 |
1.21 |
201053_s_at |
PSMF1 |
proteasome (prosome, macropain) inhibitor subunit 1 (PI31) |
| 424 |
0.0007318 |
1.1 |
40225_at |
GAK |
cyclin G associated kinase |
| 425 |
0.0007329 |
2.14 |
209729_at |
GAS2L1 |
growth arrest-specific 2 like 1 |
| 426 |
0.0007344 |
1.55 |
221027_s_at |
PLA2G12A |
phospholipase A2, group XIIA |
| 427 |
0.0007348 |
1.28 |
209724_s_at |
ZFP161 |
zinc finger protein 161 homolog (mouse) |
| 428 |
0.0007380 |
1.4 |
214494_s_at |
SPG7 |
spastic paraplegia 7 (pure and complicated autosomal recessive) |
| 429 |
0.0007392 |
1.58 |
205131_x_at |
CLEC11A |
C-type lectin domain family 11, member A |
| 430 |
0.0007393 |
2.07 |
204019_s_at |
SH3YL1 |
SH3 domain containing, Ysc84-like 1 (S. cerevisiae) |
| 431 |
0.0007417 |
1.42 |
214861_at |
JMJD2C |
jumonji domain containing 2C |
| 432 |
0.0007421 |
1.69 |
242965_at |
NA |
NA |
| 433 |
0.0007485 |
1.99 |
228167_at |
KLHL6 |
kelch-like 6 (Drosophila) |
| 434 |
0.0007547 |
2.15 |
209269_s_at |
SYK |
spleen tyrosine kinase |
| 435 |
0.0007563 |
1.5 |
244663_at |
NA |
NA |
| 436 |
0.0007563 |
2.14 |
203802_x_at |
NSUN5 |
NOL1/NOP2/Sun domain family, member 5 |
| 437 |
0.0007578 |
1.62 |
242108_at |
NA |
NA |
| 438 |
0.0007655 |
1.46 |
205632_s_at |
PIP5K1B |
phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase, type I, beta |
| 439 |
0.0007691 |
2.28 |
238604_at |
NA |
NA |
| 440 |
0.0007694 |
1.25 |
219084_at |
NSD1 |
nuclear receptor binding SET domain protein 1 |
| 441 |
0.0007712 |
1.4 |
223716_s_at |
ZRANB2 |
zinc finger, RAN-binding domain containing 2 |
| 442 |
0.0007728 |
1.82 |
209760_at |
KIAA0922 |
KIAA0922 |
| 443 |
0.0007796 |
1.29 |
214437_s_at |
SHMT2 |
serine hydroxymethyltransferase 2 (mitochondrial) |
| 444 |
0.0007836 |
1.46 |
224704_at |
TNRC6A |
trinucleotide repeat containing 6A |
| 445 |
0.0007841 |
2.01 |
223339_at |
ATPIF1 |
ATPase inhibitory factor 1 |
| 446 |
0.0007848 |
1.59 |
222622_at |
PGP |
phosphoglycolate phosphatase |
| 447 |
0.0007851 |
1.62 |
218231_at |
NAGK |
N-acetylglucosamine kinase |
| 448 |
0.0007878 |
1.79 |
1554544_a_at |
MBP |
myelin basic protein |
| 449 |
0.0007894 |
2.2 |
1554250_s_at |
TRIM73 |
tripartite motif-containing 73 |
| 450 |
0.0007896 |
2.19 |
216199_s_at |
MAP3K4 |
mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 4 |
| 451 |
0.0007925 |
1.3 |
206881_s_at |
LILRA3 |
leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor, subfamily A (without TM domain), member 3 |
| 452 |
0.0007976 |
1.65 |
226716_at |
PRR12 |
proline rich 12 |
| 453 |
0.0007989 |
1.67 |
202534_x_at |
DHFR |
dihydrofolate reductase |
| 454 |
0.0007995 |
2.43 |
202369_s_at |
TRAM2 |
translocation associated membrane protein 2 |
| 455 |
0.0008009 |
2.59 |
218112_at |
MRPS34 |
mitochondrial ribosomal protein S34 |
| 456 |
0.0008035 |
1.48 |
230925_at |
APBB1IP |
amyloid beta (A4) precursor protein-binding, family B, member 1 interacting protein |
| 457 |
0.0008086 |
1.16 |
213027_at |
TROVE2 |
TROVE domain family, member 2 |
| 458 |
0.0008124 |
2.99 |
1562289_at |
NA |
NA |
| 459 |
0.0008148 |
1.41 |
202615_at |
GNAQ |
guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), q polypeptide |
| 460 |
0.0008150 |
1.71 |
219151_s_at |
RABL2B |
RAB, member of RAS oncogene family-like 2B |
| 461 |
0.0008158 |
2.1 |
1559214_at |
NA |
NA |
| 462 |
0.0008161 |
1.84 |
203711_s_at |
HIBCH |
3-hydroxyisobutyryl-Coenzyme A hydrolase |
| 463 |
0.0008187 |
1.87 |
233955_x_at |
CXXC5 |
CXXC finger 5 |
| 464 |
0.0008205 |
1.26 |
201804_x_at |
TBCB |
tubulin folding cofactor B |
| 465 |
0.0008207 |
1.44 |
211100_x_at |
LILRA2 |
leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor, subfamily A (with TM domain), member 2 |
| 466 |
0.0008229 |
5.13 |
212757_s_at |
CAMK2G |
calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CaM kinase) II gamma |
| 467 |
0.0008232 |
1.76 |
214202_at |
NA |
NA |
| 468 |
0.0008255 |
2.01 |
221746_at |
UBL4A |
ubiquitin-like 4A |
| 469 |
0.0008277 |
1.35 |
1560587_s_at |
PRDX5 |
peroxiredoxin 5 |
| 470 |
0.0008278 |
1.41 |
211070_x_at |
DBI |
diazepam binding inhibitor (GABA receptor modulator, acyl-Coenzyme A binding protein) |
| 471 |
0.0008279 |
1.53 |
242887_at |
KCMF1 |
potassium channel modulatory factor 1 |
| 472 |
0.0008283 |
1.29 |
206200_s_at |
ANXA11 |
annexin A11 |
| 473 |
0.0008318 |
1.72 |
203607_at |
INPP5F |
inositol polyphosphate-5-phosphatase F |
| 474 |
0.0008344 |
1.9 |
205282_at |
LRP8 |
low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 8, apolipoprotein e receptor |
| 475 |
0.0008347 |
1.42 |
209566_at |
INSIG2 |
insulin induced gene 2 |
| 476 |
0.0008361 |
1.54 |
223306_at |
EBPL |
emopamil binding protein-like |
| 477 |
0.0008444 |
3.9 |
210166_at |
TLR5 |
toll-like receptor 5 |
| 478 |
0.0008451 |
1.44 |
225050_at |
ZNF512 |
zinc finger protein 512 |
| 479 |
0.0008463 |
1.9 |
226480_at |
NA |
NA |
| 480 |
0.0008510 |
1.22 |
211152_s_at |
HTRA2 |
HtrA serine peptidase 2 |
| 481 |
0.0008526 |
1.9 |
222603_at |
ERMP1 |
endoplasmic reticulum metallopeptidase 1 |
| 482 |
0.0008590 |
1.42 |
226078_at |
RPUSD1 |
RNA pseudouridylate synthase domain containing 1 |
| 483 |
0.0008602 |
1.89 |
203409_at |
DDB2 |
damage-specific DNA binding protein 2, 48kDa |
| 484 |
0.0008607 |
1.79 |
222996_s_at |
CXXC5 |
CXXC finger 5 |
| 485 |
0.0008619 |
1.42 |
229597_s_at |
WDFY4 |
WDFY family member 4 |
| 486 |
0.0008625 |
1.21 |
209420_s_at |
SMPD1 |
sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 1, acid lysosomal |
| 487 |
0.0008648 |
2.16 |
213333_at |
MDH2 |
malate dehydrogenase 2, NAD (mitochondrial) |
| 488 |
0.0008654 |
1.57 |
232524_x_at |
ANAPC4 |
anaphase promoting complex subunit 4 |
| 489 |
0.0008674 |
1.63 |
238058_at |
FLJ27365 |
FLJ27365 protein |
| 490 |
0.0008682 |
2.88 |
212660_at |
PHF15 |
PHD finger protein 15 |
| 491 |
0.0008701 |
2.47 |
209197_at |
SYT11 |
synaptotagmin XI |
| 492 |
0.0008755 |
1.49 |
200875_s_at |
NOL5A |
nucleolar protein 5A (56kDa with KKE/D repeat) |
| 493 |
0.0008868 |
5.04 |
207008_at |
IL8RB |
interleukin 8 receptor, beta |
| 494 |
0.0008925 |
1.33 |
233694_at |
HSPA1L |
heat shock 70kDa protein 1-like |
| 495 |
0.0008958 |
1.35 |
217957_at |
C16orf80 |
chromosome 16 open reading frame 80 |
| 496 |
0.0008961 |
1.64 |
228070_at |
PPP2R5E |
protein phosphatase 2, regulatory subunit B@#$%&, epsilon isoform |
| 497 |
0.0008967 |
1.56 |
225997_at |
MOBKL1A |
MOB1, Mps One Binder kinase activator-like 1A (yeast) |
| 498 |
0.0009020 |
1.98 |
65438_at |
KIAA1609 |
KIAA1609 |
| 499 |
0.0009056 |
1.82 |
218921_at |
SIGIRR |
single immunoglobulin and toll-interleukin 1 receptor (TIR) domain |
| 500 |
0.0009103 |
1.06 |
240001_at |
NA |
NA |
| 501 |
0.0009114 |
1.51 |
227533_at |
NA |
NA |
| 502 |
0.0009136 |
1.47 |
226333_at |
IL6R |
interleukin 6 receptor |
| 503 |
0.0009154 |
1.68 |
1562249_at |
LOC285965 |
hypothetical protein LOC285965 |
| 504 |
0.0009189 |
3.86 |
204301_at |
KBTBD11 |
kelch repeat and BTB (POZ) domain containing 11 |
| 505 |
0.0009197 |
1.67 |
213296_at |
RER1 |
RER1 retention in endoplasmic reticulum 1 homolog (S. cerevisiae) |
| 506 |
0.0009228 |
1.32 |
224688_at |
C7orf42 |
chromosome 7 open reading frame 42 |
| 507 |
0.0009245 |
1.91 |
221843_s_at |
KIAA1609 |
KIAA1609 |
| 508 |
0.0009272 |
1.24 |
1569808_at |
NA |
NA |
| 509 |
0.0009308 |
5.94 |
38290_at |
RGS14 |
regulator of G-protein signaling 14 |
| 510 |
0.0009357 |
3.85 |
226820_at |
ZNF362 |
zinc finger protein 362 |
| 511 |
0.0009370 |
1.35 |
241344_at |
NA |
NA |
| 512 |
0.0009378 |
1.73 |
228512_at |
PTCD3 |
Pentatricopeptide repeat domain 3 |
| 513 |
0.0009417 |
1.63 |
210830_s_at |
PON2 |
paraoxonase 2 |
| 514 |
0.0009436 |
1.44 |
219493_at |
SHCBP1 |
SHC SH2-domain binding protein 1 |
| 515 |
0.0009471 |
1.38 |
230122_at |
MLLT10 |
myeloid/lymphoid or mixed-lineage leukemia (trithorax homolog, Drosophila); translocated to, 10 |
| 516 |
0.0009526 |
1.67 |
218380_at |
NLRP1 |
NLR family, pyrin domain containing 1 |
| 517 |
0.0009562 |
1.42 |
202200_s_at |
SRPK1 |
SFRS protein kinase 1 |
| 518 |
0.0009575 |
1.63 |
202741_at |
PRKACB |
protein kinase, cAMP-dependent, catalytic, beta |
| 519 |
0.0009592 |
1.43 |
228869_at |
NA |
NA |
| 520 |
0.0009614 |
1.25 |
224252_s_at |
FXYD5 |
FXYD domain containing ion transport regulator 5 |
| 521 |
0.0009626 |
1.45 |
221488_s_at |
CUTA |
cutA divalent cation tolerance homolog (E. coli) |
| 522 |
0.0009634 |
1.7 |
244687_at |
DBT |
dihydrolipoamide branched chain transacylase E2 |
| 523 |
0.0009679 |
1.17 |
209445_x_at |
C7orf44 |
chromosome 7 open reading frame 44 |
| 524 |
0.0009703 |
1.14 |
244537_at |
NA |
NA |
| 525 |
0.0009717 |
1.7 |
226104_at |
RNF170 |
ring finger protein 170 |
| 526 |
0.0009730 |
1.31 |
205240_at |
GPSM2 |
G-protein signaling modulator 2 (AGS3-like, C. elegans) |
| 527 |
0.0009732 |
1.73 |
200766_at |
CTSD |
cathepsin D |
| 528 |
0.0009734 |
1.41 |
231844_at |
MGC27345 |
hypothetical protein MGC27345 |
| 529 |
0.0009738 |
1.29 |
202634_at |
POLR2K |
polymerase (RNA) II (DNA directed) polypeptide K, 7.0kDa |
| 530 |
0.0009760 |
1.58 |
224938_at |
NUFIP2 |
nuclear fragile X mental retardation protein interacting protein 2 |
| 531 |
0.0009764 |
2.26 |
204089_x_at |
MAP3K4 |
mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 4 |
| 532 |
0.0009776 |
1.93 |
211985_s_at |
CALM1 |
calmodulin 1 (phosphorylase kinase, delta) |
| 533 |
0.0009778 |
2.65 |
213280_at |
GARNL4 |
GTPase activating Rap/RanGAP domain-like 4 |
| 534 |
0.0009805 |
1.48 |
236016_at |
NA |
NA |
| 535 |
0.0009828 |
1.84 |
217394_at |
NA |
NA |
| 536 |
0.0009900 |
1.58 |
201030_x_at |
LDHB |
lactate dehydrogenase B |
| 537 |
0.0009925 |
1.81 |
227379_at |
MBOAT1 |
membrane bound O-acyltransferase domain containing 1 |
| 538 |
0.0009997 |
-1.19 |
236663_at |
NA |
NA |
| 539 |
0.0009983 |
-1.6 |
219766_at |
B9D2 |
B9 protein domain 2 |
| 540 |
0.0009949 |
-1.71 |
204157_s_at |
KIAA0999 |
KIAA0999 protein |
| 541 |
0.0009891 |
-1.23 |
214060_at |
SSBP1 |
single-stranded DNA binding protein 1 |
| 542 |
0.0009868 |
-1.47 |
226276_at |
TMEM167A |
transmembrane protein 167A |
| 543 |
0.0009825 |
-1.75 |
203596_s_at |
IFIT5 |
interferon-induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats 5 |
| 544 |
0.0009805 |
-1.64 |
226310_at |
RICTOR |
rapamycin-insensitive companion of mTOR |
| 545 |
0.0009772 |
-2.29 |
218986_s_at |
DDX60 |
DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 60 |
| 546 |
0.0009758 |
-1.52 |
217618_x_at |
HUS1 |
HUS1 checkpoint homolog (S. pombe) |
| 547 |
0.0009746 |
-2.4 |
219017_at |
ETNK1 |
ethanolamine kinase 1 |
| 548 |
0.0009745 |
-1.24 |
201957_at |
PPP1R12B |
protein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 12B |
| 549 |
0.0009737 |
-1.26 |
240887_at |
NA |
NA |
| 550 |
0.0009681 |
-1.33 |
209514_s_at |
RAB27A |
RAB27A, member RAS oncogene family |
| 551 |
0.0009661 |
-2.54 |
219026_s_at |
RASAL2 |
RAS protein activator like 2 |
| 552 |
0.0009592 |
-1.49 |
211395_x_at |
FCGR2C |
Fc fragment of IgG, low affinity IIc, receptor for (CD32) |
| 553 |
0.0009568 |
-3.72 |
205126_at |
VRK2 |
vaccinia related kinase 2 |
| 554 |
0.0009560 |
-1.22 |
1556514_at |
LOC338809 |
hypothetical protein LOC338809 |
| 555 |
0.0009506 |
-2.66 |
206991_s_at |
CCR5 |
chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 5 |
| 556 |
0.0009500 |
-1.47 |
212840_at |
UBXN7 |
UBX domain protein 7 |
| 557 |
0.0009443 |
-1.25 |
244496_at |
NA |
NA |
| 558 |
0.0009406 |
-1.21 |
236108_at |
KIAA1632 |
KIAA1632 |
| 559 |
0.0009366 |
-1.2 |
203654_s_at |
COIL |
coilin |
| 560 |
0.0009338 |
-2.95 |
236156_at |
LIPA |
lipase A, lysosomal acid, cholesterol esterase |
| 561 |
0.0009309 |
-1.3 |
212462_at |
MYST4 |
MYST histone acetyltransferase (monocytic leukemia) 4 |
| 562 |
0.0009278 |
-2.58 |
219403_s_at |
HPSE |
heparanase |
| 563 |
0.0009220 |
-1.58 |
1554747_a_at |
2-Sep |
septin 2 |
| 564 |
0.0009134 |
-1.08 |
203291_at |
CNOT4 |
CCR4-NOT transcription complex, subunit 4 |
| 565 |
0.0009077 |
-1.25 |
243772_at |
SDCCAG8 |
serologically defined colon cancer antigen 8 |
| 566 |
0.0009071 |
-1.7 |
201656_at |
ITGA6 |
integrin, alpha 6 |
| 567 |
0.0009063 |
-3.06 |
201325_s_at |
EMP1 |
epithelial membrane protein 1 |
| 568 |
0.0009031 |
-1.27 |
209531_at |
GSTZ1 |
glutathione transferase zeta 1 |
| 569 |
0.0008974 |
-1.42 |
208779_x_at |
DDR1 |
discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinase 1 |
| 570 |
0.0008959 |
-1.19 |
242654_at |
FANCC |
Fanconi anemia, complementation group C |
| 571 |
0.0008945 |
-1.16 |
220386_s_at |
EML4 |
echinoderm microtubule associated protein like 4 |
| 572 |
0.0008922 |
-1.32 |
227003_at |
RAB28 |
RAB28, member RAS oncogene family |
| 573 |
0.0008910 |
-3.14 |
224009_x_at |
DHRS9 |
dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR family) member 9 |
| 574 |
0.0008877 |
-1.67 |
32069_at |
N4BP1 |
NEDD4 binding protein 1 |
| 575 |
0.0008870 |
-1.29 |
232141_at |
U2AF1 |
U2 small nuclear RNA auxiliary factor 1 |
| 576 |
0.0008761 |
-1.35 |
240468_at |
NA |
NA |
| 577 |
0.0008698 |
-1.32 |
204367_at |
SP2 |
Sp2 transcription factor |
| 578 |
0.0008616 |
-1.87 |
225076_s_at |
ZNFX1 |
zinc finger, NFX1-type containing 1 |
| 579 |
0.0008599 |
-1.25 |
225056_at |
SIPA1L2 |
signal-induced proliferation-associated 1 like 2 |
| 580 |
0.0008580 |
-1.13 |
207070_at |
RGR |
retinal G protein coupled receptor |
| 581 |
0.0008574 |
-1.28 |
217129_at |
NA |
NA |
| 582 |
0.0008537 |
-1.22 |
225268_at |
KPNA4 |
karyopherin alpha 4 (importin alpha 3) |
| 583 |
0.0008463 |
-1.07 |
232295_at |
GFM1 |
G elongation factor, mitochondrial 1 |
| 584 |
0.0008408 |
-1.33 |
211975_at |
ARFGAP2 |
ADP-ribosylation factor GTPase activating protein 2 |
| 585 |
0.0008385 |
-1.24 |
244625_at |
NA |
NA |
| 586 |
0.0008384 |
-1.49 |
202083_s_at |
SEC14L1 |
SEC14-like 1 (S. cerevisiae) |
| 587 |
0.0008274 |
-1.34 |
232987_at |
ARL17 |
ADP-ribosylation factor-like 17 |
| 588 |
0.0008198 |
-1.33 |
1570541_s_at |
NA |
NA |
| 589 |
0.0008196 |
-2.91 |
201324_at |
EMP1 |
epithelial membrane protein 1 |
| 590 |
0.0008172 |
-1.42 |
222408_s_at |
YPEL5 |
yippee-like 5 (Drosophila) |
| 591 |
0.0008164 |
-1.3 |
201585_s_at |
SFPQ |
splicing factor proline/glutamine-rich (polypyrimidine tract binding protein associated) |
| 592 |
0.0008160 |
-1.35 |
243492_at |
THEM4 |
thioesterase superfamily member 4 |
| 593 |
0.0008023 |
-1.53 |
222537_s_at |
CDC42SE1 |
CDC42 small effector 1 |
| 594 |
0.0007993 |
-1.38 |
223225_s_at |
SEH1L |
SEH1-like (S. cerevisiae) |
| 595 |
0.0007951 |
-1.4 |
231139_at |
NA |
NA |
| 596 |
0.0007921 |
-3.08 |
206911_at |
TRIM25 |
tripartite motif-containing 25 |
| 597 |
0.0007824 |
-1.55 |
1554390_s_at |
ACTR2 |
ARP2 actin-related protein 2 homolog (yeast) |
| 598 |
0.0007777 |
-1.32 |
208824_x_at |
PCTK1 |
PCTAIRE protein kinase 1 |
| 599 |
0.0007732 |
-1.36 |
214258_x_at |
KAT5 |
K(lysine) acetyltransferase 5 |
| 600 |
0.0007729 |
-1.47 |
208751_at |
NAPA |
N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein, alpha |
| 601 |
0.0007690 |
-1.16 |
238337_s_at |
DNAJC21 |
DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 21 |
| 602 |
0.0007673 |
-1.31 |
211314_at |
CACNA1G |
calcium channel, voltage-dependent, T type, alpha 1G subunit |
| 603 |
0.0007657 |
-1.53 |
217834_s_at |
SYNCRIP |
synaptotagmin binding, cytoplasmic RNA interacting protein |
| 604 |
0.0007625 |
-1.85 |
208653_s_at |
CD164 |
CD164 molecule, sialomucin |
| 605 |
0.0007608 |
-1.45 |
209091_s_at |
SH3GLB1 |
SH3-domain GRB2-like endophilin B1 |
| 606 |
0.0007426 |
-1.25 |
1557533_at |
NA |
NA |
| 607 |
0.0007405 |
-2.01 |
1555785_a_at |
XRN1 |
5@#$%&-3@#$%& exoribonuclease 1 |
| 608 |
0.0007371 |
-1.41 |
236961_at |
NA |
NA |
| 609 |
0.0007346 |
-1.14 |
204080_at |
TOE1 |
target of EGR1, member 1 (nuclear) |
| 610 |
0.0007341 |
-1.29 |
243852_at |
LUC7L2 |
LUC7-like 2 (S. cerevisiae) |
| 611 |
0.0007227 |
-1.29 |
210317_s_at |
YWHAE |
tyrosine 3-monooxygenase/tryptophan 5-monooxygenase activation protein, epsilon polypeptide |
| 612 |
0.0007183 |
-1.4 |
209284_s_at |
C3orf63 |
chromosome 3 open reading frame 63 |
| 613 |
0.0007169 |
-3.19 |
227361_at |
HS3ST3B1 |
heparan sulfate (glucosamine) 3-O-sulfotransferase 3B1 |
| 614 |
0.0007139 |
-1.19 |
211066_x_at |
PCDHGC3 |
protocadherin gamma subfamily C, 3 |
| 615 |
0.0006984 |
-1.09 |
202814_s_at |
HEXIM1 |
hexamethylene bis-acetamide inducible 1 |
| 616 |
0.0006943 |
-1.35 |
226710_at |
C8orf82 |
chromosome 8 open reading frame 82 |
| 617 |
0.0006932 |
-3.2 |
209969_s_at |
STAT1 |
signal transducer and activator of transcription 1, 91kDa |
| 618 |
0.0006882 |
-1.56 |
225242_s_at |
CCDC80 |
coiled-coil domain containing 80 |
| 619 |
0.0006875 |
-1.5 |
214121_x_at |
PDLIM7 |
PDZ and LIM domain 7 (enigma) |
| 620 |
0.0006868 |
-1.41 |
203916_at |
NDST2 |
N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase (heparan glucosaminyl) 2 |
| 621 |
0.0006826 |
-1.32 |
208901_s_at |
TOP1 |
topoisomerase (DNA) I |
| 622 |
0.0006769 |
-2.95 |
206028_s_at |
MERTK |
c-mer proto-oncogene tyrosine kinase |
| 623 |
0.0006749 |
-1.35 |
205724_at |
PKP1 |
plakophilin 1 (ectodermal dysplasia/skin fragility syndrome) |
| 624 |
0.0006737 |
-1.23 |
228121_at |
NA |
NA |
| 625 |
0.0006701 |
-1.04 |
226928_x_at |
SLC25A37 |
solute carrier family 25, member 37 |
| 626 |
0.0006700 |
-1.37 |
1555301_a_at |
DIP2A |
DIP2 disco-interacting protein 2 homolog A (Drosophila) |
| 627 |
0.0006616 |
-1.27 |
1566301_at |
PPP1R11 |
protein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 11 |
| 628 |
0.0006570 |
-1.46 |
234519_at |
NOBOX |
NOBOX oogenesis homeobox |
| 629 |
0.0006553 |
-1.24 |
218520_at |
TBK1 |
TANK-binding kinase 1 |
| 630 |
0.0006552 |
-1.55 |
201878_at |
ARIH1 |
ariadne homolog, ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 binding protein, 1 (Drosophila) |
| 631 |
0.0006495 |
-1.3 |
1564131_a_at |
NA |
NA |
| 632 |
0.0006472 |
-1.49 |
209102_s_at |
HBP1 |
HMG-box transcription factor 1 |
| 633 |
0.0006450 |
-1.18 |
238586_at |
LOC731489 |
hypothetical protein LOC731489 |
| 634 |
0.0006425 |
-1.03 |
216231_s_at |
B2M |
beta-2-microglobulin |
| 635 |
0.0006398 |
-1.79 |
1552772_at |
CLEC4D |
C-type lectin domain family 4, member D |
| 636 |
0.0006384 |
-1.42 |
201586_s_at |
SFPQ |
splicing factor proline/glutamine-rich (polypyrimidine tract binding protein associated) |
| 637 |
0.0006373 |
-1.74 |
41644_at |
SASH1 |
SAM and SH3 domain containing 1 |
| 638 |
0.0006346 |
-1.11 |
216652_s_at |
DR1 |
down-regulator of transcription 1, TBP-binding (negative cofactor 2) |
| 639 |
0.0006313 |
-1.3 |
212436_at |
TRIM33 |
tripartite motif-containing 33 |
| 640 |
0.0006284 |
-1.57 |
212264_s_at |
WAPAL |
wings apart-like homolog (Drosophila) |
| 641 |
0.0006259 |
-1.2 |
226481_at |
VPRBP |
Vpr (HIV-1) binding protein |
| 642 |
0.0006104 |
-1.35 |
217490_at |
NA |
NA |
| 643 |
0.0006091 |
-1.29 |
1557463_at |
NA |
NA |
| 644 |
0.0005929 |
-1.35 |
238273_at |
PL-5283 |
PL-5283 protein |
| 645 |
0.0005927 |
-1.77 |
203840_at |
BLZF1 |
basic leucine zipper nuclear factor 1 |
| 646 |
0.0005896 |
-1.17 |
237604_at |
LOC415056 |
hypothetical gene LOC415056 |
| 647 |
0.0005883 |
-1.9 |
222881_at |
HPSE |
heparanase |
| 648 |
0.0005855 |
-1.25 |
220634_at |
TBX4 |
T-box 4 |
| 649 |
0.0005853 |
-1.3 |
200669_s_at |
UBE2D3 |
ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2D 3 (UBC4/5 homolog, yeast) |
| 650 |
0.0005801 |
-1.05 |
232017_at |
TJP2 |
tight junction protein 2 (zona occludens 2) |
| 651 |
0.0005772 |
-1.35 |
213918_s_at |
NIPBL |
Nipped-B homolog (Drosophila) |
| 652 |
0.0005770 |
-1.62 |
215357_s_at |
POLDIP3 |
polymerase (DNA-directed), delta interacting protein 3 |
| 653 |
0.0005750 |
-1.4 |
1561354_at |
NA |
NA |
| 654 |
0.0005678 |
-1.08 |
206516_at |
AMH |
anti-Mullerian hormone |
| 655 |
0.0005652 |
-2.05 |
211030_s_at |
SLC6A6 |
solute carrier family 6 (neurotransmitter transporter, taurine), member 6 |
| 656 |
0.0005634 |
-2.18 |
222651_s_at |
TRPS1 |
trichorhinophalangeal syndrome I |
| 657 |
0.0005618 |
-2.05 |
57703_at |
SENP5 |
SUMO1/sentrin specific peptidase 5 |
| 658 |
0.0005604 |
-11.89 |
211372_s_at |
IL1R2 |
interleukin 1 receptor, type II |
| 659 |
0.0005547 |
-1.2 |
1567246_at |
OR5H1 |
olfactory receptor, family 5, subfamily H, member 1 |
| 660 |
0.0005488 |
-1.85 |
205003_at |
DOCK4 |
dedicator of cytokinesis 4 |
| 661 |
0.0005371 |
-2.37 |
222262_s_at |
ETNK1 |
ethanolamine kinase 1 |
| 662 |
0.0005358 |
-1.38 |
201684_s_at |
TOX4 |
TOX high mobility group box family member 4 |
| 663 |
0.0005357 |
-1.85 |
206011_at |
CASP1 |
caspase 1, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase (interleukin 1, beta, convertase) |
| 664 |
0.0005349 |
-1.16 |
211505_s_at |
STAU1 |
staufen, RNA binding protein, homolog 1 (Drosophila) |
| 665 |
0.0005342 |
-1.47 |
1554049_s_at |
WDR42A |
WD repeat domain 42A |
| 666 |
0.0005321 |
-1.36 |
225978_at |
FAM80B |
family with sequence similarity 80, member B |
| 667 |
0.0005228 |
-1.15 |
215056_at |
NA |
NA |
| 668 |
0.0005162 |
-1.38 |
202066_at |
PPFIA1 |
protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, f polypeptide (PTPRF), interacting protein (liprin), alpha 1 |
| 669 |
0.0005087 |
-1.13 |
226128_at |
NA |
NA |
| 670 |
0.0005005 |
-1.17 |
1562449_s_at |
NA |
NA |
| 671 |
0.0004997 |
-1.51 |
217847_s_at |
THRAP3 |
thyroid hormone receptor associated protein 3 |
| 672 |
0.0004992 |
-1.6 |
229845_at |
MAPKAP1 |
mitogen-activated protein kinase associated protein 1 |
| 673 |
0.0004955 |
-2.82 |
211806_s_at |
KCNJ15 |
potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 15 |
| 674 |
0.0004947 |
-2.32 |
217503_at |
NA |
NA |
| 675 |
0.0004946 |
-1.2 |
221147_x_at |
WWOX |
WW domain containing oxidoreductase |
| 676 |
0.0004897 |
-1.26 |
1552684_a_at |
SENP8 |
SUMO/sentrin specific peptidase family member 8 |
| 677 |
0.0004707 |
-1.17 |
206251_s_at |
AVPR1A |
arginine vasopressin receptor 1A |
| 678 |
0.0004609 |
-1.24 |
223546_x_at |
LUC7L |
LUC7-like (S. cerevisiae) |
| 679 |
0.0004595 |
-1.33 |
208576_s_at |
HIST1H3B |
histone cluster 1, H3b |
| 680 |
0.0004582 |
-1.97 |
202684_s_at |
RNMT |
RNA (guanine-7-) methyltransferase |
| 681 |
0.0004567 |
-1.36 |
201378_s_at |
UBAP2L |
ubiquitin associated protein 2-like |
| 682 |
0.0004553 |
-1.15 |
202178_at |
PRKCZ |
protein kinase C, zeta |
| 683 |
0.0004545 |
-1.13 |
1555139_a_at |
OTUD7B |
OTU domain containing 7B |
| 684 |
0.0004543 |
-1.47 |
244595_at |
NA |
NA |
| 685 |
0.0004511 |
-1.32 |
210592_s_at |
04/01/12 |
spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase 1 |
| 686 |
0.0004444 |
-1.21 |
1554327_a_at |
CANT1 |
calcium activated nucleotidase 1 |
| 687 |
0.0004435 |
-1.41 |
223430_at |
SNF1LK2 |
SNF1-like kinase 2 |
| 688 |
0.0004430 |
-1.42 |
232437_at |
CPSF3L |
cleavage and polyadenylation specific factor 3-like |
| 689 |
0.0004418 |
-1.11 |
202230_s_at |
CHERP |
calcium homeostasis endoplasmic reticulum protein |
| 690 |
0.0004358 |
-1.8 |
211782_at |
IDS |
iduronate 2-sulfatase |
| 691 |
0.0004288 |
-1.63 |
208869_s_at |
GABARAPL1 |
GABA(A) receptor-associated protein like 1 |
| 692 |
0.0004258 |
-1.14 |
1554646_at |
OSBPL1A |
oxysterol binding protein-like 1A |
| 693 |
0.0004189 |
-1.29 |
224410_s_at |
LMBR1 |
limb region 1 homolog (mouse) |
| 694 |
0.0004130 |
-1.09 |
201698_s_at |
SFRS9 |
splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich 9 |
| 695 |
0.0004109 |
-1.57 |
218578_at |
CDC73 |
cell division cycle 73, Paf1/RNA polymerase II complex component, homolog (S. cerevisiae) |
| 696 |
0.0003904 |
-1.3 |
1566456_at |
NA |
NA |
| 697 |
0.0003884 |
-2.78 |
226026_at |
DIRC2 |
disrupted in renal carcinoma 2 |
| 698 |
0.0003884 |
-1.49 |
222035_s_at |
PAPOLA |
poly(A) polymerase alpha |
| 699 |
0.0003882 |
-1.25 |
240313_at |
DMRTB1 |
DMRT-like family B with proline-rich C-terminal, 1 |
| 700 |
0.0003880 |
-1.65 |
242943_at |
ST8SIA4 |
ST8 alpha-N-acetyl-neuraminide alpha-2,8-sialyltransferase 4 |
| 701 |
0.0003868 |
-2.87 |
243271_at |
NA |
NA |
| 702 |
0.0003850 |
-1.43 |
234173_s_at |
NXF2 |
nuclear RNA export factor 2 |
| 703 |
0.0003839 |
-1.93 |
211368_s_at |
CASP1 |
caspase 1, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase (interleukin 1, beta, convertase) |
| 704 |
0.0003823 |
-1.24 |
227712_at |
LYRM2 |
LYR motif containing 2 |
| 705 |
0.0003803 |
-1.63 |
201377_at |
UBAP2L |
ubiquitin associated protein 2-like |
| 706 |
0.0003785 |
-1.4 |
204858_s_at |
TYMP |
thymidine phosphorylase |
| 707 |
0.0003695 |
-1.53 |
205415_s_at |
ATXN3 |
ataxin 3 |
| 708 |
0.0003684 |
-2.46 |
209237_s_at |
SLC23A2 |
solute carrier family 23 (nucleobase transporters), member 2 |
| 709 |
0.0003661 |
-1.25 |
235833_at |
PPAT |
phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate amidotransferase |
| 710 |
0.0003575 |
-1.29 |
209590_at |
BMP7 |
bone morphogenetic protein 7 |
| 711 |
0.0003529 |
-3.5 |
215966_x_at |
GK3P |
glycerol kinase 3 pseudogene |
| 712 |
0.0003527 |
-1.22 |
202807_s_at |
TOM1 |
target of myb1 (chicken) |
| 713 |
0.0003455 |
-1.18 |
201198_s_at |
PSMD1 |
proteasome (prosome, macropain) 26S subunit, non-ATPase, 1 |
| 714 |
0.0003409 |
-3.97 |
202068_s_at |
LDLR |
low density lipoprotein receptor |
| 715 |
0.0003389 |
-1.07 |
200914_x_at |
KTN1 |
kinectin 1 (kinesin receptor) |
| 716 |
0.0003355 |
-1.77 |
225395_s_at |
FAM120AOS |
family with sequence similarity 120A opposite strand |
| 717 |
0.0003300 |
-1.17 |
216306_x_at |
PTBP1 |
polypyrimidine tract binding protein 1 |
| 718 |
0.0003300 |
-1.38 |
208985_s_at |
EIF3J |
eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3, subunit J |
| 719 |
0.0003231 |
-1.15 |
1569932_at |
NHSL2 |
NHS-like 2 |
| 720 |
0.0003229 |
-1.41 |
204781_s_at |
FAS |
Fas (TNF receptor superfamily, member 6) |
| 721 |
0.0003210 |
-2 |
209593_s_at |
TOR1B |
torsin family 1, member B (torsin B) |
| 722 |
0.0003206 |
-1.3 |
237285_at |
SORBS2 |
sorbin and SH3 domain containing 2 |
| 723 |
0.0003169 |
-1.19 |
202550_s_at |
VAPB |
VAMP (vesicle-associated membrane protein)-associated protein B and C |
| 724 |
0.0003084 |
-1.34 |
201461_s_at |
MAPKAPK2 |
mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2 |
| 725 |
0.0003068 |
-1.11 |
1563069_at |
NA |
NA |
| 726 |
0.0002955 |
-1.14 |
218382_s_at |
U2AF2 |
U2 small nuclear RNA auxiliary factor 2 |
| 727 |
0.0002940 |
-1.11 |
205570_at |
PIP4K2A |
phosphatidylinositol-5-phosphate 4-kinase, type II, alpha |
| 728 |
0.0002921 |
-1.28 |
208642_s_at |
XRCC5 |
X-ray repair complementing defective repair in Chinese hamster cells 5 (double-strand-break rejoining) |
| 729 |
0.0002910 |
-1.24 |
221603_at |
PEX16 |
peroxisomal biogenesis factor 16 |
| 730 |
0.0002863 |
-1.21 |
231211_s_at |
LOC541469 |
hypothetical protein LOC541469 |
| 731 |
0.0002857 |
-2.02 |
219062_s_at |
ZCCHC2 |
zinc finger, CCHC domain containing 2 |
| 732 |
0.0002808 |
-1.2 |
218570_at |
KBTBD4 |
kelch repeat and BTB (POZ) domain containing 4 |
| 733 |
0.0002799 |
-1.16 |
223545_at |
FANCD2 |
Fanconi anemia, complementation group D2 |
| 734 |
0.0002764 |
-1.34 |
1555614_at |
SUGT1P |
suppressor of G2 allele of SKP1 pseudogene (S. cerevisiae) |
| 735 |
0.0002736 |
-1.53 |
1556283_s_at |
FGFR1OP2 |
FGFR1 oncogene partner 2 |
| 736 |
0.0002703 |
-1.66 |
226022_at |
SASH1 |
SAM and SH3 domain containing 1 |
| 737 |
0.0002699 |
-1.87 |
214838_at |
SFT2D2 |
SFT2 domain containing 2 |
| 738 |
0.0002674 |
-1.26 |
206307_s_at |
FOXD1 |
forkhead box D1 |
| 739 |
0.0002668 |
-1.41 |
208108_s_at |
AVPR2 |
arginine vasopressin receptor 2 |
| 740 |
0.0002633 |
-1.21 |
239949_at |
THNSL2 |
threonine synthase-like 2 (S. cerevisiae) |
| 741 |
0.0002619 |
-1.76 |
1554096_a_at |
RBM33 |
RNA binding motif protein 33 |
| 742 |
0.0002577 |
-1.25 |
203039_s_at |
NDUFS1 |
NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) Fe-S protein 1, 75kDa (NADH-coenzyme Q reductase) |
| 743 |
0.0002569 |
-3.7 |
1563541_at |
NA |
NA |
| 744 |
0.0002547 |
-1.33 |
210569_s_at |
SIGLEC9 |
sialic acid binding Ig-like lectin 9 |
| 745 |
0.0002484 |
-1.44 |
203922_s_at |
CYBB |
cytochrome b-245, beta polypeptide |
| 746 |
0.0002482 |
-1.33 |
220012_at |
ERO1LB |
ERO1-like beta (S. cerevisiae) |
| 747 |
0.0002373 |
-2.41 |
236106_at |
NA |
NA |
| 748 |
0.0002362 |
-1.34 |
242834_at |
NA |
NA |
| 749 |
0.0002316 |
-1.2 |
220498_at |
ACTL7B |
actin-like 7B |
| 750 |
0.0002303 |
-1.44 |
240873_x_at |
DAB2 |
disabled homolog 2, mitogen-responsive phosphoprotein (Drosophila) |
| 751 |
0.0002296 |
-1.19 |
221471_at |
SERINC3 |
serine incorporator 3 |
| 752 |
0.0002267 |
-1.74 |
213236_at |
SASH1 |
SAM and SH3 domain containing 1 |
| 753 |
0.0002262 |
-1.62 |
213988_s_at |
04/01/12 |
spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase 1 |
| 754 |
0.0002220 |
-1.2 |
239372_at |
NA |
NA |
| 755 |
0.0002208 |
-1.35 |
240079_at |
ZNF81 |
zinc finger protein 81 |
| 756 |
0.0002182 |
-1.65 |
205227_at |
IL1RAP |
interleukin 1 receptor accessory protein |
| 757 |
0.0002149 |
-1.5 |
223751_x_at |
TLR10 |
toll-like receptor 10 |
| 758 |
0.0002132 |
-1.35 |
1553677_a_at |
TIPRL |
TIP41, TOR signaling pathway regulator-like (S. cerevisiae) |
| 759 |
0.0002103 |
-1.44 |
AFFX-HUMISGF3A/M97935_5_at |
STAT1 |
signal transducer and activator of transcription 1, 91kDa |
| 760 |
0.0002103 |
-1.11 |
202240_at |
PLK1 |
polo-like kinase 1 (Drosophila) |
| 761 |
0.0002099 |
-1.28 |
1556281_at |
NA |
NA |
| 762 |
0.0002093 |
-1.53 |
222989_s_at |
UBQLN1 |
ubiquilin 1 |
| 763 |
0.0002070 |
-1.16 |
204682_at |
LTBP2 |
latent transforming growth factor beta binding protein 2 |
| 764 |
0.0002018 |
-1.37 |
225830_at |
PDZD8 |
PDZ domain containing 8 |
| 765 |
0.0002016 |
-1.34 |
229208_at |
CEP27 |
centrosomal protein 27kDa |
| 766 |
0.0002006 |
-1.38 |
202211_at |
ARFGAP3 |
ADP-ribosylation factor GTPase activating protein 3 |
| 767 |
0.0001969 |
-1.21 |
208696_at |
CCT5 |
chaperonin containing TCP1, subunit 5 (epsilon) |
| 768 |
0.0001905 |
-1.71 |
219207_at |
EDC3 |
enhancer of mRNA decapping 3 homolog (S. cerevisiae) |
| 769 |
0.0001804 |
-1.31 |
221248_s_at |
WHSC1L1 |
Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome candidate 1-like 1 |
| 770 |
0.0001758 |
-1.59 |
211781_x_at |
NA |
NA |
| 771 |
0.0001730 |
-1.36 |
226037_s_at |
TAF9B |
TAF9B RNA polymerase II, TATA box binding protein (TBP)-associated factor, 31kDa |
| 772 |
0.0001724 |
-1.14 |
200901_s_at |
M6PR |
mannose-6-phosphate receptor (cation dependent) |
| 773 |
0.0001713 |
-1.67 |
213173_at |
PCNX |
pecanex homolog (Drosophila) |
| 774 |
0.0001667 |
-2.06 |
206038_s_at |
NR2C2 |
nuclear receptor subfamily 2, group C, member 2 |
| 775 |
0.0001616 |
-1.24 |
225397_at |
C15orf57 |
chromosome 15 open reading frame 57 |
| 776 |
0.0001297 |
-2.14 |
211367_s_at |
CASP1 |
caspase 1, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase (interleukin 1, beta, convertase) |
| 777 |
0.0001209 |
-1.66 |
222810_s_at |
RASAL2 |
RAS protein activator like 2 |
| 778 |
0.0001196 |
-1.23 |
231718_at |
SLU7 |
SLU7 splicing factor homolog (S. cerevisiae) |
| 779 |
0.0001187 |
-1.32 |
223905_at |
CCDC135 |
coiled-coil domain containing 135 |
| 780 |
0.0001127 |
-1.28 |
211672_s_at |
ARPC4 |
actin related protein 2/3 complex, subunit 4, 20kDa |
| 781 |
0.0001127 |
-1.38 |
200828_s_at |
ZNF207 |
zinc finger protein 207 |
| 782 |
0.0001073 |
-1.29 |
244211_at |
NA |
NA |
| 783 |
0.0001070 |
-12.04 |
205403_at |
IL1R2 |
interleukin 1 receptor, type II |
| 784 |
0.0001065 |
-1.83 |
209970_x_at |
CASP1 |
caspase 1, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase (interleukin 1, beta, convertase) |
| 785 |
0.0001034 |
-6.35 |
217502_at |
IFIT2 |
interferon-induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats 2 |
| 786 |
0.0001029 |
-2.07 |
237867_s_at |
PID1 |
phosphotyrosine interaction domain containing 1 |
| 787 |
0.0001028 |
-1.26 |
218516_s_at |
IMPAD1 |
inositol monophosphatase domain containing 1 |
| 788 |
9.94E-005 |
-1.64 |
226312_at |
RICTOR |
rapamycin-insensitive companion of mTOR |
| 789 |
9.41E-005 |
-1.2 |
210940_s_at |
GRM1 |
glutamate receptor, metabotropic 1 |
| 790 |
9.02E-005 |
-1.36 |
1554556_a_at |
ATP11B |
ATPase, class VI, type 11B |
| 791 |
8.89E-005 |
-1.14 |
226735_at |
TAPT1 |
transmembrane anterior posterior transformation 1 |
| 792 |
8.70E-005 |
-3.84 |
213006_at |
CEBPD |
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP), delta |
| 793 |
8.35E-005 |
-1.31 |
207787_at |
KRT33B |
keratin 33B |
| 794 |
8.34E-005 |
-1.29 |
207410_s_at |
TLX2 |
T-cell leukemia homeobox 2 |
| 795 |
8.21E-005 |
-1.6 |
223596_at |
SLC12A6 |
solute carrier family 12 (potassium/chloride transporters), member 6 |
| 796 |
7.98E-005 |
-1.23 |
231859_at |
C14orf132 |
chromosome 14 open reading frame 132 |
| 797 |
7.81E-005 |
-1.25 |
228277_at |
FBXL19 |
F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 19 |
| 798 |
7.75E-005 |
-1.35 |
210470_x_at |
NONO |
non-POU domain containing, octamer-binding |
| 799 |
7.52E-005 |
-1.29 |
222432_s_at |
CCDC47 |
coiled-coil domain containing 47 |
| 800 |
7.19E-005 |
-1.8 |
238496_at |
NA |
NA |
| 801 |
7.11E-005 |
-1.38 |
208698_s_at |
NONO |
non-POU domain containing, octamer-binding |
| 802 |
7.08E-005 |
-4.66 |
203946_s_at |
ARG2 |
arginase, type II |
| 803 |
7.03E-005 |
-1.17 |
1559952_x_at |
LOC100132923 |
similar to hCG1993470 |
| 804 |
6.19E-005 |
-2.35 |
220104_at |
ZC3HAV1 |
zinc finger CCCH-type, antiviral 1 |
| 805 |
5.57E-005 |
-2.43 |
203595_s_at |
IFIT5 |
interferon-induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats 5 |
| 806 |
5.53E-005 |
-1.33 |
1569859_at |
NA |
NA |
| 807 |
5.31E-005 |
-1.5 |
224359_s_at |
HOOK3 |
hook homolog 3 (Drosophila) |
| 808 |
4.19E-005 |
-2.51 |
205921_s_at |
SLC6A6 |
solute carrier family 6 (neurotransmitter transporter, taurine), member 6 |
| 809 |
3.18E-005 |
-2.18 |
205749_at |
CYP1A1 |
cytochrome P450, family 1, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 |
| 810 |
2.93E-005 |
-1.38 |
1566136_at |
NA |
NA |
| 811 |
2.02E-005 |
-1.51 |
210992_x_at |
FCGR2C |
Fc fragment of IgG, low affinity IIc, receptor for (CD32) |
| 812 |
1.61E-005 |
-1.22 |
207801_s_at |
RNF10 |
ring finger protein 10 |
| 813 |
1.32E-005 |
-2.03 |
222816_s_at |
ZCCHC2 |
zinc finger, CCHC domain containing 2 |
| 814 |
1.29E-005 |
-1.25 |
211884_s_at |
CIITA |
class II, major histocompatibility complex, transactivator |
| 815 |
8.60E-006 |
-1.68 |
212664_at |
TUBB4 |
tubulin, beta 4 |
| 816 |
4.60E-006 |
-1.16 |
212081_x_at |
BAT2 |
HLA-B associated transcript 2 |
| 817 |
3.60E-006 |
-1.21 |
1554177_a_at |
ATP5S |
ATP synthase, H+ transporting, mitochondrial F0 complex, subunit s (factor B) |
| 818 |
7.00E-007 |
-1.82 |
224783_at |
FAM100B |
family with sequence similarity 100, member B |
| 819 |
6.00E-007 |
-1.57 |
208840_s_at |
G3BP2 |
GTPase activating protein (SH3 domain) binding protein 2 |
| 820 | 4.00E-007 | -1.59 | 206717_at | MYH8 | myosin, heavy chain 8, skeletal muscle, perinatal |
Figure 3.
Supervised microarray analysis. A.) Hierarchical cluster analysis showing the 820 probe sets which were differentially expressed at the 0.001 significance level. The arrays clustering on the left are from control samples, whereas the cluster on the right shows the LT treated samples. Up-regulated genes are shown in red and down-regulated genes are shown in blue. B.) Biocarta pathway analysis showing the pathways most significantly affected by LT, along with the number of genes and p-value within each pathway that were affected. C.) Correlation of genes altered after treatment with anthrax LT using microarray analysis versus RT-PCR. Spearman correlation coefficient = 0.885.
Using the Gene Set Expression Comparison Analysis, as implemented in BRB Array tools, the Biocarta pathways that were associated with the differentially regulated genes were identified. Over 60 differentially regulated pathways were discovered in monocytes in response to LT treatment. As expected, the most significant pathway affected by LT treatment was the MAPK signaling pathway, with the p38 MAPK signaling pathway being most impacted with 103 genes affected (Figure 3B). Additional pathways altered by LT at the p < 0.001 significance level included the IL-18, Toll-Like Receptor, IFN alpha, and G-Protein Family signaling pathways. It is interesting to note that a previous study measuring the transcriptional response of human alveolar macrophages to anthrax spores detected an activation of the TLR pathways [22], and our results indicated anthrax LT targets 87 genes within the TLR signaling pathway (Figure 3B).
RGS14 is a protein involved in the regulation of G-protein signaling through attenuation of G-protein heterotrimer signaling, thereby inactivating this signaling cascade. The Affymetrix microarrays revealed that RGS14 expression in LT treated monocytes showed a 6 fold increase in expression (Table 2). This is a potentially significant finding in that RGS14 inhibits G-proteins important for chemotaxis. Therefore LT could be impairing chemotaxis not only by blocking Hsp27 phosphorylation through disruption of the p38 pathway [23], but also by causing over-expression of RGS14, thereby inhibiting G-protein mediated signaling required for actin-based motility.
Table 2.
Predicted effects of LT on monocyte function.1
| Gene | Microarray | Effects |
|---|---|---|
| RGS-14 |
5.61 |
Blockade of monocyte maturation to dendritic cells, inhibition of chemotaxis |
| CXCR2 |
5.04 |
Increased monocyte transendothelial migration into tissues |
| HPSE |
-2.58 |
Diminished inflammatory response |
| CCR5 |
-2.33 |
Reduced responsiveness to the inflammatory mediators RANTES, MIP1 beta |
| ILIR2 | -12.5 | Increased IL1 alpha responsiveness and increased fever |
1 Calculated fold changes compared to mock treated samples.
RGS14 expression is down-regulated during the maturation of monocytes to dendritic cells [24] and over-expression of this G-protein regulator would be expected to block monocyte maturation. RGS14 levels are also known to decrease in dendritic cells exposed to Leishmania major or Toxoplasma gondii, suggesting that RGS14 downregulation may be an important step in a normal immune response, and up-regulation of RGS14 by LT could be contributing to LT’s immunosuppressive effects [25].
Three chemokine receptors were also altered after LT treatment, suggesting that LT may be inducing functional defects in monocyte response signaling. IL-8 receptor beta (CXCR2) was up-regulated after LT treatment (Table 2). CXCR2 transduces signaling through a G-protein activated second messenger system. This receptor is important for monocyte transendothelial migration, and up-regulation of CXCR2 could serve to enhance the delivery of monocytes to tissues. Anthrax spores must be phagocytosed by macrophages in order to germinate into viable bacteria. An increase in the macrophage pool may aid in a reservoir for increased germination of viable bacteria. IL-1 receptor type II (IL-1R2), was found to be markedly down-regulated. IL-1R2 is a decoy receptor for IL-1 that functions either at the cell surface or in a soluble form [26]. The decreased expression of the decoy receptor would presumably increase IL-1a levels and increase the febrile response of the host potentially at least in part explaining the high fever that commonly accompanies systemic anthrax [27]. CCR5 is a receptor for the monocyte chemokines RANTES and MIP. The down-regulation of CCR5 by LT could reflect an inability of toxin-treated monocytes to differentiate into macrophages [28] (Table 2). During the early stages of infection, macrophages play a critical role in assisting B. anthracis pathogenesis by providing a place for bacteria germination from their spore form to viable bacteria. An increase in monocyte trafficking to allow an increase in spore uptake and subsequent germination would prove beneficial for B. anthracis. During later stages of infection, after release of viable bacteria, limiting monocyte differentiation to macrophages would assist in preventing clearance of viable bacteria.
In addition to an alteration in the chemokine response by LT, an additional enzyme, heparanase (HPSE), was found to be decreased in LT-treated human monocytes. This enzyme is an endoglycosidase that degrades heparin sulfate, resulting in disassembly of extracellular barriers required for cell migration [29]. Heparanase has also been postulated to play a role in inflammation [30] and our results showed a 2.6 fold decrease in heparanase gene expression (Table 2). One study has concluded that an in vivo siRNA against heparanase, along with an inhibitor of its enzymatic activity, results in a diminished inflammatory response [31]. Thus LT- mediated inhibition of heparanase expression could also contribute to the inhibition of the host immune response during an anthrax infection.
An external verification method using quantitative real-time PCR was utilized to confirm the microarray data. The eight genes corresponding to RGS14, IL8RB, TLR5, PPM1H, CD47, SYK, CCR5, and IL1R2 were chosen for microarray confirmation in monocytes. CCR5 and IL1R2 were confirmed to be down-regulated at 4 h after LT treatment, reinforcing the microarray data, while the other six genes were up-regulated, again confirming the microarray data (Table 3). A correlation curve was plotted (Figure 3C) and analyzed, showing a linear relationship between the microarray results and RT-PCR with a correlation coefficient of 0.885. Results were performed in duplicates and fold values were normalized to GAPDH. To exclude the possibility the lymphocyte contamination might be contributing to our microarray findings, a higher purity monocyte population (98% purity), obtained by adherence followed by washing off non-adherent lymphocytes, was treated with 500 ng/mL LT for 4 h and gene expression was assessed using real-time PCR. These experiments verified 3 genes to be increased after LT treatment: RGS14, TLR5, and CD47 (1.21-1.70), as observed by the microarray of suspended cells. These findings suggest that the changes in messenger RNA observed are primarily contributed by monocytes, but we cannot entirely exclude a contribution by lymphocytes.
Table 3.
q-RTPCR confirmation of LT-induced genes.1
| Probe | Microarray | q-RT-PCR | Gene name | Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 38290_at |
5.61 |
7.40 |
RGS14-F |
CAGGGATCTGTGAGAAACGAG |
| |
|
|
RGS14-R |
AGGTGATCCTGTTTTCCAGC |
| 207008_at |
5.04 |
7.50 |
IL8RB-F |
GTCTAACAGCTCTGACTACCAC |
| |
|
|
L8RB-R |
TTAAATCCTGACTGGGTCGC |
| 210166_at |
3.90 |
2.24 |
TLR5-F |
TTTTCAGGAGCCCGAGC |
| |
|
|
TLR5-R |
AGCCGAGATTGTGTCACTG |
| 212686_at |
2.65 |
3.85 |
PPM1H-F |
GAGTACAGAGAAAGGAGCTTGG |
| |
|
|
PPM1H-R |
TCCAATAGTTGCCATTACCCG |
| 226016_at |
2.38 |
1.60 |
CD47-F |
TTTGCTATACTCCTGTTCTGGG |
| |
|
|
CD47-R |
TGGGACGAAAAGAATGGCTC |
| 209269_at |
2.15 |
1.60 |
SYK-F |
CAAGTTCTCCAGCAAAAGCG |
| |
|
|
SYK-R |
CATCCGCTCTCCTTTCTCTAAC |
| 206991_at |
-2.66 |
-2.33 |
CCR5-F |
CCAAAAGCACATTGCCAAACG |
| |
|
|
CCR5-R |
ACTTGAGTCCGTGTCACAAGCC |
| 205403_at |
-12.5 |
-28.0 |
IL1R2-F |
TGGCACCTACGTCTGCACTACT |
| IL1R2-R | TTGCGGGTATGAGATGAACG |
1 Calculated fold changes comparedtomock treated samples.
Conclusions
Our investigations show human peripheral monocytes are susceptible to the actions of anthrax LT and do not undergo LT-mediated cytotoxicity after a four hour toxin treatment. We also find that LT induces changes in several genes involved in previously unidentified pathways including the TLR pathway, IFN alpha pathway, and G-Protein family signaling pathways. The identification of several previously unappreciated gene products including RGS14, IL8 receptor beta, CD47, TNF ligand, IL-16, Syk, CCR5, and IL-1 receptor II adds to our understanding of how LT impacts the immune response. Our pathway analysis reveals that anthrax LT targets multiple normal immune-regulatory pathways that would be expected to protect the host against anthrax infection. The increase in RGS14 levels and decrease in CCR5, along with IL-1R2, would likely impair monocyte functions and help to facilitate bacteria survival. B. anthracis maintains a selective advantage by impairing the host immune responses, thereby allowing for invasion and dissemination of the highly fatal bacilli. Our findings encourage further investigations into how these pathways converge functionally to impair normal monocyte function, along with providing new insights into the regulation of the host defense system and inflammation.
Methods
Monocyte isolation and toxin treatment
Whole blood was collected by venous puncture from healthy human volunteers into 8 mL vacutainer tubes containing Ficoll (BD Biosciences). The study followed US Department of Health and Human Services guidelines and was approved by the University of Florida Institutional Review Board. Whole blood was incubated with a monocyte negative selection antibody (Stem Cell Technologies) for 20 min., centrifuged 1700 × g for 25 min at RT, no brake over Ficoll, re-suspended in 10 mL RPMI (Mediatech) complete media, centrifuged at 250 × g for 9 min. to remove platelets, and re-suspended to 7-9 × 105 cells/mL in RPMI. Monocytes were inverted at 37°C with 500 ng/mL LF and 500 ng/mL PA for 4 h. Additional qRT-PCR experiments were performed using higher monocyte purities (98%), obtained by first using a negative selection antibody cocktail (Stem Cell Technologies) isolation technique, followed by plastic adherence for 4 h, as described previously [32].
Toxin purification
LF and PA were purified as previously described [33]. Briefly, Bacillus anthracis culture media was filtered through a 0.22 uM filter, followed by diethylaminoethyl cellulose (DEAE) anion exchange chromatography. The toxins were then subjected to gel filtration and hydrophobic interaction fast protein liquid chromatography (FPLC) and highly purified toxin components were confirmed by Coomassie Blue staining.
Monocyte purity and apoptosis analysis
Monocytes were inverted at 37°C with 500 ng/mL LF and 500 ng/mL PA for 4 h, stained with CD-14 Pac Blue (BD Biosciences), Annexin-V-Fluorescein and propidium iodide (Roche). The cell population was gated first for CD14-Pac-Blue followed by analysis of the relative amount of Annexin (FL1) and PI (FL2) using flow cytometry FACScan (BD), and analyzed by FCS Express (De Novo).
MEK cleavage
Purified monocytes were incubated at 37°C with 500 ng/mL lethal toxin for 4 h. Cells were lysed, ran on a 10% SDS-PAGE gel (Pierce), transferred to a PVDF membrane (Bio-rad) and probed for MEK1 (Upstate). Membranes were then stripped and probed for MEK3 (Santa Cruz). β-actin (Sigma) was used to check consistent loading amounts.
RNA isolation
Purified monocytes from 4 healthy volunteers were incubated at 37°C with media alone or with 500 ng/mL LT for 4 h. Total RNA was collected using RNAeasy mini kit (Qiagen) and RNA quantity and quality was assessed using NanoDrop (Thermo Scientific) technology.
Microarray procedure
100 ng total RNA was labeled using Affymetrix GeneChip® 3' IVT Express Kit for each replicate. Amplified labeled RNA was purified, fragmented, then hybridized for 16 h on Affymetrix GeneChips® (HG U133 plus 2.0) representing approximately 22,000 well-characterized human genes. Arrays were washed using Affymetrix GeneChip® Fluidics Station FS450 and scanned using GeneChip® Scanner 3000 7 G.
Microarray analysis
Low-level analysis was performed using dChipmodeled-based expression matrix (dChip 2007 (DNA-Chip Analyzer), Build date: Jan 4, 2008). Unsupervised analysis - probes sets whose hybridization signal intensity exhibited a coefficient of variation of greater than 0.5 were analyzed by unsupervised hierarchical cluster analysis using algorithms implemented in dChip. Supervised analysis - significant probe sets between the treatment groups were identified using a paired t-test (by donor) at a significance threshold of p < 0.001. Leave-one-out-cross-validation using 4 prediction models was used to test the ability of probe sets significant at p < 0.001 to distinguish between the treatment groups. Microarray analyses were done using dCHIP and BRB-ArrayTools by Richard Simon ( http://linus.nci.nih.gov/BRB-ArrayTools.html). The microarray data for this study was deposited in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) [30] with accession numbersGSM848717 through GSM 848724. The microarray data is also available in a series with accession number GSE34407.
Quantitative real time-PCR (qRT-PCR)
RNA was collected using RNAeasy mini kit (Qiagen), quantitated using a Nanodrop system (Thermo Scientific), and 233 μg total RNA was used for cDNAsynthesis using SuperScript III First-Strand Synthesis (Invitrogen). cDNA was quantitated using SYBR Green JumpStart TaqReadyMix (Sigma) and 10 mM forward and 10 mM reverse primers were used for each indicated reaction. Primers used were as follows ACTB-F TCACCGAGCGCGGCT,ACTB-R TAATGTCACGCACGATTTCCC,GAPDH-F GGTGAAGGTCGGAGTCAACG, and GAPDH-R AGAGTTAAAAGCAGCCCTGGTG. All other primers are listed in Table 2. Reactions were run on the MJR Opticon Continuous Fluorescence detector (Bio-Rad) and analyzed with Opticon Monitor Software 1.08 (Bio-Rad).
Authors’ contributions
KC performed the experiments, analyzed data, interpreted study, drafted, and wrote the manuscript. CL performed the gene expression profiling, biostatistical analysis, and helped design the study. SZ participated in the study design and assisted with experiments. GS participated in the design and interpretation of the study, as well as edited the manuscript. HB participated in the design and analyses of the study. CQ supplied the purified toxin and assisted in data interpretation. FS conceived the study and participated in the design and coordination, as well as edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Contributor Information
Kassidy M Chauncey, Email: kassidy@ufl.edu.
M Cecilia Lopez, Email: mclopez@ufl.edu.
Gurjit Sidhu, Email: gssidhu@ufl.edu.
Sarah E Szarowicz, Email: sguilmai@ufl.edu.
Henry V Baker, Email: hvbaker@ufl.edu.
Conrad Quinn, Email: cquinn@cdc.gov.
Frederick S Southwick, Email: southfs@medicine.ufl.edu.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Lyle Moldawer for his guidance and assistance in the flow cytometry analysis. The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health RO1AI064891. Publication of this article was funded in part by the University of Florida Open-Access Publishing Fund.
References
- Fukao T. Immune system paralysis by anthrax lethal toxin: the roles of innate and adaptive immunity. Lancet Infect Dis. 2004;4:166–170. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(04)00940-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mock M, Fouet A. Anthrax. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2001;55:647–671. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.55.1.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier RJ, Young JA. Anthrax toxin. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2003;19:45–70. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.19.111301.140655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellizzari R, Guidi-Rontani C, Vitale G, Mock M, Montecucco C. Lethal factor of Bacillus anthracis cleaves the N-terminus of MAPKKs: analysis of the intracellular consequences in macrophages. Int J Med Microbiol. 2000;290:421–427. doi: 10.1016/S1438-4221(00)80056-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesbery NS, Webb CP, Leppla SH, Gordon VM, Klimpel KR, Copeland TD, Ahn NG, Oskarsson MK, Fukasawa K, Paull KD. et al. Proteolytic inactivation of MAP-kinase-kinase by anthrax lethal factor. Science. 1998;280:734–737. doi: 10.1126/science.280.5364.734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppla SH. Anthrax toxin edema factor: a bacterial adenylate cyclase that increases cyclic AMP concentrations of eukaryotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982;79:3162–3166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna PC, Acosta D, Collier RJ. On the role of macrophages in anthrax. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993;90:10198–10201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna PC, Kruskal BA, Ezekowitz RA, Bloom BR, Collier RJ. Role of macrophage oxidative burst in the action of anthrax lethal toxin. Mol Med. 1994;1:7–18. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popov SG, Villasmil R, Bernardi J, Grene E, Cardwell J, Popova T, Wu A, Alibek D, Bailey C, Alibek K. Effect of Bacillus anthracis lethal toxin on human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. FEBS Lett. 2002;527:211–215. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(02)03228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassam A, Der SD, Mogridge J. Differentiation of human monocytic cell lines confers susceptibility to Bacillus anthracis lethal toxin. Cell Microbiol. 2005;7:281–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2004.00458.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stearns-Kurosawa DJ, Lupu F, Taylor FB Jr, Kinasewitz G, Kurosawa S. Sepsis and pathophysiology of anthrax in a nonhuman primate model. Am J Pathol. 2006;169:433–444. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.051330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarner J, Jernigan JA, Shieh WJ, Tatti K, Flannagan LM, Stephens DS, Popovic T, Ashford DA, Perkins BA, Zaki SR. Pathology and pathogenesis of bioterrorism-related inhalational anthrax. Am J Pathol. 2003;163:701–709. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63697-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twenhafel NA, Leffel E, Pitt ML. Pathology of inhalational anthrax infection in the african green monkey. Vet Pathol. 2007;44:716–721. doi: 10.1354/vp.44-5-716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu W, Mehta H, Chakrabarty K, Booth JL, Duggan ES, Patel KB, Ballard JD, Coggeshall KM, Metcalf JP. Resistance of human alveolar macrophages to Bacillus anthracis lethal toxin. J Immunol. 2009;183:5799–5806. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comer JE, Galindo CL, Chopra AK, Peterson JW. GeneChip analyses of global transcriptional responses of murine macrophages to the lethal toxin of Bacillus anthracis. Infect Immun. 2005;73:1879–1885. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.3.1879-1885.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesters RM, Florke N, Ostermann H, Kienast J. Increase of plasminogen activator inhibitor levels predicts outcome of leukocytopenic patients with sepsis. Thromb Haemost. 1996;75:902–907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradburne C, Chung MC, Zong Q, Schlauch K, Liu D, Popova T, Popova A, Bailey C, Soppet D, Popov S. Transcriptional and apoptotic responses of THP-1 cells to challenge with toxigenic, and non-toxigenic Bacillus anthracis. BMC Immunol. 2008;9:67. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-9-67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serbina NV, Jia T, Hohl TM, Pamer EG. Monocyte-mediated defense against microbial pathogens. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008;26:421–452. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.26.021607.090326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser DM. The many faces of macrophage activation. J Leukoc Biol. 2003;73:209–212. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0602325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koski GK, Lyakh LA, Rice NR. Rapid lipopolysaccharide-induced differentiation of CD14(+) monocytes into CD83(+) dendritic cells is modulated under serum-free conditions by exogenously added IFN-gamma and endogenously produced IL-10. Eur J Immunol. 2001;31:3773–3781. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200112)31:12<3773::AID-IMMU3773>3.0.CO;2-W. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R. Origin and turnover of monocytes and macrophages. Curr Top Pathol. 1989;79:125–150. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-73855-5_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dozmorov M, Wu W, Chakrabarty K, Booth JL, Hurst RE, Coggeshall KM, Metcalf JP. Gene expression profiling of human alveolar macrophages infected by B. anthracis spores demonstrates TNF-alpha and NF-kappab are key components of the innate immune response to the pathogen. BMC Infect Dis. 2009;9:152. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-9-152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- During RL, Gibson BG, Li W, Bishai EA, Sidhu GS, Landry J, Southwick FS. Anthrax lethal toxin paralyzes actin-based motility by blocking Hsp27 phosphorylation. EMBO J. 2007;26:2240–2250. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi GX, Harrison K, Han SB, Moratz C, Kehrl JH. Toll-like receptor signaling alters the expression of regulator of G protein signaling proteins in dendritic cells: implications for G protein- coupled receptor signaling. J Immunol. 2004;172:5175–5184. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.9.5175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaussabel D, Semnani RT, McDowell MA, Sacks D, Sher A, Nutman TB. Unique gene expression profiles of human macrophages and dendritic cells to phylogenetically distinct parasites. Blood. 2003;102:672–681. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-10-3232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colotta F, Re F, Muzio M, Bertini R, Polentarutti N, Sironi M, Giri JG, Dower SK, Sims JE, Mantovani A. Interleukin-1 type II receptor: a decoy target for IL-1 that is regulated by IL-4. Science. 1993;261:472–475. doi: 10.1126/science.8332913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jernigan DB, Raghunathan PL, Bell BP, Brechner R, Bresnitz EA, Butler JC, Cetron M, Cohen M, Doyle T, Fischer M. et al. Investigation of bioterrorism-related anthrax, United States, 2001: epidemiologic findings. Emerg Infect Dis. 2002;8:1019–1028. doi: 10.3201/eid0810.020353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuttle DL, Harrison JK, Anders C, Sleasman JW, Goodenow MM. Expression of CCR5 increases during monocyte differentiation and directly mediates macrophage susceptibility to infection by human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1998;72:4962–4969. doi: 10.1128/jvi.72.6.4962-4969.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I, Eldor A, Haimovitz-Friedman A, Matzner Y, Ishai-Michaeli R, Lider O, Naparstek Y, Cohen IR, Fuks Z. Expression of heparanase by platelets and circulating cells of the immune system: possible involvement in diapedesis and extravasation. Invasion Metastasis. 1992;12:112–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaday GG, Lider O. Extracellular matrix moieties, cytokines, and enzymes: dynamic effects on immune cell behavior and inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. 2000;67:149–159. doi: 10.1002/jlb.67.2.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edovitsky E, Lerner I, Zcharia E, Peretz T, Vlodavsky I, Elkin M. Role of endothelial heparanase in delayed-type hypersensitivity. Blood. 2006;107:3609–3616. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-08-3301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkord E, Williams PE, Kynaston H, Rowbottom AW. Human monocyte isolation methods influence cytokine production from in vitro generated dendritic cells. Immunology. 2005;114:204–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2004.02076.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn CP, Shone CC, Turnbull PC, Melling J. Purification of anthrax-toxin components by high- performance anion-exchange, gel-filtration and hydrophobic-interaction chromatography. Biochem J. 1988;252:753–758. doi: 10.1042/bj2520753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]