Abstract
Three parameters of rotavirus infection, i.e., clinical disease, viral antigen in infected intestines, and infectious virus in feces, were assessed in infant mice nursed by mothers with or without preexisting rotavirus antibody. Diarrhea was the only consistent sign of clinical disease, and its course followed that of infection by about 1 day. Infected intestinal epithelial cells, except crypt cells, were observed by immunofluorescence microscopy in the duodenum, jejunum, ileum, and colon. Infection progressed in a proximal-to-distal direction with time. Viral antigen appeared in intestinal tissue later, was present in lower amounts, and disappeared sooner from infants nursed by mothers with preexisting rotavirus antibody, indicating that protection was passively transferred to these infants although the course of clinical disease was not changed.
Full text
PDF

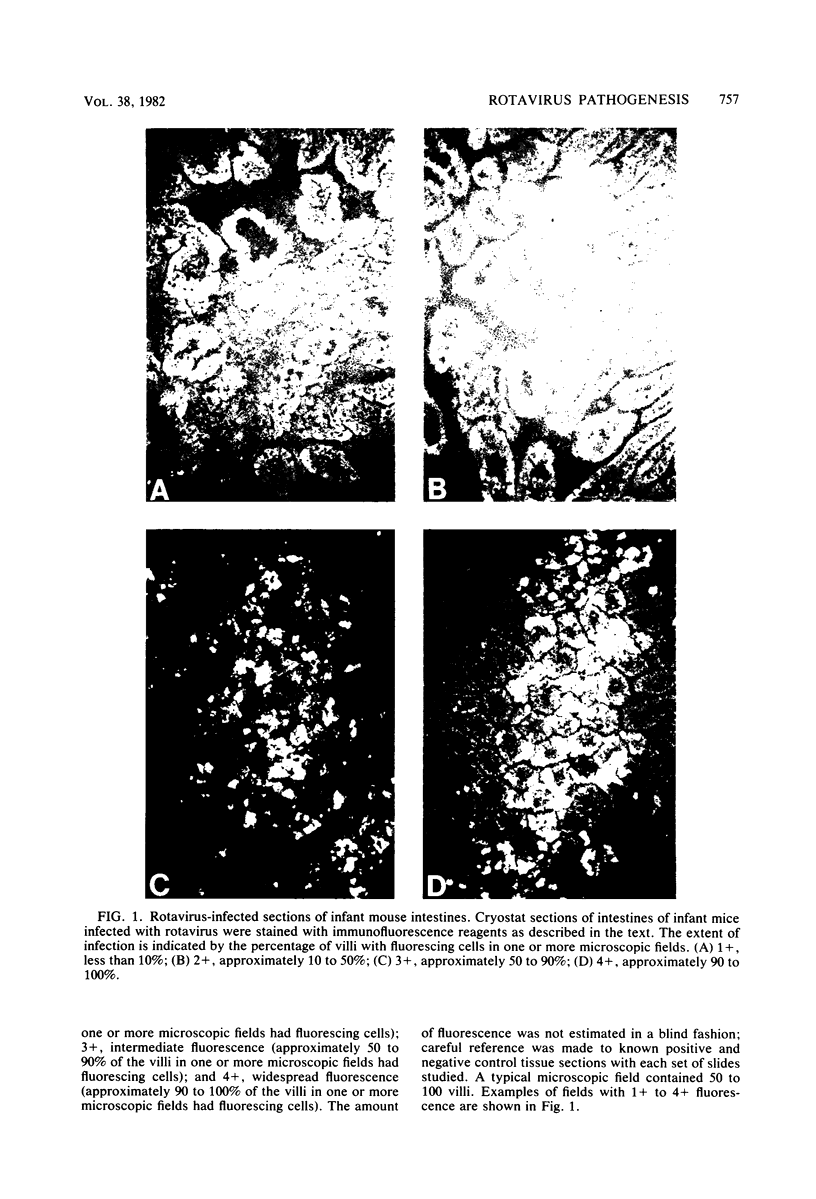
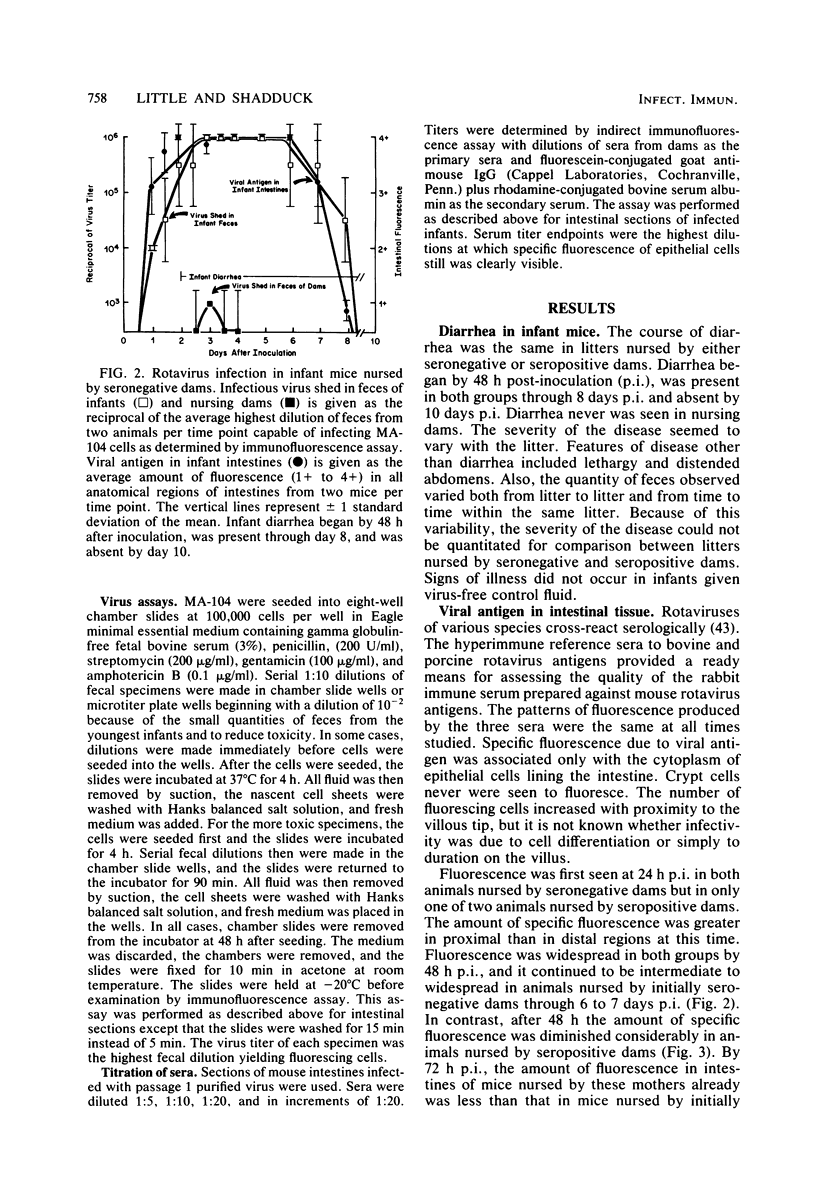
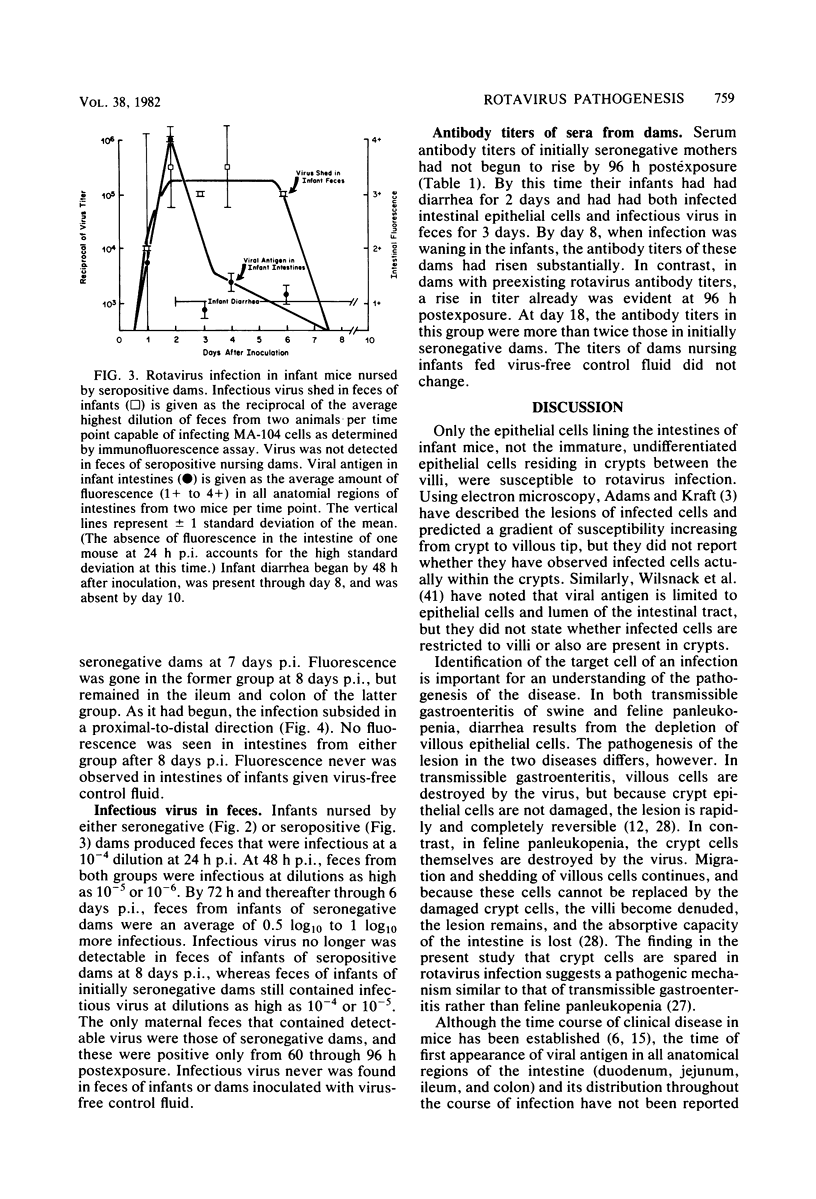
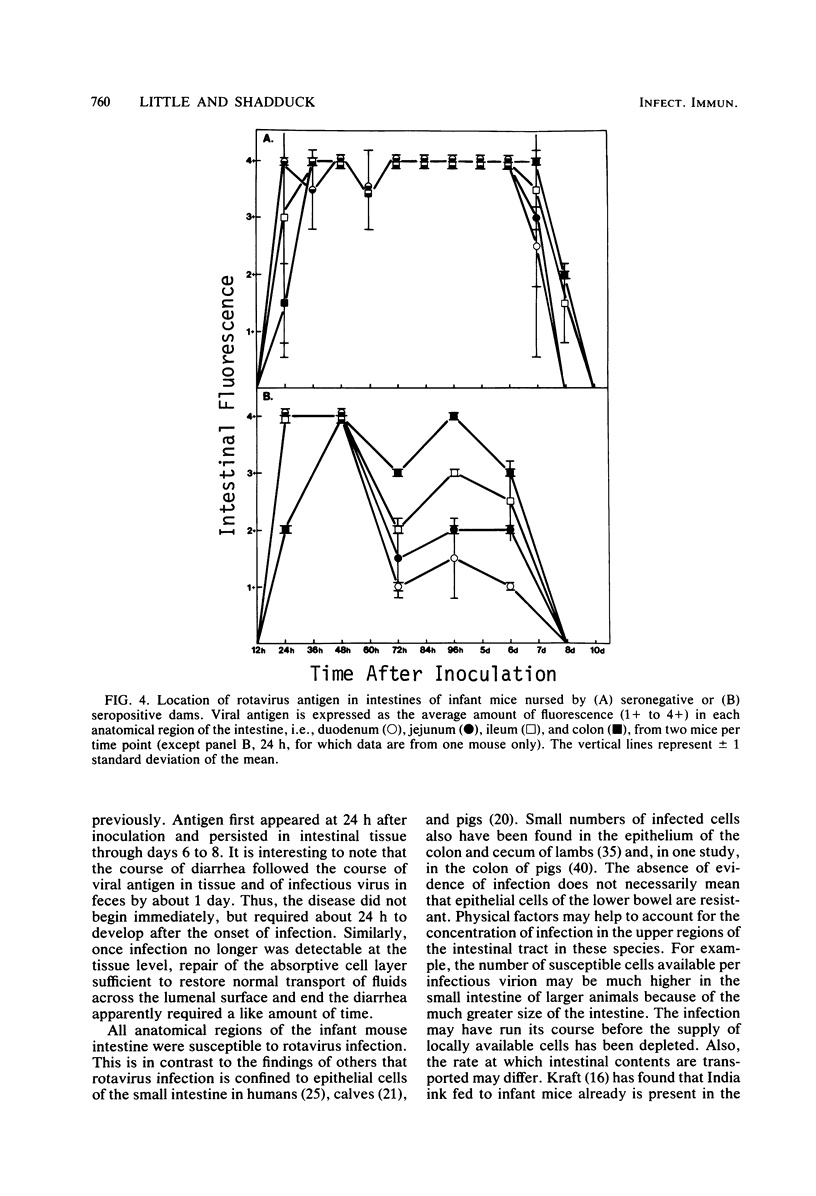
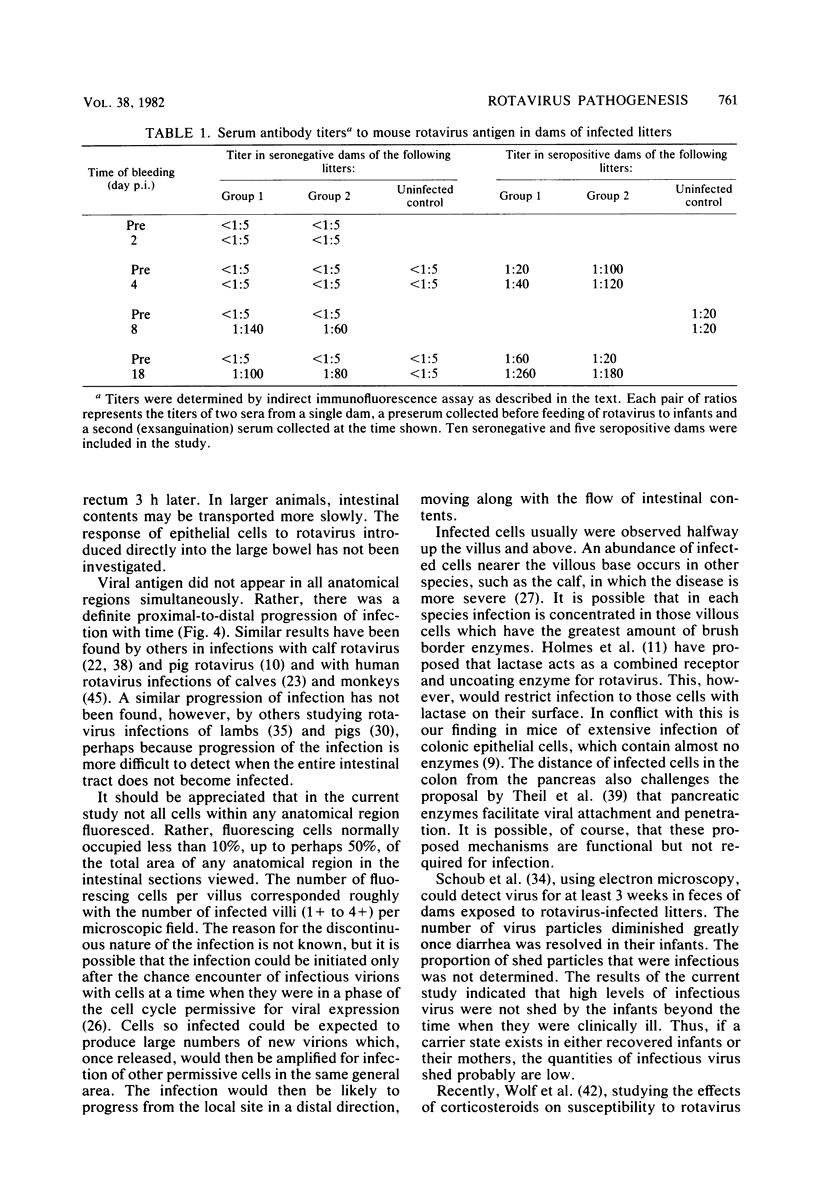


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADAMS W. R., KRAFT L. M. Epizootic diarrhea of infant mice: indentification of the etiologic agent. Science. 1963 Jul 26;141(3578):359–360. doi: 10.1126/science.141.3578.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abou-Youssef M. H., Ristic M. Protective effect of immunoglobulins in serum and milk of sows exposed to transmissible gastroenteritis virus. Can J Comp Med. 1975 Jan;39(1):41–45. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams W. R., Kraft L. M. Electron-Microscopic Study of the Intestinal Epithelium of Mice Infected with the Agent of Epizootic Diarrhea of Infant Mice (EDIM Virus). Am J Pathol. 1967 Jul;51(1):39–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop R. F., Davidson G. P., Holmes I. H., Ruck B. J. Detection of a new virus by electron microscopy of faecal extracts from children with acute gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1974 Feb 2;1(7849):149–151. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92440-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohl E. H., Saif L. J. Passive immunity in transmissible gastroenteritis of swine: immunoglobulin characteristics of antibodies in milk after inoculating virus by different routes. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):23–32. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.23-32.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch C. F., Woode G. N. Serial studies of virus multiplication and intestinal damage in gnotobiotic piglets infected with rotavirus. J Med Microbiol. 1978 Aug;11(3):325–334. doi: 10.1099/00222615-11-3-325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cukor G., Blacklow N. R., Capozza F. E., Panjvani Z. F., Bednarek F. Persistence of antibodies to rotavirus in human milk. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):93–96. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.93-96.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall G. A., Bridger J. C., Chandler R. L., Woode G. N. Gnotobiotic piglets experimentally infected with neonatal calf diarrhoea reovirus-like agent (Rotavirus). Vet Pathol. 1976;13(3):197–210. doi: 10.1177/030098587601300304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes I. H., Rodger S. M., Schnagl R. D., Ruck B. J., Gust I. D., Bishop R. F., Barnes G. L. Is lactase the receptor and uncoating enzyme for infantile enteritis (rota) viruses? Lancet. 1976 Jun 26;1(7974):1387–1388. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)93032-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper B. E., Haelterman E. O. Lesions of the gastrointestinal tract of pigs infected with transmissible gastroenteritis. Can J Comp Med. 1969 Jan;33(1):29–36. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAFT L. M. Observations on the control and natural history of epidemic diarrhea of infant mice (EDIM). Yale J Biol Med. 1958 Dec;31(3):121–137. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAFT L. M. Studies on the etiology and transmission of epidemic diarrhea of infant mice. J Exp Med. 1957 Nov 1;106(5):743–755. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.5.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Kim H. W., Wyatt R. G., Cline W. L., Arrobio J. O., Brandt C. D., Rodriguez W. J., Sack D. A., Chanock R. M., Parrott R. H. Human reovirus-like agent as the major pathogen associated with "winter" gastroenteritis in hospitalized infants and young children. N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 29;294(18):965–972. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197604292941801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. W., Brandt C. D., Kapikian A. Z., Wyatt R. G., Arrobio J. O., Rodriguez W. J., Chanock R. M., Parrott R. H. Human reovirus-like agent infection. Occurrence in adult contacts of pediatric patients with gastroenteritis. JAMA. 1977 Aug 1;238(5):404–407. doi: 10.1001/jama.238.5.404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loria R. M., Kibrick S., el-Bermani al-W, Broitman S. A. Preparation of intestine and other elongated specimens for histologic and immunofluorescent studies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1973 Sep;60(3):424–427. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/60.3.424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAdaragh J. P., Bergeland M. E., Meyer R. C., Johnshoy M. W., Stotz I. J., Benfield D. A., Hammer R. Pathogenesis of rotaviral enteritis in gnotobiotic pigs: a microscopic study. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Oct;41(10):1572–1581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mebus C. A., Newman L. E. Scanning electron, light, and immunofluorescent microscopy of intestine of gnotobiotic calf infected with reovirus-like agent. Am J Vet Res. 1977 May;38(5):553–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mebus C. A., Wyatt R. G., Sharpee R. L., Sereno M. M., Kalica A. R., Kapikian A. Z., Twiehaus M. J. Diarrhea in gnotobiotic calves caused by the reovirus-like agent of human infantile gastroenteritis. Infect Immun. 1976 Aug;14(2):471–474. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.2.471-474.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W. Mechanisms in the pathogenesis of diarrhea: a review. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1978 Feb 15;172(4):443–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Norman J. O., Lambert G. Age dependent resistance to transmissible gastroenteritis of swine (TGE). I. Clinical signs and some mucosal dimensions in small intestine. Can J Comp Med. 1973 Apr;37(2):157–166. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Much D. H., Zajac I. Purification and characterization of epizootic diarrhea of infant mice virus. Infect Immun. 1972 Dec;6(6):1019–1024. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.6.1019-1024.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. R., McNulty M. S. Pathological changes in the small intestine of neonatal pigs infected with a pig reovirus-like agent (rotavirus). J Comp Pathol. 1977 Jul;87(3):363–375. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(77)90026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RILEY V. Adaptation of orbital bleeding technic to rapid serial blood studies. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Aug-Sep;104:751–754. doi: 10.3181/00379727-104-25975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Schnagl R. D., Holmes I. H. Biochemical and biophysical characteristics of diarrhea viruses of human and calf origin. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1229–1235. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1229-1235.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoub B. D., Prozesky O. W., Lecatsas G., Oosthuizen R. The role of breast-feeding in the prevention of rotavirus infection. J Med Microbiol. 1978 Feb;11(1):25–31. doi: 10.1099/00222615-11-1-25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Angus K. W., Gray E. W. Rotavirus infection in lambs: pathogenesis and pathology. Arch Virol. 1977;55(4):263–274. doi: 10.1007/BF01315048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Ferguson A., Allan F., Angus K. W., Mitchell B. Small intestinal morphology and epithelial cell kinetics in lamb rotavirus infections. Gastroenterology. 1979 Mar;76(3):477–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Wells P. W. Rotavirus infection in lambs: studies on passive protection. Arch Virol. 1976;52(3):201–205. doi: 10.1007/BF01348017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stair E. L., Mebus C. A., Twiehaus M. J., Underdahl N. R. Neonatal calf diarrhea. Electron microscopy of intestines infected with a reovirus-like agent. Vet Pathol. 1973;10(2):155–170. doi: 10.1177/030098587301000208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., Bohl E. H., Agnes A. G. Cell culture propagation of porcine rotavirus (reovirus-like agent). Am J Vet Res. 1977 Nov;38(11):1765–1768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., Bohl E. H., Cross R. F., Kohler E. M., Agnes A. G. Pathogenesis of porcine rotaviral infection in experimentally inoculated gnotobiotic pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1978 Feb;39(2):213–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilsnack R. E., Blackwell J. H., Parker J. C. Identification of an agent of epizootic diarrhea of infant mice by immunofluorescent and complement-fixation tests. Am J Vet Res. 1969 Jul;30(7):1195–1204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf J. L., Cukor G., Blacklow N. R., Dambrauskas R., Trier J. S. Susceptibility of mice to rotavirus infection: effects of age and administration of corticosteroids. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):565–574. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.565-574.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Bridger J. C., Jones J. M., Flewett T. H., Davies H. A., Davis H. A., White G. B. Morphological and antigenic relationships between viruses (rotaviruses) from acute gastroenteritis of children, calves, piglets, mice, and foals. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):804–810. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.804-810.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Jones J., Bridger J. Levels of colostral antibodies against neonatal calf diaahoea virus. Vet Rec. 1975 Aug 23;97(8):148–149. doi: 10.1136/vr.97.8.148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., Sly D. L., London W. T., Palmer A. E., Kalica A. R., Van Kirk D. H., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Induction of diarrhea in colostrum-deprived newborn rhesus monkeys with the human reovirus-like agent of infantile gastroenteritis. Arch Virol. 1976;50(1-2):17–27. doi: 10.1007/BF01317997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Wyatt R. G., Mata L., Urrutia J. J., Garciá B., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Secretory antibody directed against rotavirus in human milk--measurement by means of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Pediatr. 1978 Dec;93(6):916–921. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)81211-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]