Abstract
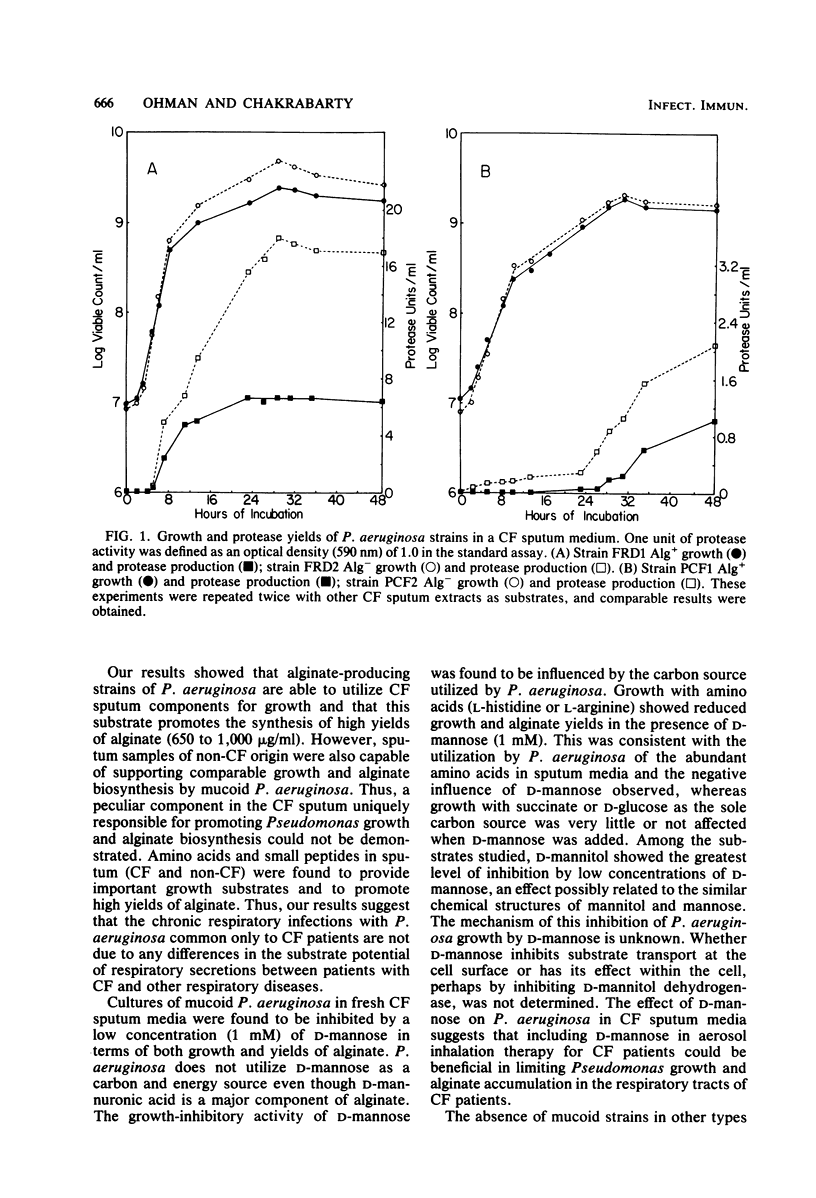
Growth and exoproduct production were examined with sputum from patients with respiratory diseases serving as the growth substrate for mucoid strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from cystic fibrosis (CF) patients. Mucoid strains are uniquely common to chronic respiratory infections of CF patients. The mucoid colonial morphology of P. aeruginosa is due to the biosynthesis of the exopolysaccharide alginate. Alginate-producing (Alg+) strains utilized CF sputum for growth and high yields of alginate; however, sputum from patients with other respiratory diseases produced comparable results. Analysis of CF sputum medium indicated that amino acids and small peptides were major substrates for P. aeruginosa in respiratory secretions. Cultures of Alg+ strains in CF sputum medium were inhibited in growth and reduced in alginate yields by a low concentration (1 mM) of D-mannose, suggesting therapeutic applications. The rates of growth of two Alg+ strains in CF sputum medium were found to be slightly lower compared with their respective spontaneous Alg- mutants, indicating that the mucoid phenotype does not enhance the ability of P. aeruginosa to utilize respiratory secretions. At all stages of growth in CF sputum medium, two Alg+ strains produced lower yields of protease than did their respective Alg- mutants. When seven Alg+ strains of CF origin were compared with their respective Alg- mutants, the Alg+ phenotype correlated with reduced yields of extracellular proteases. These data are consistent with the hypothesis that mucoid strains of P. aeruginosa are more suited to chronic rather than to acute respiratory infections in that reduced yields of proteases temper the level of damage to the lungs and result in a reduced infiltration of phagocytic cells.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore R. S., Mitchell M. Immunologic investigations of mucoid strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: comparison of susceptibility to opsonic antibody in mucoid and nonmucoid strains. J Infect Dis. 1980 Feb;141(2):238–247. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.2.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood L. L., Pennington J. E. Influence of mucoid coating on clearance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from lungs. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):443–448. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.443-448.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P. B., di Sant'Agnese P. A. A review. Cystic fibrosis at forty--quo vadis? Pediatr Res. 1980 Feb;14(2):83–87. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198002000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz E., Mosovich L. L., Neter E. Serogroups of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and the immune response of patients with cystic fibrosis. J Infect Dis. 1970 Mar;121(3):269–274. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.3.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doggett R. G., Harrison G. M., Carter R. E. Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with chronic illnesses. Lancet. 1971 Jan 30;1(7692):236–237. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90973-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doggett R. G., Harrison G. M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: immune status in patients with cystic fibrosis. Infect Immun. 1972 Oct;6(4):628–635. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.4.628-635.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. R., Linker A. Production and characterization of the slime polysaccharide of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):915–924. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.915-924.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govan J. R., Fyfe J. A., McMillan C. The instability of mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa: fluctuation test and improved stability of the mucoid form in shaken culture. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Jan;110(1):229–232. doi: 10.1099/00221287-110-1-229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govan J. R., Fyfe J. A. Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa and cystic fibrosis: resistance of the mucoid from to carbenicillin, flucloxacillin and tobramycin and the isolation of mucoid variants in vitro. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 May;4(3):233–240. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.3.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govan J. R. Mucoid strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: the influence of culture medium on the stability of mucus production. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Nov;8(4):513–522. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-4-513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray L., Kreger A. Microscopic characterization of rabbit lung damage produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa proteases. Infect Immun. 1979 Jan;23(1):150–159. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.1.150-159.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson C. A., Jeanes A. A new modification of the carbazole analysis: application to heteropolysaccharides. Anal Biochem. 1968 Sep;24(3):470–481. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90154-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulczycki L. L., Murphy T. M., Bellanti J. A. Pseudomonas colonization in cystic fibrosis. A study of 160 patients. JAMA. 1978 Jul 7;240(1):30–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam J., Chan R., Lam K., Costerton J. W. Production of mucoid microcolonies by Pseudomonas aeruginosa within infected lungs in cystic fibrosis. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):546–556. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.546-556.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linker A., Jones R. S. A new polysaccharide resembling alginic acid isolated from pseudomonads. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 25;241(16):3845–3851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz S. M., Macrina F. L., Phibbs P. V., Jr R-factor inheritance and plasmid content in mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):530–539. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.530-539.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May J. R., Herrick N. C., Thompson D. Bacterial infection in cystic fibrosis. Arch Dis Child. 1972 Dec;47(256):908–913. doi: 10.1136/adc.47.256.908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mian F. A., Jarman T. R., Righelato R. C. Biosynthesis of exopolysaccharide by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1978 May;134(2):418–422. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.2.418-422.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman D. E., Chakrabarty A. M. Genetic mapping of chromosomal determinants for the production of the exopolysaccharide alginate in a Pseudomonas aeruginosa cystic fibrosis isolate. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):142–148. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.142-148.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman D. E., Cryz S. J., Iglewski B. H. Isolation and characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO mutant that produces altered elastase. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jun;142(3):836–842. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.3.836-842.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington J. E., Reynolds H. Y., Wood R. E., Robinson R. A., Levine A. S. Use of a Pseudomonas Aeruginosa vaccine in pateints with acute leukemia and cystic fibrosis. Am J Med. 1975 May;58(5):629–636. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90498-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections: persisting problems and current research to find new therapies. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Jun;82(6):819–831. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-82-6-819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht H., Geokas M. C., Silverman P., Haverback B. J. A new ultrasensitive method for the determination of proteolytic activity. Clin Chim Acta. 1968 Aug;21(2):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(68)90127-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shwachman H., Kowalski M., Khaw K. T. Cystic fibrosis: a new outlook. 70 patients above 25 years of age. Medicine (Baltimore) 1977 Mar;56(2):129–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokol P. A., Ohman D. E., Iglewski B. H. A more sensitive plate assay for detection of protease production by Pseudomanas aeruginosa. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Apr;9(4):538–540. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.4.538-540.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomassen M. J., Demko C. A., Boxerbaum B., Stern R. C., Kuchenbrod P. J. Multiple of isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa with differing antimicrobial susceptibility patterns from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Infect Dis. 1979 Dec;140(6):873–880. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.6.873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. E., Boat T. F., Doershuk C. F. Cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Jun;113(6):833–878. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.113.6.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wretlind B., Hedén L., Sjöberg L., Wadström T. Production of enzymes and toxins by hospital strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in relation to serotype and phage-typing pattern. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Feb;6(1):91–100. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-1-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierdt C. H., Schmidt P. J. Dissociation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1964 May;87(5):1003–1010. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.5.1003-1010.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Sant'Agnese P. A., Davis P. B. Research in cystic fibrosis (second of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Sep 2;295(10):534–541. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197609022951005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Sant'agnese P. A., Davis P. B. Cystic fibrosis in adults. 75 cases and a review of 232 cases in the literature. Am J Med. 1979 Jan;66(1):121–132. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90491-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



