Abstract
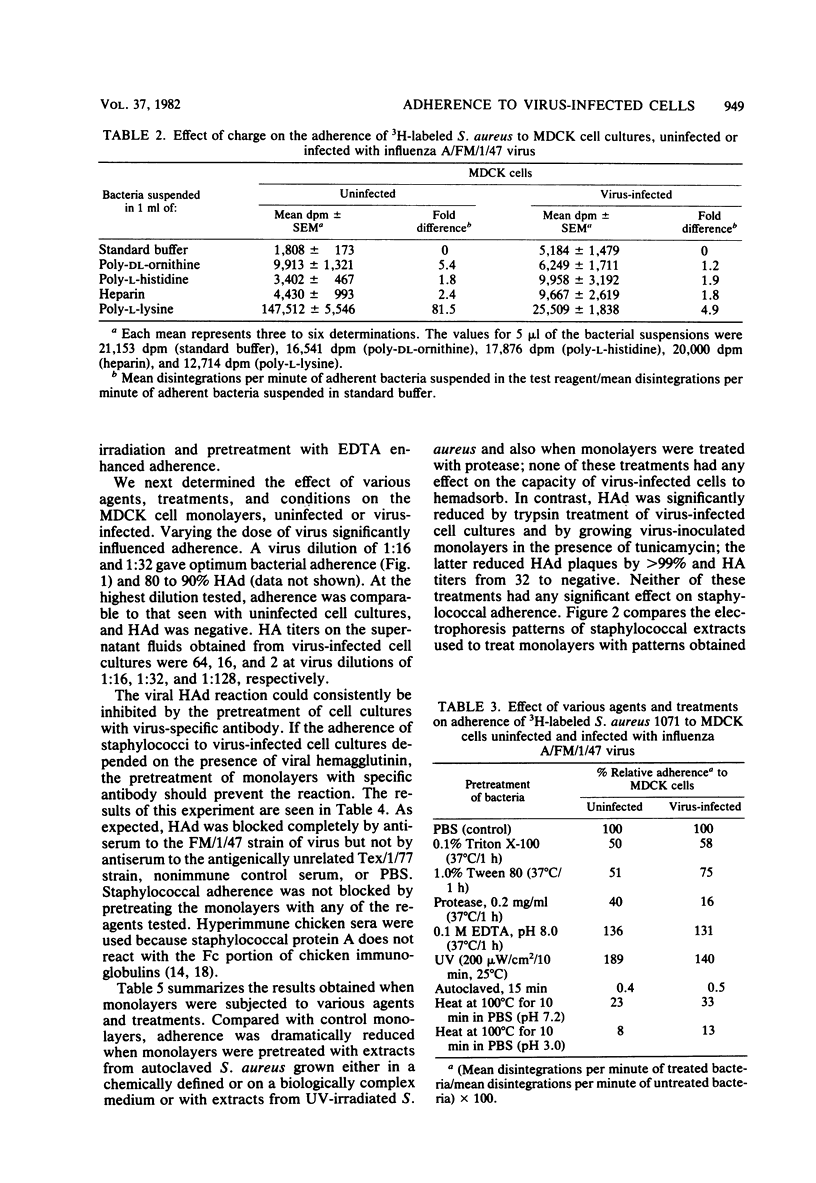
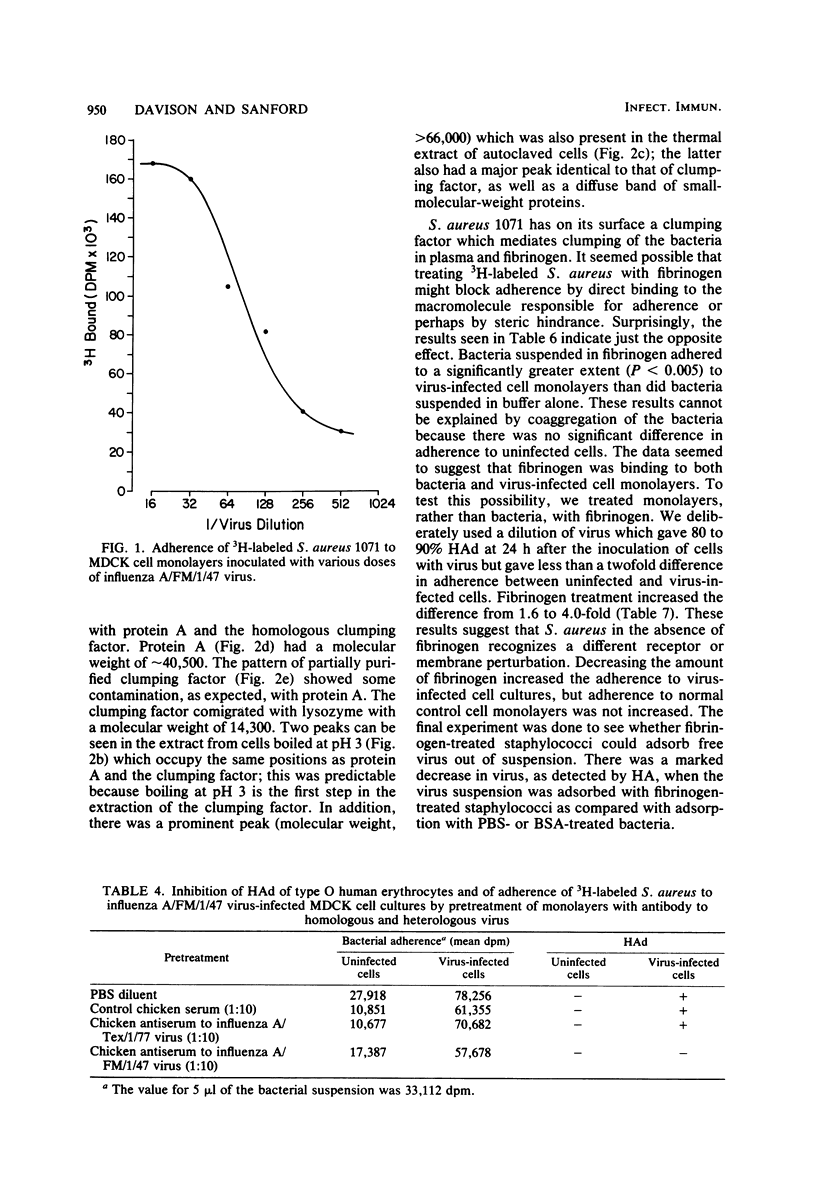
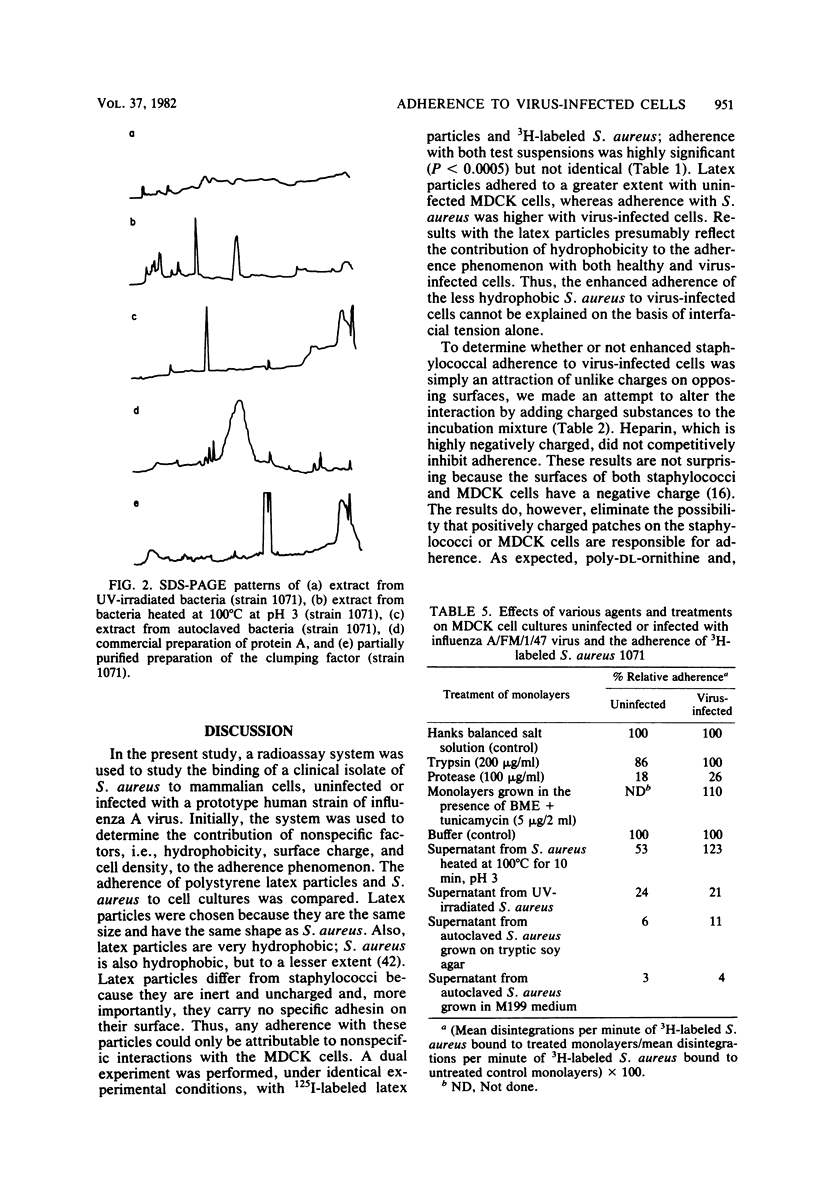
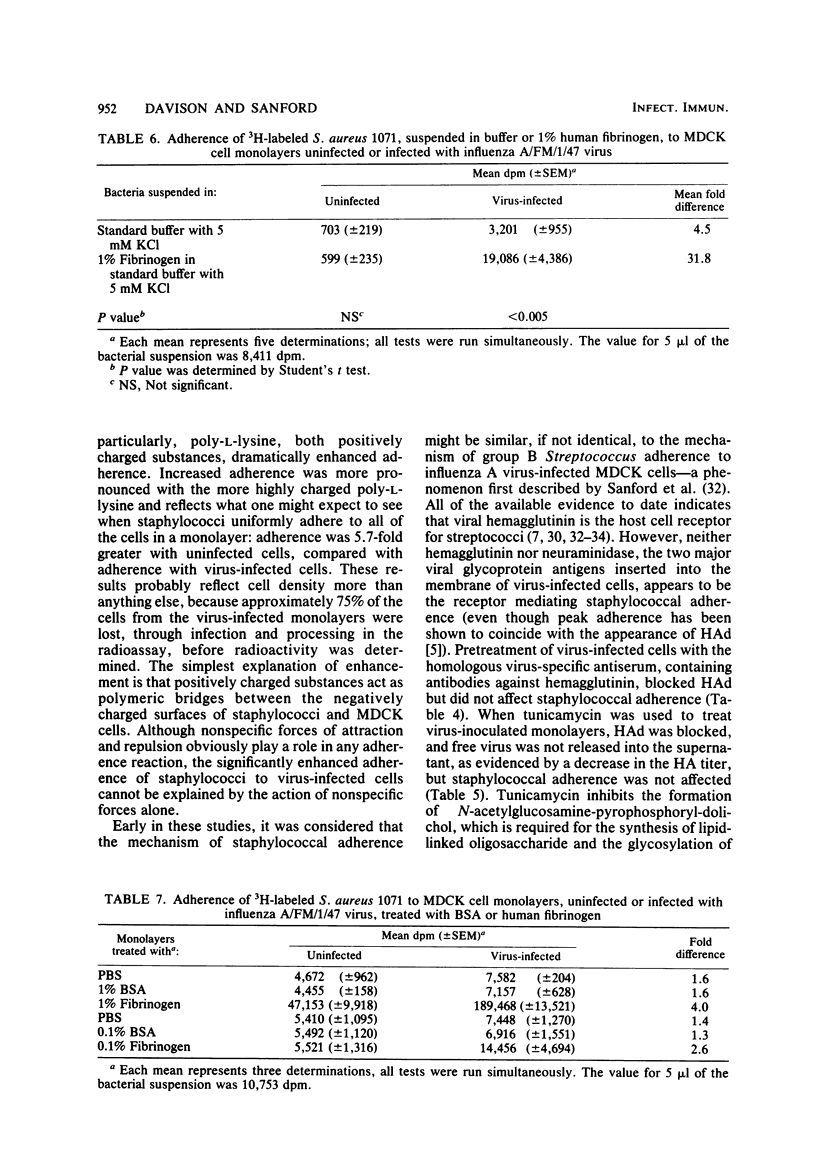
A quantitative radioassay was used to study the factors affecting the adherence of 3H-labeled Staphylococcus aureus 1071 to Madin-Darby canine kidney cells, either uninfected or infected with the human FM1 strain of influenza A virus. Enhanced adherence to virus-infected cell cultures was independent of nonspecific factors—hydrophobicity, surface charge, and monolayer cell density. Viral hemagglutinin and neuraminidase did not act as the cell receptors for S. aureus because the growth of virus-inoculated monolayers in tunicamycin (an inhibitor of glycosylation) and the pretreatment of virus-infected cells with trypsin or virus-specific antiserum, which inhibit hemadsorption, had no effect on staphylococcal adherence. In contrast, adherence to uninfected and virus-infected cells was significantly reduced by protease treatment of either monolayers or staphylococci and by heat treatment of staphylococci. UV irradiation and treatment of bacteria with 0.1 M EDTA enhanced adherence. Pretreatment of monolayers with a thermal extract of S. aureus decreased adherence by 89 to 97%. The staphylococcal adhesin, which blocks adherence to virus-infected cells, appears to be a remarkably heat-stable, protease- and trypsin-sensitive macromolecule which is distinct from protein A, clumping factor, and teichoic acid. Lastly, pretreatment of S. aureus with human fibrinogen significantly enhanced adherence to virus-infected cells (P < 0.005) compared with binding with untreated S. aureus. The treated bacteria also adsorbed virus out of suspension. These results suggest that fibrinogen forms a bridge between S. aureus and receptors present on virus-infected cells and free virus.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austin R. M., Daniels C. A. The role of protein A in the attachment of staphylococci to influenza-infected cells. Lab Invest. 1978 Aug;39(2):128–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coley J., Tarelli E., Archibald A. R., Baddiley J. The linkage between teichoic acid and peptidoglycan in bacterial cell walls. FEBS Lett. 1978 Apr 1;88(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80594-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUTHIE E. S. The action of fibrinogen on certain pathogenic cocci. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Oct;13(2):383–393. doi: 10.1099/00221287-13-2-383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison V. E., Sanford B. A. Adherence of staphylococcus aureus to influenza A virus-infected Madin-Darby canine kidney cell cultures. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):118–126. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.118-126.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbein A. D., Sanford B. A., Ramsay M. A., Pan Y. T. Effect of inhibitors on glycoprotein biosynthesis and bacterial adhesion. Ciba Found Symp. 1981;80:270–287. doi: 10.1002/9780470720639.ch17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fainstein V., Musher D. M., Cate T. R. Bacterial adherence to pharyngeal cells during viral infection. J Infect Dis. 1980 Feb;141(2):172–176. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.2.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiala M. A study of the combined role of viruses, mycoplasmas and bacteria in adult pneumonia. Am J Med Sci. 1969 Jan;257(1):44–51. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196901000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A. Protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. V. Reaction with guinea pig gamma-globulins. J Immunol. 1968 May;100(5):921–926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Sjöquist J. "Protein A" from S. aureus. I. Pseudo-immune reaction with human gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):822–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Sjöquist J. "Protein A" from Staphylococcus aureus. 3. Reaction with rabbit gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1967 Jul;99(1):19–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grov A., Oeding P., Myklestad B., Aasen J. Reactions of staphylococcal antigens with normal sera, gamma G-globulins, and gamma G-globulin fragments of various species origin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1970;78(1):106–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1970.tb04275.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarstrand C., Tunevall G. Colonization and clinical superinfection with gram-negative bacilli in influenza. Scand J Infect Dis. 1976;8(4):229–235. doi: 10.3109/inf.1976.8.issue-4.02. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimek J. J., Lindenberg L. B., Cole S., Ellison L. H., Quintiliani R. Fatal case of influenza pneumonia with suprainfection by multiple bacteria and Herpes simplex virus. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 May;113(5):683–688. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.113.5.683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Seal U. S., Finstad J., Williams R. C., Jr Phylogenetic insight into evolution of mammalian Fc fragment of gamma G globulin using staphylococcal protein A. J Immunol. 1970 Jan;104(1):140–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOURIA D. B., BLUMENFELD H. L., ELLIS J. T., KILBOURNE E. D., ROGERS D. E. Studies on influenza in the pandemic of 1957-1958. II. Pulmonary complications of influenza. J Clin Invest. 1959 Jan;38(1 Pt 2):213–265. doi: 10.1172/JCI103791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loziuk L. V., Volos O. P. Porivnial'ne vyvchennia streptokokovoï, hrypoznoï ta zmishanoï infektsii v eksperimenti. Mikrobiol Zh. 1977 Jul-Aug;39(4):458–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN C. M., KUNIN C. M., GOTTLIEB L. S., FINLAND M. Asian influenza A in Boston, 1957-1958. II. Severe staphylococcal pneumonia complicating influenza. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1959 Apr;103(4):532–542. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1959.00270040018002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mausbach T. W., Cho C. T. Pneumonia and pleural effusion. Association with influenza A virus and Staphylococcus aureus. Am J Dis Child. 1976 Sep;130(9):1005–1006. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1976.02120100095016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell E. S., Ward T. G., Van Metre T. E., Jr THE RELATION OF INFLUENZA VIRUS AND BACTERIA IN THE ETIOLOGY OF PNEUMONIA. J Clin Invest. 1949 Mar;28(2):307–318. doi: 10.1172/JCI102073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mufson M. A., Chang V., Gill V., Wood S. C., Romansky M. J., Chanock R. M. The role of viruses, mycoplasmas and bacteria in acute pneumonia in civilian adults. Am J Epidemiol. 1967 Nov;86(3):526–544. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichol K. P., Cherry J. D. Bacterial-viral interrelations in respiratory infections of children. N Engl J Med. 1967 Sep 28;277(13):667–672. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196709282771301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan Y. T., Schmitt J. W., Sanford B. A., Elbein A. D. Adherence of bacteria to mammalian cells: inhibition by tunicamycin and streptovirudin. J Bacteriol. 1979 Aug;139(2):507–514. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.2.507-514.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramphal R., Small P. M., Shands J. W., Jr, Fischlschweiger W., Small P. A., Jr Adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to tracheal cells injured by influenza infection or by endotracheal intubation. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):614–619. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.614-619.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STILLE W. T., PIERCE W., CRAWFORD Y. E. Multiple infections in acute respiratory illness. I. Severity of illness of naval recruits and independence of infectious agents. J Infect Dis. 1961 Sep-Oct;109:158–165. doi: 10.1093/infdis/109.2.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanford B. A., Shelokov A., Ramsay M. A. Bacterial adherence to virus-infected cells: a cell culture model of bacterial superinfection. J Infect Dis. 1978 Feb;137(2):176–181. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.2.176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanford B. A., Smith N., Shelokov A., Ramsay M. A. Adherence of group B streptococci and human erythrocytes to influenza A virus-infected MDCK cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Feb;160(2):226–232. doi: 10.3181/00379727-160-40424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanford B. A., Smith N., Shelokov A., Ramsay M. A. Adherence of influenza A viruses to group B Streptococci. J Infect Dis. 1980 Apr;141(4):496–506. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.4.496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selinger D. S., Reed W. P., McLaren L. C. Model for studying bacterial adherence to epithelial cells infected with viruses. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):941–944. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.941-944.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. B., Golden C., Klauber M. R., Kanner R., Renzetti A. Interactions between viruses and bacteria in patients with chronic bronchitis. J Infect Dis. 1976 Dec;134(6):552–561. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.6.552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TUNEVALL G., OHLSON M., SUEDMYR A., VONZEIPEL G., FRISK A., HEDLUND P., LAMBERGER B., JERNELIUS H. AETIOLOGIC AGENTS IN RESPIRATORY ILLNESS. OCCURRENCE OF BACTERIA AND SEROLOGIC REACTIONS AGAINST VIRUSES AND BACTERIA IN ACUTE RESPIRATORY ILLNESS. Acta Med Scand. 1963 Aug;174:237–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., LaForce F. M., Head J. J., Feeley J. C., Bennett J. V. A simultaneous outbreak of meningococcal and influenza infections. N Engl J Med. 1972 Jul 6;287(1):5–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197207062870102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Oss C. J. Phagocytosis as a surface phenomenon. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:19–39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



