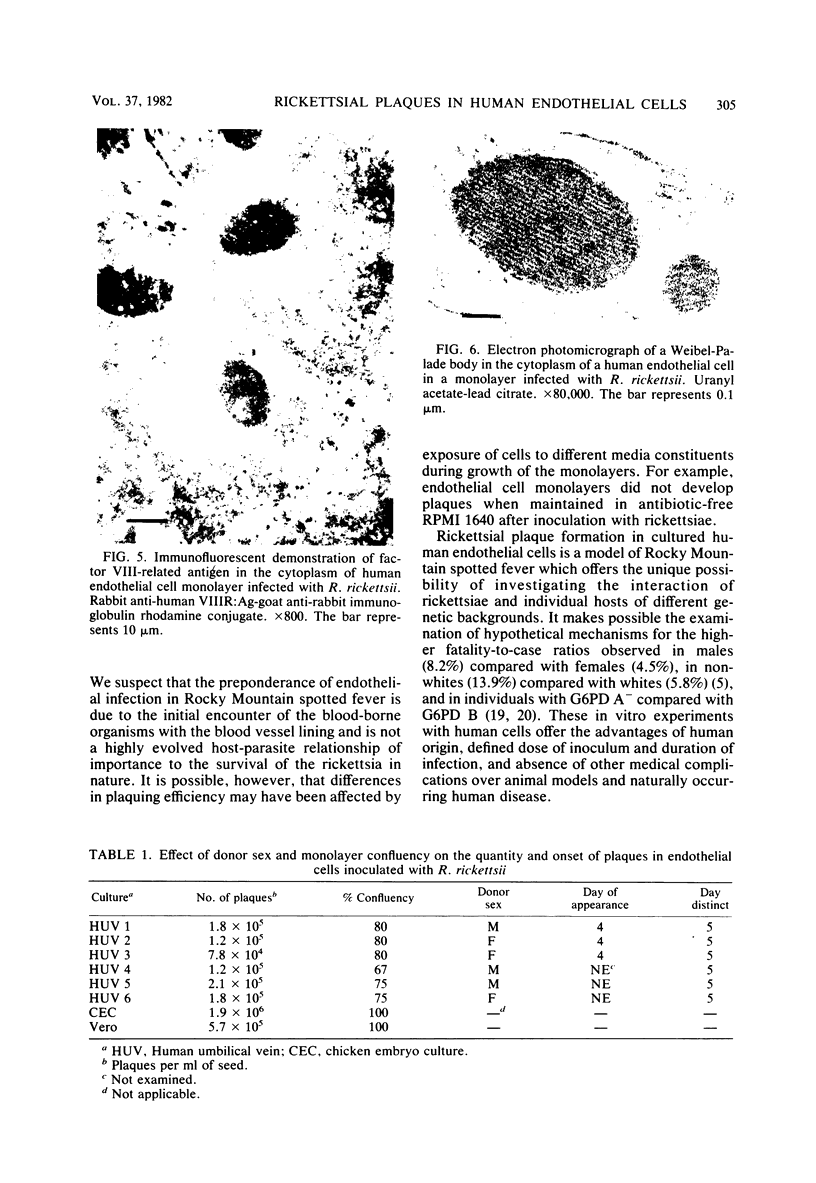
Abstract
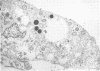
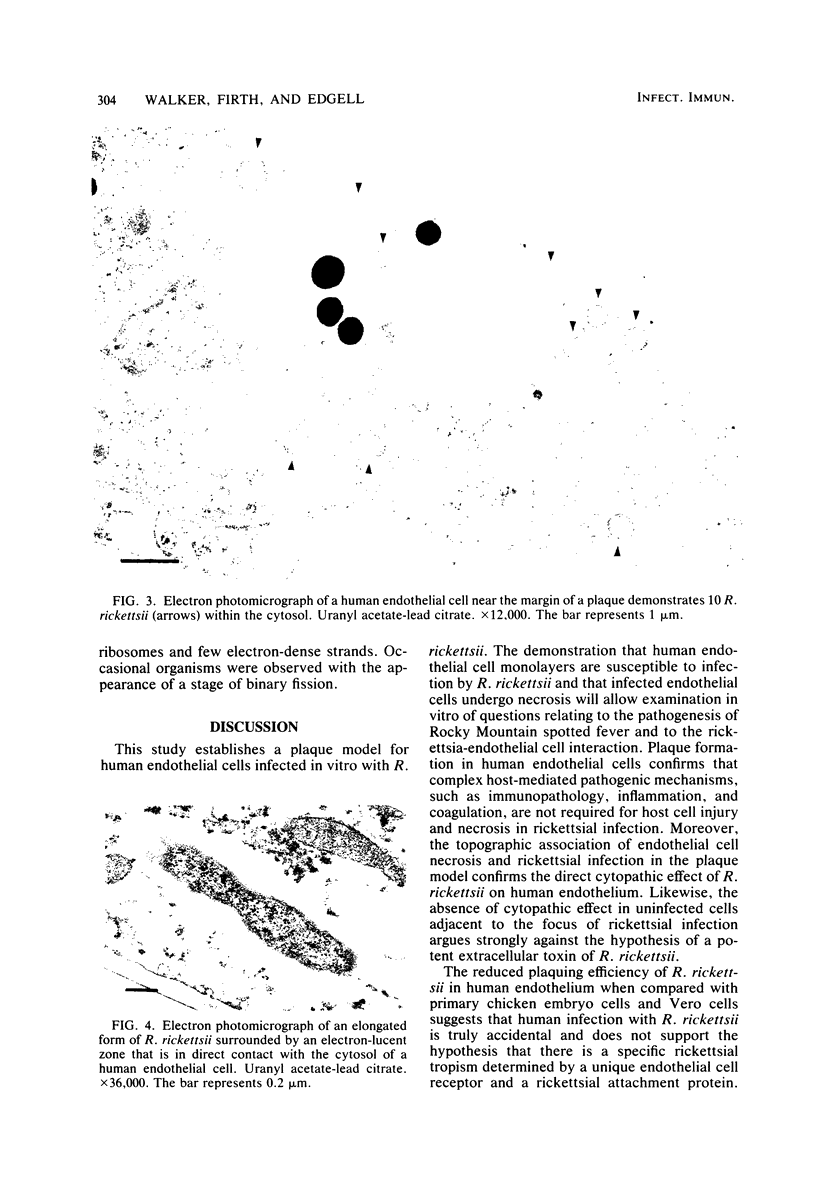
Primary cultures of human umbilical vein endothelial cells were inoculated with plaque-purified Rickettsia rickettsii. After adsorption of rickettsiae, monolayers were overlaid with medium containing 0.5% agarose. Small plaques appeared on day 4 postinoculation, and distinct 1- to 2-mm plaques were observed on day 5. Plaquing efficiency was less than that of primary chicken embryo cells in the same medium. Human endothelial cell monolayers were susceptible to infection by R. rickettsii and underwent necrosis as demonstrated by supravital staining. The topographic association of endothelial cell necrosis and rickettsial infection in the plaque model confirmed the direct cytopathic effect of R. rickettsii on human endothelium. Uninfected cells appeared normal by supravital staining and transmission electron microscopy. This model offers the possibility of investigating rickettsial pathogenesis and mechanisms of enhanced severity of Rocky Mountain spotted fever in specific genetically determined conditions.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. S., Walker D. H. The liver in Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Am J Clin Pathol. 1981 Feb;75(2):156–161. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/75.2.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford W. D., Croker B. P., Tisher C. C. Kidney lesions in Rocky Mountain spotted fever: a light-, immunofluorescence-, and electron-microscopic study. Am J Pathol. 1979 Nov;97(2):381–392. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine D., Mosher D., Yamada T., Burke D., Kenyon R. Coagulation and complement studies in Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Arch Intern Med. 1978 May;138(5):735–738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattwick M. A., O'Brien R. J., Hanson B. F. Rocky Mountain spotted fever: epidemiology of an increasing problem. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Jun;84(6):732–739. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-84-6-732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haudenschild C. C., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Folkman J. Fine structure of vascular endothelium in culture. J Ultrastruct Res. 1975 Jan;50(1):22–32. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(75)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert G. A., Tzianabos T., Gamble W. C., Chappell W. A. Development and characterization of high-titered, group-specific fluorescent-antibody reagents for direct identification of rickettsiae in clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 May;11(5):503–507. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.5.503-507.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Hoyer L. W., Nachman R. L. Synthesis of antihemophilic factor antigen by cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2757–2764. doi: 10.1172/JCI107471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moe J. B., Mosher D. F., Kenyon R. H., White J. D., Stookey J. L., Bagley L. R., Fine D. P. Functional and morphologic changes during experimental Rocky Mountain spotted fever in guinea pigs. Lab Invest. 1976 Sep;35(3):235–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F., Fine D. P., Moe J. B., Kenyon R. H., Ruch G. L. Studies of the coagulation and complement systems during experimental Rocky Mountain spotted fever in rhesus monkeys. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jun;135(6):985–989. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.6.985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOENNER H. G., LACKMAN D. B., BELL E. J. Factors affecting the growth of rickettsias of the spotted fever group in fertile hens' eggs. J Infect Dis. 1962 Mar-Apr;110:121–128. doi: 10.1093/infdis/110.2.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VENABLE J. H., COGGESHALL R. A SIMPLIFIED LEAD CITRATE STAIN FOR USE IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Cell Biol. 1965 May;25:407–408. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. H., Cain B. G., Olmstead P. M. Laboratory diagnosis of Rocky Mountain spotted fever by immunofluorescent demonstration of Rickettsia in Cutaneous lesions. Am J Clin Pathol. 1978 Jun;69(6):619–623. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/69.6.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. H., Cain B. G. The rickettsial plaque. Evidence for direct cytopathic effect of Rickettsia rickettsii. Lab Invest. 1980 Oct;43(4):388–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. H., Crawford C. G., Cain B. G. Rickettsial infection of the pulmonary microcirculation: the basis for interstitial pneumonitis in Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Hum Pathol. 1980 May;11(3):263–272. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(80)80008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. H., Harrison A., Henderson F., Murphy F. A. Identification of Rickettsia rickettsii in a guinea pig model by immunofluorescent and electron microscopic techniques. Am J Pathol. 1977 Feb;86(2):343–358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. H., Henderson F. W. Effect of immunosuppression on Rickettsia rickettsii infection in guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):221–227. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.221-227.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. H., Kirkman H. N. Rocky Mountain spotted fever and deficiency in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Infect Dis. 1980 Nov;142(5):771–771. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.5.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. H., Mattern W. D. Acute renal failure in Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Arch Intern Med. 1979 Apr;139(4):443–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wike D. A., Burgdorfer W. Plaque formation in tissue cultures by Rickettsia rickettsi isolated directly from whole blood and tick hemolymph. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):736–738. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.736-738.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wike D. A., Ormsbee R. A., Tallent G., Peacock M. G. Effects of various suspending media on plaque formation by rickettsiae in tissue culture. Infect Immun. 1972 Oct;6(4):550–556. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.4.550-556.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wike D. A., Tallent G., Peacock M. G., Ormsbee R. A. Studies of the rickettsial plaque assay technique. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):715–722. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.715-722.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Harber P., Pettit G. W., Wing D. A., Oster C. N. Activation of the kallikrein-kinin system in Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Jun;88(6):764–768. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-88-6-764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]