Abstract
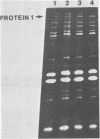
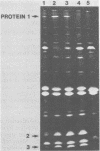
A strain of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis which harbors a 63-kilobase plasmid was found to cause a lethal infection in Swiss albino mice. The rate of infection paralleled the ability of the pathogenic organism to attach to a monolayer of HeLa cells. One novel outer membrane protein (protein 1) with a molecular weight of 140,000 was found to be associated with the possession of the 63-kilobase plasmid not at 26 degrees C, and expression was moderately affected by the concentration of calcium in the growth medium. Moreover, it was found that synthesis of protein 1 associated outer membrane protein showing similar properties was also found to be expressed in plasmid-containing strains of Yersinia enterocolitica. The properties of protein 1 indicate that it could be identical to the previously described virulence W antigen.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BACON G. A., BURROWS T. W. The basis of virulence in Pasteurella pestis: an antigen determining virulence. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Oct;37(5):481–493. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUBAKER R. R., SURGALLA M. J. Genotypic alterations associated with avirulence in streptomycin-resistant Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1962 Oct;84:615–624. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.4.615-624.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W., BACON G. A. V and W antigens in strains of Pasteurella pseudotuberculosis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1960 Feb;41:38–44. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W. VIRULENCE OF PASTEURELLA PESTIS AND IMMUNITY TO PLAGUE. Ergeb Mikrobiol Immunitatsforsch Exp Ther. 1963;37:59–113. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-36742-1_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bovallius A., Nilsson G. Ingestion and survival of Y. pseudotuberculosis in HeLa cells. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Dec;21(12):1997–2007. doi: 10.1139/m75-287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker R. R. The genus Yersinia: biochemistry and genetics of virulence. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1972;57:111–158. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65297-4_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. B., Zahorchak R. J., Brubaker R. R. Plague virulence antigens from Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):638–640. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.638-640.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devenish J. A., Schiemann D. A. HeLa cell infection by Yersinia enterocolitica: evidence for lack of intracellular multiplication and development of a new procedure for quantitative expression of infectivity. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):48–55. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.48-55.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr New surface-associated heat-labile colonization factor antigen (CFA/II) produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli of serogroups O6 and O8. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):638–647. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.638-647.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Silver R. P., Evans D. J., Jr, Chase D. G., Gorbach S. L. Plasmid-controlled colonization factor associated with virulence in Esherichia coli enterotoxigenic for humans. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):656–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.656-667.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferber D. M., Brubaker R. R. Plasmids in Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):839–841. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.839-841.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filip C., Fletcher G., Wulff J. L., Earhart C. F. Solubilization of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli by the ionic detergent sodium-lauryl sarcosinate. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):717–722. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.717-722.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Lazere J. R., Casey T. Plasmid associated with pathogenicity and calcium dependency of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):682–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.682-685.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Lazere J. R., Casey T., Wohlhieter J. A. Presence of a virulence-associated plasmid in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):1044–1047. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.1044-1047.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGUCHI K., SMITH J. L. Studies on the nutrition and physiology of Pasteurella pestis. VI. A differential plating medium for the estimation of the mutation rate to avirulence. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:605–608. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.605-608.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWTON W. D., ERDMAN R. L., SURGALLA M. J. BIOSYNTHESIS AND PURIFICATION OF V AND W ANTIGEN IN PASTEURELLA PESTIS. J Immunol. 1963 Aug;91:179–184. doi: 10.21236/ad0299868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., McGrath P. P., Carter P. H., Eide E. L. The ability of some Yersinia enterocolitica strains to invade HeLa cells. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Dec;23(12):1714–1722. doi: 10.1139/m77-247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maclagan R. M., Old D. C. Haemagglutinins and fimbriae in different serotypes and biotypes of Yersinia enterocolitica. J Appl Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;49(2):353–360. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1980.tb05135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Isaacson R. E., Pohlenz J. Mechanisms of association of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli with intestinal epithelium. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Jan;32(1):119–127. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mors V., Pai C. H. Pathogenic properties of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):292–294. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.292-294.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obwolo M. J. Yersiniosis in the Bristol Zoo (1955-1974). Acta Zool Pathol Antverp. 1976 Feb;(64):81–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F., Smith H. W., Sojka W. J. The establishment of K99, a thermolabile, transmissible escherichia coli K antigen, previously called "Kco", possessed by calf and lamb enteropathogenic strains. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1975 Feb;83(1):31–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb00066.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen K. B., Winblad S., Bitsch V. Studies on the interaction between different O-serotypes of Yersinia enterocolitica and HeLa cells. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1979 Apr;87B(2):141–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1979.tb02417.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Falkow S. Virulence-associated plasmids from Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pestis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Dec;148(3):877–883. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.3.877-883.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmids and plasmid-associated determinants of Yersinia enterocolitica pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):775–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.775-782.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipley P. L., Gyles C. L., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmids that encode for the K88 colonization antigen. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):559–566. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.559-566.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirm S., Orskov F., Orskov I., Mansa B. Episome-carried surface antigen K88 of Escherichia coli. II. Isolation and chemical analysis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):731–739. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.731-739.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Brubaker R. R. Cytoplasmic and membrane proteins of yersiniae cultivated under conditions simulating mammalian intracellular environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1224–1228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Une T., Zen-Yoji H., Maruyama T., Yanagawa Y. Correlation between epithelial cell infectivity in vitro and O-antigen groups of Yersinia enterocolitica. Microbiol Immunol. 1977;21(12):727–729. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1977.tb00340.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zink D. L., Feeley J. C., Wells J. G., Vanderzant C., Vickery J. C., Roof W. D., O'Donovan G. A. Plasmid-mediated tissue invasiveness in Yersinia enterocolitica. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):224–226. doi: 10.1038/283224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]