Abstract
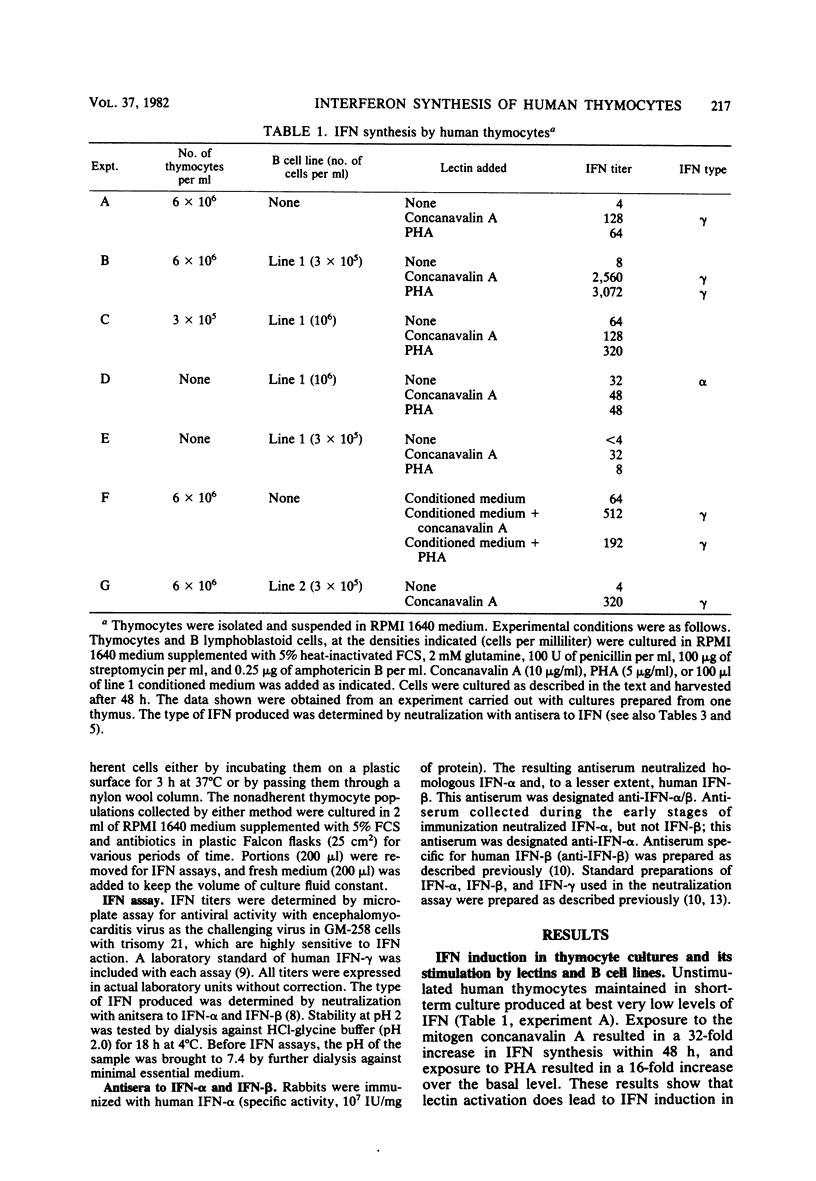
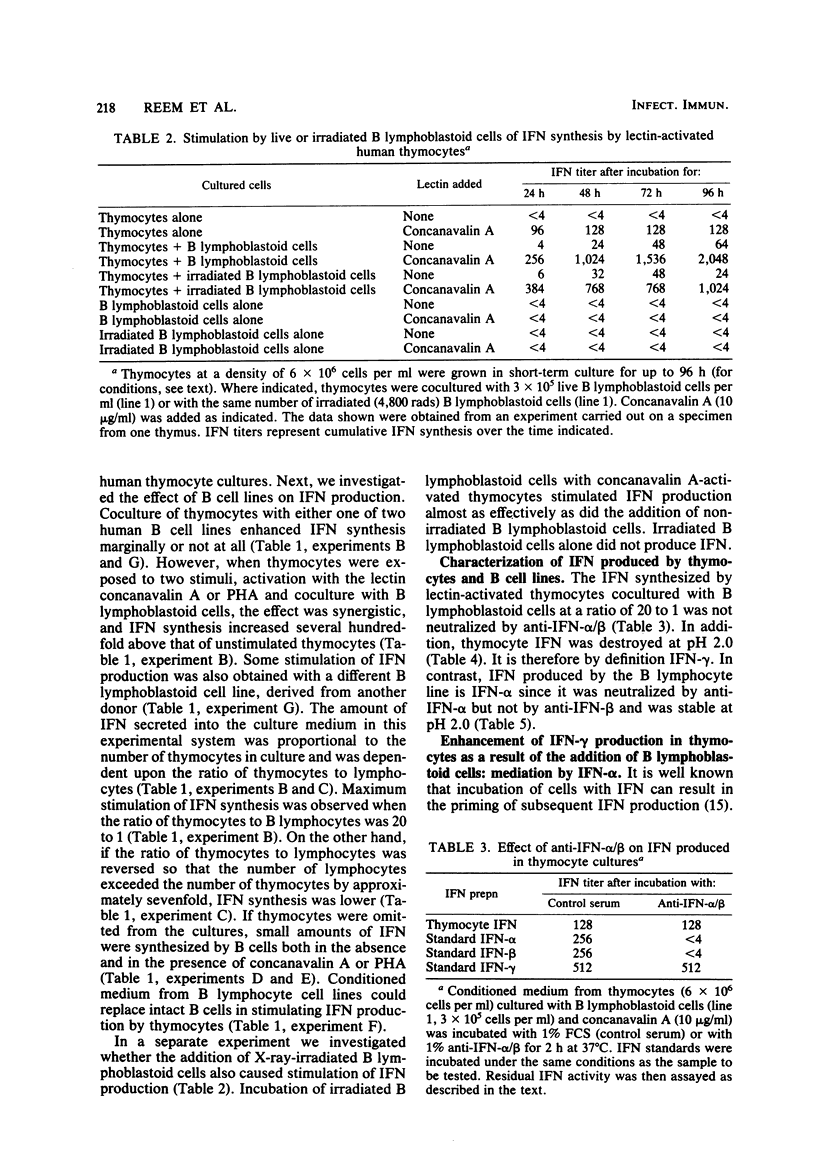
Human thymocytes in culture synthesized small quantities of interferon (IFN) when stimulated by the lectins concanavalin A or phytohemagglutinin. IFN production by lectin-activated thymocytes was enhanced in the presence of live B lymphoblastoid cells, irradiated B lymphoblastoid cells, or the conditioned medium from B lymphoblastoid cell cultures. The IFN synthesized in mixed cultures had characteristics of IFN-gamma, whereas the IFN synthesized by B lymphoblastoid cells alone could be identified as IFN-alpha on the basis of its neutralization with specific antisera and stability at pH 2. These findings indicate that human thymocytes in culture synthesize IFN-gamma and that B lymphoblastoid cells and their products considerably stimulate IFN-gamma synthesis by lectin-activated human thymocytes in culture. This stimulation was not diminished in the presence of antibodies to IFN-alpha, indicating that IFN-alpha production by B lymphoblastoid cells was not responsible for the stimulatory effect. Removal of adherent cells from thymocyte suspensions did not abrogate IFN-gamma production.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck J., Engler H., Brunner H., Kirchner H. Interferon production in cocultures between mouse spleen cells and tumor cells: possible role of mycoplasmas in interferon induction. J Immunol Methods. 1980;38(1-2):63–73. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90331-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birke C., Peter H. H., Langenberg U., Müller-Hermes W. J., Peters J. H., Heitmann J., Leibold W., Dallügge H., Krapf E., Kirchner H. Mycoplasma contamination in human tumor cell lines: effect on interferon induction and susceptibility to natural killing. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):94–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnard G. D., Yasaka K., Maca R. D. Continued growth of functional human T lymphocytes: production of human T-cell growth factor. Cell Immunol. 1980 May;51(2):390–401. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90270-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton B. J., Paucker K. Antigenic properties of human lymphoblastoid interferons. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):244–248. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.244-248.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. B., Cline M. J., Merigan T. C. PPD-stimulated interferon: in vitro macrophage-lymphocyte interaction in the production of a mediator of cellular immunity. Cell Immunol. 1971 Dec;2(6):602–613. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(71)90008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. B. Mitogen and antigen induction of interferon in vitro and in vivo. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1977;35:42–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Watson J. Biochemical and biological characterization of lymphocyte regulatory molecules. V. Identification of an interleukin 2-producing human leukemia T cell line. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1709–1719. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A., Berman B., Ogburn C. A., Berg K., Paucker K., Vilcek J. Two antigenically distinct species of human interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2185–2187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A., Vilcek J. Production of high-titered interferon in cultures of human diploid cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Dec;2(6):476–484. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.6.476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes T. G., Yip Y. K., Vilcek J. Le interferon production by human fibroblasts. Virology. 1979 Oct 30;98(2):351–363. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90558-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Vilcek J. Attempts to induce interferon production by IdUrd induction and EBV superinfection in human lymphoma lines and their hybrids. J Gen Virol. 1980 Jan;46(1):111–117. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-46-1-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcucci F., Kirchner H., Resch K. Mitogen-induced interferon production by normal and steroid-resistant mouse thymocytes. J Interferon Res. 1980 Fall;1(1):87–93. doi: 10.1089/jir.1980.1.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang R. H., Yip Y. K., Vilcek J. Immune interferon induction by monoclonal antibody specific for human T cells. Cell Immunol. 1981 Nov 1;64(2):304–311. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90482-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. A monoclonal antibody with selective reactivity with functionally mature human thymocytes and all peripheral human T cells. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1312–1317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stobo J., Green I., Jackson L., Baron S. Identification of a subpopulation of mouse lymphoid cells required for interferon production after stimulation with mitogens. J Immunol. 1974 Apr;112(4):1589–1593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Santoli D., Dee R. R., Knowles B. B. Anti-viral activity induced by culturing lymphocytes with tumor-derived or virus-transformed cells. Identification of the anti-viral activity as interferon and characterization of the human effector lymphocyte subpopulation. J Exp Med. 1978 May 1;147(5):1299–1313. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.5.1299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Santoli D., Knowles B. B. Tumour cell lines induce interferon in human lymphocytes. Nature. 1977 Dec 15;270(5638):611–613. doi: 10.1038/270611a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigent D. A., Langford M. P., Smith E. M., Blalock J. E., Stanton G. J. Human B lymphocytes produce leukocyte interferon after interaction with foreign cells. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):508–512. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.508-512.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


