Abstract
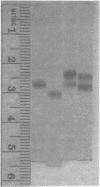
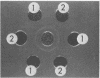
We isolated two proteins, ET-1 and ET-2, from the sporangial extracts of Clostridium perfringens type A. Both proteins had some properties in common with the well-known C. perfringens enterotoxin. ET-1 and ET-2 behaved as single and distinct entities in anion exchange chromatography and disk gel electrophoresis. ET-2 was the more anionic protein since it eluted more slowly from the anion exchange column and migrated faster toward the anode in polyacrylamide disk gel electrophoresis (pH 8.5, native gels). Additionally, in this electrophoretic system ET-2 was not distinguishable from the enterotoxin. The amino acid compositions of ET-1 and ET-2 were similar but differed in a few amino acid residues. The values for both proteins were also similar to the published reports of others for the enterotoxin. Both ET-1 and ET-2 showed lines of identity in agar gel double immunodiffusion against anti-enterotoxin antiserum. Both ET-1 and ET-2 were toxic for rat hepatocytes in primary monolayer culture as determined by accelerated exodus of L-[14C]glucose from preloaded cells and by the rapid uptake of 45Ca2+ after exposure to the proteins. In this regard, ET-1 and ET-2 appeared to be identical in mechanism of action to what has been regarded in the literature as "the" C. perfringens enterotoxin. Interestingly, ET-2 was 3 to 10 times more toxic on a weight basis than ET-1 was.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Duncan C. L., Strong D. H. Improved medium for sporulation of Clostridium perfringens. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Jan;16(1):82–89. doi: 10.1128/am.16.1.82-89.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enders G. L., Jr, Duncan C. L. Anomalous aggregation of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin under dissociating conditions. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Sep;22(9):1410–1414. doi: 10.1139/m76-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enders G. L., Jr, Duncan C. L. Preparative polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis purification of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):425–429. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.425-429.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frieben W. R., Duncan C. L. Heterogeneity of enterotoxin-like protein extracted from spores fo Clostridium perfringens type A. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jul 1;55(2):455–463. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02182.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frieben W. R., Duncan C. L. Homology between enterotoxin protein and spore structural protein in Clostridium perfringens type A. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Nov 15;39(2):393–401. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giger O., Pariza M. W. Mechanism of action of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Effects on membrane permeability and amino acid transport in primary cultures of adult rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jan 25;595(2):264–276. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90089-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granum P. E., Skjelkvåle R. Chemical modification and characterization of enterotoxin from clostridium perfringens type A. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1977 Feb;85B(1):89–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb01678.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granum P. E., Whitaker J. R. Improved method for purification of enterotoxin from Clostridium perfringens type A. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jun;39(6):1120–1122. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.6.1120-1122.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschild A. H., Hilsheimer R., Martin W. G. Improved purification and further characterization of Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Nov;19(11):1379–1382. doi: 10.1139/m73-222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschild A. H., Hilsheimer R. Purification and characteristics of the enterotoxin of Clostridium perfringens type A. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Nov;17(11):1425–1433. doi: 10.1139/m71-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEFEVRE P. G. Sugar transport in the red blood cell: structure-activity relationships in substrates and antagonists. Pharmacol Rev. 1961 Mar;13:39–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbe R. G., Rey D. K. Raffinose increases sporulation and enterotoxin production by Clostridium perfringens type A. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jun;37(6):1196–1200. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.6.1196-1200.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda M., Sugimoto N. Calcium-independent and dependent steps in action of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin on HeLa and Vero cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Nov 28;91(2):629–636. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91568-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonel J. L. Binding of Clostridium perfringens [125I]enterotoxin to rabbit intestinal cells. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 14;19(21):4801–4807. doi: 10.1021/bi00562a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi G., Uemura T., Riemann H. P. Simplified method for purification of Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Nov;26(5):762–767. doi: 10.1128/am.26.5.762-767.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schanne F. A., Kane A. B., Young E. E., Farber J. L. Calcium dependence of toxic cell death: a final common pathway. Science. 1979 Nov 9;206(4419):700–702. doi: 10.1126/science.386513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skjelkvålé R., Duncan C. L. Characterization of enterotoxin purified from Clostridium perfringens type C. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):1061–1068. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.1061-1068.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. T., Thor H., Orrenius S. Toxic injury to isolated hepatocytes is not dependent on extracellular calcium. Science. 1981 Sep 11;213(4513):1257–1259. doi: 10.1126/science.7268433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark R. L., Duncan C. L. Biological characteristics of Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1971 Aug;4(2):89–96. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.2.89-96.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark R. L., Duncan C. L. Purification and biochemical properties of Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):662–673. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.662-673.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yotis W. W., Catsimpoolas N. Scanning isoelectric focusing and isotachophoresis of Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin. J Appl Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;39(2):147–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1975.tb00556.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]