Abstract
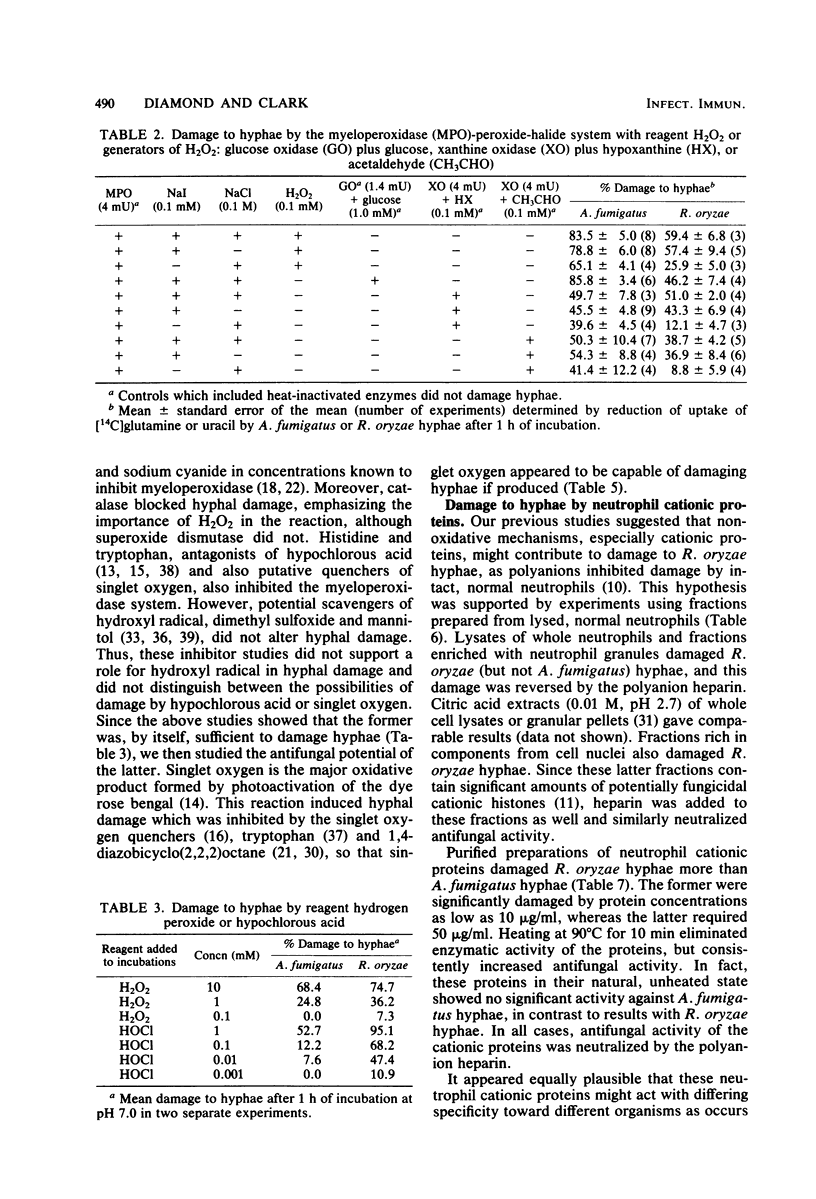
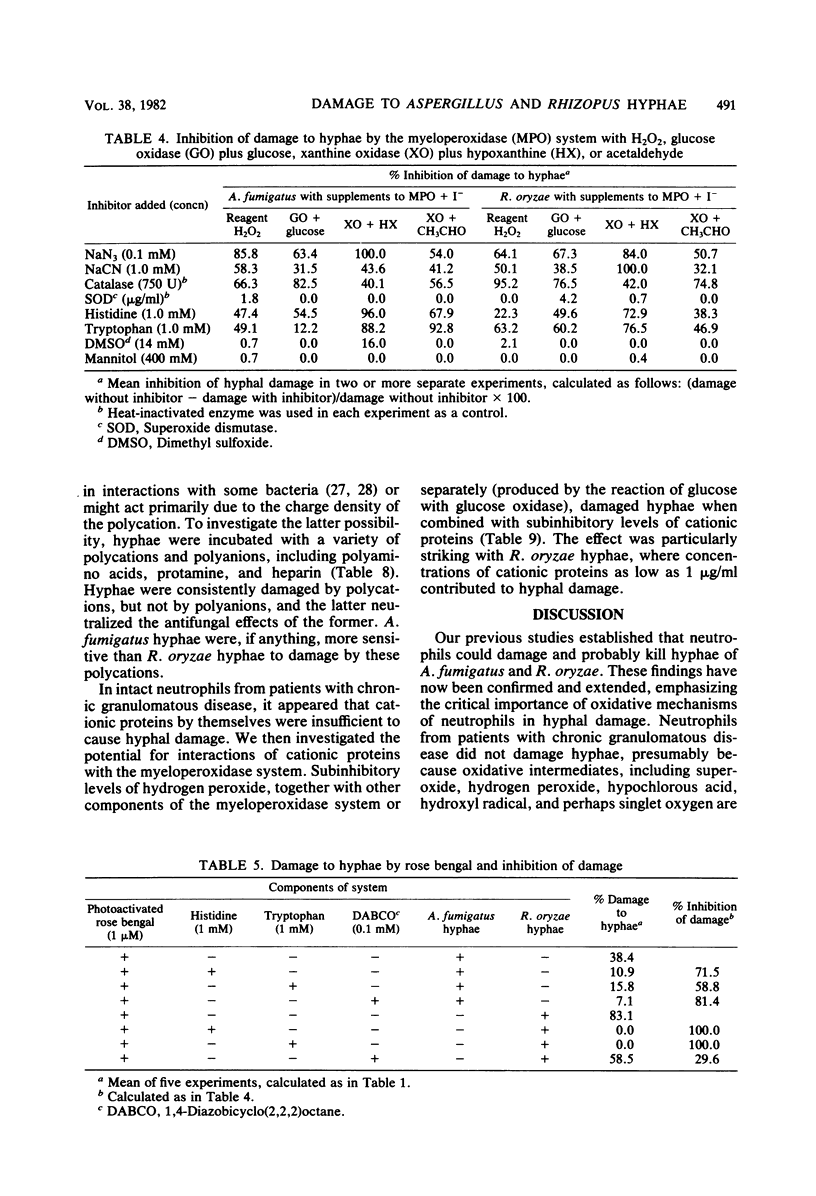
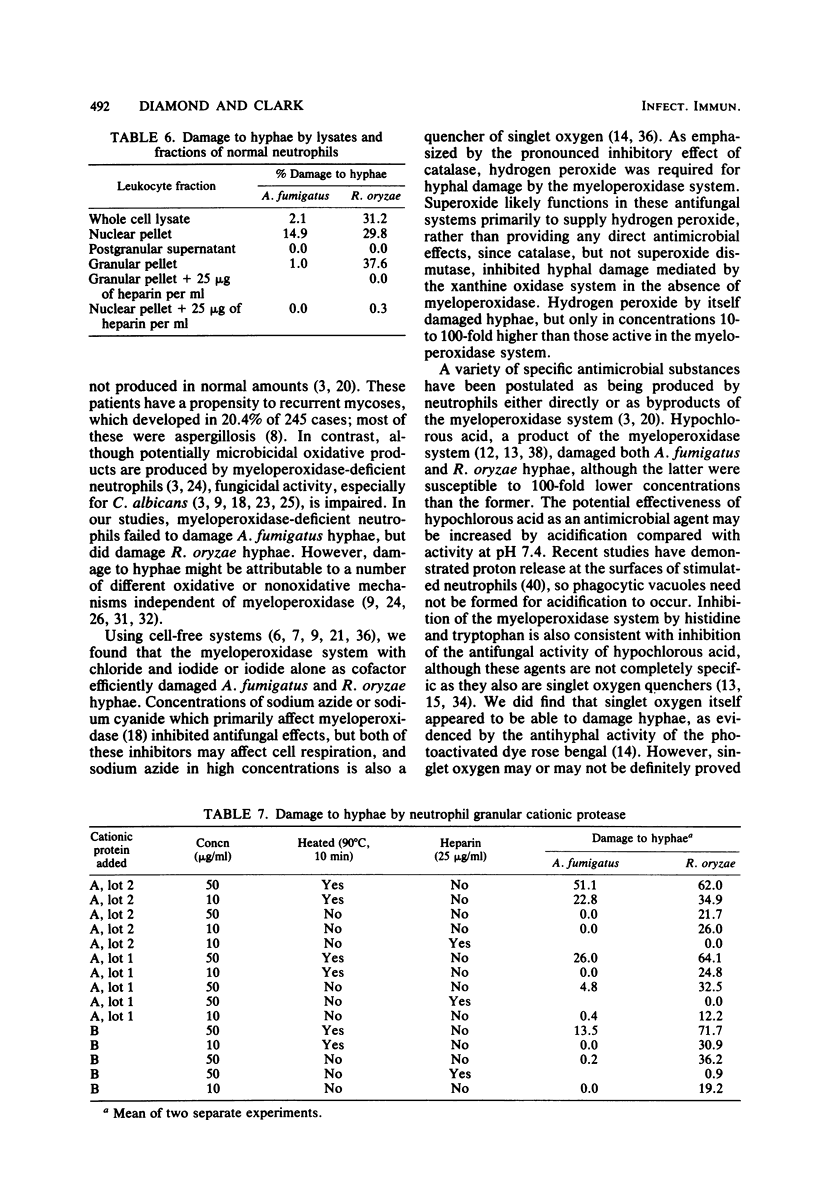
Our previous studies established that human neutrophils could damage and probably kill hyphae of Aspergillus fumigatus and Rhizopus oryzae in vitro, primarily by oxygen-dependent mechanisms active at the cell surface. These studies were extended, again quantitating hyphal damage by reduction in uptake of 14C-labeled uracil or glutamine. Neither A. fumigatus nor R. oryzae hyphae were damaged by neutrophils from patients with chronic granulomatous disease, confirming the importance of oxidative mechanisms in damage to hyphae. In contrast, neutrophils from one patient with hereditary myeloperoxidase deficiency damaged R. oryzae but not A. fumigatus hyphae. Cell-free, in vitro systems were then used to help determine the relative importance of several potentially fungicidal products of neutrophils. Both A. fumigatus and R. oryzae hyphae were damaged by the myeloperoxidase-hydrogen peroxide-halide system either with reagent hydrogen peroxide or enzymatic systems for generating hydrogen peroxide (glucose oxidase with glucose, or xanthine oxidase with either hypoxanthine or acetaldehyde). Iodide with or without chloride supported the reaction, but damage was less with chloride alone as the halide cofactor. Hydrogen peroxide alone damaged hyphae only in concentrations ≥1 mM, but 0.01 mM hypochlorous acid, a potential product of the myeloperoxidase system, significantly damaged R. oryzae hyphae (a 1 mM concentration was required for significant damage to A. fumigatus hyphae). Damage to hyphae by the myeloperoxidase system was inhibited by azide, cyanide, catalase, histidine, and tryptophan, but not by superoxide dismutase, dimethyl sulfoxide, or mannitol. Photoactivation of the dye rose bengal resulted in hyphal damage which was inhibited by histidine, tryptophan, and 1,4-diazobicyclo(2,2,2)octane. Lysates of neutrophils or separated neutrophil granules did not affect A. fumigatus hyphae, but did damage R. oryzae hyphae. Similarly, three preparations of cationic proteins purified from human neutrophil granules were more active in damaging R. oryzae than A. fumigatus hyphae. This damage, as with the separated granules and whole cell lysates, was inhibited by the polyanion heparin. Damage to R. oryzae hyphae by neutrophil cationic proteins was enhanced by activity of the complete myeloperoxidase system or by hydrogen peroxide alone in subinhibitory concentrations. These data support the importance of oxidative products in general and the myeloperoxidase system in particular in damage to hyphae by neutrophils. Cationic proteins may also contribute significantly to neutrophil-mediated damage to R. oryzae hyphae.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babior B. M. Oxygen-dependent microbial killing by phagocytes (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 30;298(13):721–725. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803302981305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Klebanoff S. J. Myeloperoxidase--H2O2--halide system: cytotoxic effect on human blood leukocytes. Blood. 1977 Jul;50(1):65–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Klebanoff S. J. Neutrophil-platelet interaction mediated by myeloperoxidase and hydrogen peroxide. J Immunol. 1980 Jan;124(1):399–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Olsson I., Klebanoff S. J. Cytotoxicity for tumor cells of cationic proteins from human neutrophil granules. J Cell Biol. 1976 Sep;70(3):719–723. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.3.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. S., Isturiz R. E., Malech H. L., Root R. K., Wilfert C. M., Gutman L., Buckley R. H. Fungal infection in chronic granulomatous disease. The importance of the phagocyte in defense against fungi. Am J Med. 1981 Jul;71(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90259-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., Clark R. A., Haudenschild C. C. Damage to Candida albicans hyphae and pseudohyphae by the myeloperoxidase system and oxidative products of neutrophil metabolism in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):908–917. doi: 10.1172/JCI109958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., Krzesicki R., Epstein B., Jao W. Damage to hyphal forms of fungi by human leukocytes in vitro. A possible host defense mechanism in aspergillosis and mucormycosis. Am J Pathol. 1978 May;91(2):313–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadebusch H. H., Johnson A. G. Natural host resistance to infection with Cryptococcus neoformans. IV. The effect of some cationic proteins on the experimental disease. J Infect Dis. 1966 Dec;116(5):551–565. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.5.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. E., Schultz J. Studies on the chlorinating activity of myeloperoxidase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1371–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. E., Watson B. D., Schultz J. Myeloperoxidase and singlet oxygen: a reappraisal. FEBS Lett. 1978 Aug 15;92(2):327–332. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80780-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Held A. M., Hurst J. K. Ambiguity associated with use of singlet oxygen trapping agents in myeloperoxidase-catalyzed oxidations. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Apr 14;81(3):878–885. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91433-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson E. K., Fridovich I. The production of superoxide radical during the decomposition of potassium peroxochromate(V). Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 27;13(18):3811–3815. doi: 10.1021/bi00715a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimball H. R., Ford G. H., Wolff S. M. Lysosomal enzymes in normal and Chediak-Higashi blood leukocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Oct;86(4):616–630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J., Clark R. A. Hemolysis and iodination of erythrocyte components by a myeloperoxidase-mediated system. Blood. 1975 May;45(5):699–707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Myeloperoxidase: contribution to the microbicidal activity of intact leukocytes. Science. 1970 Sep 11;169(3950):1095–1097. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3950.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J., Rosen H. Ethylene formation by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Role of myeloperoxidase. J Exp Med. 1978 Aug 1;148(2):490–506. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.2.490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I. Antifungal effects of peroxidase systems. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):361–365. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.361-365.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Cline M. J. Leukocyte myeloperoxidase deficiency and disseminated candidiasis: the role of myeloperoxidase in resistance to Candida infection. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1478–1488. doi: 10.1172/JCI106114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Ladra K. M., Hake R. B. Nonoxidative fungicidal mechanisms of mammalian granulocytes: demonstration of components with candidacidal activity in human, rabbit, and guinea pig leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1226–1234. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1226-1234.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I. The fungicidal mechanisms of human monocytes. I. Evidence for myeloperoxidase-linked and myeloperoxidase-independent candidacidal mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 1975 Feb;55(2):338–346. doi: 10.1172/JCI107937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odeberg H., Olsson I. Mechanisms for the microbicidal activity of cationic proteins of human granulocytes. Infect Immun. 1976 Dec;14(6):1269–1275. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.6.1269-1275.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odeberg H., Olsson I. Microbicidal mechanisms of human granulocytes: synergistic effects of granulocyte elastase and myeloperoxidase or chymotrypsin-like cationic protein. Infect Immun. 1976 Dec;14(6):1276–1283. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.6.1276-1283.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson K., Olsson I., Spitznagel K. Localization of chymotrypsin-like cationic protein, collagenase and elastase in azurophil granules of human neutrophilic polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1977 Mar;358(3):361–366. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1977.358.1.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson-Delafield J., Martinez R. J., Lehrer R. I. Microbicidal cationic proteins in rabbit alveolar macrophages: a potential host defense mechanism. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):180–192. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.180-192.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson E. M., Calderone R. A. Inhibition of specific amino acid uptake in Candida albicans by lysosomal extracts from rabbit alveolar macrophages. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):506–513. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.506-513.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repine J. E., Eaton J. W., Anders M. W., Hoidal J. R., Fox R. B. Generation of hydroxyl radical by enzymes, chemicals, and human phagocytes in vitro. Detection with the anti-inflammatory agent, dimethyl sulfoxide. J Clin Invest. 1979 Dec;64(6):1642–1651. doi: 10.1172/JCI109626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen H., Klebanoff S. J. Bactericidal activity of a superoxide anion-generating system. A model for the polymorphonuclear leukocyte. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):27–39. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen H., Klebanoff S. J. Formation of singlet oxygen by the myeloperoxidase-mediated antimicrobial system. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4803–4810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen H., Klebanoff S. J. Hydroxyl radical generation by polymorphonuclear leukocytes measured by electron spin resonance spectroscopy. J Clin Invest. 1979 Dec;64(6):1725–1729. doi: 10.1172/JCI109637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Vadasz J. A. Singlet oxygen: a major reactive species in the furocoumarin photosensitized inactivation of E. coli ribosomes. Photochem Photobiol. 1978 Oct-Nov;28(4-5):539–545. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1978.tb06966.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slivka A., LoBuglio A. F., Weiss S. J. A potential role for hypochlorous acid in granulocyte-mediated tumor cell cytotoxicity. Blood. 1980 Feb;55(2):347–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauber A. I., Babior B. M. Evidence for hydroxyl radical production by human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1977 Aug;60(2):374–379. doi: 10.1172/JCI108786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venge P., Strömberg A., Braconier J. H., Roxin L. E., Olsson I. Neutrophil and eosinophil granulocytes in bacterial infection: sequential studies of cellular and serum levels of granule proteins. Br J Haematol. 1978 Apr;38(4):475–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1978.tb01072.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Beckerdite-Quagliata S., Elsbach P. Resistance of gram-negative bacteria to purified bactericidal leukocyte proteins: relation to binding and bacterial lipopolysaccharide structure. J Clin Invest. 1980 Mar;65(3):619–628. doi: 10.1172/JCI109707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Rustagi P. K., LoBuglio A. F. Human granulocyte generation of hydroxyl radical. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):316–323. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zwieten R., Wever R., Hamers M. N., Weening R. S., Roos D. Extracellular proton release by stimulated neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jul;68(1):310–313. doi: 10.1172/JCI110250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



