Abstract
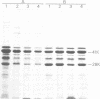
Although effective polysaccharide vaccines have been developed for meningococcal groups A, C, Y, and W135, the purified group B polysaccharide has proven to be nonimmunogenic. Earlier studies indicated that serotype 2 outer membrane protein vaccines induced bactericidal antibodies in animals and protected them from meningococcal challenge. However, a similar vaccine induced only low levels of antiprotein antibodies in both adults and children (C.E. Frasch et al., in J.B. Robbins et al., ed., Seminars in Infectious Disease vol. 4, p. 263-267, 1982). Methods were therefore developed to produce more immunogenic serotype 2 protein vaccines. We found that, by growing the organism for 65 to 72 h at 32 degrees C, three to four times more outer membrane protein was released into the culture medium than could be extracted from overnight-grown cells. The outer membranes were therefore purified directly from the broth by ultrafiltration followed by ammonium sulfate precipitation. Most of the lipopolysaccharide was selectively removed from the membranes by treatment with the nonionic detergent Brij-96. The Brij-96 was then removed and the resulting vaccine was filter sterilized. Some vaccines were prepared by combining equal parts of detergent-treated membrane protein and high-molecular-weight group B polysaccharide producing highly soluble vaccines. These new vaccines were compared by using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent inhibition assay to an insoluble vaccine (E-06) found to be poorly immunogenic in humans. A human serum with serotype 2 specificity was used in the inhibition assay, and 5 microgram of E-06 was required for 50% inhibition, whereas less than 1 microgram of the soluble vaccines was required. Addition of group B polysaccharide slightly increased the inhibitory capacity of the protein component.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashton F. E., Ryan A., Diena B. B., MacKenzie A. M., Chan F. Serotypes among Neisseria meningitidis serogroups B and C strains isolated in Canada. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Dec;26(12):1480–1488. doi: 10.1139/m80-245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S. The size and detergent binding of membrane proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 25;250(14):5459–5469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven D. E., Frasch C. E. Protection against group B meningococcal disease: evaluation of serotype 2 protein vaccines in a mouse bacteremia model. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):110–117. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.110-117.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven D. E., Frasch C. E., Robbins J. B., Feldman H. A. Serogroup identification of Neisseria meningitidis: comparison of an antiserum agar method with bacterial slide agglutination. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 May;7(5):410–414. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.5.410-414.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Maeyer S., Seba J. M., Reginster G. Epidemiology of meningococcal meningitis in Belgium. J Infect. 1981 Mar;3(1 Suppl):63–70. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(81)80010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devoe I. W., Gilchrist J. E. Release of endotoxin in the form of cell wall blebs during in vitro growth of Neisseria meningitidis. J Exp Med. 1973 Nov 1;138(5):1156–1167. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.5.1156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Gotschlich E. C. An outer membrane protein of Neisseria meningitidis group B responsible for serotype specificity. J Exp Med. 1974 Jul 1;140(1):87–104. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Robbins J. D. Protection against group B meningococcal disease. III. Immunogenicity of serotype 2 vaccines and specificity of protection in a guinea pig model. J Exp Med. 1978 Mar 1;147(3):629–644. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschneider I., Gotschlich E. C., Artenstein M. S. Human immunity to the meningococcus. II. Development of natural immunity. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1327–1348. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstein H. D., Elfin R. J., Cooper J. F., Seligmann E. B., Jr, Wolff S. M. Further developments of Limulus Amebocyte Lysate test. Bull Parenter Drug Assoc. 1973 May-Jun;27(3):139–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H. J., Lugowski C. Immunochemistry of groups A, B, and C meningococcal polysaccharide-tetanus toxoid conjugates. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1011–1018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. G., Perry M. B. Improved techniques for the preparation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Jan;22(1):29–34. doi: 10.1139/m76-004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. M., Eldridge J. Development of antibodies to meningococcal protein and lipopolysaccharide serotype antigens in healthy-carriers. J Med Microbiol. 1979 Feb;12(1):107–111. doi: 10.1099/00222615-12-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J. STUDIES ON THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL. I. EVIDENCE FOR THE ROLE OF 2-KETO- 3-DEOXYOCTONATE IN THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:499–506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peppler M. S., Frasch C. E. Protection against group B Neisseria meningitidis disease: effect of serogroup B polysaccharide and polymyxin B on immunogenicity of serotype protein preparations. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):264–270. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.264-270.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen B. H., Lee T. J., Snyderman R., Brooks G. F. Neisseria meningitidis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacteremia associated with C6, C7, or C8 deficiency. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Jun;90(6):917–920. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-6-917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVENNERHOLM L. Quantitative estimation of sialic acids. II. A colorimetric resorcinol-hydrochloric acid method. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Jun;24(3):604–611. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90254-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonntag I., Schwarz H., Hirota Y., Henning U. Cell envelope and shape of Escherichia coli: multiple mutants missing the outer membrane lipoprotein and other major outer membrane proteins. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):280–285. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.280-285.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiesjema R. H., Beuvery E. C., te Pas B. J. Enhanced stability of meningococcal polysaccharide vaccines by using lactose as a menstruum for lyophilization. Bull World Health Organ. 1977;55(1):43–48. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyle F. A., Artenstein M. S., Brandt B. L., Tramont E. C., Kasper D. L., Altieri P. L., Berman S. L., Lowenthal J. P. Immunologic response of man to group B meningococcal polysaccharide vaccines. J Infect Dis. 1972 Nov;126(5):514–521. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.5.514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Mandrell R. E., Altieri P., Berman S., Lowenthal J., Artenstein M. S. Safety and immunogenicity of a Neisseria meningitidis type 2 protein vaccine in animals and humans. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jun;137(6):728–739. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.6.728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Mandrell R. E., Griffiss J. M., Altieri P., Berman S. Complex of meningococcal group B polysaccharide and type 2 outer membrane protein immunogenic in man. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):836–848. doi: 10.1172/JCI109383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Mandrell R. E. Outer-membrane protein and lipopolysaccharide serotyping of Neisseria meningitidis by inhibition of a solid-phase radioimmunoassay. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):424–433. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.424-433.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]