Abstract
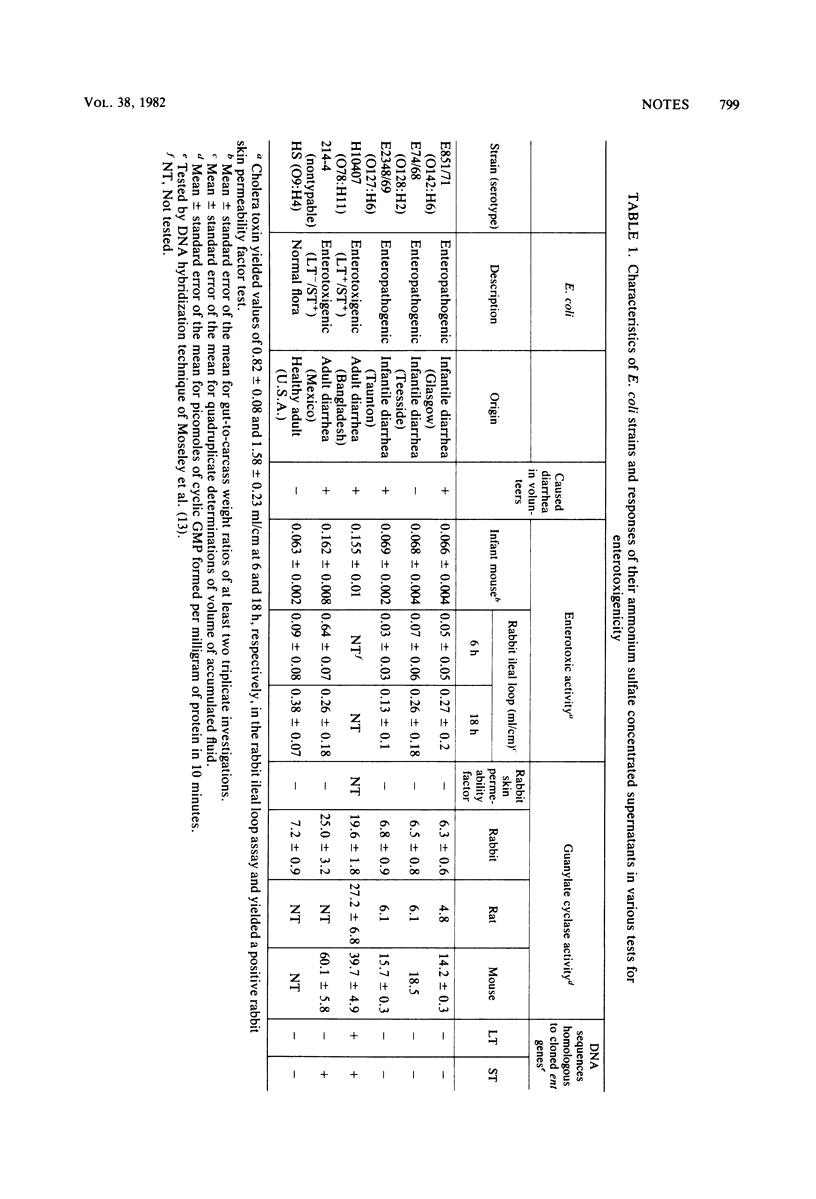
Ammonium sulfate-precipitated supernatants of classical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli strains were negative when investigated for enterotoxin production in rabbit ligated ileal loops, rabbit skin vascular permeability factor tests, suckling mice, and Y-1 adrenal cells. They also failed to stimulate guanylate cyclase activity in homogenates of rabbit, rat, and infant mouse intestines. Furthermore, DNA from enteropathogenic E. coli lacked sequences that encode heat-labile and heat-stable enterotoxins. These studies fail to show conventional enterotoxin synthesis by classical enteropathogenic E. coli.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DuPont H. L., Formal S. B., Hornick R. B., Snyder M. J., Libonati J. P., Sheahan D. G., LaBrec E. H., Kalas J. P. Pathogenesis of Escherichia coli diarrhea. N Engl J Med. 1971 Jul 1;285(1):1–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197107012850101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman R., Levine M. M. Acute diarrheal infections in infants I. Bacterial and viral causes. Hosp Pract. 1980 Jan;15(1):97–104. doi: 10.1080/21548331.1980.11946543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Graf L. H., Jr, Laird W. J., Smith P. L. Heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: in vitro effects on guanylate cyclase activity, cyclic GMP concentration, and ion transport in small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2800–2804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R. J., Scotland S. M., Rowe B. Enterotoxin testing of Escherichia coli causing epidemic infantile enteritis in the U.K. Lancet. 1976 Mar 20;1(7960):629–631. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90429-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai G. J., Burrows W. The titration of cholera toxin and antitoxin in the rabbit ileal loop. J Infect Dis. 1966 Dec;116(5):606–614. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.5.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Rowe B., Engert R. F., Short H. B., Gross R. J. Enterotoxigenicity of enteropathogenic serotypes of Escherichia coli isolated from infants with epidemic diarrhea. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):171–178. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.171-178.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Bergquist E. J., Nalin D. R., Waterman D. H., Hornick R. B., Young C. R., Sotman S. Escherichia coli strains that cause diarrhoea but do not produce heat-labile or heat-stable enterotoxins and are non-invasive. Lancet. 1978 May 27;1(8074):1119–1122. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90299-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Caplan E. S., Waterman D., Cash R. A., Hornick R. B., Snyder M. J. Diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli that produce only heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):78–82. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.78-82.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Rennels M. B., Cisneros L., Hughes T. P., Nalin D. R., Young C. R. Lack of person-to-person transmission of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli despite close contact. Am J Epidemiol. 1980 Mar;111(3):347–355. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Huq I., Alim A. R., So M., Samadpour-Motalebi M., Falkow S. Detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by DNA colony hybridization. J Infect Dis. 1980 Dec;142(6):892–898. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.6.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosley W. H., Aziz K. M. Serological evidence for the identity of the vascular permeability factor and ileal loop toxin of Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1970 Mar;121(3):243–250. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.3.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NETER E. Enteritis due to enteropathogenic Escherichia coli; present-day status and unsolved problems. J Pediatr. 1959 Aug;55(2):223–239. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(59)80091-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalin D. R., Levine M. M., Young C. R., Bergquist E. J., McLaughlin J. C. Increased Escherichia coli enterotoxin detection after concentrating culture supernatants: possible new enterotoxin detectable in dogs but not in infant mice. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Dec;8(6):700–703. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.6.700-703.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M., Levine M. M. Effect of chlorpromazine on intestinal secretion mediated by Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin and 8-Br-cyclic GMP in infant mice. Gastroenterology. 1981 Feb;80(2):321–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M., Still C. S., Miliotis M. D., Koornhof H. J. Mechanism of action of Yersinia enterocolitica enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):680–684. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.680-684.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe B. The role of Escherichia coli in gastroenteritis. Clin Gastroenterol. 1979 Sep;8(3):625–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Human diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:333–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandefur P. D., Peterson J. W. Isolation of skin permeability factors from culture filtrates of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):671–679. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.671-679.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


