Abstract
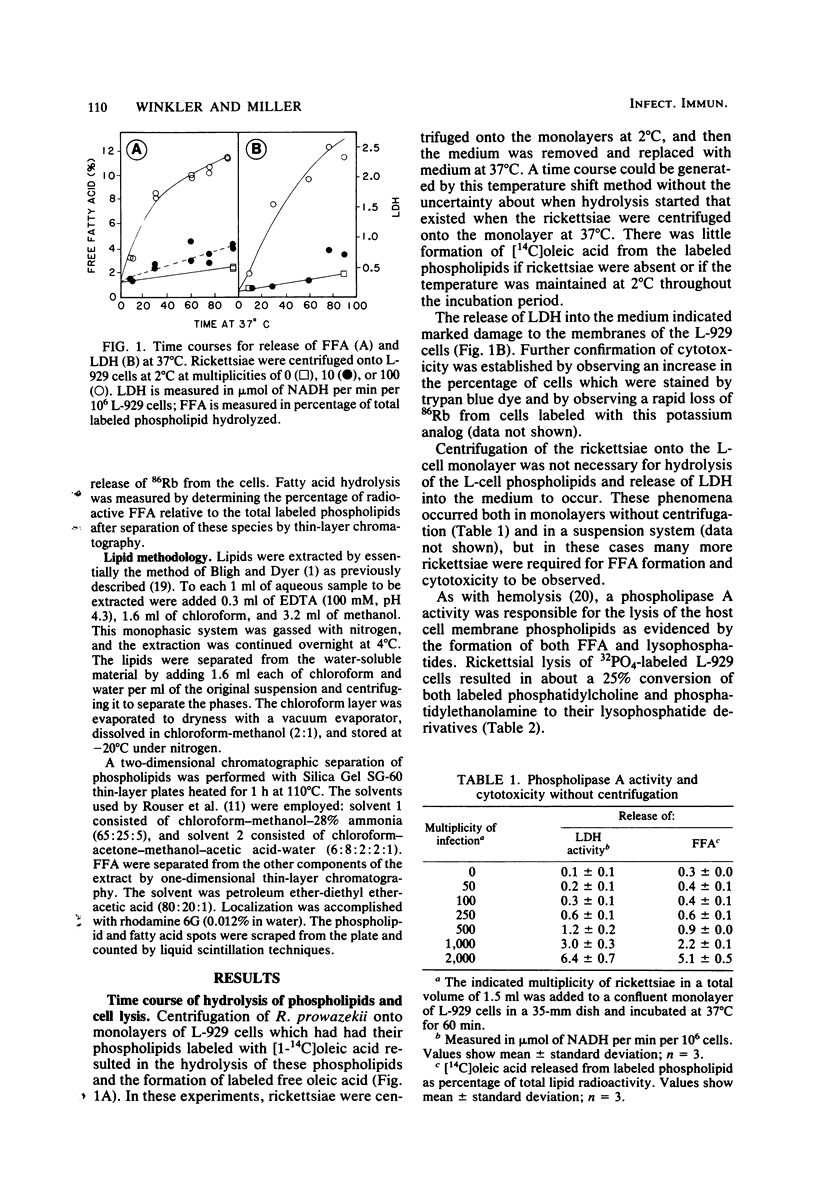
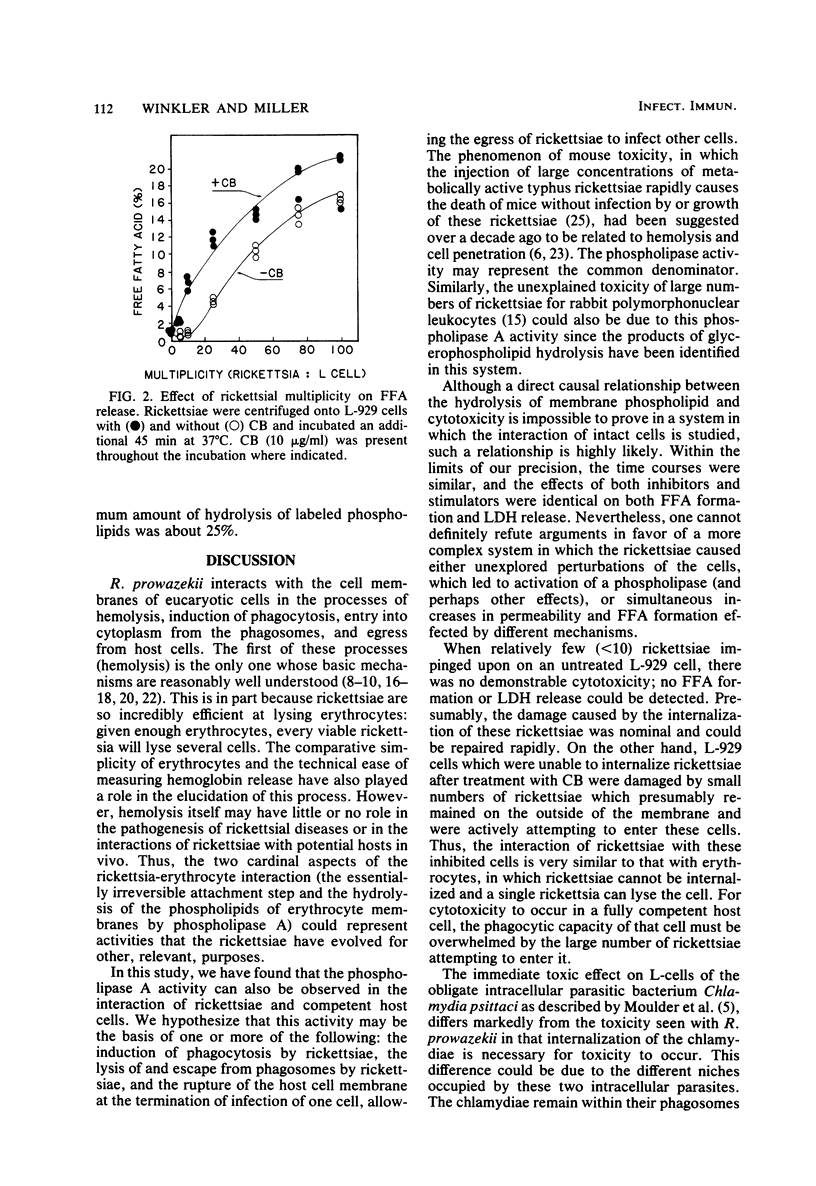
L-929 cells were killed when approximately 50 viable Rickettsia prowazekii organisms per L-cell were centrifuged onto a monolayer. The glycerophospholipids of the L-cell were hydrolyzed to lysophosphatides and free fatty acids. Concomitantly, there was a loss of membrane integrity as shown by release of lactate dehydrogenase and 86Rb and permeability to trypan blue dye. No glycerophospholipid hydrolysis or cytotoxicity occurred when the rickettsiae were inactivated by heat, UV irradiation, N-ethylmaleimide, or metabolic inhibitors before their addition to the L-929 cells. On the other hand, treatment of the L929 cells with the cytoskeleton agents colchicine or cytochalasin B or with N-ethylmaleimide inhibited neither the phospholipase A activity nor the loss of membrane integrity. Cytochalasin B-treated cells could be damaged by even small numbers of rickettsiae. We suggest that this phospholipase A activity is used by the rickettsiae to escape from the phagosomes into the cytoplasm of host cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOVARNICK M. R., MILLER J. C., SNYDER J. C. The influence of certain salts, amino acids, sugars, and proteins on the stability of rickettsiae. J Bacteriol. 1950 Apr;59(4):509–522. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.4.509-522.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., BOZEMAN F. M., CAMPBELL J. M., HUMPHRIES J. W., SAWYER T. K. Study on growth of Rickettsia. V. Penetration of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi into mammalian cells in vitro. J Exp Med. 1959 Mar 1;109(3):271–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.109.3.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W., Hatch T. P., Byrne G. I., Kellogg K. R. Immediate toxicity of high multiplicities of Chlamydia psittaci for mouse fibroblasts (L cells). Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):277–289. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.277-289.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormsbee R. A. Rickettsiae (as organisms). Annu Rev Microbiol. 1969;23:275–292. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.23.100169.001423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phibbs P. V., Jr, Winkler H. H. Regulatory properties of citrate synthase from Rickettsia prowazekii. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):718–725. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.718-725.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramm L. E., Winkler H. H. Identification of cholesterol in the receptor site for rickettsiae on sheep erythrocyte membranes. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):120–126. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.120-126.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramm L. E., Winkler H. H. Rickettsial hemolysis: adsorption of rickettsiae to erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1973 Jan;7(1):93–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.1.93-99.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramm L. E., Winkler H. H. Rickettsial hemolysis: effect of metabolic inhibitors upon hemolysis and adsorption. Infect Immun. 1973 Apr;7(4):550–555. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.4.550-555.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouser G., Fkeischer S., Yamamoto A. Two dimensional then layer chromatographic separation of polar lipids and determination of phospholipids by phosphorus analysis of spots. Lipids. 1970 May;5(5):494–496. doi: 10.1007/BF02531316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. K., Winkler H. H. Characterization of a lysine-specific active transport system in Rickettsia prowazeki. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1349–1355. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1349-1355.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISSEMAN C. L., Jr, JACKSON E. B., HAHN F. E., LEY A. C., SMADEL J. E. Metabolic studies of rickettsiae. I. The effects of antimicrobial substances and enzyme inhibitors on the oxidation of glutamate by purified rickettsiae. J Immunol. 1951 Aug;67(2):123–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISSEMAN C. L., Jr, PAZOUREK L., BOCCUTI A., JAMES H., OLDSTONE M. B. Studies on rickettsial toxins. V. Dissimilarity between the action of rickettsial mouse lethal toxin and bacterial endotoxin in mice. J Immunol. 1961 Jun;86:613–617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker T. S., Winkler H. H. Interactions between Rickettsia prowazekii and rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes: rickettsiacidal and leukotoxic activities. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):289–296. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.289-296.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker T. S., Winkler H. H. Penetration of cultured mouse fibroblasts (L cells) by Rickettsia prowazeki. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):200–208. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.200-208.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker T. S., Winkler H. H. Rickettsial hemolysis: rapid method for enumeration of metabolically active typhus rickettsiae. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 May;9(5):645–647. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.5.645-647.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H. Inhibitory and restorative effects of adenine nucleotides on rickettsial adsorption and hemolysis. Infect Immun. 1974 Jan;9(1):119–126. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.1.119-126.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Miller E. T. Phospholipase A activity in the hemolysis of sheep and human erythrocytes by Rickettsia prowazeki. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):316–321. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.316-321.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Miller E. T. Phospholipid composition of Rickettsia prowazeki grown in chicken embryo yolk sacs. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):175–178. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.175-178.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Ramm L. E. Adsorption of typhus rickettsiae to ghosts of sheep erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1244–1251. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1244-1251.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H. Rickettsial hemolysis: adsorption, desorption, readsorption, and hemagglutination. Infect Immun. 1977 Sep;17(3):607–612. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.3.607-612.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisseman C. L., Jr Some biological properties of rickettsiae pathogenic for man. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1968 Apr;206(3):299–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



