Abstract
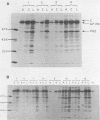
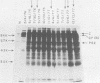
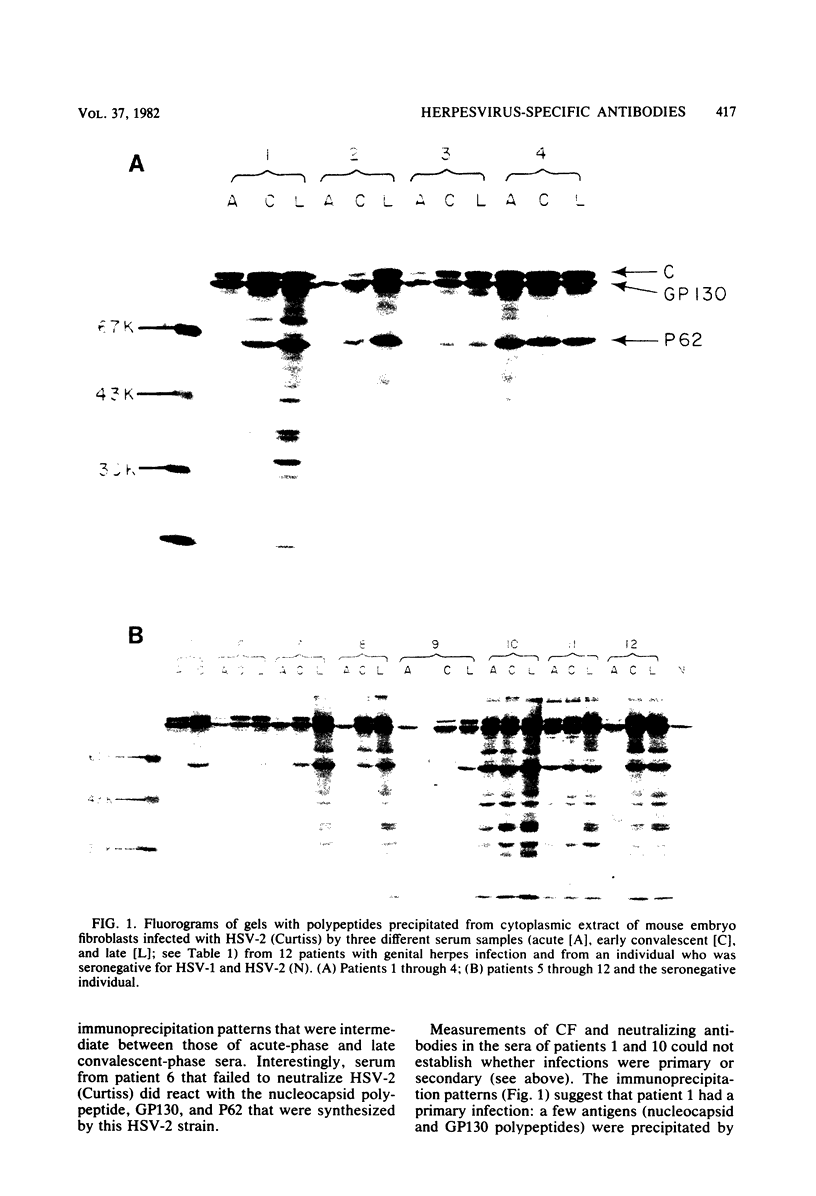
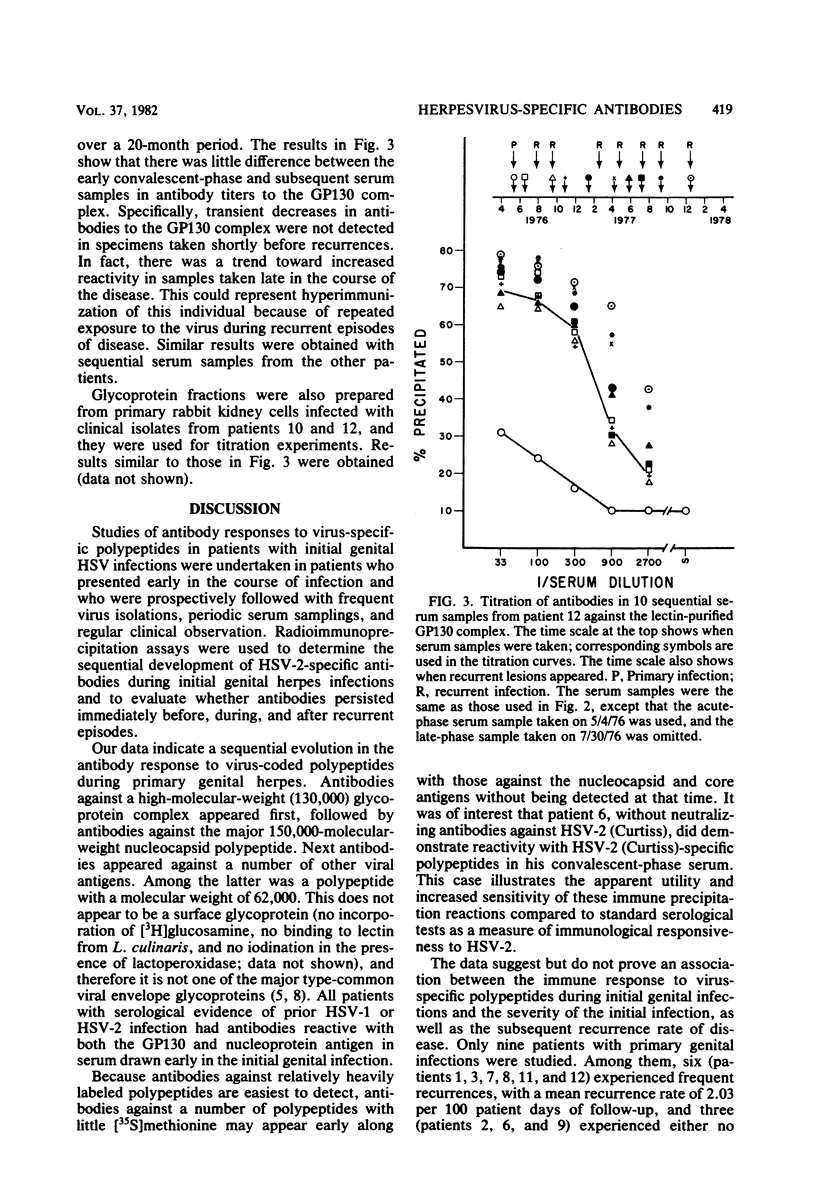
Virus-specific antibodies against a number of herpes simplex virus type 2 antigens were determined by radioimmunoprecipitation assays in sequential serum samples obtained from 12 patients with initial genital herpes simplex virus infection. The progressive appearance of antibodies to virus-specific antigens was observed; antibodies against a 130,000-molecular-weight glycoprotein complex appeared first, followed by antibodies against the major nucleocapsid polypeptide and then antibodies against a number of other viral antigens, including a polypeptide with a molecular weight of 62,000. Patients who developed a wide variety of antibodies to viral polypeptides shortly after resolution of their initial episode seemed to experience more severe initial infections and more recurrences than did those who reacted poorly with these virus-specific antigens. This was most apparent with respect to antibodies to virus-specific polypeptides with molecular weights between 30,000 and 43,000. Antibody specificity did not change during the course of follow-up regardless of whether serum samples were taken shortly before, during, or after recurrent episodes. Glycoprotein-specific antibodies were quantitated with the purified 130,000-molecular-weight glycoprotein material. No significant fluctuations in these antibody titers were observed before or after recurrences of the disease.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong D., Young L. S., Meyer R. D., Blevins A. H. Infectious complications of neoplastic disease. Med Clin North Am. 1971 May;55(3):729–745. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)32514-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aston D. L., Cohen A., Spindler M. A. Herpesvirus hominis infection in patients with myeloproliferative and lymphoproliferative disorders. Br Med J. 1972 Nov 25;4(5838):462–465. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5838.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin D. R. Rapid typing of herpes simplex virus strains using the indirect immunoperoxidase method. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):568–571. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.568-571.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassai E. N., Sarmiento M., Spear P. G. Comparison of the virion proteins specified by herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1327–1331. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1327-1331.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Katze M., Hydrean-Stern C., Eisenberg R. J. Type-common CP-1 antigen of herpes simplex virus is associated with a 59,000-molecular-weight envelope glycoprotein. J Virol. 1978 Jul;27(1):172–181. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.1.172-181.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey L., Reeves W. C., Chiang W. T., Vontver L. A., Remington M., Winter C., Holmes K. K. Ineffectiveness of topical ether for the treatment of genital herpes simplex virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1978 Aug 3;299(5):237–239. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197808032990507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey L., Reeves W. C., Holmes K. K. Cellular immune response in genital herpes simplex virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1978 Nov 2;299(18):986–991. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197811022991805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glorioso J. C., Wilson L. A., Fenger T. W., Smith J. W. Complement-mediated cytolysis of HSV-1 and HSV-2 infected cells: plasma membrane antigens reactive with type-specific and cross-reactive antibody. J Gen Virol. 1978 Aug;40(2):443–454. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-40-2-443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. J., Friedman-Kien A. E., Yellin P. B. Orofacial herpes simplex virus infection in hairless mice: latent virus in trigeminal ganglia after topical antiviral treatment. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):130–135. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.130-135.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonsdale D. M. A rapid technique for distinguishing herpes-simplex virus type 1 from type 2 by restriction-enzyme technology. Lancet. 1979 Apr 21;1(8121):849–852. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91265-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez C., O'Reilly R. J. Cell-mediated immune responses in recurrent herpesvirus infections. I. Lymphocyte proliferation assay. J Immunol. 1977 Mar;118(3):895–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller S. A., Herrmann E. C., Jr, Winkelmann R. K. Herpes simplex infections in hematologic malignancies. Am J Med. 1972 Jan;52(1):102–114. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahmias A. J., Josey W. E., Naib Z. M., Luce C. F., Duffey A. Antibodies to Herpesvirus hominis types 1 and 2 in humans. I. Patients with genital herpetic infections. Am J Epidemiol. 1970 Jun;91(6):539–546. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly R. J., Chibbaro A., Anger E., Lopez C. Cell-mediated immune responses in patients with recurrent Herpes Simplex infections. II. Infection-associated deficiency of lymphokine production in patients with recurrent herpes labialis or herpes progenitalis. J Immunol. 1977 Mar;118(3):1095–1102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakes J. E., Rosemond-Hornbeak H. Antibody-mediated recovery from subcutaneous herpes simplex virus type 2 infection. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):489–495. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.489-495.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pien F. D., Smith T. F., Anderson C. F., Webel M. L., Taswell H. F. Herpesviruses in renal transplant patients. Transplantation. 1973 Nov;16(5):489–495. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197311000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rager-Zisman B., Merigan T. C. A useful quantitative semimicromethod for viral plaque assay. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Apr;142(4):1174–1179. doi: 10.3181/00379727-142-37202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves W. C., Corey L., Adams H. G., Vontver L. A., Holmes K. K. Risk of recurrence after first episodes of genital herpes. Relation to HSV type and antibody response. N Engl J Med. 1981 Aug 6;305(6):315–319. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198108063050604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. V. Purification and structural proteins of the herpesvirion. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):143–159. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.143-159.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. G., Cook M. L. Maintenance of latent herpetic infection: an apparent role for anti-viral IgG. J Immunol. 1974 Dec;113(6):1685–1693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz M. A., Yamamoto H., Notkins A. L. Immunological response restricts number of cells in sensory ganglia infected with herpes simplex virus. Nature. 1976 Dec 9;264(5586):554–556. doi: 10.1038/264554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth B. B., Alexander E. R. Seroepidemiology of infectious due to members of the herpesvirus group. Am J Epidemiol. 1971 Nov;94(5):496–507. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth B. B., Bonin P., Holmes K. K., Gutman L., Wiesner P., Alexander E. R. Isolation of viruses, bacteria and other organisms from venereal disease clinic patients: methodology and problems associated with multiple isolations. Health Lab Sci. 1973 Apr;10(2):75–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweerink H. J., Martinez D., Lynch R. J., Stanton L. W. Immune responses in mice against herpes simplex virus: mechanisms of protection against facial and ganglionic infections. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):267–275. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.267-275.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweerink H. J., Stanton L. W. Immune response to herpes simplex virus infections: virus-specific antibodies in sera from patients with recurrent facial infections. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):624–630. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.624-630.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]