Abstract
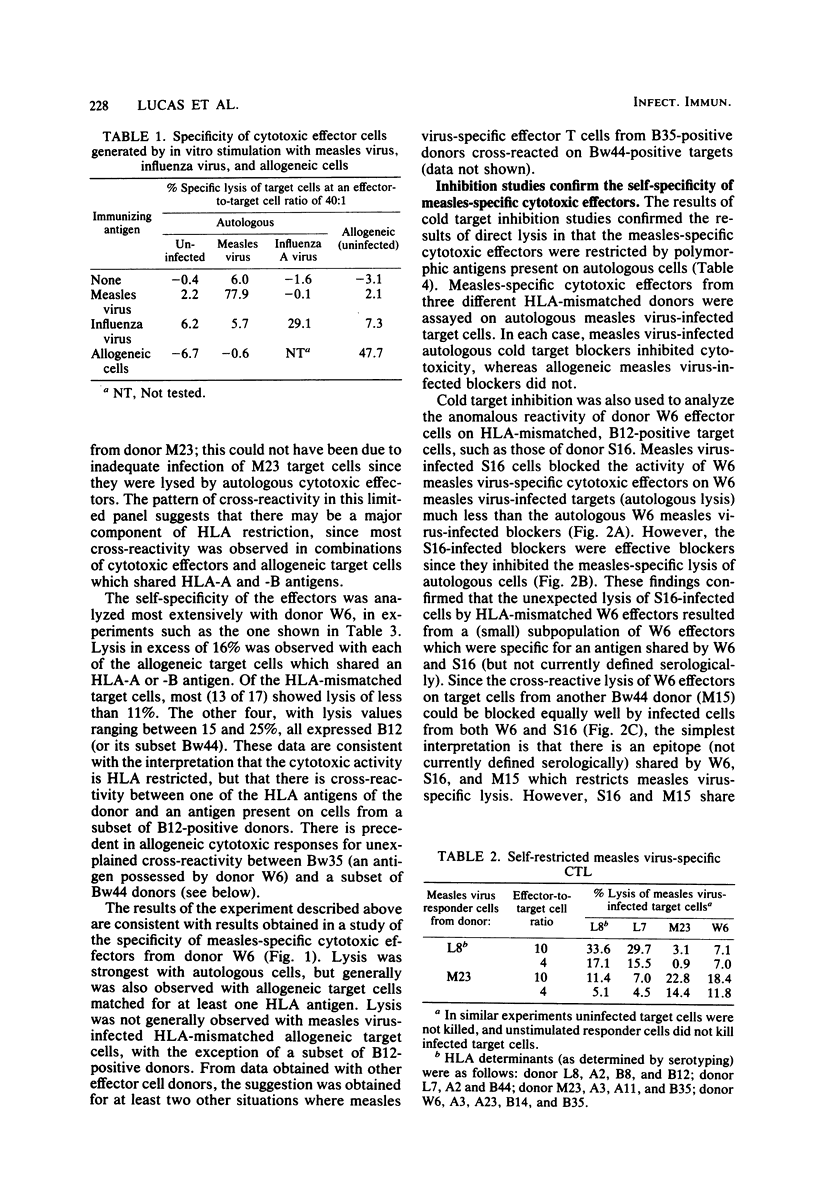
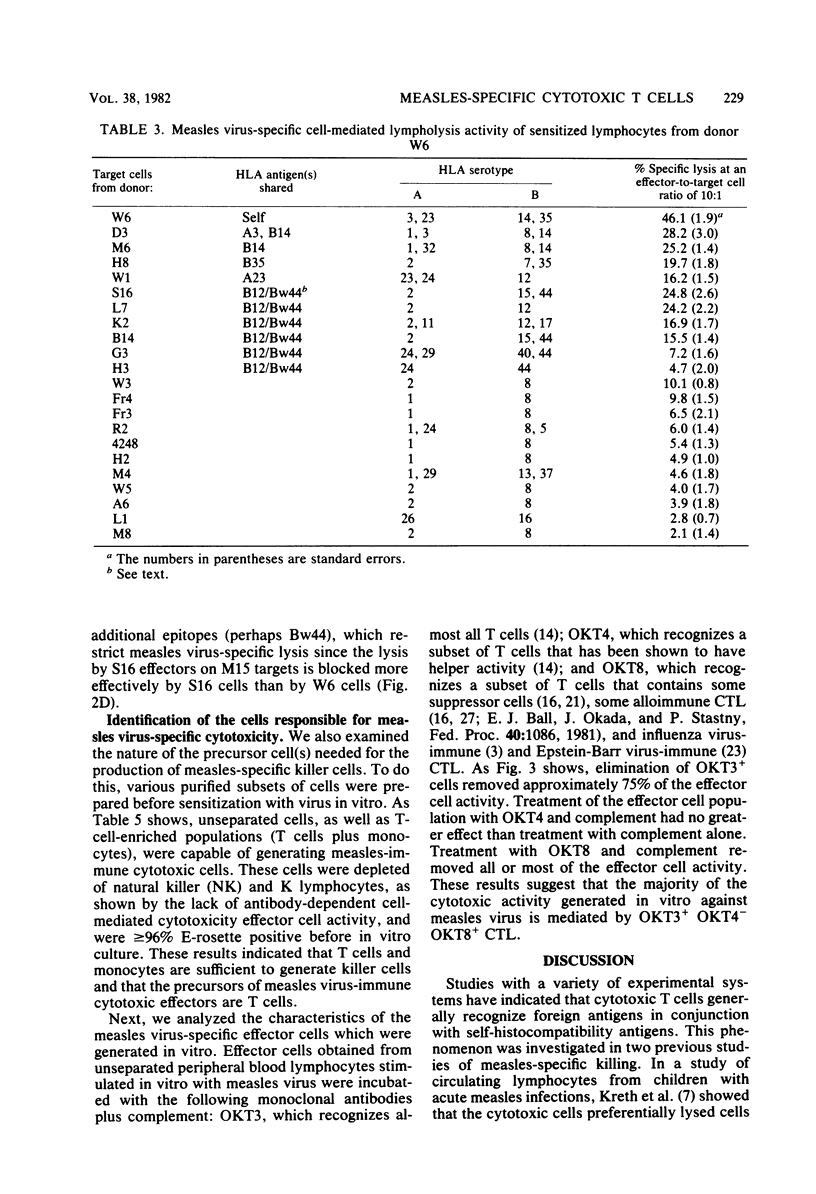
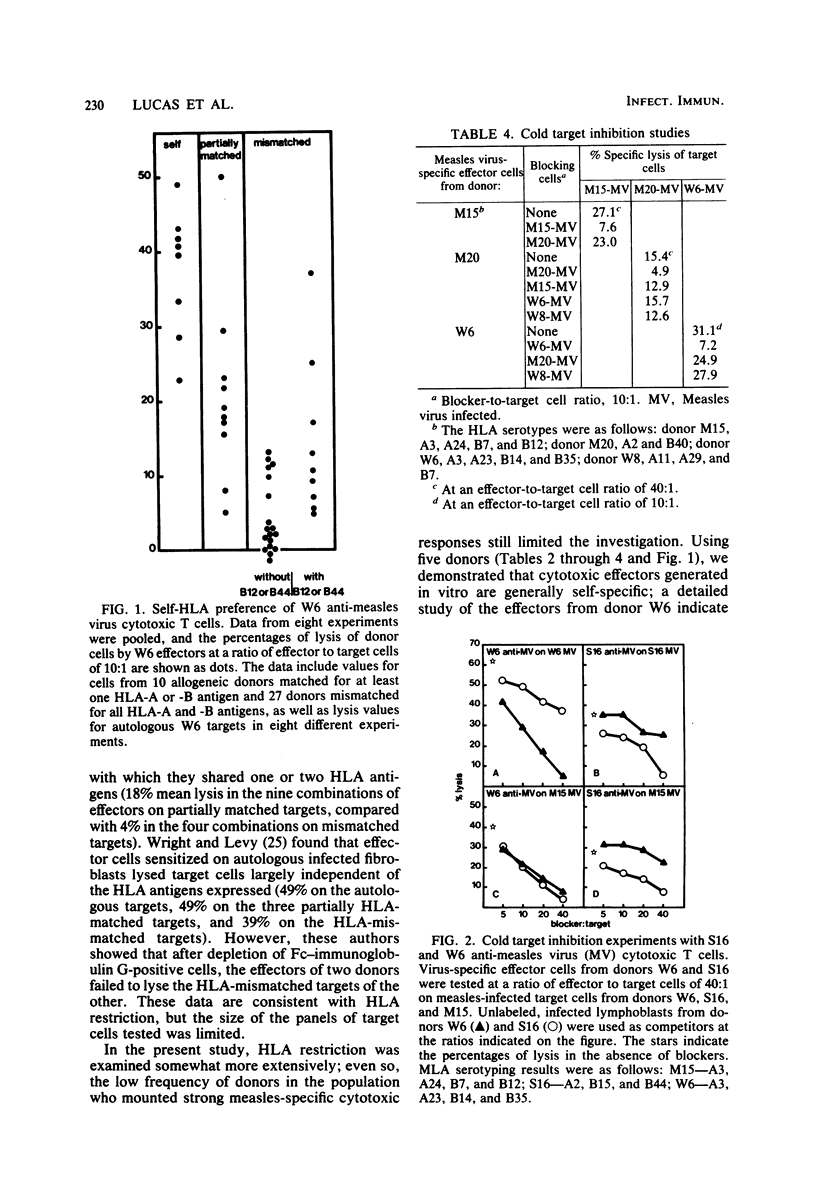
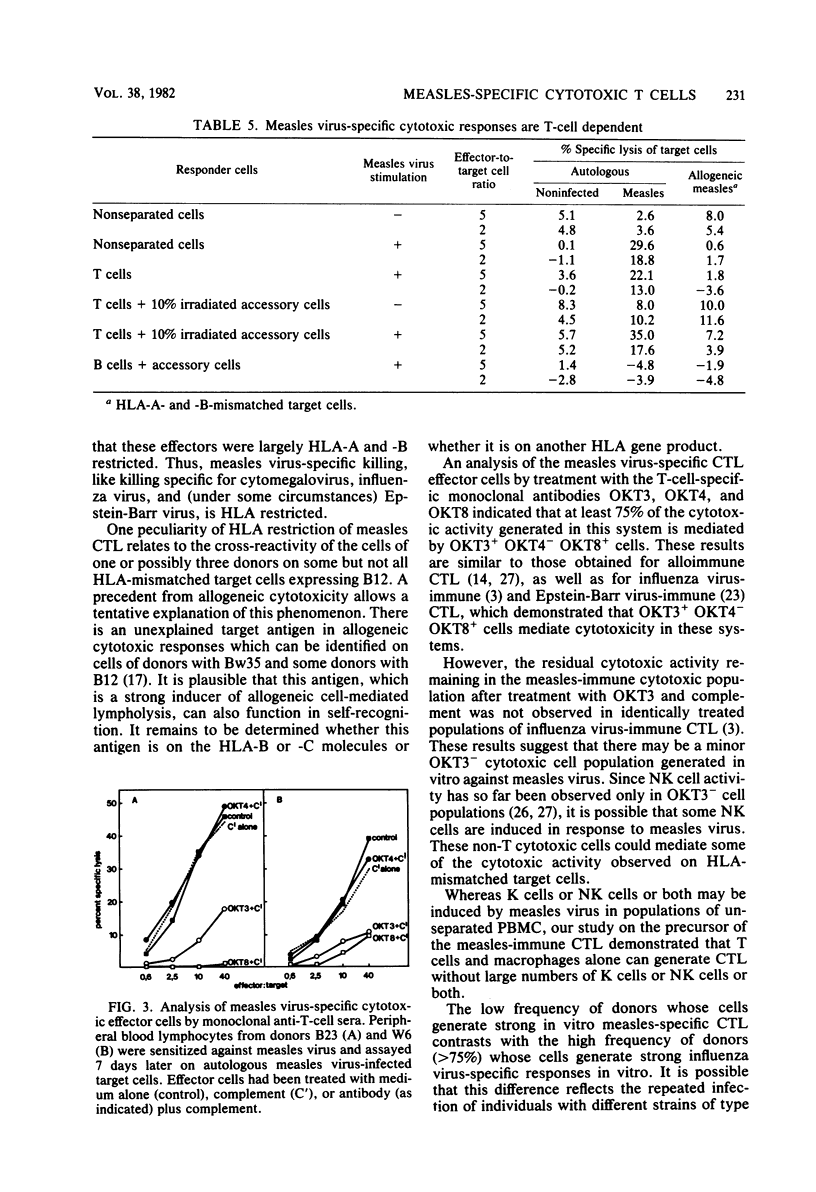
Lymphocytes from normal individuals were tested for the capacity to generate measles virus-specific cytotoxic T-cell responses after in vitro stimulation with measles virus. Approximately 12% (5 of 40) of the normal adults tested produced significant cytotoxic responses. The cytotoxic response was measles virus specific both at the level of stimulation and at the effector level. Studies of the specificity of cytotoxic effectors from five normal donors by direct lysis or cold target inhibition or both indicated that most, if not all, of the virus-specific activity was self-specific. A detailed analysis of one donor (W6) indicated that measles-specific cytotoxicity was largely HLA-A and -B restricted; unexplained cross-reactive lysis was observed with some targets, but this lysis appeared to be HLA related, since all of the targets expressed HLA-B12. An analysis of the cellular requirements for the production of measles-immune cytotoxic T lymphocytes demonstrated that T cells and macrophages (depleted of natural killer and K cells) were sufficient for the generation of killer cells. Most of the cytotoxic effector activity was mediated by OKT3+ OKT4- OKT8+ cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biddison W. E., Payne S. M., Shearer G. M., Shaw S. Human cytotoxic T cell responses to trinitrophenyl hapten and influenza virus. Diversity of restriction antigens and specificity of HLA-linked genetic regulation. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2 Pt 2):204s–217s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biddison W. E., Sharrow S. O., Shearer G. M. T cell subpopulations required for the human cytotoxic T lymphocyte response to influenza virus: evidence for T cell help. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):487–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biddison W. E. The role of the human major histocompatibility complex in cytotoxic T-cell responses to virus-infected cells. J Clin Immunol. 1982 Jan;2(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF00915971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickmeiss E., Soeberg B., Svejgaard A. Human cell-mediated cytotoxicity against modified target cells is restricted by HLA. Nature. 1977 Dec 8;270(5637):526–528. doi: 10.1038/270526a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galama J. M., Lucas C. J., Vos A. Lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity to cells infected with measles virus. I. Use of in vitro infected leukocytes as autologous target cells; absence of virus-specific cytotoxic lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1978 Jul;38(2):365–377. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90067-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulmy E., Termijtelen A., Bradley B. A., van Rood J. J. Y-antigen killing by T cells of women is restricted by HLA. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):544–545. doi: 10.1038/266544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreth H. W., ter Meulen V., Eckert G. Demonstration of HLA restricted killer cells in patients with acute measles. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1979 Jan 24;165(4):203–214. doi: 10.1007/BF02152920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung P., Goldstein G., Reinherz E. L., Schlossman S. F. Monoclonal antibodies defining distinctive human T cell surface antigens. Science. 1979 Oct 19;206(4416):347–349. doi: 10.1126/science.314668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipinski M., Fridman W. H., Tursz T., Vincent C., Pious D., Fellous M. Absence of allogeneic restriction in human T-cell-mediated cytotoxicity to Epstein-Barr virus-infected target cells. Demonstration of an HLA-linked control at the effector level. J Exp Med. 1979 Dec 1;150(6):1310–1322. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.6.1310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael A. J. HLA restriction of human cytotoxic T cells. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1980 May;3(1):3–22. doi: 10.1007/BF00199923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael A. J., Ting A., Zweerink H. J., Askonas B. A. HLA restriction of cell-mediated lysis of influenza virus-infected human cells. Nature. 1977 Dec 8;270(5637):524–526. doi: 10.1038/270524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. L., Bundy B. M., Pitchon H. E., Blaese R. M., Strober W. The effector cells in human peripheral blood mediating mitogen-induced cellular cytotoxicity and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 Pt 1):1472–1481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinnan G. V., Jr, Kirmani N., Esber E., Saral R., Manischewitz J. F., Rogers J. L., Rook A. H., Santos G. W., Burns W. H. HLA-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocyte and nonthymic cytotoxic lymphocyte responses to cytomegalovirus infection of bone marrow transplant recipients. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):2036–2041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. A monoclonal antibody reactive with the human cytotoxic/suppressor T cell subset previously defined by a heteroantiserum termed TH2. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1301–1307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. Further characterization of the human inducer T cell subset defined by monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2894–2896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. Separation of functional subsets of human T cells by a monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):4061–4065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.4061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schendel D. J., Wank R., Hansen J. A., Dupont B. Cell-mediated lympholysis in man: identification of a common target determinant associated with HLA-B12 and Bw35. Transplant Proc. 1977 Dec;9(4):1777–1780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethi K. K., Stroehmann I., Brandis H. Human T-cell cultures from virus-sensitized donors can mediate virus-specific and HLA-restricted cell lysis. Nature. 1980 Aug 14;286(5774):718–720. doi: 10.1038/286718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw S., Nelson D. L., Shearer G. M. Human cytotoxic response in vitro to trinitrophenyl-modified autologous cells. I. T cell recognition of TNP in association with widely shared antigens. J Immunol. 1978 Jul;121(1):281–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw S., Shearer G. M. Human cytotoxic response in vitro to trinitrophenyl-modified autologous cells. II. Diversity of self determinants recognized in association with TNP. J Immunol. 1978 Jul;121(1):290–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas Y., Rogozinski L., Irigoyen O. H., Friedman S. M., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Chess L. Functional analysis of human T cell subsets defined by monoclonal antibodies. IV. Induction of suppressor cells within the OKT4+ population. J Exp Med. 1981 Aug 1;154(2):459–467. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas Y., Sosman J., Irigoyen O., Friedman S. M., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Chess L. Functional analysis of human T cell subsets defined by monoclonal antibodies. I. Collaborative T-T interactions in the immunoregulation of B cell differentiation. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2402–2408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsoukas C. D., Fox R. I., Slovin S. F., Carson D. A., Pellegrino M., Fong S., Pasquali J. L., Ferrone S., Kung P., Vaughan J. H. T lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity against autologous EBV-genome-bearing B cells. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1742–1746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tursz T., Fridman W. H., Senik A., Tsapis A., Fellous M. Human virus-infected target cells lacking HLA antigens resist specific T-lymphocyte cytolysis. Nature. 1977 Oct 27;269(5631):806–808. doi: 10.1038/269806a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright L. L., Levy N. L. Generation on infected fibroblasts of human T and non-T lymphocytes with specific cytotoxicity, influenced by histocompatibility, against measles virus-infected cells. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2379–2387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarling J. M., Clouse K. A., Biddison W. E., Kung P. C. Phenotypes of human natural killer cell populations detected with monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2575–2580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarling J. M., Kung P. C. Monoclonal antibodies which distinguish between human NK cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):394–396. doi: 10.1038/288394a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. MHC-restricted cytotoxic T cells: studies on the biological role of polymorphic major transplantation antigens determining T-cell restriction-specificity, function, and responsiveness. Adv Immunol. 1979;27:51–177. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



