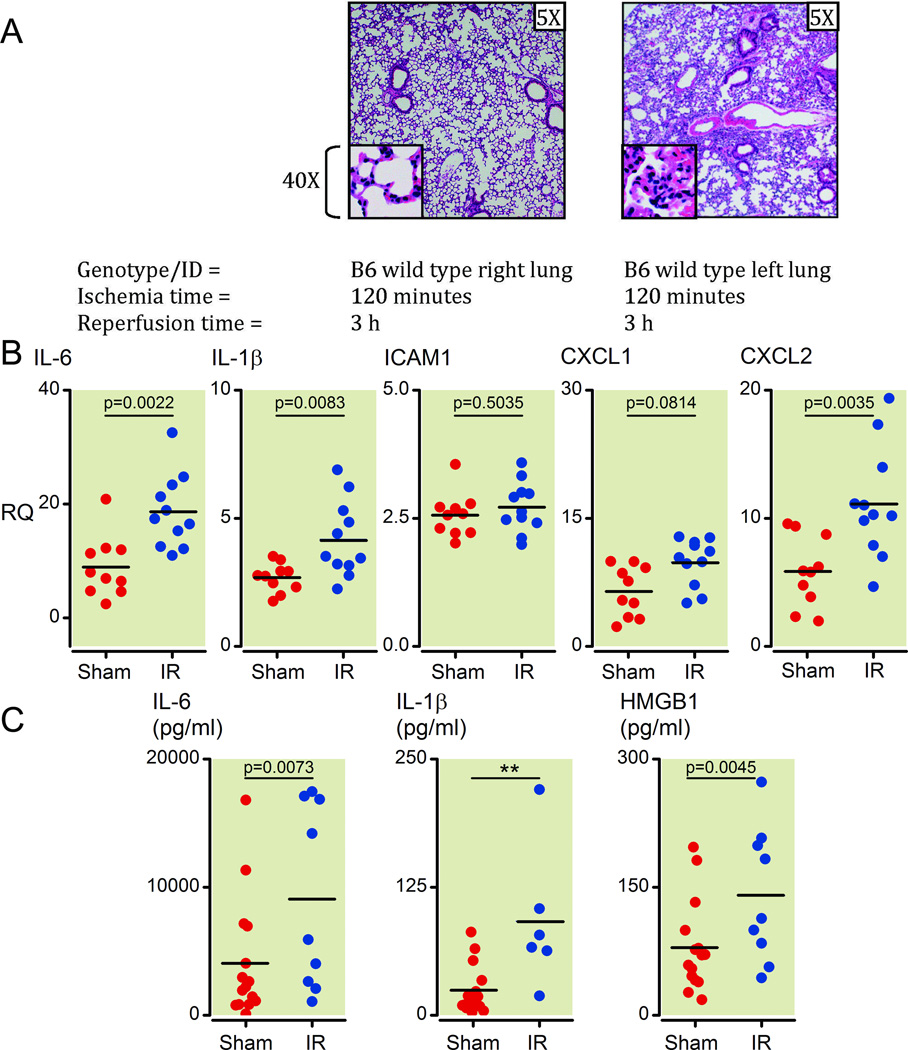
Figure 1. Unilateral pulmonary artery occlusion as a model of ventilated lung ischemia reperfusion (I/R) injury in mice results in inflammatory marker upregulation and neutrophil infiltration.
(A) Histology from prolonged ventilated left lung ischemia (2 h) followed by reperfusion (3 h) in the left versus right lung in C57/BL6 wild type mice (H&E staining, 5X and 40X magnifications). Each image is representative of histology images from 4 independent surgeries.
(B) Inflammatory cytokines and neutrophil-specific chemokines (mRNA) measured early (1 h) after reperfusion (Ischemia time=30 minutes). Lower segments of left lungs were collected and relative mRNA levels measured by Q-PCR. All measurements were normalized to GAPDH message levels and RQ values obtained using the relative ΔΔCt method with an independent sample (right lung sham surgery) used to set as an internal reference RQ of 1. Values from sham surgery left lungs are higher compared to sham surgery right lungs because of the injury generated during the thoracotomy procedure that affects the left and not right lungs (see materials and methods section for more details). Each point represents RNA from left lung lower segments of individual mice that underwent either sham or I/R surgery. Mice that died before completion of surgery or collection of lungs or had inadvertent esophageal intubation were excluded from analysis (2 sham and 6 I/R mice).
(C) Inflammatory cytokine and HMGB1 protein levels measured at 1 h after reperfusion (ischemia time = 30 minutes). Plasma from blood collected from mice prior to collection of lungs was analyzed by ELISA for protein levels of IL-1β, IL-6 and HMGB1. Each point represents plasma from blood collected from individual mice that underwent either sham or I/R surgery. Mice that died before completion of surgery or collection of lungs, yielded insufficient blood volumes, from whom blood was not collected or had inadvertent esophageal intubation were excluded from analysis (2 sham and 8 I/R mice).
H&E: hematoxylin and eosin; mRNA: messenger RNA; Q-PCR: real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase;
RQ: relative quantification; Ct: threshold count; HMGB1: high-mobility group protein B1; IL: interleukin; ICAM: intercellular adhesion molecule; CXCL: Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand.