Abstract
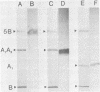
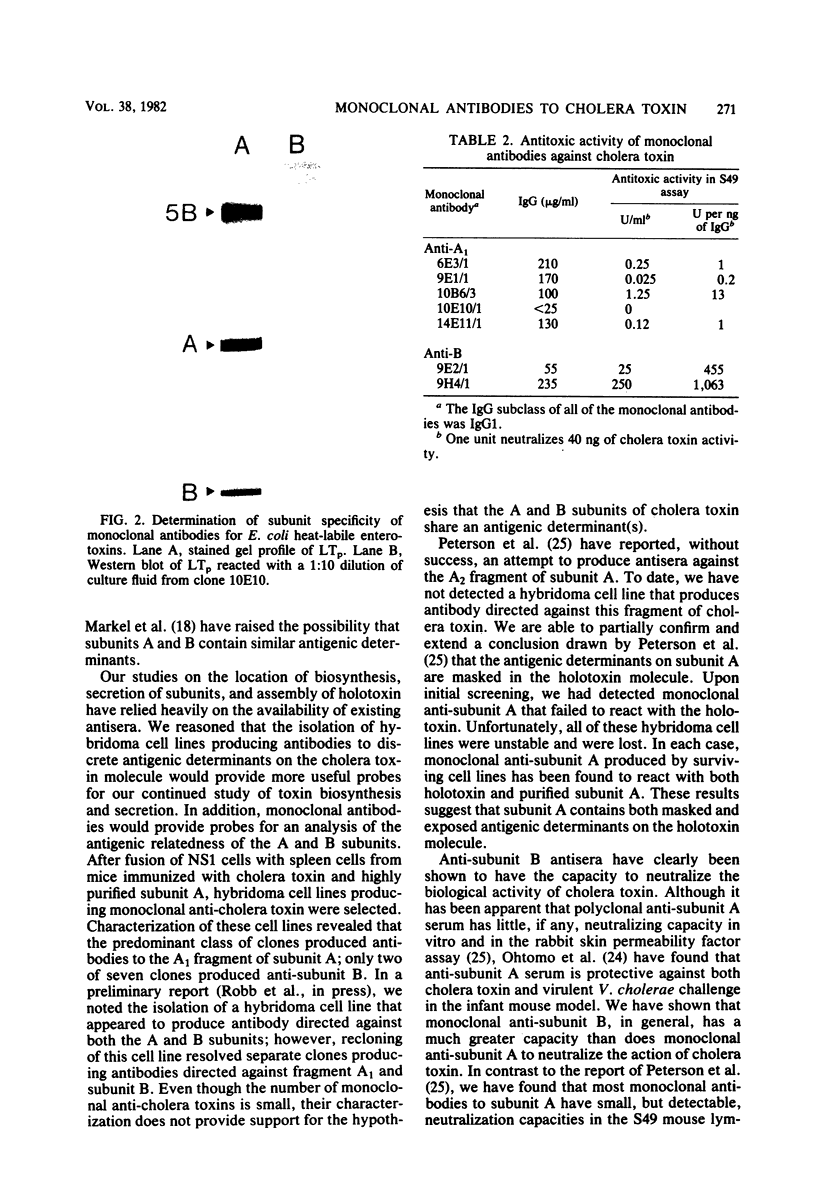
Hybridoma cell lines which produced monoclonal antibodies against cholera toxin were isolated. These cell lines were detected with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay screening procedure with purified cholera toxin or subunit A of cholera toxin. Seven cell lines were characterized with respect to their reactivity with cholera toxin subunits by Western blot analysis. Five clones produced antibodies which were directed against subunit A, and two clones produced antibodies which reacted with subunit B. These antibodies were also characterized by Western blot analysis for reactivity with the heat-labile enterotoxin produced by porcine and human enterotoxinogenic strains of Escherichia coli. Monoclonal antibodies which reacted with subunit A of cholera toxin also reacted with subunit A of both porcine and human heat-labile enterotoxins. In contrast, monoclonal antibodies to subunit B of cholera toxin did not react with subunit B of the heat-labile enterotoxin. Antibodies directed against subunit B neutralized the biological activity of cholera toxin in vitro in the S49 mouse lymphosarcoma assay. In contrast to polyclonal anti-subunit A antisera, monoclonal anti-subunit A from four of five clones had small but measurable neutralizing capacities in vitro.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassel D., Pfeuffer T. Mechanism of cholera toxin action: covalent modification of the guanyl nucleotide-binding protein of the adenylate cyclase system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2669–2673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Demonstration of shared and unique immunological determinants in enterotoxins from Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):709–713. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.709-713.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Immunological cross-reactivity between a heat-labile enterotoxin(s) of Escherichia coli and subunits of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):1036–1039. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.1036-1039.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Isolation and characterization of homogeneous heat-labile enterotoxins with high specific activity from Escherichia coli cultures. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):760–769. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.760-769.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas W. S., Falkow S. Amino acid sequence homology between cholera toxin and Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin. Nature. 1980 Dec 4;288(5790):499–501. doi: 10.1038/288499a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHEY J. L., MCKELVEY E. M. QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF SERUM IMMUNOGLOBULINS IN ANTIBODY-AGAR PLATES. J Immunol. 1965 Jan;94:84–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M: Intestinal secretion: effect of cyclic AMP and its role in cholera. N Engl J Med. 1971 May 20;284(20):1137–1144. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197105202842008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Boesman M., Neoh S. H., LaRue M. K., Delaney R. Dissociation and recombination of the subunits of the cholera enterotoxin (choleragen). J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):145–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., LoSpalluto J. J. Pathogenesis of experimental cholera. Preparation and isolation of choleragen and choleragenoid. J Exp Med. 1969 Jul 1;130(1):185–202. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M. Mechanism of action of cholera toxin. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1977;8:85–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Meren R. ADP-ribosylation of membrane proteins catalyzed by cholera toxin: basis of the activation of adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3050–3054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Richardson S. H. Adenosine diphosphate-ribosylation of adenylate cyclase catalyzed by heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: comparison with cholera toxin. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jan;141(1):64–70. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hejtmancik K. E., Peterson J. W., Markel D. E., Kurosky A. Radioimmunoassay for the antigenic determinants of cholera toxin and its components. Infect Immun. 1977 Sep;17(3):621–628. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.3.621-628.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Lönnroth I., Svennerholm L. Tissue receptor for cholera exotoxin: postulated structure from studies with GM1 ganglioside and related glycolipids. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):208–214. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.208-214.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markel D. E., Hejtmancik K. E., Peterson J. W., Martin F. B., Kurosky A. Characterization of the antigenic determinants of cholera toxin subunits. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):615–626. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.615-626.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Collier R. J., Romig W. R. Purification of cholera toxin and its subunits: new methods of preparation and the use of hypertoxinogenic mutants. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):552–558. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.552-558.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Collier R. J., Romig W. R. Simple method for purifying choleragenoid, the natural toxoid of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):789–795. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.789-795.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Vaughan M. Mechanism of action of choleragen. Evidence for ADP-ribosyltransferase activity with arginine as an acceptor. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 10;252(7):2455–2457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols J. C., Tai P. C., Murphy J. R. Cholera toxin is synthesized in precursor form on free polysomes in Vibrio cholerae 569B. J Bacteriol. 1980 Nov;144(2):518–523. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.2.518-523.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowinski R. C., Lostrom M. E., Tam M. R., Stone M. R., Burnette W. N. The isolation of hybrid cell lines producing monoclonal antibodies against the p15(E) protein of ecotropic murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1979 Feb;93(1):111–126. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90280-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. W., Hejtmancik K. E., Markel D. E., Craig J. P., Kurosky A. Antigenic specificity of neutralizing antibody to cholera toxin. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):774–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.774-779.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruch F. E., Jr, Murphy J. R., Graf L. H., Field M. Isolation of nontoxinogenic mutants of Vibrio cholerae in a colorimetric assay for cholera toxin using the S49 mouse lymphosarcoma cell line. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jun;137(6):747–755. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.6.747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Heyningen S. The subunits of cholera toxin: structure, stoichiometry, and function. J Infect Dis. 1976 Mar;133 (Suppl):5–13. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.supplement_1.s5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]