Abstract
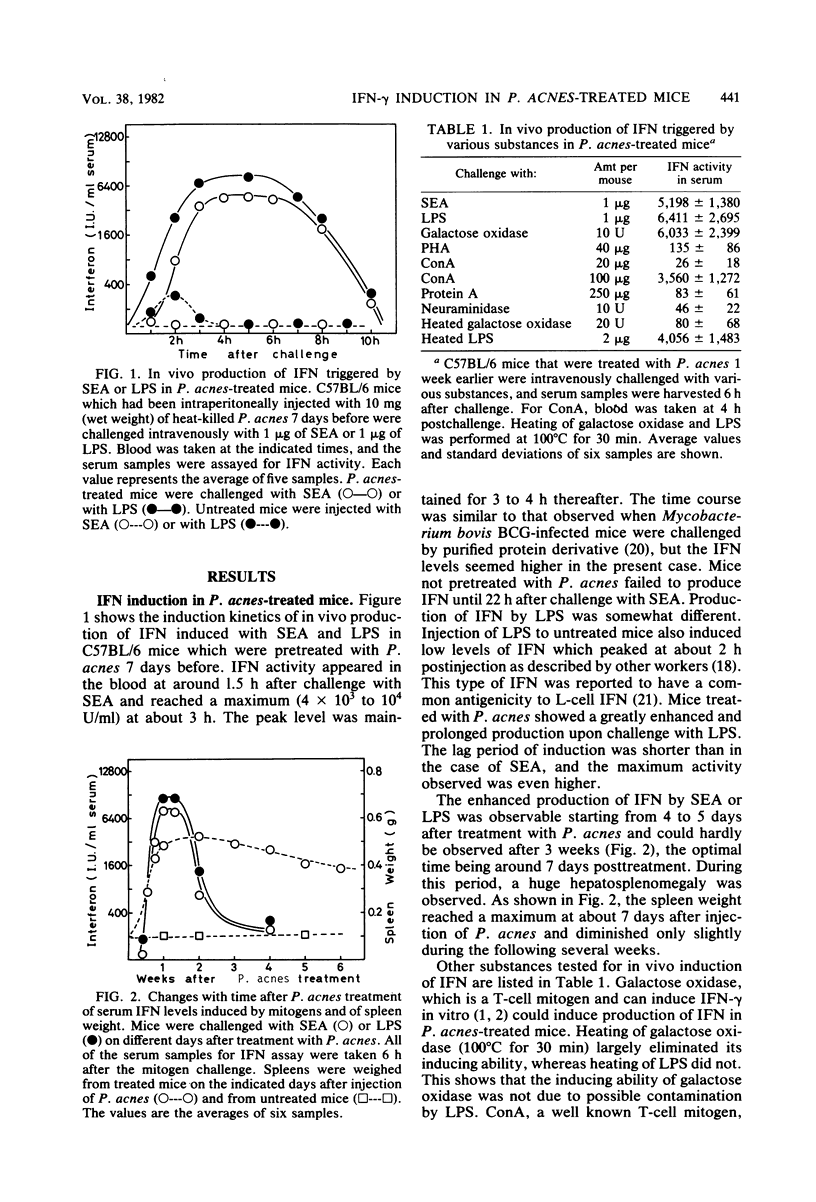
Various T-cell mitogens induced high levels of circulating gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) in mice that had been pretreated with Propionibacterium acnes. Administration of lipopolysaccharide, a B-cell mitogen, to these mice also caused pronounced production of IFN-gamma in addition to IFN-alpha and IFN-beta. The enhanced induction was most marked at about 1 week after the pretreatment.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biniaminov M., Ramot B., Rosenthal E., Novogrodsky A. Galactose oxidase-induced blastogenesis of human lymphocytes and the effect of macrophages on the reaction. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Jan;19(1):93–98. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dianzani F., Monahan T. M., Scupham A., Zucca M. Enzymatic induction of interferon production by galactose oxidase treatment of human lymphoid cells. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):879–882. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.879-882.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans S. R., Johnson H. M. The induction of at least two distinct types of interferon in mouse spleen cell cultures by Corynebacterium parvum. Cell Immunol. 1981 Oct;64(1):64–72. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90458-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmann W. R., Jr, Georgiades J. A., Osborne L. C., Johnson H. M. Potentiation of interferon activity by mixed preparations of fibroblast and immune interferon. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):248–253. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.248-253.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Dobrjansky A., Chiasson M. A., Carswell E., Schwartz M. K., Old L. J. Corynebacterium parvum as the priming agent in the production of tumor necrosis factor in the mouse. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 Nov;59(5):1519–1522. doi: 10.1093/jnci/59.5.1519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt H. M., Becker H., Kirchner H. Induction of interferon production in mouse spleen cell cultures by corynebacterium parvum. Cell Immunol. 1978 Jun;38(1):168–175. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90042-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawade Y. An analysis of neutralization reaction of interferon by antibody: a proposal on the expression of neutralization titer. J Interferon Res. 1980 Fall;1(1):61–70. doi: 10.1089/jir.1980.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawade Y., Watanabe Y., Yamamoto Y., Fujisawa J., Dalton B. J., Paucker K. Antigenic cross-reaction between the alpha types of human and mouse interferon. Antiviral Res. 1981 Sep;1(3):167–178. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(81)90005-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neta R. Mechanisms in the in vivo release of lymphokines. II. Regulation of in vivo release of type II interferon IFN gamma. Cell Immunol. 1981 May 1;60(1):100–108. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90251-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne L. C., Georgiades J. A., Johnson H. M. Classification of interferons with antibody to immune interferon. Cell Immunol. 1980 Jul 15;53(1):65–70. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90426-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribi E. E., Granger D. L., Milner K. C., Strain S. M. Tumor regression caused by endotoxins and mycobacterial fractions. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Nov;55(5):1253–1257. doi: 10.1093/jnci/55.5.1253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STINEBRING W. R., YOUNGNER J. S. PATTERNS OF INTERFERON APPEARANCE IN MICE INFECTED WITH BACTERIA OR BACTERIAL ENDOTOXIN. Nature. 1964 Nov 14;204:712–712. doi: 10.1038/204712a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvin S. B., Youngner J. S., Lederer W. H. Migration inhibitory factor and interferon in the circulation of mice with delayed hypersensitivity. Infect Immun. 1973 Jan;7(1):68–75. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.1.68-75.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinagawa K., Kunita N., Sakaguchi G. [Purfication of staphylococcal enterotoxins A and C and preparation of anti-enterotoxin sera]. Nihon Saikingaku Zasshi. 1975 Nov;30(6):683–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanos S., Catinot L., Wietzerbin J., Falcoff E. Production of antibodies against mouse immune T (type II) interferon and their neutralizing properties. J Gen Virol. 1980 Sep;50(1):225–229. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-1-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama M., Epstein L. B. Effect of Corynebacterium parvum on human T-lymphocyte interferon production and T-lymphocyte proliferation in vitro. Cancer Res. 1978 Dec;38(12):4467–4473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeyama H., Kawashima K., Yamada K., Ito Y. Properties of interferon induced by purified protein derivative of tuberculin in mice sensitized with BCG or cell-wall skeleton of BCG. Gan. 1979 Aug;70(4):421–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wietzerbin J., Falcoff R., Catinot L., Falcoff E. Affinity chromatographic analysis of murine interferons induced by viruses and by T and B cell stimulants. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1977 Apr-Jun;128C(3):699–708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto Y., Kawade Y. Antigenicity of mouse interferons: distinct antigenicity of the two L cell interferon species. Virology. 1980 May;103(1):80–88. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90127-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngner J. S., Salvin S. B. Production and properties of migration inhibitory factor and interferon in the circulation of mice with delayed hypersensitivity. J Immunol. 1973 Dec;111(6):1914–1922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


