Abstract
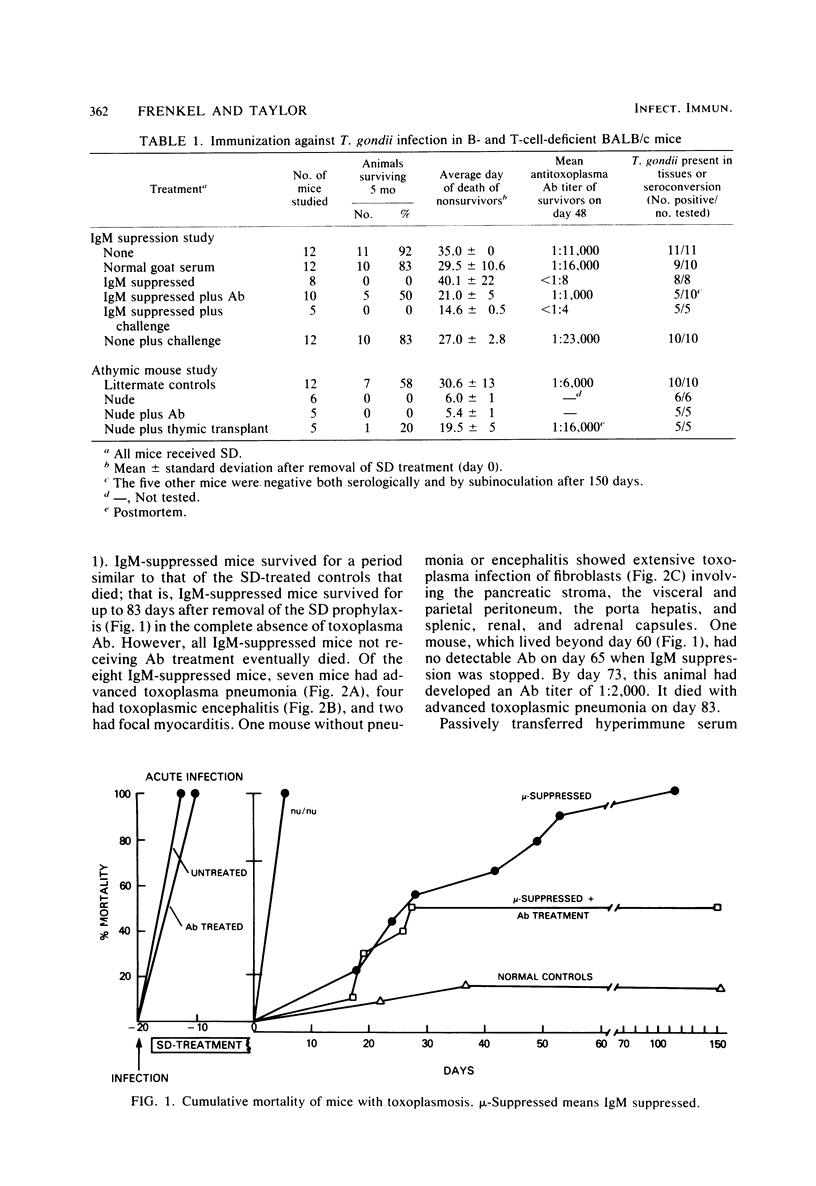
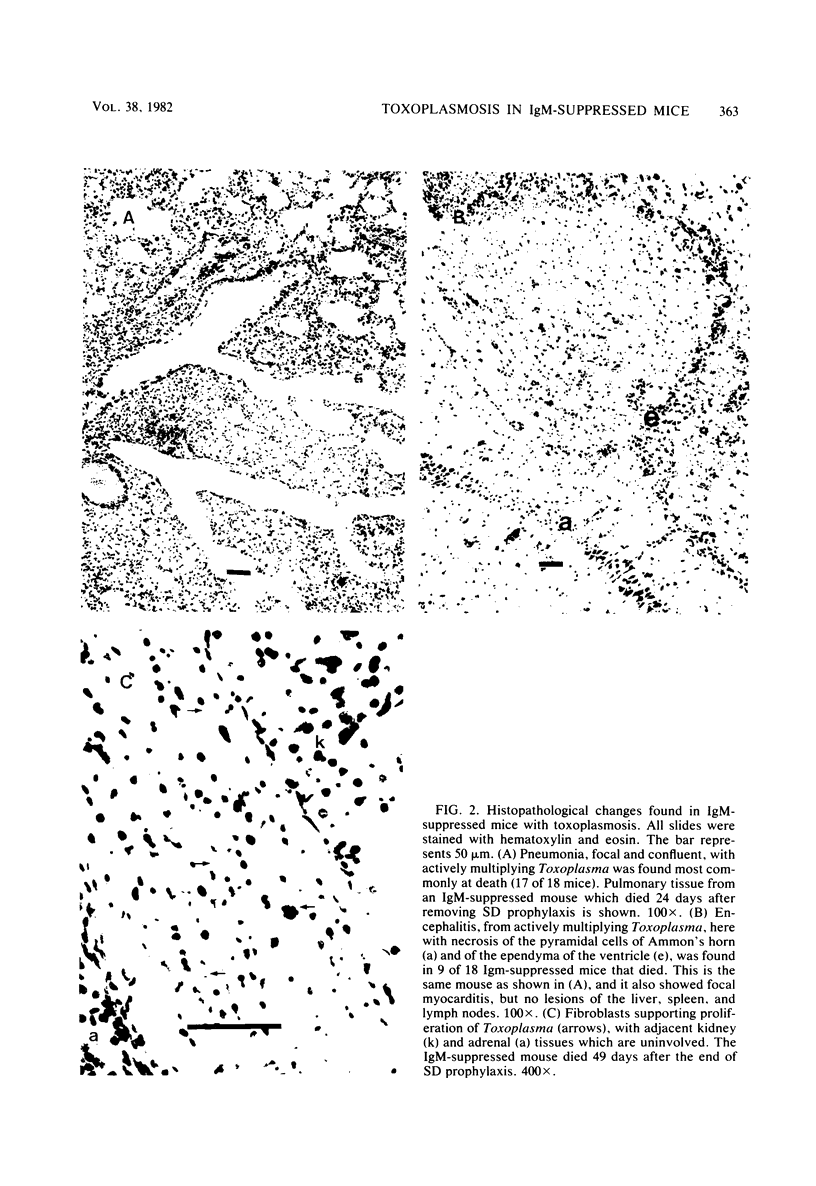
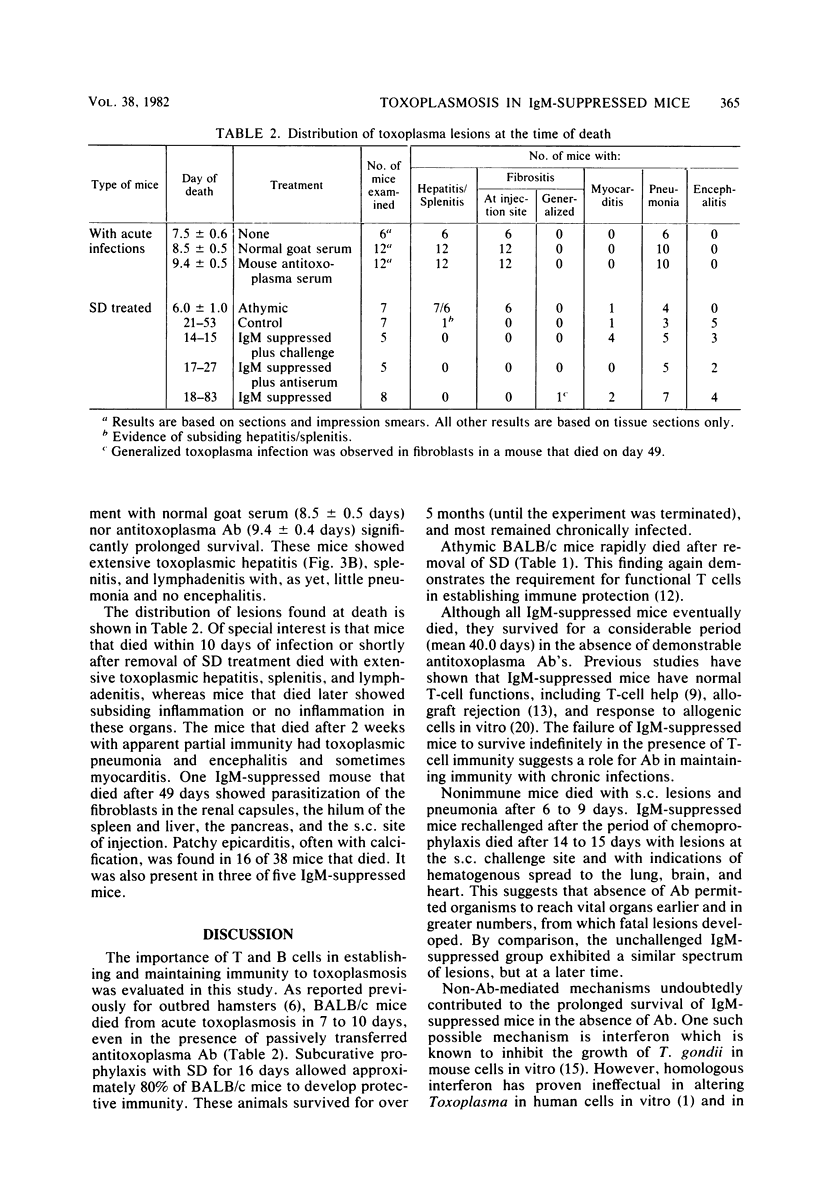
Mice challenged with a pathogenic strain of Toxoplasma gondii develop fatal infections. However, if such mice are initially treated with sulfadiazine (SD), they develop immunity and survive with chronic infections. The role of antibody (Ab) in establishing protective immunity against acute parasitemias and in maintaining chronic infections was investigated using B-cell-deficient (immunoglobulin M-suppressed), T-cell-deficient (athymic), and normal BALB/c mice. All mice not receiving SD treatment rapidly died (mean 7.5 days) after infection, but the majority (80%) of intact mice developed immunity during SD treatment and survived for over 5 months with chronic toxoplasmosis. Athymic mice rapidly died (mean 6.0 days) after the removal of SD treatment. Although all SD-treated immunoglobulin M-suppressed mice eventually died, they lived considerably longer (18 to 83 days) in the complete absence of antitoxoplasma Ab than unprotected mice (7 to 9 days). Histopathological sections of liver, lung, brain, and other tissues showed that toxoplasma organisms gave rise to fatal lesions in all nonsurviving animals. The injection of Ab into acutely infected and athymic mice imparted no protection, but transfer of antitoxoplasma Ab (titer greater than 1:8,000) to immunoglobulin M-suppressed mice after SD treatment resulted in elimination of the parasites in 50% of the mice. Results of this study suggest that Ab may not be decisive in acute infections, but may be important in controlling long-term toxoplasmosis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahronheim G. A. Toxoplasma gondii: human interferon studies by plaque assay. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Sep;161(4):522–526. doi: 10.3181/00379727-161-40588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen D. H., Tigelaar R. E., Weinbaum F. I. Immunity to sporozoite-induced malaria infeciton in mice. I. The effect of immunization of T and B cell-deficient mice. J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1322–1327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinchilla M., Frenkel J. K. Mediation of immunity to intracellular infection (Toxoplasma and Besnoitia) within somatic cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):999–1012. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.999-1012.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eby W. C., Kim B. S., Dray S., Young-Cooper G. O., Mage R. G. Detection of the e14 and e15 rabbit allotypic specificities by immunodiffusion in PEG agar. Immunochemistry. 1973 Jun;10(6):417–418. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(73)90149-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K. Adoptive immunity to intracellular infection. J Immunol. 1967 Jun;98(6):1309–1319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K., Caldwell S. A. Specific immunity and nonspecific resistance to infection: listeria, protozoa, and viruses in mice and hamsters,. J Infect Dis. 1975 Mar;131(3):201–209. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.3.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K., Nelson B. M., Arias-Stella J. Immunosuppression and toxoplasmic encephalitis: clinical and experimental aspects. Hum Pathol. 1975 Jan;6(1):97–111. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(75)80111-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., Murgita R. A., Tomasi T. B., Jr The immune response of mice treated with anti-mu antibodies: the effect on antibody-forming cells, their precursors and helper cells assayed in vitro. J Immunol. 1975 Jun;114(6):1808–1812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. D., Monjan A. A., Morse H. C., 3rd Lack of B-cell participation in acute lymphocyte choriomeningitis disease of the central nervous system. Cell Immunol. 1978 Mar 1;36(1):143–150. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90257-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawton A. R., 3rd, Asofsky R., Hylton M. B., Cooper M. D. Suppression of immunoglobulin class synthesis in mice. I. Effects of treatment with antibody to -chain. J Exp Med. 1972 Feb 1;135(2):277–297. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg R. E., Frenkel J. K. Toxoplasmosis in nude mice. J Parasitol. 1977 Apr;63(2):219–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning D. D., Jutila J. W. Effect of anti-immunoglobulin antisera on homograft rejection in mice. Nat New Biol. 1972 May 10;237(71):58–59. doi: 10.1038/newbio237058a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto Y., Nagasawa H., Sakurai H., Sasaki S., Suzuki N. Mouse spleen cell-derived toxoplasma growth inhibitory factor: its effect on toxoplasma multiplication in the mouse kidney cells. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1981 Sep;250(3):383–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Merigan T. C. Interferon: protection of cells infected with an intracellular protozoan (Toxoplasma gondii). Science. 1968 Aug 23;161(3843):804–806. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3843.804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez A. M., Santoro F., Afchain D., Bazin H., Capron A. Trypanosoma cruzi infection in B-cell-deficient rats. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):524–529. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.524-529.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg Y. J., Evans C. B. Resistance of mice suppressed for IgM production to Babesia microti infection. Nature. 1979 Sep 27;281(5729):302–304. doi: 10.1038/281302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabin A. B., Feldman H. A. Dyes as Microchemical Indicators of a New Immunity Phenomenon Affecting a Protozoon Parasite (Toxoplasma). Science. 1948 Dec 10;108(2815):660–663. doi: 10.1126/science.108.2815.660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirahata T., Shimizu K., Noda S., Suzuki N. Studies on production of biologically active substance which inhibits the intracellular multiplication of Toxoplasma within mouse macrophages. Z Parasitenkd. 1977 Aug 25;53(1):31–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00383112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinbaum F. I., Evans C. B., Tigelaar R. E. Immunity to Plasmodium Berghei yoelii in mice. I. The course of infection in T cell and B cell deficient mice. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 PT2):1999–2005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]