Background: Diarylheptanoid (ASPP 049) isolated from C. comosa exhibits high estrogenic activity.
Results: ASPP 049 rapidly induced β-catenin accumulation in the nucleus and activated TCF/LEF-mediated activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
Conclusion: ASPP 049 from C. comosa induces preosteoblastic cell proliferation and differentiation through activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
Significance: Providing a scientific rationale for using C. comosa as a dietary supplement to prevent bone loss in postmenopausal women.
Keywords: β-Catenin, Bone, Estrogen, Estrogen Receptor, Wnt Signaling, GSK-3β, Diarylheptanoid
Abstract
Estrogen promotes growth in many tissues by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Recently, ASPP 049, a diarylheptanoid isolated from Curcuma comosa Roxb., has been identified as a phytoestrogen. This investigation determined the involvement of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in the estrogenic activity of this diarylheptanoid in transfected HEK 293T and in mouse preosteoblastic (MC3T3-E1) cells using a TOPflash luciferase assay and immunofluorescence. ASPP 049 rapidly activated T-cell-specific transcription factor/lymphoid enhancer binding factor-mediated transcription activity and induced β-catenin accumulation in the nucleus. Interestingly, the effects of ASPP 049 on the transcriptional activity and induction and accumulation of β-catenin protein in the nucleus of MC3T3-E1 cells were greater compared with estradiol. Activation of β-catenin in MC3T3-E1 cells was inhibited by ICI 182,780, suggesting that an estrogen receptor is required. In addition, ASPP 049 induced phosphorylations at serine 473 of Akt and serine 9 of GSK-3β. Moreover, ASPP 049 also induced proliferation and expressions of Wnt target genes Axin2 and Runx2 in MC3T3-E1 cells. In addition, ASPP 049 increased alkaline phosphatase expression, and activity that was abolished by DKK-1, a blocker of the Wnt/β-catenin receptor. Taken together, these results suggest that ASPP 049 from C. comosa induced osteoblastic cell proliferation and differentiation through ERα-, Akt-, and GSK-3β-dependent activation of β-catenin signaling. Our findings provide a scientific rationale for using C. comosa as a dietary supplement to prevent bone loss in postmenopausal women.
Introduction
The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway has been demonstrated to be responsible for a variety of biological processes, including tissue homeostasis and cancer. Cytosolic β-catenin protein is the principal mediator of Wnt signaling (1). In the absence of extracellular Wnt ligands, β-catenin is recruited into a destruction complex comprising Axin, adenomatous polyposis coli (APC),2 and glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK-3β) (2). Axin and APC act as the scaffolding proteins that facilitate GSK-3β to phosphorylate β-catenin at amino acid residues 33, 37, and 41 and target it for ubiquitination by β-transducin repeat-containing homologue protein (β-TrCP) in proteasome. Thus, the cytosolic β-catenin level is kept low. In the presence of Wnt ligands, on the other hand, Wnt protein binds to its coreceptors Frizzled (Fz) receptor, a seven-transmembrane protein, and a low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP). This binding activates Dishevelled (Dvl) protein, which then inhibits the formation of Axin-APC-GSK-3β destruction complex. Therefore, GSK-3β-mediated phosphorylation of β-catenin is inhibited. Non-phosphorylated β-catenin is not targeted for degradation and is accumulated in the cytoplasm. Ιt translocates into the nucleus, binds with T-cell-specific transcription factor/lymphoid enhancer binding factor (TCF/LEF), and activates target gene expression. Many of the Wnt target genes are responsible for several cellular processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation, transformation, migration, and adhesion (3).
Wnt and estrogen signaling play critical roles both in normal development and diseases. The interactions between these two signaling pathways have been reported in many tissues. Several physiological consequences associated with estrogen signaling, such as neuronal development (4) and bone formation (5), are mediated through the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Thus, in neuroblastoma cells and primary cortical neurons, estradiol increased cytosolic β-catenin protein levels and activated the transcriptional activity of Wnt/β-catenin signaling by an inhibition of GSK-3β functions (4). Also, in bone cells, the transcriptional activity of Wnt/β-catenin signaling was activated by binding between the TCF and estrogen receptor (6). Mutation in low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) was shown to cause osteoporosis pseudoglioma syndrome (7), which is characterized by low bone mass. In contrast, mutant mice that overexpressed the constitutive active LRP5 (G171V) in osteoblasts exhibited an enhanced osteoblastic activity, a reduction in osteoblast apoptosis, and high bone mass phenotype (8). It is well established that estrogen deficiency is associated with bone loss (9), whereas administration of estrogen inhibits bone resorption by reducing osteoclasts number and is mediated via the estrogen receptor (10). Thus, both estrogen and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways play an important role in bone remodeling. Therefore, the regulation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and estrogen replacement therapy are considered as the effective treatments for bone loss. However, long-term supplementation with estrogen increased the risk of breast cancer (11) and endometrial cancer (12). In view of these undesirable effects, the development of drugs with a lower risk of cancer is needed.
Phytoestrogens are a diverse group of naturally occurring non-steroidal plant compounds that exert estrogenic-like activity and become one of the alternative interventions for treatment of menopausal symptoms. Curcuma comosa Roxb. (C. comosa) has long been used in Thai traditional medicine for treatments of illness in the uterus and ovarian hormone deficiency (13). C. comosa exhibits an estrogen-like activity and induces cornification of the vaginal epithelium in the smear and keratinization of the mucosal surface of the vagina (13). Recently, a study reported that the hexane extract of this plant prevented bone loss induced by estrogen deficiency (14). However, the molecular mechanism underlying the effect of C. comosa in protecting bone loss is still unknown. A number of diarylheptanoids have been isolated from C. comosa. Of these, ASPP 049 ((3R)-1,7-diphenyl-(4E,6E)-4,6-heptadien-3-ol) is the major component (15), which exhibits high estrogenic activity (16). ASPP 049 mediated transcriptional activation through a ligand-dependent ERα-estrogen-responsive element-driven pathway (17) and a non-genomic action on vascular relaxation through the ER-Akt-endothelium nitric oxide synthase pathway (18). However, the estrogenic activity of this compound in relation with Wnt/β-catenin signaling, which is associated with bone cell proliferation and differentiation, has not yet been investigated.
In this study, we reported for the first time the non-genomic action of a novel phytoestrogen, ASPP 049, from C. comosa on Wnt/β-catenin signaling and osteogenesis. ASPP 049 mediates the ER/Akt/GSK-3β-dependent activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and induces preosteoblastic cell proliferation and differentiation. Therefore, this compound may have a potential use as an osteogenic agent to protect osteoporosis in postmenopausal women.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell Culture and Transfection
HEK 293T cells and mouse preosteoblastic (MC3T3-E1) cells were obtained from the ATCC and cultured in minimal essential medium and minimal essential medium α modification supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Invitrogen), respectively. Cells were incubated at 37 °C under a 5% CO2 incubator. HEK 293T and MC3T3-E1 cells were transfected using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) according to the instructions of the manufacturer. For the differentiation assay, cells were cultured in differentiation medium, which was growth medium containing β-glycerophosphase (10 mm), ascorbic acid (50 μg/ml), and CaCl2 (2 mm), for 5 days prior to treatments with test compounds.
Plasmids, Antibodies, Reagents, and ASPP 049 from C. comosa
β-catenin-FLAG was generated as described previously (19). The following reagents were used: 17β-estradiol (E2) from Sigma-Aldrich; ICI 182,780 from Tocris Cookson, Inc; charcoal-stripped fetal bovine serum, TRIzol reagent from Invitrogen; BCA from Pierce; complete Mini EDTA-free from Roche; dual luciferase reporter assay from Promega; cDNA kit from Bio-Rad; SYBR kit from Biosystem, SuperSignal West Pico chemiluminescent from ThermoScientific; and recombinant human Dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK-1) from R&D Systems. The following antibodies were used: anti-β-catenin (H-102) from Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.; anti-dephosphorylated β-catenin (anti-ABC) clone 8E7 monoclonal antibody from Millipore; anti-β-actin from Sigma-Aldrich; anti-phospho-GSK-3β (Ser-9), anti-GSK-3β, anti-phospho-Akt (Ser-473), and anti-Akt from Cell Signaling Technology; HRP goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L), and HRP goat anti-rabbit IgG (H+L) antibodies from Jackson Immuno Research Laboratories, Inc; and goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) Alexa Fluor 568, goat anti-rabbit IgG (H+L) Alexa Fluor 488, and TO-PRO3 from Invitrogen. ASPP 049 was isolated and purified as described previously (15).
Luciferase Reporter Assay
HEK 293T cells were maintained in phenol red-free minimal essential medium containing 10% dextran-coated charcoal FBS (stripped FBS, SFBS) for 48 h prior to use in the experiments. At 60–70% confluence, HEK 293T cells grown in 96-well culture plates were transiently transfected with 0.2 μg of mERα plasmid. After 24 h, the transfected cells were then transiently transfected with 0.1 μg of TOPflash TCF reporter plasmid, 0.01 μg of Renilla luciferase reporter plasmid, which was used to evaluate the efficiency of transfection, and 0.1 μg of β-catenin-FLAG plasmid using Lipofectamine 2000 according to the instructions of the manufacturer. 48 h after the first transfection, cells were treated with different concentrations of E2 and ASPP 049 and incubated for various times, as indicated in the individual experiments. Luciferase activities were measured using the dual-luciferase reporter assay system (Promega) according to the recommendations of the manufacturer. The firefly luciferase activity was normalized to Renilla luciferase activity and expressed as the fold change compared with the cells transfected with the pcDNA3.1 empty vector alone.
Western Blot Analysis
Cells were lysed with modified radioimmunoprecipitation assay lysis buffer (50 mm Tris-HCl (pH7.4), 150 mm NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 1% TritonX-100, 1 mm NaF, 1 mm Na3VO4, 1 mm PMSF, and protease inhibitor mixture (Roche)). After 20-min incubation on ice, cells were subjected to brief sonication and centrifugation at 14,000 × g for 20 min. The supernatants were collected, and the protein concentration was measured. An equal amount of protein was used for Western blot analysis. Protein was resolved by SDS-PAGE; subsequently transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane by electroblotting; and probed with indicated antibodies, anti-β-catenin, anti-phospho-GSK3 (Ser-9), anti-GSK-3β, anti-phospho-Akt (Ser-473), anti-Akt, and anti-β-actin antibodies. The signal was detected using the enhanced SuperSignal West Pico chemiluminescent.
Immunofluorescence Microscopy
MC3T3-E1 cells were grown on glass coverslips in 24-well culture plates. At 60–70% confluence, cells were treated with 0.1 μm ASPP 049 or E2 for 60 min. Cells were washed with cold PBS containing Ca2+/Mg2+ (PBS2+), fixed with cold methanol for 10 min, and permeabilized with permeabilizing buffers (0.3% Triton X-100 and 0.3% BSA) for 30 min. The samples were then incubated with mouse anti-dephosphorylated β-catenin and rabbit anti-β-catenin diluted in 5% normal goat serum and left overnight at 4°C. Cells were washed with 0.3% Triton X-100 in PBS2+ five times and then incubated with Alexa Fluor 488 goat anti-rabbit IgG (H+L) and Alexa Fluor 568 goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) diluted in 5% normal goat serum for 1 h. Cells were washed with 0.3% Triton X-100 in PBS2+ five times, stained with TO-PRO3 for 10 min at room temperature, and then washed again with PBS2+ three times. The stained coverslips were mounted and visualized at room temperature with a confocal laser microscopy (FV10i/w, Olympus).
Total RNA Isolation and RT-PCR Quantification
MC3T3-E1 cells were treated with 0.1 μm E2 or ASPP 049 at various time points. Total RNAs were extracted from treated MC3T3-E1 cells using TRIzol reagent according to the recommendations of the manufacturer with a slight modification. Briefly, cells (1 × 106) were homogenized in 1 ml of TRIzol reagent, and cell lysate was cleared by centrifugation at 14,000 × g for 10 min. Supernatants were then added to 200 μl of chloroform and followed by centrifugation at 14,000 × g for 15 min. The clear supernatants were transferred to a new tube, and the RNA was precipitated by adding 500 μl of isopropanol, followed by centrifugation at 14,000 × g for 10 min. The obtained RNA pellets were washed with ethanol and dried at room temperature for 10–15 min before dissolving in 50 μl of RNase-free water. The quality and quantity of total RNA were determined using NanoDrop 2000C (Thermo Scientific). Equal amounts of total RNA samples were incubated with deoxyribonuclease I (DNase I) at 25 °C for 15 min. cDNA synthesis was conducted using the iScriptTM Select cDNA synthesis kit according to the protocol of the manufacturer (Bio-Rad). Quantitative real-time PCRs of Axin2, RUNX2, ALP, and COL1A1 were performed on an equal amount of cDNA using KAPA SYBR® FAST quantitative PCR kit according to the instructions of the manufacturer (Kapa Biosystems) with the ABI PRISM 7500 sequence detection system and analysis software (Applied Biosystems). The primers used were as follows: Axin2, 5′-TGACTCTCCTTCCAGATCCCA-3′ and 5′-TGCCCACACTAGGTCGACA-3′, NM_015732; Runx2, 5′-CTGACGTGCCCAGGCGTATT-3′ and 5′-GCACCTGCCTGGCTCTTCTT-3′, NM_0001145920; ALP, 5′-AGAGCGCACGCGATGCAACA-3′ and 5′-AATGCCCACGGACTTCCCAGC-3′, NM_007431; COL1A1, 5′-TCGAGCTCAGAGGCGAAGGCA-3′ and 5′-CGTGTGACTCGTGCAGCCGT-3′, NM_007742; and GAPDH, 5′-CGAGACCCCACTAACATCAAA-3′ and 5′-TTTGGCTCCACCCTTCAAG-3′, NM_008084.
Alkaline Phosphatase Assay
For the ALP staining assay, MC3T3-E1 cells were cultured in differentiation medium and treated with 0.1 μm E2 or various concentrations of ASPP 049 for 21 days. After treatments, cells were washed with PBS containing Ca2+/Mg2+ (PBS2+), fixed with a fixative solution for 1 min, and washed three times with deionized water. Cells were incubated in buffer containing 0.4 mg/ml Naphthol AS-MX phosphate disodium salt (Sigma) and 1 mg/ml Fast Blue RR salt (Sigma) for 15 min, washed with deionized water, and observed under a light microscope. For the ALP activity assay, MC3T3-E1 cells were cultured in differentiation medium for 5 days and then treated with 0.1 μm E2 or various concentrations of ASPP 049 in differentiation medium for 7 days. Cells were harvested with lysis buffer containing 0.2% Triton X-100, 1 mm DTT, and 100 mm potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.8). ALP activity was determined by mixing the cell extract with 5 mm freshly prepared p-nitrophenyl phosphate (Sigma) substrate in 0.1 m glycine (pH 10.4), 1 mm MgCl2, and 1 mm ZnCl2 at room temperature for 60 min, the enzymatic reaction was stopped by adding 3 m NaOH solution, and absorbance was measured at 405 nm. ALP activity was normalized to total protein concentration by using the BCA method. For the DKK-1 inhibition study, cells were pretreated with 0.2 μg/ml of DKK-1 for 3 h before the application of ASPP 049 or E2.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical significance was determined by a two-tailed unpaired Student's t test or one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc (Bonferroni) multiple comparisons between treatment groups using GraphPad Prism version 4.0 for Windows (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA). p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
ASPP 049 Activates the Canonical Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
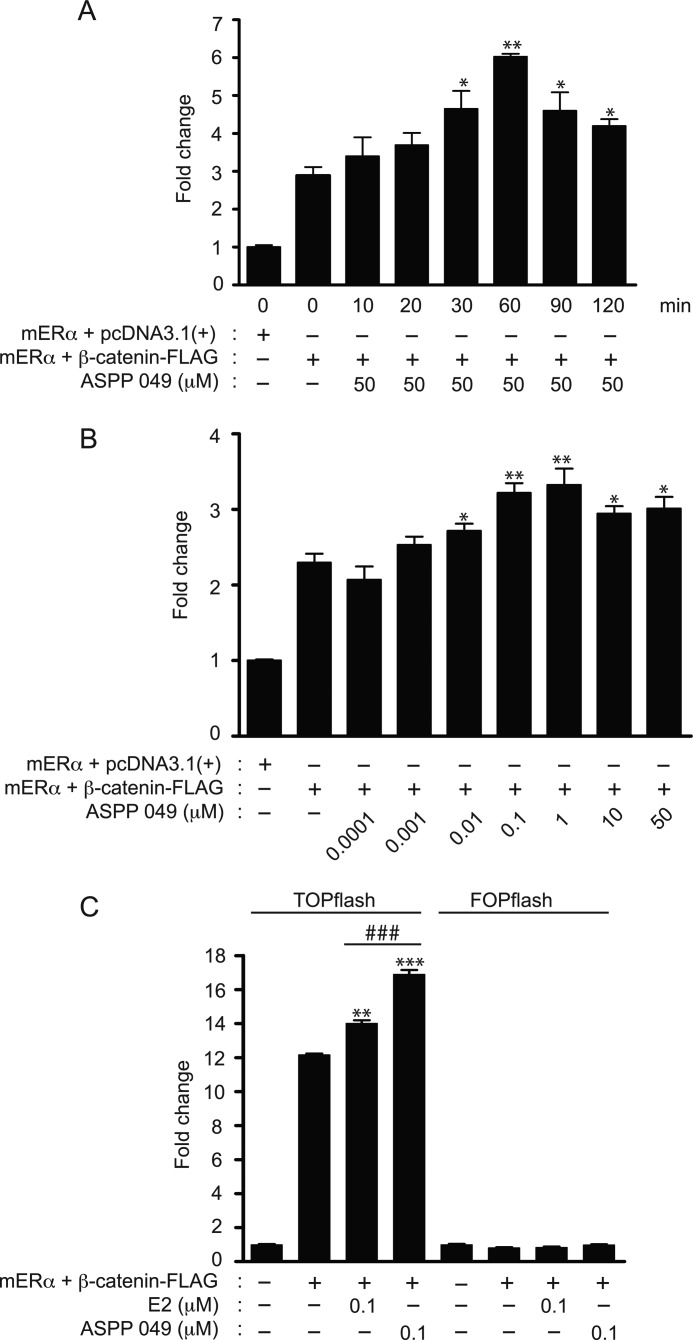
Estradiol (E2) has been reported to activate TCF/LEF-mediated transcription activity in neuronal cells (20) and bone cells (8). To evaluate whether ASPP 049, which exhibits an estrogenic-like activity (17), activates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, a TOPflash reporter assay in HEK 293T cells was employed by transient transfection with TOPflash, mERα, β-catenin-FLAG, and Renilla plasmids. As shown in Fig. 1A, expression of β-catenin induced an up-regulation of the canonical Wnt/β-catenin activity as indicated by enhanced luciferase activity. ASPP 049 exhibited both time- and concentration-dependent activations of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. At a concentration of 50 μm, the increase in TOPflash luciferase activity peaked at 60 min after treatment (Fig. 1A), whereas maximum activation occurred in the presence of ASPP 049 at 0.1 μm (B). The molecular mechanisms by which this diarylheptanoid and E2 regulate TCF/LEF-dependent activation of Wnt/β-catenin activity were evaluated in HEK 293T cells transfected with TOPflash and FOPflash, the LEF mutant reporter plasmid, after treatment with 0.1 μm ASPP 049 or 0.1 μm E2 for 60 min. In the TOPflash-transfected cells, β-catenin expression led to an up-regulation of the Wnt/β-catenin activity. Treatment with ASPP 049 or E2 further enhanced the increase in luciferase activity induced by β-catenin expression. In contrast, the activation of Wnt/β-catenin activity was not observed in FOPflash-transfected HEK 293T cells (Fig. 1C). These data suggest that ASPP 049 from C. comosa mediates TCF/LEF-dependent activation of the canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling, similar to that of E2. Interestingly, ASPP 049 had a greater (p < 0.001) effect than E2 at the same concentration.
FIGURE 1.
ASPP 049 and E2 activate TCF/LEF reporter activity. A, time-dependent activation of TCF/LEF reporter activity by ASPP 049. HEK 293T cells were transiently cotransfected with TOPflash, β-catenin-FLAG, ERα, and Renilla luciferase vectors. After 48 h, cells were treated with ASPP 049 for the indicated time. Activity of the β-catenin signaling was quantified by measuring the relative firefly luciferase activity units normalized to Renilla luciferase activity. Data are expressed as the fold change compared with the cells transfected with pcDNA3.1 empty vector. B, concentration-dependent activation of TCF/LEF reporter activity by ASPP 049. HEK 293T cells were transiently cotransfected with TOPflash, β-catenin-FLAG, ERα, and Renilla luciferase vectors. After 48 h, cells were treated with the indicated concentration of ASPP 049 for 60 min and harvested for luciferase-based TOPflash assay for Wnt signaling. C, ASPP 049 and E2 activate TCF/LEF-driven luciferase activity. HEK 293T cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids. Treatment with ASPP 049 or E2 (60 min, 0.1 μm) selectively increased transcription from the TOPflash reporter plasmid compared with FOPflash. Data are represented as corrected luciferase; means ± S.E. (n = 4). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 compared with β-catenin-FLAG-transfected cells and treatment with vehicle (ANOVA). ###, p < 0.001 compared with β-catenin-FLAG-transfected cells and treatment with E2 (Student's t test).
ASPP 049 Induces TCF/LEF-dependent Activation of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling through Up-regulation of the β-Catenin Protein in Preosteoblastic Cells
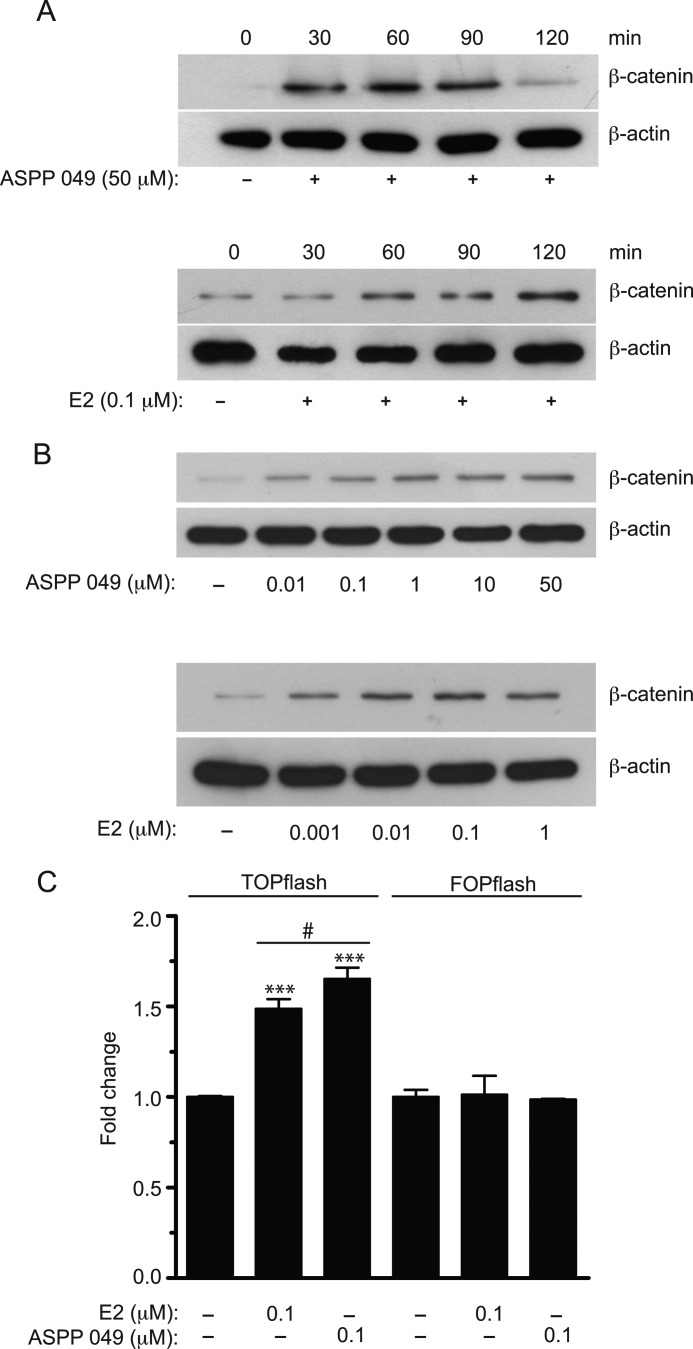
The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway plays an important role in bone mass homeostasis. Recently, we have demonstrated that the hexane extract of C. comosa prevents bone loss induced by estrogen deficiency in a mouse model (14). To test whether ASPP 049 activates Wnt signaling in bone cells as in transfected HEK 293T cells, we examined the effects of this compound and E2 on endogenous Wnt/β-catenin signaling in preosteoblastic cells (MC3T3-E1). As shown in Fig. 2A, ASPP 049 (50 μm) induced a significant increase in the β-catenin protein level, which peaked at 60–90 min and declined substantially by 120 min after treatment. In contrast, E2 (0.1 μm) induced a progressive increase in β-catenin protein expression until 120 min after treatment. In addition, ASPP 049 and E2 exhibited a concentration-dependent induction of β-catenin protein (Fig. 2B). ASPP 049 and E2 exhibited a maximum induction at 50 μm and 0.01 μm, respectively. To determine whether the increased accumulations of β-catenin by ASPP 049 and E2 induce β-catenin-mediated transcription activity, a luciferase reporter assay was performed in MC3T3-E1 transiently transfected with TOPflash or FOPflash luciferase constructs. Consistent with HEK 293T cells, only the TOPflash-transfected MC3T3-E1 cells demonstrated a significant increase in luciferase signal, whereas the activity was not altered in the FOPflash-transfected cells. Of note, ASPP 049 exerted a greater effect than E2 at the same concentration (Fig. 2C). Collectively, these results suggest that ASPP 049 and E2 mediate TCF/LEF-dependent activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling by promoting the accumulation of intracellular levels of the β-catenin protein in preosteoblastic cells.
FIGURE 2.
ASPP 049 and E2 increase β-catenin protein expression and transactivation in mouse preosteoblastic (MC3T3-E1) cells. A, representative blot showing time-dependent effects of ASPP 049 and E2 on β-catenin protein expression. MC3T3-E1 cells were treated with ASPP 049 (50 μm) or E2 (0.1 μm) for different times (30–120 min) and harvested for immunoblotting using anti-β-catenin and anti-β-actin antibodies. Maximum increase in β-catenin protein occurred by 60 min and then markedly decreased by 120 min after treatment with ASPP 049, whereas E2 induced a gradual increment of β-catenin up to 120 min. B, representative blot showing concentration-dependent effects of ASPP 049 and E2 on β-catenin protein expression. MC3T3-E1 cells were treated with various concentrations of ASPP 049 (0.01–50 μm) or E2 (0.001–1 μm) for 60 min and harvested for immunoblotting using anti-β-catenin and anti-β-actin antibodies. C, ASPP 049 and E2 augment TCF/LEF-dependent transcription in MC3T3-E1 cells. After 24 h of transfection with the indicated reporter plasmids, cells were treated with 0.1 μm ASPP 049 or 0.1 μm E2 for 60 min. Activity of the β-catenin signaling pathway was quantified by measuring the relative firefly luciferase activity units normalized to Renilla luciferase activity. ASPP 049 and E2 selectively increased transcription only from the TOPflash reporter plasmid. Data are represented as mean ± S.E. (n = 4). ***, p < 0.001 compared with vehicle control treatments (ANOVA); #, p < 0.05 compared with E2-treated cells (Student's t test).
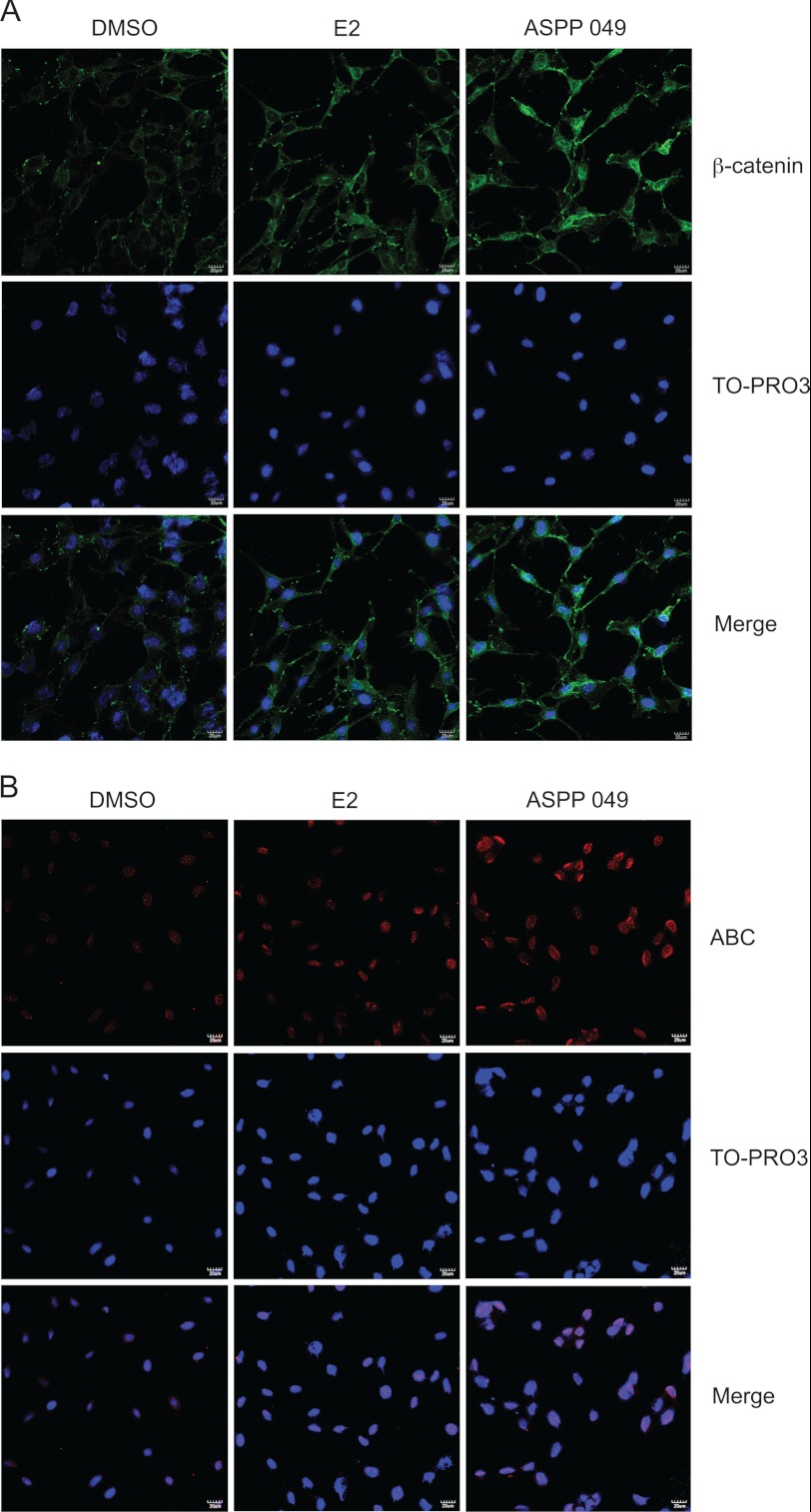
An accumulation of β-catenin in the nucleus is an important step in the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. The effect of ASPP 049 and E2 on subcellular localization of β-catenin was further explored by immunofluorescence in MC3T3-E1 cells. After treatment with 0.1 μm ASPP 049 and 0.1 μm E2 for 60 min, β-catenin immunostaining was increased significantly (Fig. 3A). Interestingly, the staining was more intense and localized in the nucleus upon treatment with ASPP 049 compared with E2, in which the immunostaining was predominantly found in the cytosol and perinuclear regions (Fig. 3A). To investigate whether these compounds induced nuclear accumulation of the activated β-catenin, immunofluorescence was performed in MC3T3-E1 cells using anti-dephosphorylated β-catenin. As illustrated in Fig. 3B, MC3T3-E1 cells treated with ASPP 049 and E2 showed nuclear accumulation of the activated β-catenin. Again, ASPP 049 exhibited a greater effect than that of E2. These data demonstrate that both compounds activate Wnt/β-catenin signaling by promoting nuclear localization of β-catenin protein.
FIGURE 3.
ASPP 049 and E2 increase nuclear localization of β-catenin. MC3T3-E1 cells were treated with 0.1 μm ASPP 049 or 0.1 μm E2 for 60 min. Cells were fixed and immunostained for β-catenin using anti-β-catenin (A) and anti-dephosphorylated β-catenin (anti-ABC) (B) antibodies (red). TO-PRO3 was used as a nuclear marker (blue). Samples were visualized with confocal laser microscopy. β-catenin immunostaining was predominantly localized in the nucleus after treatments with ASPP 049 and E2. Scale bar = 20 μm. DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide.
GSK-3β-, Akt- and ER-dependent Activation of Canonical Wnt Signaling by ASPP 049 and E2 in Preosteoblastic Cells
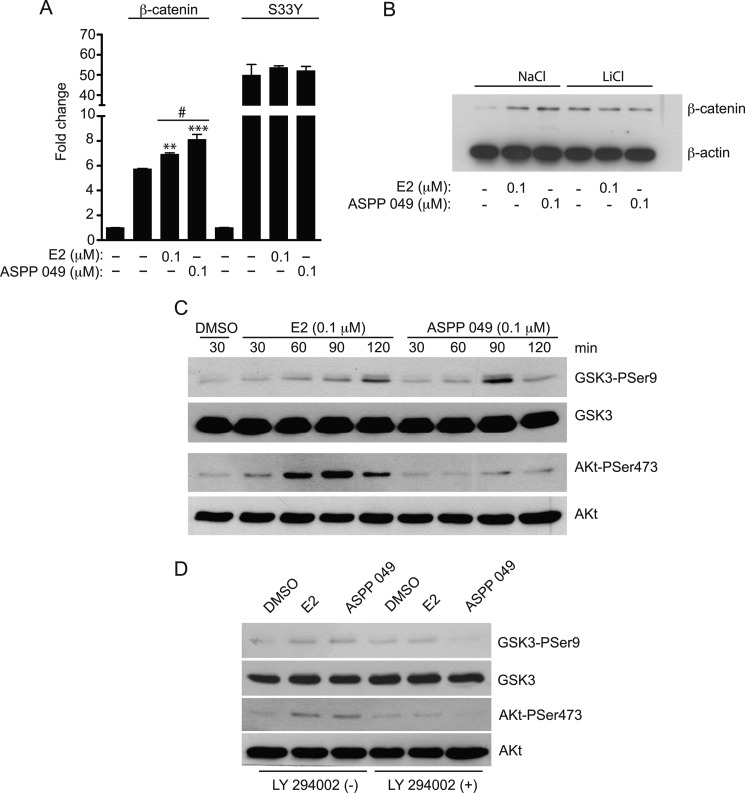
Because GSK-3β phosphorylates β-catenin and prevents TCF-activated transcription activity, we next determined whether the activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling mediated by ASPP 049 involves GSK-3β. To address this question, we used the constitutively active β-catenin mutant S33Y, which is insensitive to GSK-3β-mediated phosphorylation and, therefore, is not a substrate for proteasome-induced protein degradation. As shown in Fig. 4A, overexpression of the β-catenin mutant (S33Y) resulted in a greater activation of the TOPflash luciferase activity compared with the β-catenin wild type. ASPP 049 and E2 further increased the Wnt/β-catenin activity in the HEK 293T cells expressing the β-catenin wild type. In contrast, Wnt/β-catenin activity induced by β-catenin mutant was not susceptible to activation by ASPP 049 and E2. The involvement of GSK-3β in β-catenin protein expression activated by ASPP 049 and E2 in preosteoblastic cells after inhibition of GSK-3β activity by LiCl was also determined. LiCl itself caused an accumulation of β-catenin in MC3T3-E1 cells. Addition of ASPP 049 or E2 failed to further enhance the accumulation of β-catenin protein. In contrast, both compounds significantly increased β-catenin protein levels in the cells treated with NaCl (Fig. 4B). These data suggest that the activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling induced by ASPP 049 and E2 is dependent on GSK-3β activity.
FIGURE 4.
Activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling by ASPP 049 and E2 is GSK-3β- and Akt-dependent. A, GSK-3β-dependent activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. The activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling by ASPP 049 or E2 was measured in the presence of constitutively active β-catenin mutant S33Y, which is insensitive to GSK-3β-mediated phosphorylation. HEK 293T cells were transiently cotransfected with TOPflash, Renilla luciferase vector, and the indicated plasmids. After 24 h, cells were incubated with 0.1 μm ASPP 049 or 0.1 μm E2 for 60 min. Activity of the β-catenin signaling pathway was quantified by measuring the relative firefly luciferase activity units normalized to Renilla luciferase activity. Data is expressed as fold change compared with pcDNA3.1-transfected cells and represented as mean ± S.E. (n = 4). **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 compared with β-catenin-FLAG-transfected cells treated with vehicle (ANOVA); #, p < 0.05 compared with β-catenin-FLAG-transfected cells and treatment with E2 (Student's t test). B, ASPP 049 and E2 induce GSK-3β-dependent β-catenin expression. MC3T3-E1 cells were pretreated with 40 mm LiCl or 40 mm NaCl for 16 h and then incubated in medium containing 0.1 μm ASPP 049 or 0.1 μm E2 for 60 min. Cells were harvested and analyzed by Western blotting using anti-β-catenin and anti-β-actin antibodies. ASPP 049 and E2 failed to increase β-catenin expression after LiCl pretreatment. C, ASPP 049 and E2 increase GSK-3β and Akt phosphorylation in MC3T3-E1 cells. MC3T3-E1 cells were treated with 0.1 μm ASPP 049 or 0.1 μm E2 for different times (30–120 min) and then harvested for Western blotting using anti-phospho-GSK-3β (Ser-9), anti-GSK-3β, anti-phospho-Akt (Ser-473), and anti-Αkt antibodies. DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide. D, LY 294002 blocks ASPP 049- and E2-induced GSK-3β and Akt phosphorylation. MC3T3-E1 cells were treated with 0.1 μm ASPP 049 or 0.1 μm E2 for 60 min with or without pretreatment with LY 294002, a specific PI3 Kinase inhibitor (10 μm for 3 h), and then harvested for Western blotting using the indicated antibodies.
The phosphorylation of Akt at serine 473 residues resulted in its activation and, therefore, promoted GSK-3β phosphorylation at serine 9 (21). Moreover, it has recently been shown that E2 inhibited GSK-3β activity via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in neurons (22). To test whether ASPP 049-mediated GSK-3β-dependent activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling proceeds through the activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway, MC3T3-E1 cells were treated with 0.1 μm ASPP 049 or 0.1 μm E2 for 30–120 min, lysed for immunoblotting using anti-phospho-GSK-3β (Ser-9) and anti-phospho-Akt (Ser-473) antibodies. As shown in Fig. 4C and supplemental Fig. S1, E2 and ASPP 049 induced phosphorylations of GSK-3β and Akt in a time-dependent manner. In addition, E2 and ASPP 049 failed to induce phosphorylations of GSK-3β (Ser-9) and Akt (Ser-473) in the cells preincubated with LY 294002, a PI3K inhibitor (Fig. 4D). These observations indicate that ASPP 049 and E2 induced the phosphorylation of Akt at serine 473 and subsequently activated the phosphorylation of GSK-3β at serine 9, leading to inhibition of GSK-3β activity and, hence, activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
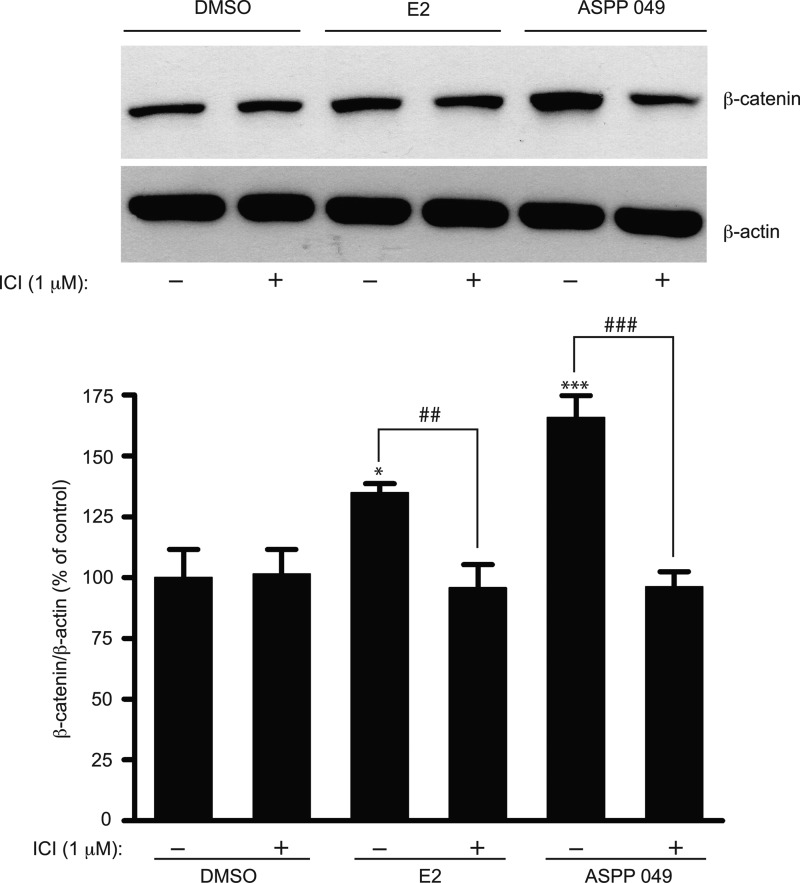
A previous study showed the involvement of ERα in Wnt/β-catenin signaling in osteoblastic cells (5). To determine whether ERα plays a role in the regulation of β-catenin in preosteoblastic cells, we treated MC3T3-E1 cells with ICI 182,780 (an ER blocker) for 2 h prior to treatment with ASPP 049 or E2. As shown in Fig. 5, both compounds significantly increased the level of β-catenin protein, but the expression was decreased by pretreatment with ICI 182,780. Moreover, the induction of Akt and GSK-3β phosphorylations mediated by ASPP 049 and E2 was abolished in the presence of ICI 182,780 (supplemental Fig. S2). These data strongly suggest that ERα is required for the activation of Wnt signaling by ASPP 049 and E2 in MC3T3-E1 cells.
FIGURE 5.
Induction of β-catenin protein expression by ASPP 049 and E2 requires estrogen receptors. MC3T3-E1 cells were preincubated with ER antagonist ICI 182,780 (1 μm) for 2 h prior to treatment with 0.1 μm ASPP 049 or 0.1 μm E2 for 60 min. Cells were harvested and immunoblotted for β-catenin protein expression using anti-β-catenin and anti-β-actin antibodies. Bar graphs show the mean normalized densitometry values and the corresponding standard deviations from four independent experiments. Data are represented as means ± S.E. (n = 4). *, p < 0.05 and ***, p < 0.001 compared with vehicle control treatments (ANOVA); ##, p < 0.01; ###, p < 0.001 compared with E2 and ASPP 049 treatments (Student's t test). DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide.
ASPP 049 and E2 Induce Preosteoblastic Cell Proliferation and the Expression of Wnt Target Genes
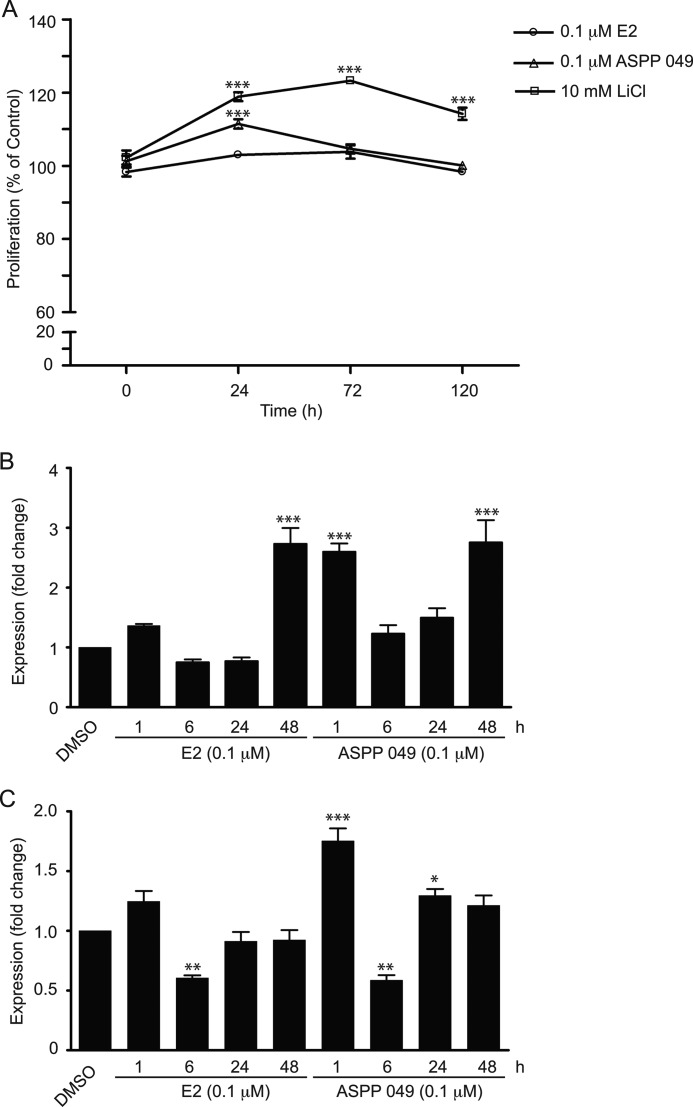
Because Wnt/β-catenin signaling regulates cell proliferation and differentiation of multiple tissues, including bone cells, we then assessed the proliferative effects of ASPP 049 and E2 on preosteoblastic cells using an MTT assay. Only a slight increase in cell proliferation occurred after treatment with E2 for 24 h, whereas a marked enhancement was observed after ASPP 049 treatment. In addition, activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling by specific inhibition of GSK-3β activity using LiCl produced a profound and sustained increase in preosteoblastic cell proliferation from 24 to 120 h (Fig. 6A). The results suggest that ASPP 049-mediated Wnt/β-catenin activation induces bone cell proliferation. This effect was further confirmed by the expression of Wnt target genes. MC3T3-E1 cells were treated with 0.1 μm ASPP 049 or 0.1 μm E2 at various time points (1–48 h), and quantitative real time PCR was performed to determine Axin2 and RUNX2 mRNA expression. As shown in Fig. 6B, both E2 and ASPP 049 induced a transient elevation of Axin2 mRNA at 1 h, followed by a reduction during 6–24 h and then a marked increase at 48 h. Interestingly, the effect of ASPP 049 at 1 h was significantly greater, but at 48 h it was not different from that of E2. The expression profiles of RUNX2 mRNA following treatment with these two estrogenic compounds were similar to those of Axin2. Thus, transient increases at 1 h followed by decreases at 6 h were also observed (Fig. 6C). Nonetheless, the level of expression returned to control (after E2) or was higher than control (after ASPP 049) at 24 h. Because RUNX2 plays a role as an early transcription factor essential for osteoblast differentiation, our data suggest that ASPP 049-activated Wnt/β-catenin signaling may enhance differentiation of preosteoblast cells. Collectively, our results indicate that ASPP 049 and E2 increase preosteoblastic cell proliferation and may enhance differentiation through the mechanisms related to activation of Wnt target gene expression, including Axin2 and Runx2.
FIGURE 6.
ASPP 049 and E2 enhance cell proliferation and Wnt target gene expression. A, ASPP 049 increases MC3T3-E1 cell proliferation. MC3T3-E1 cells were treated with 0.1 μm ASPP 049, 0.1 μm E2 or 10 mm LiCl for the indicated times. The proliferation of MC3T3-E1 cells was observed by MTT assay. Cell proliferation is expressed as % of control group (dimethyl sulfoxide, DMSO). B and C, ASPP 049 and E2 increase Wnt target gene expression. MC3T3-E1 cells were treated with 0.1 μm ASPP 049 or 0.1 μm E2 for the indicated times (1, 6, 24, and 48 h). Total RNAs were extracted for quantitative PCR of the Wnt target genes: Axin2 (B) and RUNX2 (C). Data are represented as mean ± S.E. (n = 3). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 compared with vehicle control treatments (ANOVA).
ASPP 049 and E2 Induce Preosteoblastic Cell Differentiation via Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling
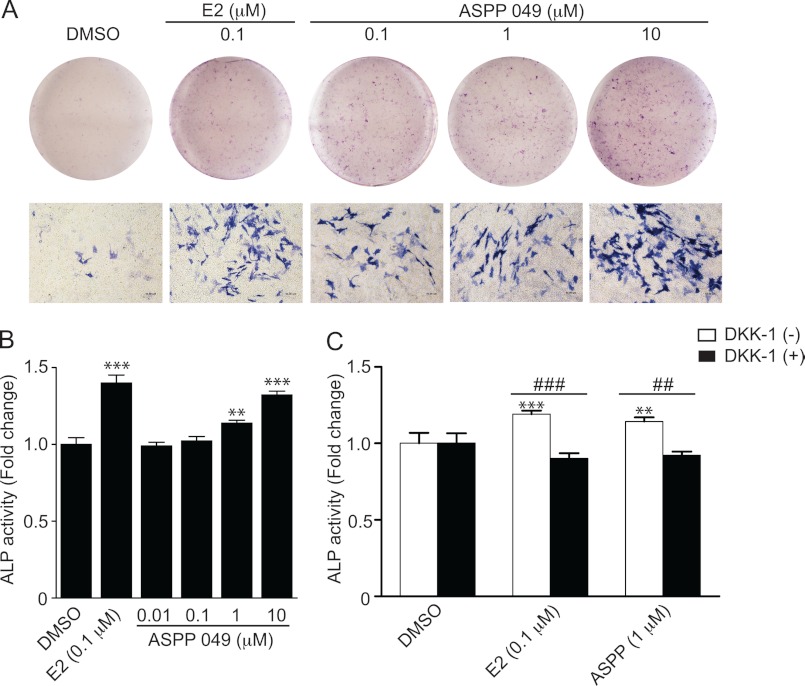
To determine the effect of ASPP 049 in promoting preosteoblastic cell differentiation, MC3T3-E1 cells were cultured in differentiation medium with ASPP 049 (0.1–10 μm) for 21 days. As shown in Fig. 7A, ASPP 049 induced the expression of ALP, a bone differentiation marker, in a dose-dependent manner. To confirm the induction of ALP expression, ALP activity was assayed in MC3T3-E1 cells after treatment with ASPP 049 at various concentrations (0.01–10 μm) or E2 (0.1 μm) for 7 days. Consistent with ALP staining, ASPP 049 induced a dose-dependent increase in ALP activity (Fig. 7B). In addition, the expression of ALP and its activity were increased significantly after treatment with E2. This effect was further confirmed by the up-regulation of bone differentiation marker genes, including ALP and COL1A1. MC3T3-E1 cells were treated with various concentrations of ASPP 049 or 0.1 μm E2 for 14 days, and the quantitative real-time PCR was performed to determine the effect on ALP and COL1A1 mRNA expression. As shown in supplemental Fig. S3, A and B, both E2 and ASPP 049 induced significant increases in ALP and COL1A1 mRNA expression. To investigate whether the estrogenic compounds induced MC3T3-E1 cell differentiation through activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, MC3T3-E1 cells were pretreated with DKK-1, a blocker that prevents the binding of Wnt ligands to its receptors for signal induction, for 3 h before treatment with ASPP 049 or E2. Indeed, the ASPP 049- and E2-induced ALP activity was significantly inhibited by DKK-1 (Fig. 7C), indicating that ASPP 049 and E2 could act on the Wnt receptors. Collectively, our results strongly suggest that ASPP 049 and E2 increase preosteoblastic cell differentiation through the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
FIGURE 7.
ASPP 049-induced preosteoblastic cell differentiation is mediated by Wnt/β-catenin signaling. A, ASPP 049 induces ALP expression. MC3T3-E1 cells were cultured in differentiation medium and treated with various concentrations of ASPP 049 or E2 for 21 days. The ALP expression was stained with Naphthol AS-MX phosphate. DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide. B, ASPP 049 induces ALP activity. MC3T3-E1 cells were cultured in differentiation medium and treated with indicated concentrations of ASPP 049 or E2 for 7 days. Cells were harvested, and ALP activity was measured at 405 nm and normalized with total protein. C, DKK-1 blocks ASPP 049-induced ALP activity. MC3T3-E1 cells were cultured in differentiation medium and treated with 1 μm ASPP 049 or 0.1 μm E2 for 7 days with or without pretreatment with DKK-1 (0.2 μg/ml) for 3 h, as indicated. Cells were harvested, and ALP activity was measured at 405 nm and normalized with total protein. Data are expressed as fold change compared with the cells treated with vehicle control and are mean ± S.E. (n = 4). **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 compared with treatments (ANOVA). ##, p < 0.01; ###, p < 0.001 compared with the presence and absence of DKK-1 (Student's t test).
DISCUSSION
Wnt/β-catenin signaling has currently been recognized as an important regulator of bone mass and bone cell differentiation. It cross-talks with other signaling pathways, including estrogen receptor signaling (24). Both Wnt/β-catenin and estrogen receptor signaling pathways play an important role in bone remodeling, particularly in menopausal women (25). The main purpose of this study was to investigate the mechanisms by which a phytoestrogen isolated from C. comosa, ASPP 049, prevents bone loss in estrogen deficiency, with a specific emphasis on the activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. By using the ERα-Wnt/β-catenin expression system in HEK 293T cells and mouse preosteoblastic (MC3T3-E1) cells, we demonstrated that, indeed, this phytoestrogen activated the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. The activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling was ERα-/Akt-/GSK-3β-dependent. In addition, the compound increased the expressions of Wnt target genes (Axin2 and Runx2) and enhanced proliferation and differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells. Taken together, our results strongly suggest that ASPP 049 promotes preosteoblastic cell proliferation and differentiation through the activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling, which is mediated through a non-genomic estrogenic action. To our knowledge, this is the first study reporting the action of diarylheptanoid from C. comosa on the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
In preosteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells, both E2 and ASPP 049 increased the expression of β-catenin protein, which was predominantly localized in the nucleus. It is known that in the absence of Wnt ligands, cytosolic β-catenin is kept low by GSK-3β-induced phosphorylation and subsequent degradation in the proteasome (2). Our finding that LiCl, which is a specific inhibitor of GSK-3β, and transfection with S33Y (a β-catenin mutant) in HEK 293T cells increased the expression of β-catenin protein and activity support the above notion. In addition, we also found that E2 and ASPP 049 induced phosphorylation of GSK-3β at the serine 9 residue. Furthermore, the activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling by these estrogens was associated with phosphorylation of Akt at the serine 473 residue, suggesting that PI3K/Akt signaling is also involved, as in the neuroblastoma N2a-m cells (20). However, it is noteworthy that some differences exist between the effects of these two estrogens. Thus, ASPP 049 is more potent than E2 in activating cytosolic β-catenin expression, although it has weaker effects on Akt and GSK-3β phosphorylation. This is likely due to the fact that ASPP 049 has only a weak estrogenic activity compared with E2 (16). Another possible explanation for the different potency might be that the stabilization of β-catenin by ASPP 049 is mediated through additional signaling events that are independent of the canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling. The canonical pathway is regulated by PI3K/Akt and involves the GSK-3β-induced phosphorylation of β-catenin and subsequent proteasome-mediated degradation. The alternative pathway for regulation of β-catenin levels is Akt/GSK-3β-independent. It is mediated by p53-induced expression of Siah-1 protein. Siah-1 interacts with Siah-interacting protein, Skp1, and Ebi. The latter protein binds and recruits β-catenin to the complex for proteasome-mediated degradation (26, 27). In addition, the cytosolic level of β-catenin is also regulated by the GSK-3β/Siah-independent pathway. Our previous study reported that tetraspanins reduced the cellular pool of β-catenin by enhancing the exosome-associated export of β-catenin from cells (28). Conversely, ASPP 049 might increase cytosolic β-catenin by reducing the exosomal transport from the cells. Alternatively, ASPP 049 is more efficient in translocating β-catenin into the nucleus. However, further experiments are required to completely understand the precise mechanisms through which activation of Wnt/β-catenin is mediated by ASPP 049.
ASPP 049 slightly increased the phosphorylation levels of Akt on serine 473 as early as 30 min. However, marked stimulation of Akt phosphorylation was observed at 90 and 120 min (supplemental Fig. S1). The time course of Akt phosphorylation coincided with phosphorylation of GSK-3β (Fig. 4C). These effects of ASPP 049 resemble those of E2. Of interest, ASPP 049-induced phospho-Akt was less than that enhanced by E2, suggesting that additional mechanisms are involved in the effect of ASPP 049. Consistent with this notion, Akt-independent phosphorylation of GSK-3β has been reported. 8-Br-cAMP and forskolin treatments resulted in the phosphorylation of GSK-3β at serine 9 residue in Rat1 and NIH3T3 cell lines, which were not altered by pretreatment with PI3K inhibitors, wortmannin, and LY294002 (29). A study in cerebellar granule neurons also showed that forskolin stimulated GSK-3β phosphorylation at serine 9 but not Akt phosphorylation at serine 473 (30). In addition, in human myoblasts, amino acids rapidly inactivated GSK-3β, demonstrated by increased serine 9 phosphorylation, whereas no significant change in protein kinase B/Akt activity was observed (31). Taken together, our results indicate that inactivation of GSK-3β induced by ASPP 049 occurred, at least in part, through the Akt-dependent mechanism.
Previously, our group has shown that ASPP 049 is the major phytoestrogen found in C. comosa and that the hexane extract of C. comosa protected bone loss in ovariectomized mice (14, 15). Our data, therefore, provide evidence suggesting that ASPP 049 may prevent bone loss by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling as E2 does (5). However, a previous study reported that, in the absence of mechanical strain, E2 failed to induce β-catenin protein expression and transcription activity in ROS17/2.8 cells (5). This discrepancy could be due to the difference in the cell type used. It has recently been shown in preosteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells that mechanically induced Cox-2 expression, which is involved in the synthesis of prostaglandins (a modulator of bone remodeling), is sensitized by E2 via ERα, whereas activation of Wnt signaling is diminished in the absence of mechanical stress (25). On the other hand, the synergy between activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling by inhibition of GSK-3β and mechanical loading has been demonstrated in osteoblastic cells (5). Whether ASPP 049-induced activation of Wnt/β-catenin is modulated by mechanical force warrants further investigation. We have also shown in this study that activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling by both E2 and ASPP 049 was diminished in the presence of a specific ER antagonist, ICI 182,780. The results corroborate well with the previous study showing that ERα is required for the E2-stimulated bone formation (32) and suggest that ASPP 049 activated Wnt/β-catenin signaling via the non-genomic estrogenic action.
Axin2 is a negative regulator of Wnt/β-catenin signaling by promoting the degradation of β-catenin in the proteasome (33). Activation of Wnt/β-catenin through TCF/LEF sites induces the transcription of Axin2 (33). In our study, Axin2 mRNA was rapidly (within 1 h) up-regulated by ASPP 049, followed by a suppression from 6 to 24 h. Then, the expression was again increased at 48 h. This pattern of Axin2 expression is consistent with the role of this protein in maintaining the cytosolic β-catenin at a steady state by a negative feedback mechanism, and that the Axin2 gene is the downstream target of β-catenin (33). Loss of Axin2 was associated with increased proliferation of osteoblast cells (34). The enhanced proliferation of MC3T3-E1 cells by ASPP 049 as early as 24 h in this study is likely related with the decrease in Axin2 expression. On the other hand, RUNX2 is a transcription factor that plays a major role in chondrocyte and osteoblast differentiation (35). However, it is still unclear how this protein regulates these processes. Activation of Wnt signaling up-regulates Runx2 gene expression and activates RUNX2 protein (36). Our finding that ASPP 049 markedly increases RUNX2 mRNA expression further confirms the action of this diarylheptanoid through Wnt/β-catenin signaling. That the expression of this gene is down-regulated at 6 h and then again up-regulated could be explained by mutual regulations between RUNX2 and Wnt/β-catenin signaling (35).
The mechanism underlying the effect of ASPP 049 on bone formation is not known at present. However, it has been shown in MC3T3-E1 cells that E2 and genistein induce the production of bone formation markers through estrogen receptors (37). E2-induced prevention of bone loss is mediated through the suppression of osteoclastogenesis by stimulating the production of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), modulating the expressions of osteoprotegerin and receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL) in osteoblastic cells (38). Indeed, Wnt signaling regulates the expression of receptor activator of NF-κB ligand and inhibits osteoclastogenesis (23). Therefore, it is likely that ASPP 049 exerts its action on osteoblastic cell proliferation and differentiation via similar mechanisms.
In conclusion, the diarylheptanoid, ASPP 049, from C. comosa, mediated its estrogenic activity through the ERα/Akt signaling pathway to activate Wnt/β-catenin signaling, which, in turn, induced osteoblastic cell proliferation and differentiation. Our findings shed light on the action of ASPP 049 on bone cells and provide a scientific rationale for using C. comosa as a dietary supplement to prevent bone loss in postmenopausal women.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Chumpol Pholpramool for critical reading and comments on the manuscript.
This project was supported by Faculty of Science, Mahidol University, the office of the Higher Education Commission and Mahidol University under the National Research Universities Initiative (NRU), and the National Research Council of Thailand.

This article contains supplemental Figs. S1–S3.
- APC
- adenomatous polyposis coli
- E2
- 17β-estradiol
- ERα
- estrogen receptor α
- GSK-3β
- glycogen synthase kinase 3β
- LEF
- lymphoid enhancer factor
- TCF
- T-cell factor
- ASPP 049
- (3R)-1,7-diphenyl-(4E,6E)-4,6-heptadien-3-ol
- ALP
- alkaline phosphatase
- H+L
- heavy and light chain
- MTT
- 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide.
REFERENCES
- 1. Gordon M. D., Nusse R. (2006) Wnt signaling. Multiple pathways, multiple receptors, and multiple transcription factors. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 22429–22433 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Moon R. T., Kohn A. D., De Ferrari G. V., Kaykas A. (2004) WNT and β-catenin signalling. Diseases and therapies. Nat. Rev. Genet. 5, 691–701 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Chien A. J., Conrad W. H., Moon R. T. (2009) A Wnt survival guide. From flies to human disease. J. Invest. Dermatol. 129, 1614–1627 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Varea O., Arevalo M. A., Garrido J. J., Garcia-Segura L. M., Wandosell F., Mendez P. (2010) Interaction of estrogen receptors with insulin-like growth factor-I and Wnt signaling in the nervous system. Steroids 75, 565–569 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Armstrong V. J., Muzylak M., Sunters A., Zaman G., Saxon L. K., Price J. S., Lanyon L. E. (2007) Wnt/β-catenin signaling is a component of osteoblastic bone cell early responses to load-bearing and requires estrogen receptor α. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 20715–20727 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Westendorf J. J., Kahler R. A., Schroeder T. M. (2004) Wnt signaling in osteoblasts and bone diseases. Gene 341, 19–39 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Gong Y., Slee R. B., Fukai N., Rawadi G., Roman-Roman S., Reginato A. M., Wang H., Cundy T., Glorieux F. H., Lev D., Zacharin M., Oexle K., Marcelino J., Suwairi W., Heeger S., Sabatakos G., Apte S., Adkins W. N., Allgrove J., Arslan-Kirchner M., Batch J. A., Beighton P., Black G. C., Boles R. G., Boon L. M., Borrone C., Brunner H. G., Carle G. F., Dallapiccola B., De Paepe A., Floege B., Halfhide M. L., Hall B., Hennekam R. C., Hirose T., Jans A., Jüppner H., Kim C. A., Keppler-Noreuil K., Kohlschuetter A., LaCombe D., Lambert M., Lemyre E., Letteboer T., Peltonen L., Ramesar R. S., Romanengo M., Somer H., Steichen-Gersdorf E., Steinmann B., Sullivan B., Superti-Furga A., Swoboda W., van den Boogaard M. J., Van Hul W., Vikkula M., Votruba M., Zabel B., Garcia T., Baron R., Olsen B. R., Warman M. L. (2001) LDL receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) affects bone accrual and eye development. Cell 107, 513–523 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Krishnan V., Bryant H. U., Macdougald O. A. (2006) Regulation of bone mass by Wnt signaling. J. Clin. Invest. 116, 1202–1209 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Seeman E., Szmukler G. I., Formica C., Tsalamandris C., Mestrovic R. (1992) Osteoporosis in anorexia nervosa. The influence of peak bone density, bone loss, oral contraceptive use, and exercise. J. Bone Miner. Res. 7, 1467–1474 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Harada S., Rodan G. A. (2003) Control of osteoblast function and regulation of bone mass. Nature 423, 349–355 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Colditz G. A., Hankinson S. E., Hunter D. J., Willett W. C., Manson J. E., Stampfer M. J., Hennekens C., Rosner B., Speizer F. E. (1995) The use of estrogens and progestins and the risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women. N. Engl. J. Med. 332, 1589–1593 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Wood C. E., Kaplan J. R., Fontenot M. B., Williams J. K., Cline J. M. (2010) Endometrial profile of tamoxifen and low-dose estradiol combination therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 16, 946–956 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Piyachaturawat P., Ercharuporn S., Suksamrarn A. (1995) Estrogenic activity of Curcuma comosa extract in rats. Asia Pacific Journal of Pharmacology 10, 121–126 [Google Scholar]
- 14. Weerachayaphorn J., Chuncharunee A., Mahagita C., Lewchalermwongse B., Suksamrarn A., Piyachaturawat P. (2011) A protective effect of Curcuma comosa Roxb. on bone loss in estrogen-deficient mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 137, 956–962 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Suksamrarn A., Ponglikitmongkol M., Wongkrajang K., Chindaduang A., Kittidanairak S., Jankam A., Yingyongnarongkul B. E., Kittipanumat N., Chokchaisiri R., Khetkam P., Piyachaturawat P. (2008) Diarylheptanoids, new phytoestrogens from the rhizomes of Curcuma comosa. Isolation, chemical modification, and estrogenic activity evaluation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 16, 6891–6902 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Winuthayanon W., Piyachaturawat P., Suksamrarn A., Ponglikitmongkol M., Arao Y., Hewitt S. C., Korach K. S. (2009) Diarylheptanoid phytoestrogens isolated from the medicinal plant Curcuma comosa. Biologic actions in vitro and in vivo indicate estrogen receptor-dependent mechanisms. Environ. Health Perspect. 117, 1155–1161 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Winuthayanon W., Suksen K., Boonchird C., Chuncharunee A., Ponglikitmongkol M., Suksamrarn A., Piyachaturawat P. (2009) Estrogenic activity of diarylheptanoids from Curcuma comosa Roxb. requires metabolic activation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 57, 840–845 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Intapad S., Suksamrarn A., Piyachaturawat P. (2009) Enhancement of vascular relaxation in rat aorta by phytoestrogens from Curcuma comosa Roxb. Vascul. Pharmacol. 51, 284–290 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Kolligs F. T., Hu G., Dang C. V., Fearon E. R. (1999) Neoplastic transformation of RK3E by mutant β-catenin requires deregulation of TCF/LEF transcription but not activation of c-myc expression. Mol. Cell Biol. 19, 5696–5706 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Varea O., Garrido J. J., Dopazo A., Mendez P., Garcia-Segura L. M., Wandosell F. (2009) Estradiol activates β-catenin dependent transcription in neurons. PLoS ONE 4, e5153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Fukumoto S., Hsieh C. M., Maemura K., Layne M. D., Yet S. F., Lee K. H., Matsui T., Rosenzweig A., Taylor W. G., Rubin J. S., Perrella M. A., Lee M. E. (2001) Akt participation in the Wnt signaling pathway through Dishevelled. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 17479–17483 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Wandosell F., Varea O., Arevalo M. A., Garcia-Segura L. M. (2011) J. Neuroendocrinol. 24, 191–194 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Spencer G. J., Utting J. C., Etheridge S. L., Arnett T. R., Genever P. G. (2006) Wnt signalling in osteoblasts regulates expression of the receptor activator of NF-κB ligand and inhibits osteoclastogenesis in vitro. J. Cell Sci. 119, 1283–1296 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Kouzmenko A. P., Takeyama K., Ito S., Furutani T., Sawatsubashi S., Maki A., Suzuki E., Kawasaki Y., Akiyama T., Tabata T., Kato S. (2004) Wnt/β-catenin and estrogen signaling converge in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 40255–40258 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Liedert A., Wagner L., Seefried L., Ebert R., Jakob F., Ignatius A. (2010) Estrogen receptor and Wnt signaling interact to regulate early gene expression in response to mechanical strain in osteoblastic cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 394, 755–759 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Matsuzawa S. I., Reed J. C. (2001) Siah-1, SIP, and Ebi collaborate in a novel pathway for β-catenin degradation linked to p53 responses. Mol. Cell 7, 915–926 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Liu J., Stevens J., Rote C. A., Yost H. J., Hu Y., Neufeld K. L., White R. L., Matsunami N. (2001) Siah-1 mediates a novel β-catenin degradation pathway linking p53 to the adenomatous polyposis coli protein. Mol. Cell 7, 927–936 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Chairoungdua A., Smith D. L., Pochard P., Hull M., Caplan M. J. (2010) Exosome release of β-catenin. A novel mechanism that antagonizes Wnt signaling. J. Cell Biol. 190, 1079–1091 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Fang X., Yu S. X., Lu Y., Bast R. C., Jr., Woodgett J. R., Mills G. B. (2000) Phosphorylation and inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 by protein kinase A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97, 11960–11965 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Li M., Wang X., Meintzer M. K., Laessig T., Birnbaum M. J., Heidenreich K. A. (2000) Cyclic AMP promotes neuronal survival by phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase 3β. Mol. Cell Biol. 20, 9356–9363 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Armstrong J. L., Bonavaud S. M., Toole B. J., Yeaman S. J. (2001) Regulation of glycogen synthesis by amino acids in cultured human muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 952–956 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. McDougall K. E., Perry M. J., Gibson R. L., Colley S. M., Korach K. S., Tobias J. H. (2003) Estrogen receptor-α dependency of estrogen's stimulatory action on cancerous bone formation in male mice. Endocrinology 144, 1994–1999 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Jho E. H., Zhang T., Domon C., Joo C. K., Freund J. N., Costantini F. (2002) Wnt/β-catenin/Tcf signaling induces the transcription of Axin2, a negative regulator of the signaling pathway. Mol. Cell Biol. 22, 1172–1183 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Yu H. M., Jerchow B., Sheu T. J., Liu B., Costantini F., Puzas J. E., Birchmeier W., Hsu W. (2005) The role of Axin2 in calvarial morphogenesis and craniosynostosis. Development 132, 1995–2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Komori T. (2010) Regulation of bone development and extracellular matrix protein genes by RUNX2. Cell Tissue Res. 339, 189–195 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Gaur T., Lengner C. J., Hovhannisyan H., Bhat R. A., Bodine P. V., Komm B. S., Javed A., van Wijnen A. J., Stein J. L., Stein G. S., Lian J. B. (2005) Canonical WNT signaling promotes osteogenesis by directly stimulating Runx2 gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 33132–33140 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Chen X., Garner S. C., Quarles L. D., Anderson J. J. (2003) Effects of genistein on expression of bone markers during MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cell differentiation. J. Nutr. Biochem. 14, 342–349 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Rubin J., Ackert-Bicknell C. L., Zhu L., Fan X., Murphy T. C., Nanes M. S., Marcus R., Holloway L., Beamer W. G., Rosen C. J. (2002) IGF-I regulates osteoprotegerin (OPG) and receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand in vitro and OPG in vivo. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 87, 4273–4279 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]