Abstract
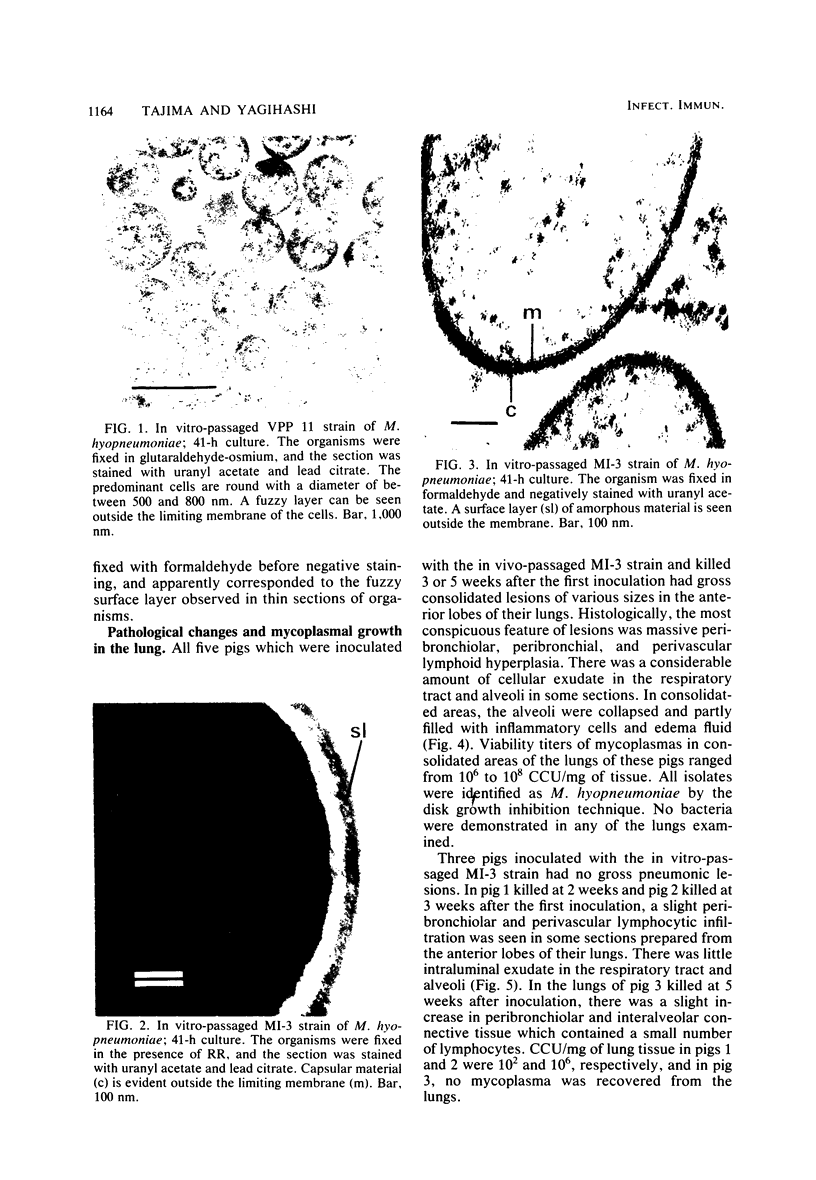
An in vivo-passaged strain of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae attained viability titers of 10(6) to 10(8) color-changing units per mg of tissue in pig lungs and caused gross and histological pulmonic lesions. Mycoplasmas were readily located in the lumina of the respiratory tract by electron microscopy. In sections of tissue fixed in glutaraldehyde-osmium, the organisms were found to possess many radial fibrils on the outer surface of the limiting membrane. These fibrils appeared to interconnect adjacent mycoplasmas and to extend between the organism and epithelial cell. Ruthenium red staining demonstrated a thick, dark layer of capsular material enveloping the entire mycoplasma cell. The capsular material was seen to bridge the space between the mycoplasma and host cell. The general morphology of the in vitro-passaged strains grown in broth medium was essentially similar to that of the in vivo-passaged strain. In these organisms, however, no long fibrils were seen, although a fuzzy layer was present outside the cell membrane. The ruthenium red-positive capsule was stained less intensely, and its width was only about one-half that observed for the in vivo-passaged strain. In negatively stained preparations, the cells had an outer fringe of amorphous material apparently corresponding to the fuzzy layer seen in thin sections. The in vitro-passaged strain grew poorly in pig lungs and lost its ability to produce gross pulmonic lesions. The organisms in the respiratory tract had a capsule much thinner than that of the in vivo-passaged strain.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ajufo J. C., Whithear K. G. Evidence for a ruthenium red-staining extracellular layer as the haemagglutinin of the WVU 1853 strain of Mycoplasma synoviae. Aust Vet J. 1978 Oct;54(10):502–504. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1978.tb00311.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ajufo J. C., Whithear K. G. The surface layer of Mycoplasma synoviae as demonstrated by the negative staining technique. Res Vet Sci. 1980 Sep;29(2):268–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskerville A. Development of the early lesions in experimental enzootic pneumonia of pigs: an ultrastructural and histological study. Res Vet Sci. 1972 Nov;13(6):570–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskerville A., Wright C. L. Ultrastructural changes in experimental enzootic pneumonia of pigs. Res Vet Sci. 1973 Mar;14(2):155–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black F. T., Birch-Andersen A., Freundt E. A. Morphology and ultrastructure of human T-mycoplasmas. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jul;111(1):254–259. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.1.254-259.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLYDE W. A., Jr MYCOPLASMA SPECIES IDENTIFICATION BASED UPON GROWTH INHIBITION BY SPECIFIC ANTISERA. J Immunol. 1964 Jun;92:958–965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu H. P., Horne R. W. Electron microscopy of Mycoplasma gallisepticum and Mycoplasma mycoides using the negative staining technique and their comparison with myxovirus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):190–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27658.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier A. M., Clyde W. A. Relationships Between Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Human Respiratory Epithelium. Infect Immun. 1971 May;3(5):694–701. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.5.694-701.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOMERMUTH C. H., NIELSEN M. H., FREUNDT E. A., BIRCH-ANDERSEN A. ULTRASTRUCTURE OF MYCOPLASMA SPECIES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Sep;88:727–744. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.3.727-744.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny F. W., Taylor-Robinson D., Allison A. C. The role of thymus-dependent immunity in Mycoplasma pulmonis infections of mice. J Med Microbiol. 1972 Aug;5(3):327–336. doi: 10.1099/00222615-5-3-327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourlay R. N., Thrower K. J. Morphology of Mycoplasma mycoides thread-phase growth. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Nov;54(1):155–159. doi: 10.1099/00221287-54-1-155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green F., 3rd, Hanson R. P. Ultrastructure and capsule of Mycoplasma meleagridis. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):1011–1018. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.1011-1018.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard C. J., Gourley R. N. An electron-microscopic examination of certain bovine mycoplasmas stained with ruthenium red and the demonstration of a capsule on Mycoplasma dispar. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Aug;83(2):393–398. doi: 10.1099/00221287-83-2-393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper D. L., Onderdonk A. B., Reinap B. G., Linberg A. A. Variations of Bacteroides fragilis with in vitro passage: presence of an outer membrane-associated glycan and loss of capsular antigen. J Infect Dis. 1980 Nov;142(5):750–756. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.5.750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston C. W., Jr, Stair E. L., Underdahl N. R., Mebus C. A. Pathogenesis of mycoplasmal pneumonia in swine. Am J Vet Res. 1972 Nov;33(11):2249–2258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARE C. J., SWITZER W. P. NEW SPECIES: MYCOPLASMA HYOPNEUMONIAE; A CAUSATIVE AGENT OF VIRUS PIG PNEUMONIA. Vet Med Small Anim Clin. 1965 Aug;60:841–846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mebus C. A., Underdahl N. R. Scanning electron microscopy of trachea and bronchi from gnotobiotic pigs inoculated with Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Aug;38(8):1249–1254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J., Smook E. Cytochemical evidence of extramembranous carbohydrates on Ureaplasma urealyticum (T-strain Mycoplasma). J Bacteriol. 1976 Nov;128(2):658–660. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.2.658-660.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley D. Endotoxins and bacterial virulence. J Infect Dis. 1971 Mar;123(3):317–327. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.3.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer E. L., Roth I. L. The ultrastructure of the capsules of Diplococcus pneumoniae and Klebsiella pneumoniae stained with ruthenium red. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jan;74(1):21–31. doi: 10.1099/00221287-74-1-21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tajima M., Nunoya T., Yagihashi T. An ultrastructural study on the interaction of Mycoplasma gallisepticum with the chicken tracheal epithelium. Am J Vet Res. 1979 Jul;40(7):1009–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully J. G., Taylor-Robinson D., Cole R. M., Rose D. L. A newly discovered mycoplasma in the human urogenital tract. Lancet. 1981 Jun 13;1(8233):1288–1291. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92461-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegmann W., Bertschinger H. U., Keller H. Die enzootische Pneumonie der Schweine. Eine elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchung mit Erregernachweis im Gewebe. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1969 Jul;16(5):428–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. H., Collier A. M. Ultrastructural study of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in organ culture. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jan;125(1):332–339. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.1.332-339.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Koshimizu K., Ogata M. Selective isolation of Mycoplasma suipneumoniae from pneumonic lesions in pigs. Natl Inst Anim Health Q (Tokyo) 1971 Fall;11(3):168–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]