Abstract
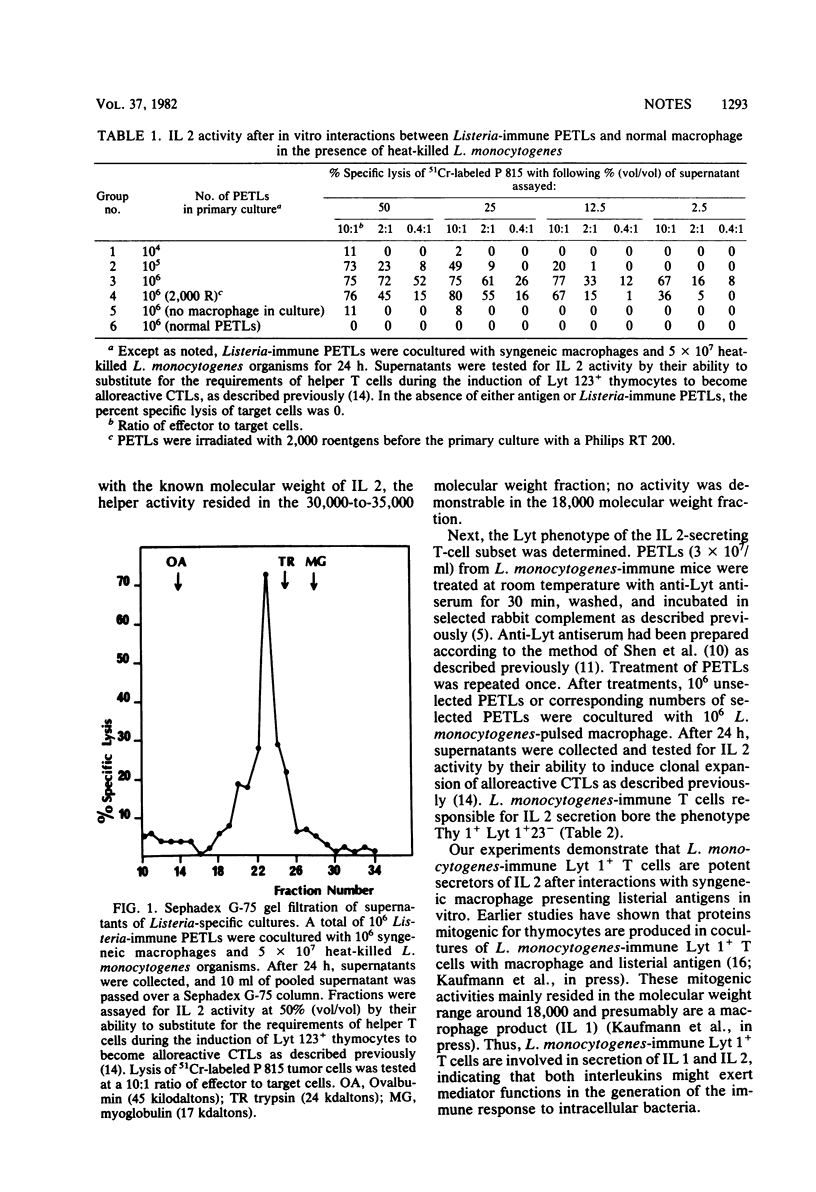
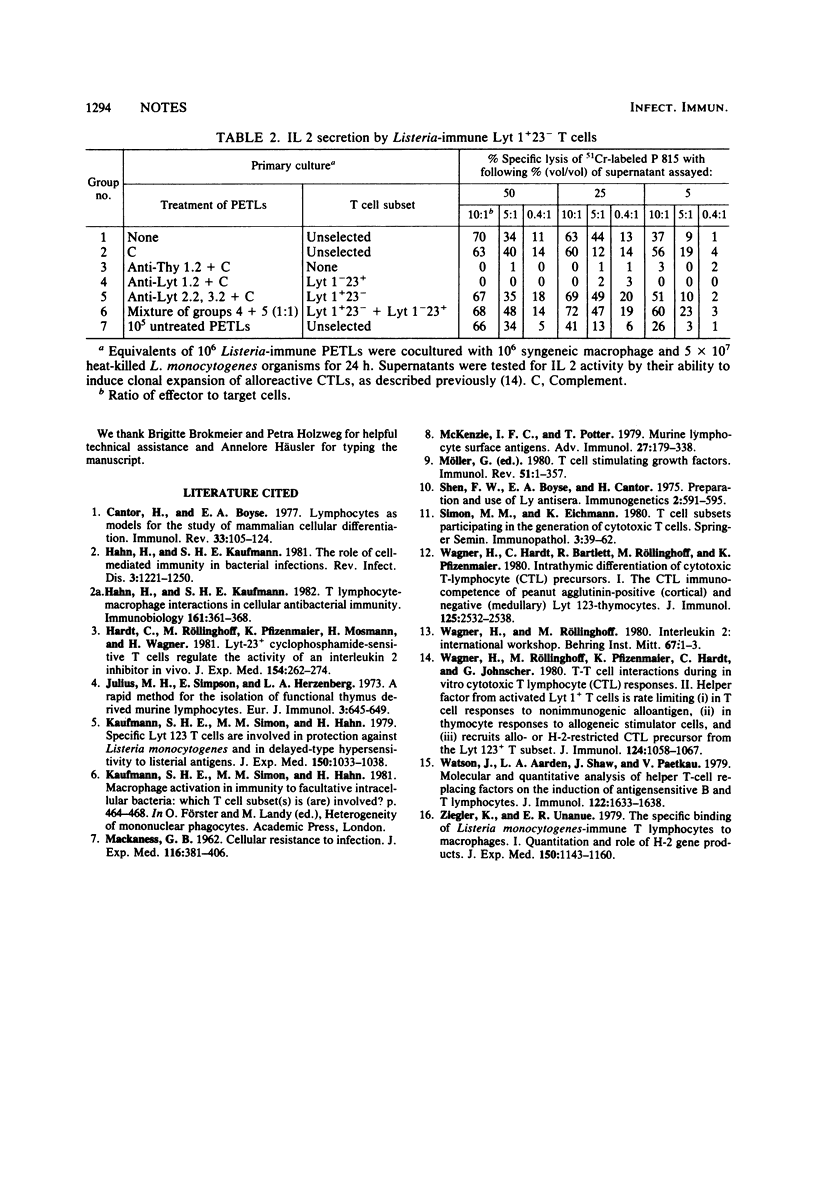
Peritoneal exudate T lymphocytes from mice experimentally infected with the intracellular bacterium Listeria monocytogenes secreted high interleukin 2 activities after interaction with syngeneic normal macrophage presenting listerial antigen in vitro. L. monocytogenes-immune cells secreting IL 2 were radioresistant and bore the phenotype Thy 1+ Lyt 1+23−.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cantor H., Boyse E. A. Lymphocytes as models for the study of mammalian cellular differentiation. Immunol Rev. 1977 Jan;33:105–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1977.tb00364.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn H., Kaufmann S. H. T lymphocyte-macrophage interactions in cellular antibacterial immunity. Immunobiology. 1982 Apr;161(3-4):361–368. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(82)80093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn H., Kaufmann S. H. The role of cell-mediated immunity in bacterial infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3(6):1221–1250. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.6.1221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardt C., Röllinghoff M., Pfizenmaier K., Mosmann H., Wagner H. Lyt-23+ cyclophosphamide-sensitive T cells regulate the activity of an interleukin 2 inhibitor in vivo. J Exp Med. 1981 Aug 1;154(2):262–274. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.2.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Simon M. M., Hahn H. Specific Lyt 123 cells are involved in protection against Listeria monocytogenes and in delayed-type hypersensitivity to listerial antigens. J Exp Med. 1979 Oct 1;150(4):1033–1038. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.4.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie I. F., Potter T. Murine lymphocyte surface antigens. Adv Immunol. 1979;27:179–338. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60263-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. M., Eichmann K. T cell subsets participating in the generation of cytotoxic T cells. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1980 May;3(1):39–62. doi: 10.1007/BF00199925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner H., Hardt C., Bartlett R., Röllinghoff M., Pfizenmaier K. Intrathymic differentiation of cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) precursors. I. The CTL immunocompetence of peanut agglutinin-positive (cortical) and negative (medullary) Lyt 123 thymocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2532–2538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner H., Räollinghoff M., Pfizenmaier K., Hardt C., Johnscher G. T-T cell interactions during in vitro cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) responses. II. Helper factor from activated Lyt 1+ T cells is rate limiting i) in T cell responses to nonimmunogenic alloantigen, ii) in thymocyte responses to allogeneic stimulator cells, and III) recruits allo- or H-2-restricted CTL precursors from the Lyt 123+ T subset. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1058–1067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J., Aarden L. A., Shaw J., Paetkau V. Molecular and quantitative analysis of helper T cell-replacing factors on the induction of antigen-sensitive B and T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1979 May;122(5):1633–1638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler K., Unanue E. R. The specific binding of Listeria monocytogenes-immune T lymphocytes to macrophages. I. Quantitation and role of H-2 gene products. J Exp Med. 1979 Nov 1;150(5):1143–1160. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.5.1143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



