Abstract
To understand the mechanism of Entamoeba histolytica adhesion, we characterized the binding of trophozoites to human erythrocytes (RBC) in suspension by measuring the kinetics of amoeba-RBC complex formation. Adhesion was very efficient, since most of the amoebae were complexed with RBC after only 5 min at 37 degrees C in mixtures containing 10(4) amoebae and 10(6) RBC per ml; the adhesion rate depended on amoeba and RBC concentrations, but not on the A, B, and O human blood groups, and was maximal at 37 degrees C and pH 7.3 in the presence of 4 mM Ca2+ and 1 mM Mg2+. Adhesion was prevented if trophozoites were fixed with glutaraldehyde, but only decreased slightly if RBC were previously fixed; it decreased in the absence of glucose and was inhibited as a function of the concentration of cytochalasin B and of the metabolic inhibitors bathophenanthroline and 8-hydroxyquinoline. From these results we conclude that E. histolytica adhesion is an active process that depends on the amoebal cytoskeleton and metabolic energy and on the mobility of both amoebal and RBC surface ligands.
Full text
PDF
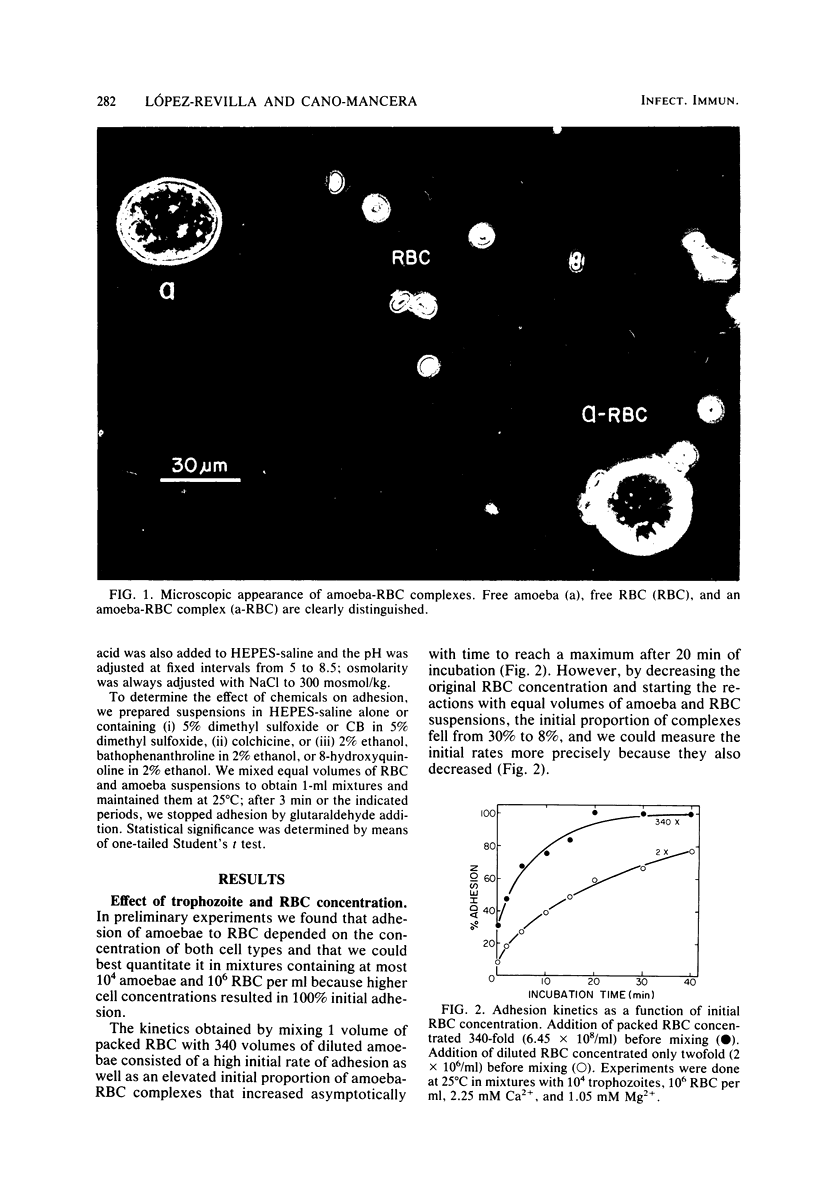
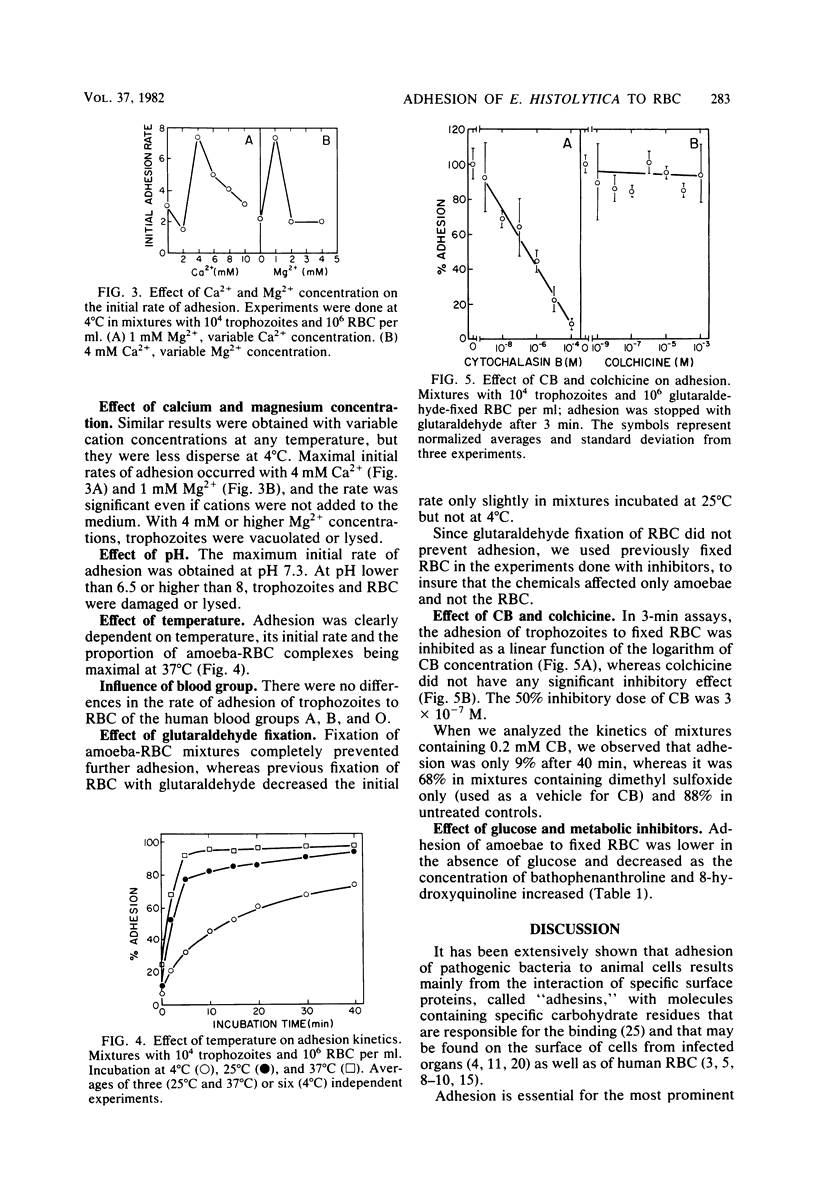


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banai M., Kahane I., Razin S., Bredt W. Adherence of Mycoplasma gallisepticum to human erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):365–372. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.365-372.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banai M., Razin S., Bredt W., Kahane I. Isolation of binding sites to glycophorin from Mycoplasma pneumoniae membranes. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):628–634. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.628-634.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows M. R., Sellwood R., Gibbons R. A. Haemagglutinating and adhesive properties associated with the K99 antigen of bovine strains of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Oct;96(2):269–275. doi: 10.1099/00221287-96-2-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S. Techniques of axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica Schaudinn, 1903 and E. histolytica-like amebae. J Parasitol. 1968 Oct;54(5):1047–1056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton R. D., Meerovitch E., Costerton J. W. The functional morphology of pathogenicity in Entamoeba histolytica. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1970 Sep;64(3):299–304. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1970.11686695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellen R. P., Fillery E. D., Chan K. H., Grove D. A. Sialidase-enhanced lectin-like mechanism for Actinomyces viscosus and Actinomyces naeslundii hemagglutination. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):335–343. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.335-343.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Tjoa W. Hemagglutination of human group A erythrocytes by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from adults with diarrhea: correlation with colonization factor. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):330–337. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.330-337.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., DuPont H. L. Hemagglutination patterns of enterotoxigenic and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli determined with human, bovine, chicken, and guinea pig erythrocytes in the presence and absence of mannose. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):336–346. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.336-346.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. A., Jones G. W., Sellwood R. An attempt to identify the intestinal receptor for the K88 adhesin by means of a haemagglutination inhibition test using glycoproteins and fractions from sow colostrum. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Feb;86(2):228–240. doi: 10.1099/00221287-86-2-228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good N. E., Winget G. D., Winter W., Connolly T. N., Izawa S., Singh R. M. Hydrogen ion buffers for biological research. Biochemistry. 1966 Feb;5(2):467–477. doi: 10.1021/bi00866a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JARUMILINTA R., KRADOLFER F. THE TOXIC EFFECT OF ENTAMOEBA HISTOLYTICA ON LEUCOCYTES. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1964 Sep;58:375–381. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1964.11686259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Rutter J. M. The association of K88 antigen with haemagglutinating activity in porcine strains of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Sep;84(1):135–144. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-1-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight R., Bird R. G., McCaul T. F. Fine structural changes at Entamoeba histolytica rabbit kidney cell (RK 13) interface. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1975 Jun;69(2):197–202. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1975.11687001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobiler D., Mirelman D. Lectin activity in Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):221–225. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.221-225.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel R., Hohmann R. Der Einfluss von Cytochalasin B, Colchicin und Vinblastin auf die Adhäsion von Entamoeba histolytica an Glasoberflächen. Z Parasitenkd. 1979 Nov 1;60(2):123–133. doi: 10.1007/BF00927969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mora Galindo J., Martinez-Palomo A., Chavez B. Interacción entre Entamoeba histolytica y el epitelio cecal del cobayo. Arch Invest Med (Mex) 1978;9 (Suppl 1):261–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Mirelman D., Sharon N. Adherence of Escherichia coli to human mucosal cells mediated by mannose receptors. Nature. 1977 Feb 17;265(5595):623–625. doi: 10.1038/265623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., Croft B. Y., Guerrant R. L. Cytopathogenic mechanisms of Entamoeba histolytica. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):377–390. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roder J. C., Kiessling R., Biberfeld P., Andersson B. Target-effector interaction in the natural killer (NK) cell system. II. The isolation of NK cells and studies on the mechanism of killing. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2509–2517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAFFER J. G., BALSAM T. Ability of Endamoeba histolytica to phagocytose red blood cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1954 Jan;85(1):21–24. doi: 10.3181/00379727-85-20773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva P. P., Martínez-Palomo A., Gonzalez-Robles A. Membrane structure and surface coat of Entamoeba histolytica. Topochemistry and dynamics of the cell surface: cap formation and microexudate. J Cell Biol. 1975 Mar;64(3):538–550. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.3.538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treviño-García Manzo N., Cruze de Lavin E., Tanimoto-Weki M. Estudio ultramicroscópico de la invasión de la mucosa del colon por Entamoeba histolytica en cultivo axénico. Arch Invest Med (Mex) 1978;9 (Suppl 1):275–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trissl D., Martínez-Palomo A., de la Torre M., de la Hoz R., Pérez de Suárez E. Surface properties of Entamoeba: increased rates of human erythrocyte phagocytosis in pathogenic strains. J Exp Med. 1978 Nov 1;148(5):1137–1143. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.5.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]