Abstract
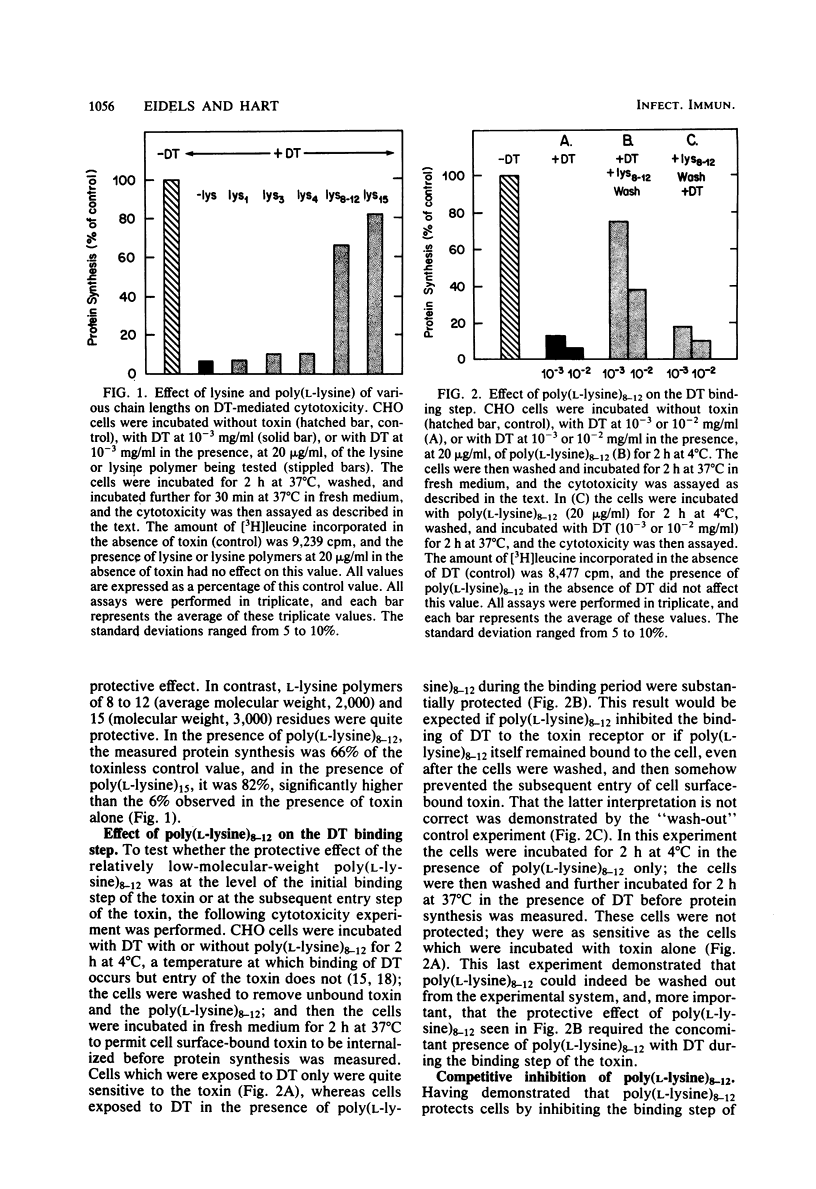
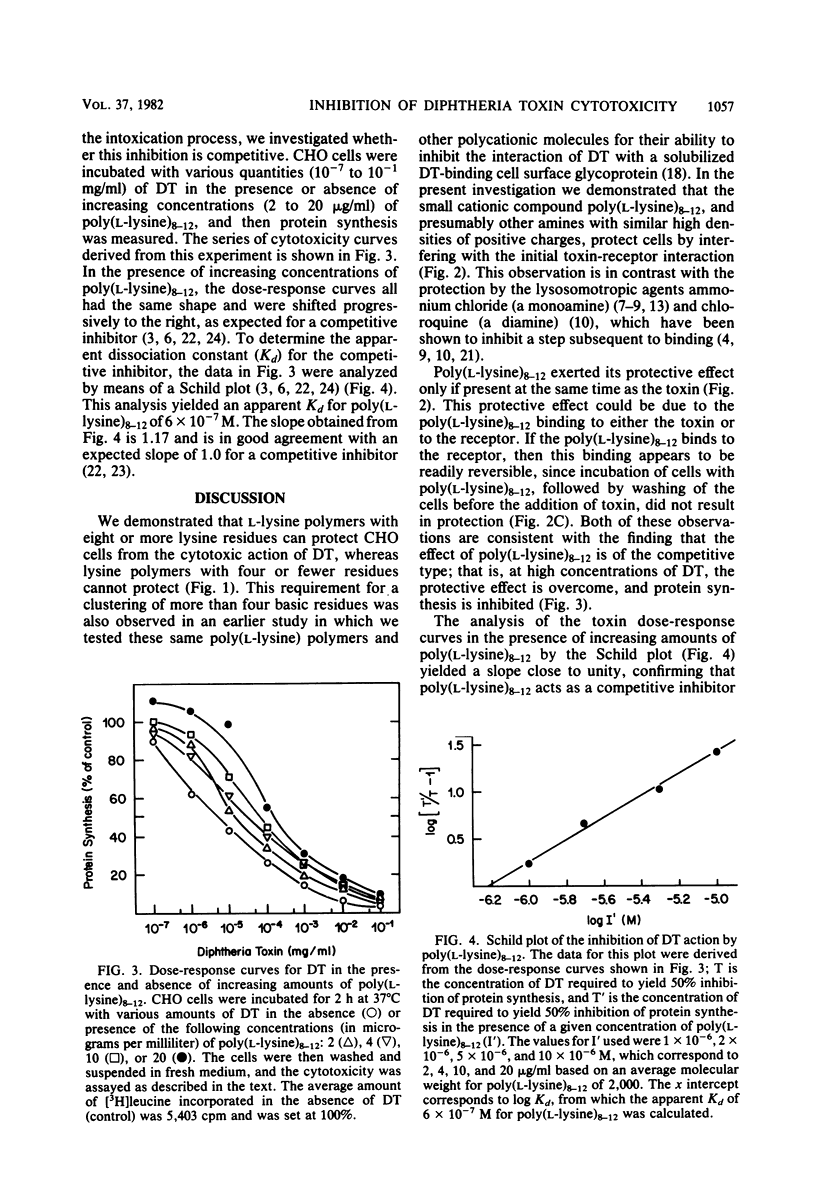
L-Lysine and poly(L-lysine) polymers of defined sizes were tested for their effect on diphtheria toxin-mediated cytotoxicity of Chinese hamster ovary cells. Poly(L-lysine)8-12 and poly(L-lysine)15 were protective, whereas lysine and lysine polymers of three and four residues were not. The protection by poly(L-lysine)8-12 occurred by affecting the initial toxin receptor interaction. Furthermore, poly(L-lysine)8-12 acted as a competitive inhibitor with an apparent dissociation constant of 6 X 10(-7) M. These observations are consistent with a previously proposed model (Proia et al., J. Biol. Chem. 256:4991-4997, 1981) in which (i) the cationic polyphosphate-binding site (P site) on the B fragment of diphtheria toxin interacts with a putative polyanionic binding site on the toxin receptor, and (ii) the protection of cells from diphtheria toxin by poly(L-lysine) and other polycationic molecules would be the result of the competition between these polycationic molecules and the cationic domain of the diphtheria toxin molecule for the polyanionic toxin-binding site on the cell surface receptor.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Collier R. J. Diphtheria toxin: mode of action and structure. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Mar;39(1):54–85. doi: 10.1128/br.39.1.54-85.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper R. K., Chin D., Eurey-Owens D., Scheffler I. E., Simon M. I. Biochemical and genetic characterization of three hamster cell mutants resistant to diphtheria toxin. J Cell Biol. 1979 Oct;83(1):116–125. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.1.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper R. K., Chin D., Simon M. I. Diphtheria toxin has the properties of a lectin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):261–265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper R. K., Simon M. I. The entry of diphtheria toxin into the mammalian cell cytoplasm: evidence for lysosomal involvement. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):849–854. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GADDUM J. H. Theories of drug antagonism. Pharmacol Rev. 1957 Jun;9(2):211–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ittelson T. R., Gill D. M. Diphtheria toxin: specific competition for cell receptors. Nature. 1973 Mar 30;242(5396):330–332. doi: 10.1038/242330b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivins B., Saelinger C. B., Bonventre P. F., Woscinski C. Chemical modulation of diphtheria toxin action on cultured mammalian cells. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):665–674. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.665-674.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K., Groman N. B. In vitro inhibition of diphtheria toxin action by ammonium salts and amines. J Bacteriol. 1965 Dec;90(6):1552–1556. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.6.1552-1556.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K., Groman N. B. Mode of inhibition of diphtheria toxin by ammonium chloride. J Bacteriol. 1965 Dec;90(6):1557–1562. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.6.1557-1562.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppla S., Dorland R. B., Middlebrook J. L. Inhibition of diphtheria toxin degradation and cytotoxic action by chloroquine. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2247–2250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lory S., Carroll S. F., Collier R. J. Ligand interactions of diphtheria toxin. II. Relationships between the NAD site and the P site. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):12016–12019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lory S., Collier R. J. Diphtheria toxin: nucleotide binding and toxin heterogeneity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):267–271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook J. L., Dorland R. B. Differential chemical protection of mammalian cells from the exotoxins of Corynebacterium diphtheriae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):232–239. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.232-239.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook J. L., Dorland R. B., Leppla S. H. Association of diphtheria toxin with Vero cells. Demonstration of a receptor. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7325–7330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook J. L., Dorland R. B. Protection of mammalian cells from diphtheria toxin by exogenous nucleotides. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Mar;25(3):285–290. doi: 10.1139/m79-046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Diphtheria toxin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:69–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Uchida T., Harper A. A. An immunological study of the diphtheria toxin molecule. Immunochemistry. 1972 Sep;9(9):891–906. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90163-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proia R. L., Eidels L., Hart D. A. Diphtheria toxin:receptor interaction. Characterization of the receptor interaction with the nucleotide-free toxin, the nucleotide-bound toxin, and the B-fragment of the toxin. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4991–4997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proia R. L., Hart D. A., Eidels L. Interaction of diphtheria toxin with phosphorylated molecules. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):942–948. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.942-948.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proia R. L., Wray S. K., Hart D. A., Eidels L. Characterization and affinity labeling of the cationic phosphate-binding (nucleotide-binding) peptide located in the receptor-binding region of the B-fragment of diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):12025–12033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHILD H. O. Drug antagonism and pAx. Pharmacol Rev. 1957 Jun;9(2):242–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Diphtheria toxin entry into cells is facilitated by low pH. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):828–832. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waud D. R. Pharmacological receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 1968 Jun;20(2):49–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanen J., Muyldermans G., Beugnier N. Competitive antagonists of the action of diphtheria toxin in HeLa cells. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jul 15;66(2):261–263. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80518-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



