Abstract
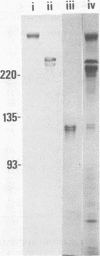
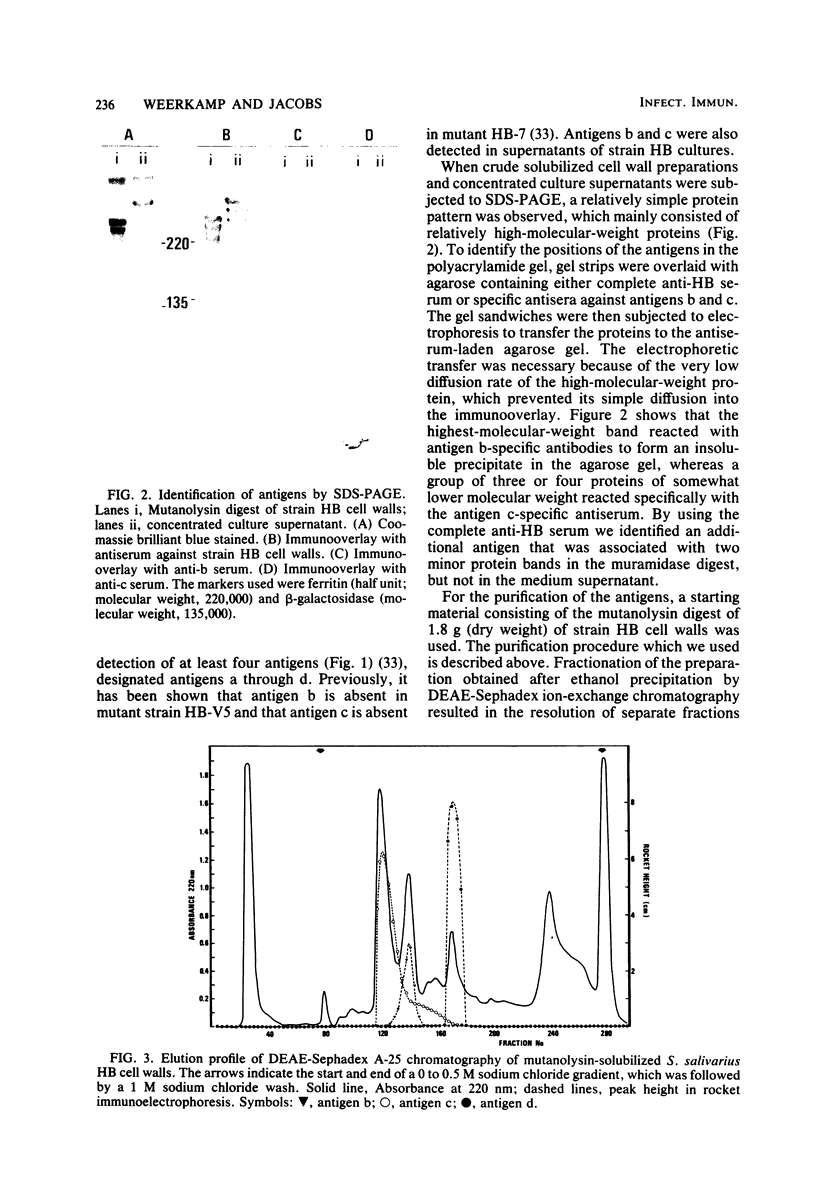
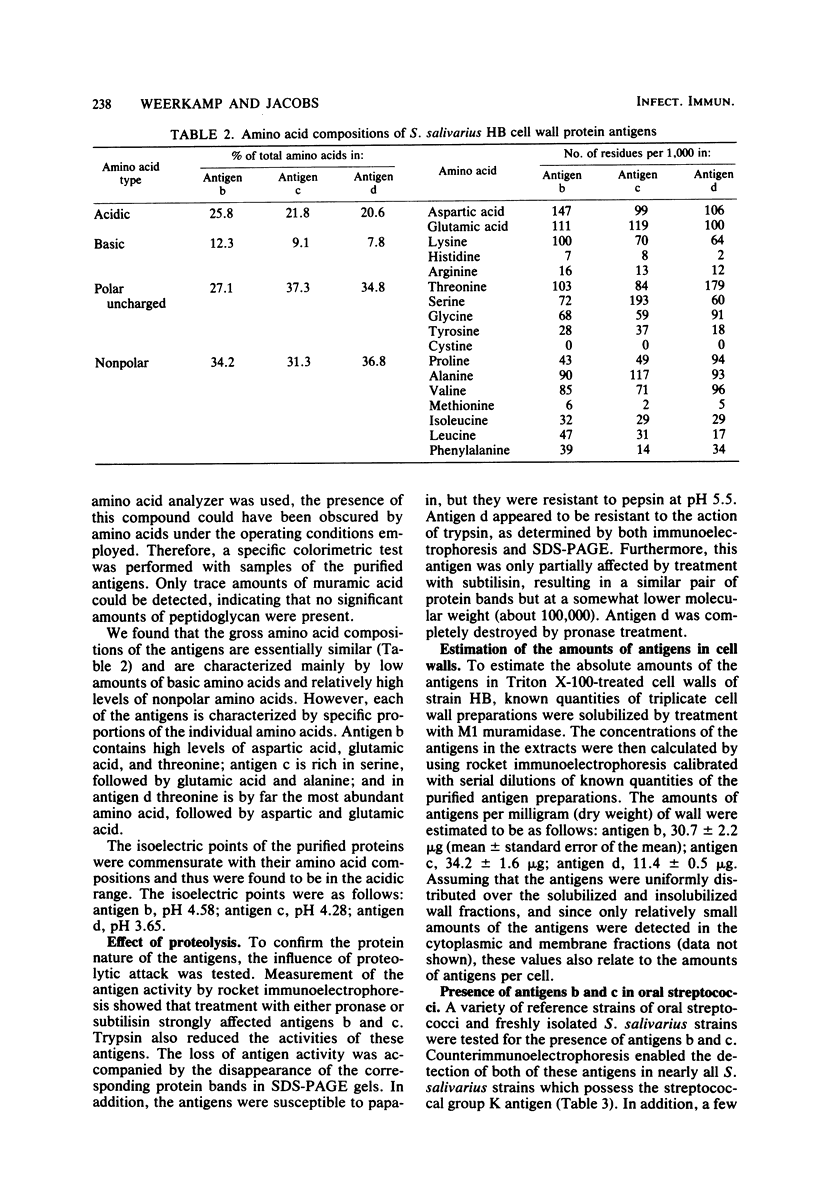
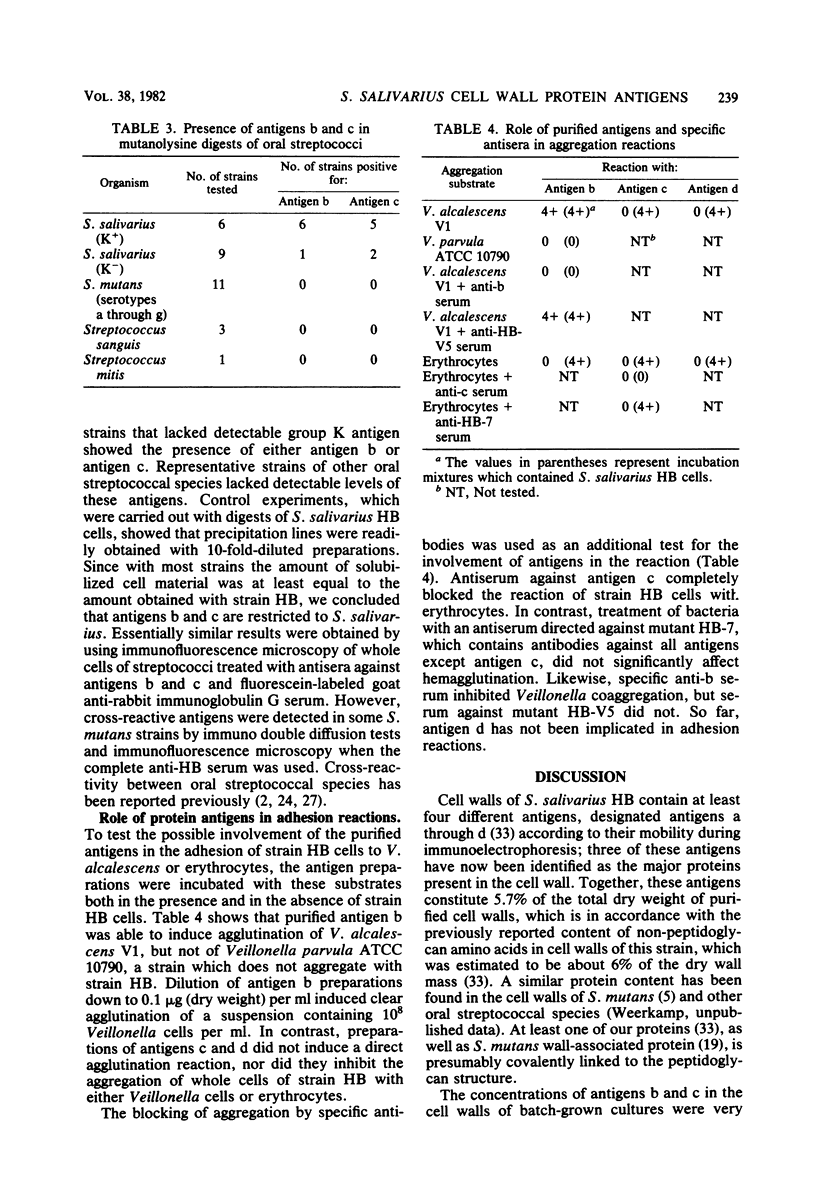
Three cell wall-associated protein antigens (antigens b, c, and d) were isolated from mutanolysin-solubilized cell walls of Streptococcus salivarius HB and purified to apparent homogeneity by a combination of ion-exchange chromatography, gel filtration, and immunoadsorption chromatography. Antigens b and c were also isolated from culture supernatants. Antigen b consisted of more than 80% protein and had an apparent molecular weight as determined by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of 320,000. Antigen c consisted of 57% protein, about 30% neutral sugar, and about 13% amino sugar, and its glycoprotein nature was confirmed by specific staining techniques. During sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis antigen c resolved into two or more bands, depending on the source or the isolation procedure, in the molecular weight range from 220,000 to 280,000. Antigen d consisted of 95% protein and was observed in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis as two bands with molecular weights of 129,000 and 121,000. Under nondenaturing conditions all three antigens had molecular weights in the range from 1 × 106 to 3 × 106 as determined by gel filtration. The amino acid compositions of antigens b, c, and d were characterized by low amounts of basic amino acids and relatively high levels of nonpolar amino acids. Among oral streptococcal species antigens b and c were virtually restricted to strains of S. salivarius and most often to serotype I strains. Antigen b was recognized as the factor that mediates coaggregation of S. salivarius with Veillonella strains. The purified protein retained its biological activity. Antigen c could be linked to functions relating to adhesion of the streptococci to host tissues on the basis of its absence in mutant strains and blocking by specific antisera. The purified molecule had no detectable biological activity. Antigen d could not be linked to an established adhesion function.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bounias M. N-(1-naphthyl)ethylenediamine dihydrochloride as a new reagent for nanomole quantification of sugars on thin-layer plates by a mathematical calibration process. Anal Biochem. 1980 Aug;106(2):291–295. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90523-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratthall D., Pettersson B. M. Common and unique antigens of Streptococcus mutants. J Dent Res. 1976 Jan;55:A60–A64. doi: 10.1177/002203457605500123011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cisar J. O., Barsumian E. L., Curl S. H., Vatter A. E., Sandberg A. L., Siraganian R. P. Detection and localization of a lectin on Actinomyces viscosus T14V by monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1318–1322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper H. R., Chorpenning F. W., Rosen S. Preparation and chemical composition of the cell walls of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):823–828. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.823-828.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ederer G. M., Herrmann M. M., Bruce R., Matsen J. M., Chapman S. S. Rapid extraction method with pronase B for grouping beta-hemolytic streptococci. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Feb;23(2):285–288. doi: 10.1128/am.23.2.285-288.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Houte J. V. Bacterial adherence in oral microbial ecology. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:19–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAY G. W., LEWIS B. A., SMITH F. THIN-FILM CHROMATOGRAPHY IN THE STUDY OF CARBOHYDRATES. J Chromatogr. 1963 Aug;11:479–486. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)80949-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadzija O. A simple method for the quantitative determination of muramic acid. Anal Biochem. 1974 Aug;60(2):512–517. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy L., Jacques N. A., Forester H., Campbell L. K., Knox K. W., Wicken A. J. Effect of fructose and other carbohydrates on the surface properties, lipoteichoic acid production, and extracellular proteins of Streptococcus mutans Ingbritt grown in continuous culture. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):78–87. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.78-87.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jermyn M. A. Increasing the sensitivity of the anthrone method for carbohydrate. Anal Biochem. 1975 Sep;68(1):332–335. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90713-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumazawa N., Yanagawa R. Chemical properties of the pili of Corynebacterium renale. Infect Immun. 1972 Jan;5(1):27–30. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.1.27-30.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T., Russell M. W., Caldwell J., Smith R. Immunization with purified protein antigens from Streptococcus mutans against dental caries in rhesus monkeys. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):407–415. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.407-415.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markham J. L., Knox K. W., Wicken A. J., Hewett M. J. Formation of extracellular lipoteichoic acid by oral streptococci and lactobacilli. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):378–386. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.378-386.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda N., Ellen R. P., Grove D. A. Purification and characterization of surface fibrils from taxonomically typical Actinomyces viscosus WVU627. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):1095–1104. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.1095-1104.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt W. E., Staat R. H., Rosan B., Taylor K. G., Doyle R. J. Association of protein with the cell wall of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):118–126. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.118-126.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETHICA B. A. The physical chemistry of cell adhesion. Exp Cell Res. 1961;Suppl 8:123–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(61)90344-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. W., Bergmeier L. A., Zanders E. D., Lehner T. Protein antigens of Streptococcus mutans: purification and properties of a double antigen and its protease-resistant component. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):486–493. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.486-493.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. W. Purification and properties of a protein surface antigen of Streptococcus mutants. Microbios. 1979;25(99):7–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. W., Zanders E. D., Bergmeier L. A., Lehner T. Affinity purification and characterization of protease-susceptible antigen I of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):999–1006. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.999-1006.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R. Wall-associated protein antigens of Streptococcus mutans. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Sep;114(1):109–115. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-1-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöller M., Klein J. P., Frank R. M. Common antigens of streptococcal and non-streptococcal oral bacteria: immunochemical studies of extracellular and cell-wall-associated antigens from Streptococcus sanguis, Streptococcus mutans, Lactobacillus salivarius, and Actinomyces viscosus. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):52–60. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.52-60.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J. L., Hurst S. F., Liberman E. S., Coleman S. E., Bleiweis A. S. Mutanolysin-induced spheroplasts of Streptococcus mutants are true protoplasts. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):808–815. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.808-815.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J., Gibbons R. J. Attachment of Bacteroides melaninogenicus subsp. asaccharolyticus to oral surfaces and its possible role in colonization of the mouth and of periodontal pockets. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):254–264. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.254-264.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A. H., McBride B. C. Adherence of Streptococcus salivarius HB and HB-7 to oral surfaces and saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):150–158. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.150-158.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A. H., McBride B. C. Characterization of the adherence properties of Streptococcus salivarius. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):459–468. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.459-468.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A. H., McBride B. C. Identification of a Streptococcus salivarius cell wall component mediating coaggregation with Veillonella alcalescens V1. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):723–730. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.723-730.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler T. T., Clark W. B. Fibril-mediated adherence of Actinomyces viscosus to saliva-treated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):577–584. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.577-584.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokogawa K., Kawata S., Nishimura S., Ikeda Y., Yoshimura Y. Mutanolysin, bacteriolytic agent for cariogenic Streptococci: partial purification and properties. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Aug;6(2):156–165. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.2.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanders E. D., Lehner T. Separation and characterization of a protein antigen from cells of Streptococcus mutans. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Feb;122(2):217–225. doi: 10.1099/00221287-122-2-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]