Abstract
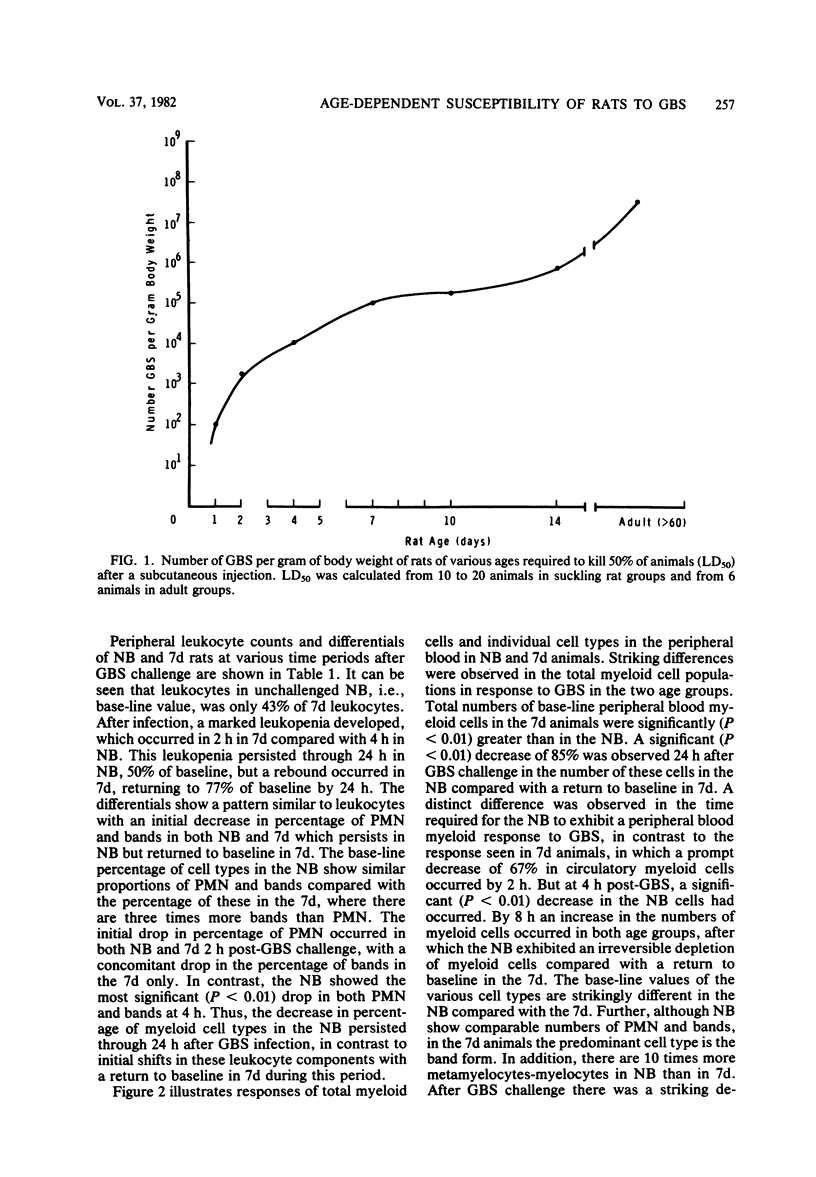
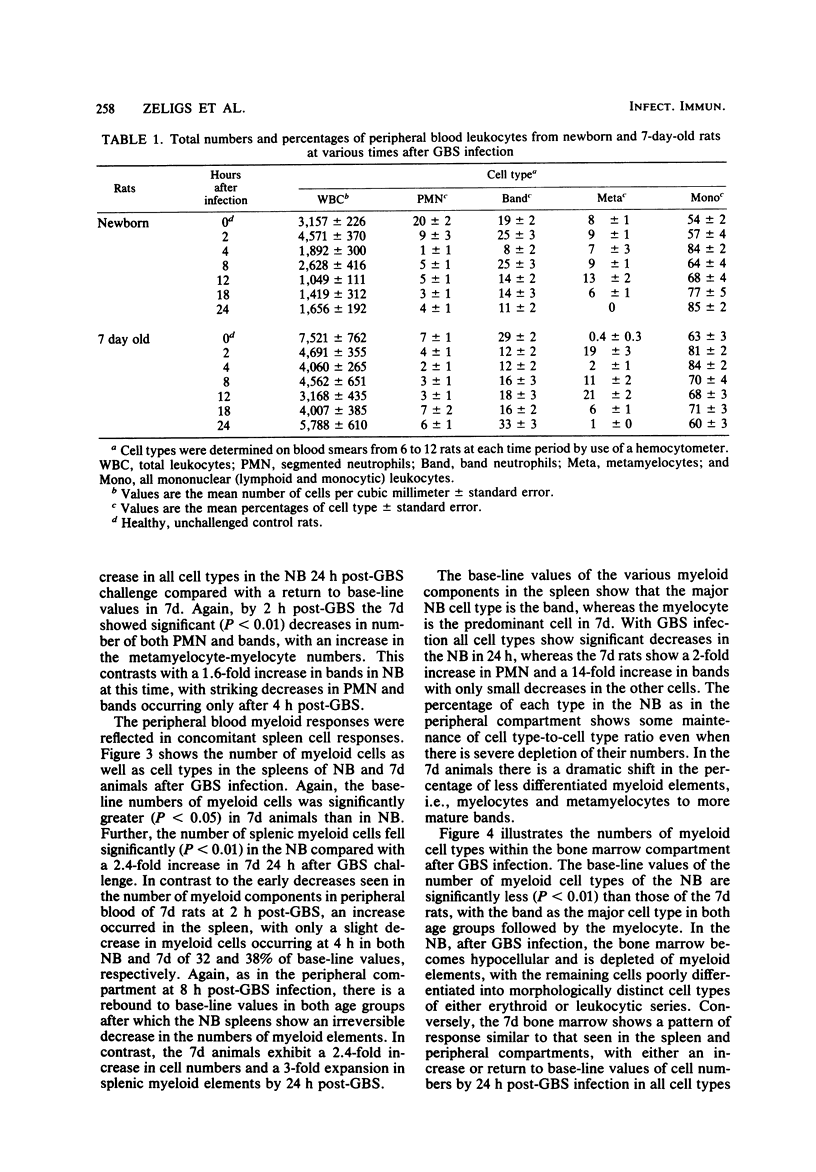
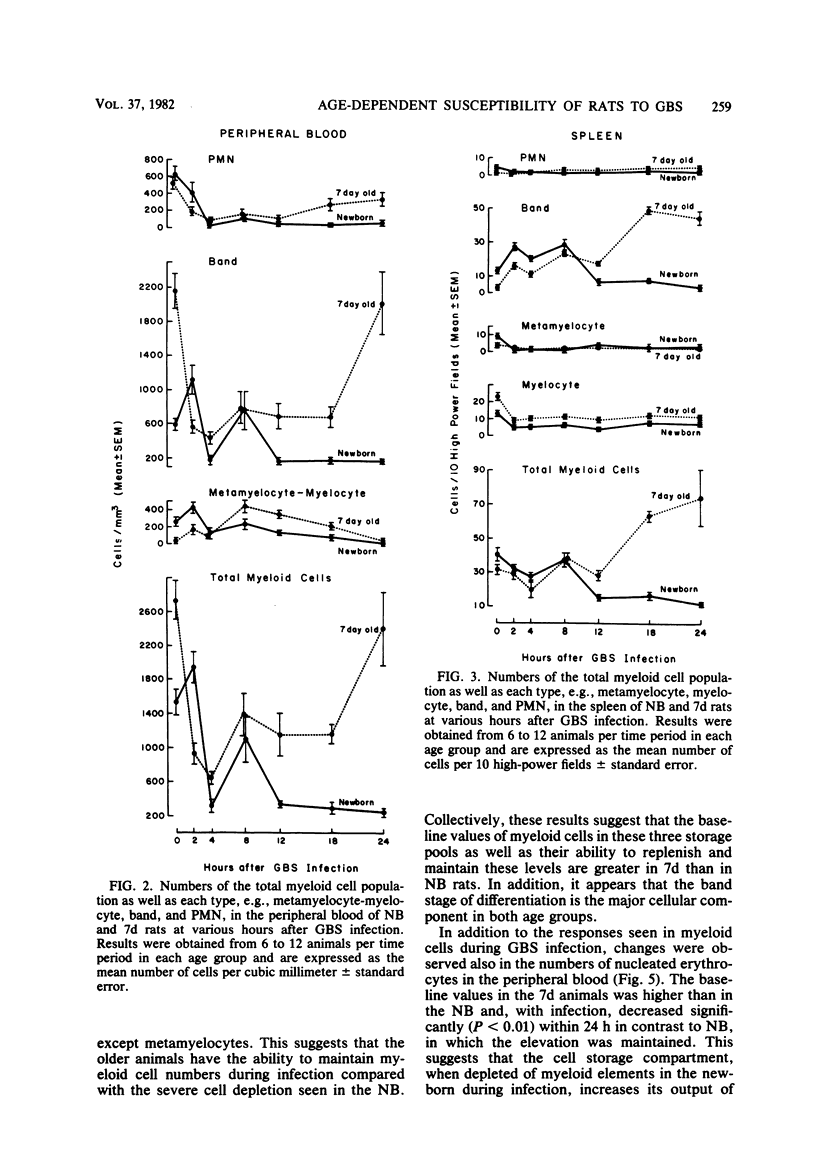
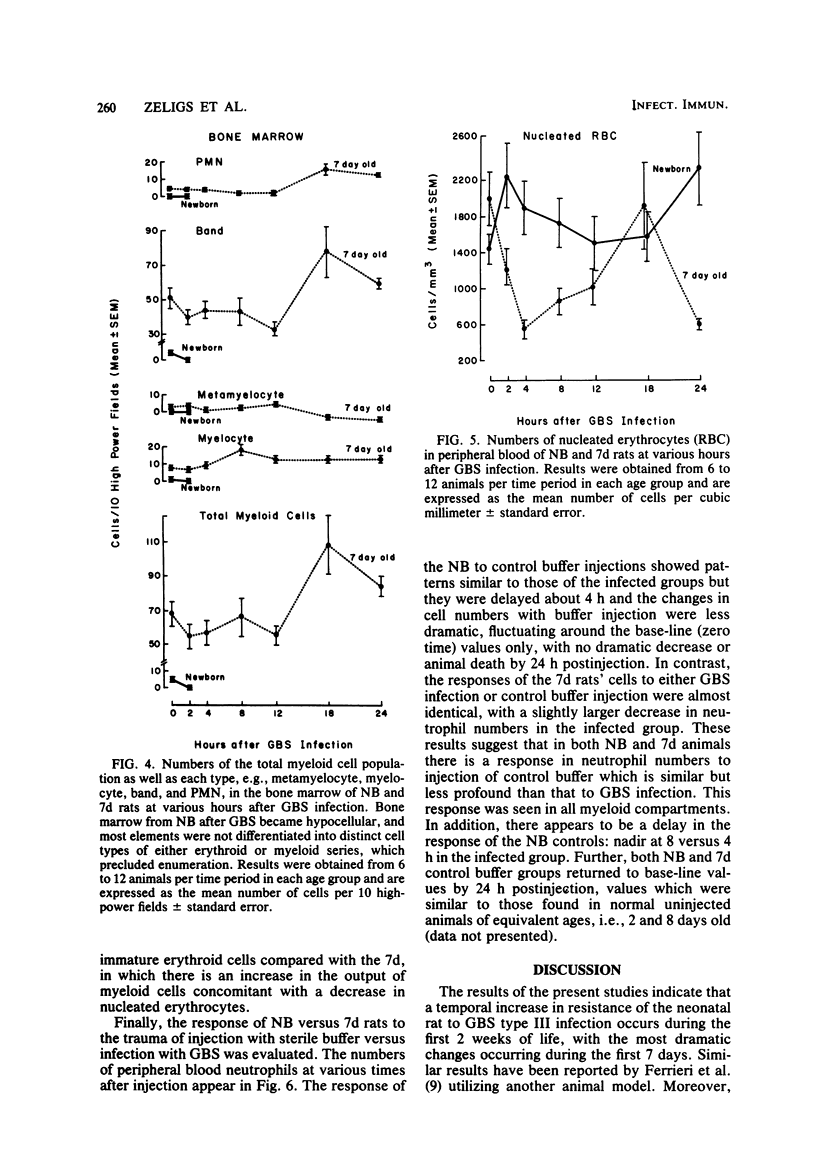
A distinct age-dependent susceptibility to group B streptococcus type III (GBS) was demonstrated, utilizing a neonatal rat model. The most dramatic changes in susceptibility occurred within the first 7 days of postnatal life. To further investigate this susceptibility, experiments were performed utilizing two age groups of rats: (i) animals within the first 24 h of life (NB) and (ii) 7-day-old animals (7d). The infective dosage used was 10(4) GBS per g of body weight, a dose lethal to 100% of NB but only to 15% of 7d. The responses of the myeloid cells in the peripheral blood, spleen, and bone marrow were evaluated at intervals during the first 24 h post-GBS infection. The susceptibility of the NB to GBS appeared to be associated with a number of events, including smaller base-line levels of myeloid elements particularly in the bone marrow, a lag of at least 2 h in their initial response to infection, and an inability to maintain the myeloid pools. The band form of neutrophils appeared to be the predominant cell type in both total number and rapidity of response to infection. Moreover, an initial depletion of this band form was seen in both groups, which returned to base-line levels with recovery in 7d but persisted until death in NB animals. Similarly, shifts in numbers of peripheral nucleated erythrocytes appeared to reflect changes in the myeloid storage pools, with numbers of nucleated erythrocytes significantly decreasing in 7d animals with recovery in contrast to persistence in NB until death. Therefore, shifts in these cells in peripheral blood during infection appear to reflect the state of myeloid storage pools which parallel disease outcome.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker I. D., Robinson O. M., Bazán T. S., López-Osuna M., Kretschmer R. R. Bactericidal capacity of newborn phagocytes against group B beta-hemolytic streptococci. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):535–539. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.535-539.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boner A., Zeligs B. J., Bellanti J. A. Chemotactic responses of various differentiational stages of neutrophils from human cord and adult blood. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):921–928. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.921-928.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chervenick P. A., Boggs D. R., Marsh J. C., Cartwright G. E., Wintrobe M. M. Quantitative studies of blood and bone marrow neutrophils in normal mice. Am J Physiol. 1968 Aug;215(2):353–360. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.2.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen R. D., Rothstein G. Efficiency of neutrophil migration in the neonate. Pediatr Res. 1980 Oct;14(10):1147–1149. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198010000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen R. D., Rothstein G. Exhaustion of mature marrow neutrophils in neonates with sepsis. J Pediatr. 1980 Feb;96(2):316–318. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80837-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dretschmer R. R., Stewardson R. B., Papierniak C. K., Gotoff S. P. Chemotactic and bactericidal capacities of human newborn monocytes. J Immunol. 1976 Oct;117(4):1303–1307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrieri P., Burke B., Nelson J. Production of bacteremia and meningitis in infant rats with group B streptococcal serotypes. Infect Immun. 1980 Mar;27(3):1023–1032. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.3.1023-1032.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer G. W., Lowell G. H., Crumrine M. H., Bass J. W. Demonstration of opsonic activity and in vivo protection against group B streptococci type III by Streptococcus pneumoniae type 14 antisera. J Exp Med. 1978 Sep 1;148(3):776–786. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.3.776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman M. L., Stiehm E. R. Impaired opsonic activity but normal phagocytosis in low-birth-weight infants. N Engl J Med. 1969 Oct 23;281(17):926–931. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196910232811704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr, Klemperer M. R., Alper C. A., Rosen F. S. The enhancement of bacterial phagocytosis by serum. The role of complement components and two cofactors. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1275–1290. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. B., Fischer T. J., Gard S. E., Biberstein M., Rich K. C., Stiehm E. R. Decreased mononuclear and polymorphonuclear chemotaxis in human newborns, infants, and young children. Pediatrics. 1977 Oct;60(4):467–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manroe B. L., Rosenfeld C. R., Weinberg A. G., Browne R. The differential leukocyte count in the assessment and outcome of early-onset neonatal group B streptococcal disease. J Pediatr. 1977 Oct;91(4):632–637. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80522-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken G. H., Jr, Eichenwald H. F. Leukocyte function and the development of opsonic and complement activity in the neonate. Am J Dis Child. 1971 Feb;121(2):120–126. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1971.02100130074008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken G. H., Jr, Mize S. G. A controlled study of intrathecal antibiotic therapy in gram-negative enteric meningitis of infancy. Report of the neonatal meningitis cooperative study group. J Pediatr. 1976 Jul;89(1):66–72. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80929-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken G. H., Jr, Sarff L. D., Glode M. P., Mize S. G., Schiffer M. S., Robbins J. B., Gotschlich E. C., Orskov I., Orskov F. Relation between Escherichia coli K1 capsular polysaccharide antigen and clinical outcome in neonatal meningitis. Lancet. 1974 Aug 3;2(7875):246–250. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91413-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills E. L., Thompson T., Björkstén B., Filipovich D., Quie P. G. The chemiluminescence response and bactericidal activity of polymorphonuclear neutrophils from newborns and their mothers. Pediatrics. 1979 Mar;63(3):429–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerurkar L. S., Zeligs B. J., Bellanti J. A. Maturation of the rabbit alveolar macrophage during animal development. II. Biochemical and enzymatic studies. Pediatr Res. 1977 Dec;11(12):1202–1207. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197712000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman M. E., Gall E. P., Taylor A., Laster L., Nilsson U. R. Serum complement profiles in infants and children. J Pediatr. 1975 Dec;87(6 Pt 1):912–916. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80904-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pahwa S. G., Pahwa R., Grimes E., Smithwick E. Cellular and humoral components of monocyte and neutrophil chemotaxis in cord blood. Pediatr Res. 1977 May;11(5):677–680. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197705000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parke J. C., Jr, Schneerson R., Robbins J. B. The attack rate, age incidence, racial distribution, and case fatality rate of Hemophilus influenzae type b meningitis in Mecklenbury County, North Carolina. J Pediatr. 1972 Oct;81(4):765–769. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80099-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patriarca P., Cramer R., Moncalvo S., Rossi F., Romeo D. Enzymatic basis of metabolic stimulation in leucocytes during phagocytosis: the role of activated NADPH oxidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Jul;145(1):255–262. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., McCracken G. H., Jr, Gotschlich E. C., Orskov F., Orskov I., Hanson L. A. Escherichia coli K1 capsular polysaccharide associated with neonatal meningitis. N Engl J Med. 1974 May 30;290(22):1216–1220. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197405302902202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuit K. E., DeBiasio R. Kinetics of phagocyte response to group B streptococcal infections in newborn rats. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):319–324. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.319-324.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wientzen R. L., Jr, McCracken G. H., Jr Pathogenesis and management of neonatal sepsis and meningitis. Curr Probl Pediatr. 1977 Dec;8(2):1–61. doi: 10.1016/s0045-9380(77)80005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright W. C., Jr, Ank B. J., Herbert J., Stiehm E. R. Decreased bactericidal activity of leukocytes of stressed newborn infants. Pediatrics. 1975 Oct;56(4):579–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthou M. Leucocyte blood picture in ill newborn babies. Arch Dis Child. 1972 Oct;47(255):741–746. doi: 10.1136/adc.47.255.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeligs B. J., Nerurkar L. S., Bellanti J. A. Maturation of the rabbit alveolar macrophage during animal development. III. Phagocytic and bactericidal functions. Pediatr Res. 1977 Dec;11(12):1208–1211. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197712000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


