Abstract
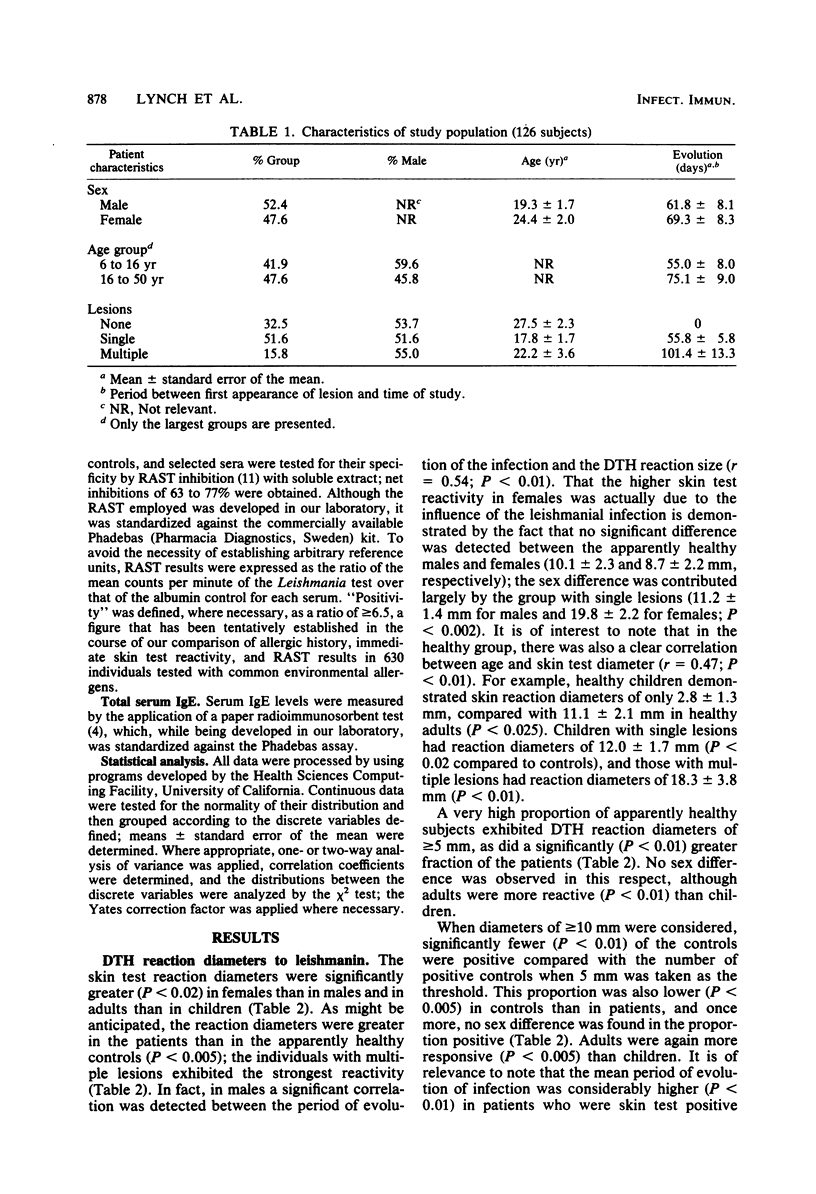
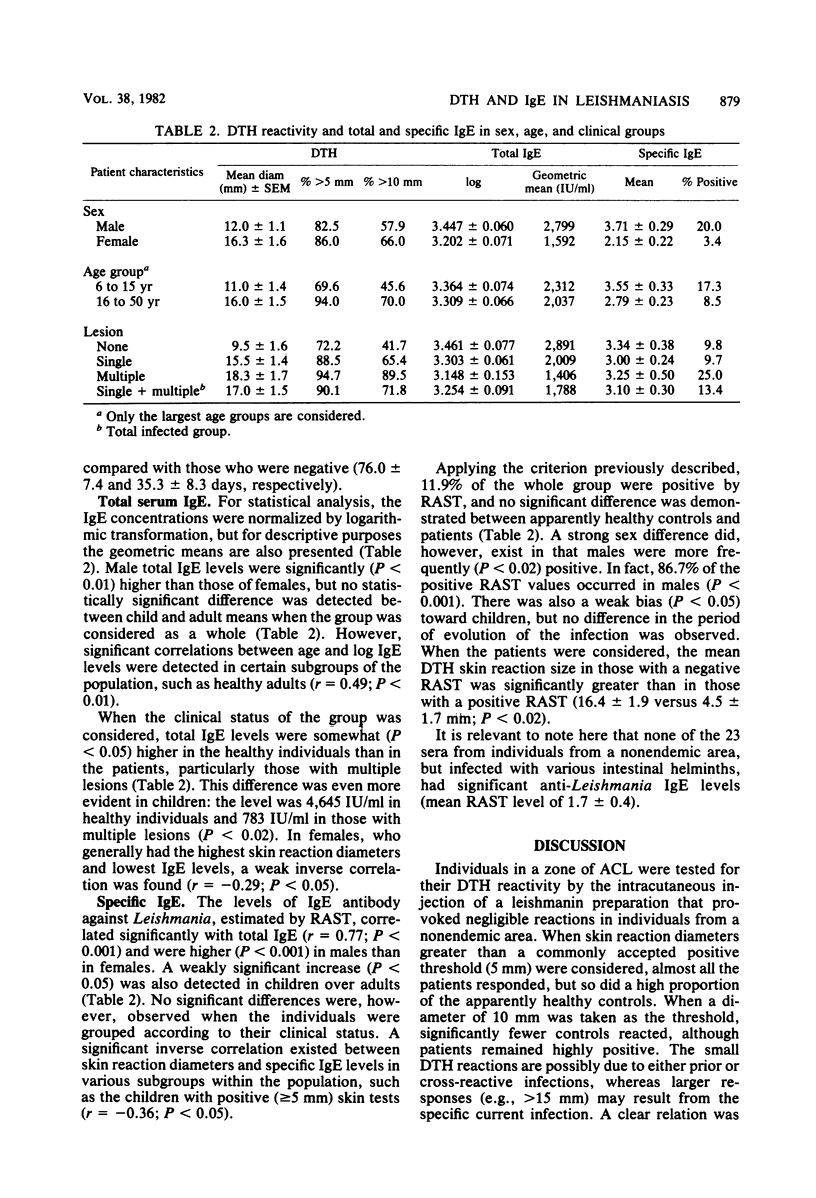
Delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) and both total and specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibody levels were studied during an outbreak of American cutaneous leishmaniasis. Direct correlations were detected between DTH reactivity and either age or the period of evolution of the infection, and a clear association with sex (strongest response in females) was observed. Extremely high, age-dependent, total serum IgE levels were measured in the study group, probably due to concurrent intestinal helminthiasis. A low proportion of the group also had detectable levels of specific anti-Leishmania IgE antibody. Total and specific IgE levels were also sex dependent (lowest in females), and an inverse correlation was found between these levels and DTH responsiveness, possibly reflecting the intervention of regulatory influences of T-lymphocyte activity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bryceson A. D., Bray R. S., Wolstencroft R. A., Dumonde D. C. Immunity in cutaneous leishmaniasis of the guinea-pig. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Sep;7(3):301–341. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley R. H., Becker W. G. Abnormalities in the regulation of human IgE synthesis. Immunol Rev. 1978;41:288–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb01469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceska M., Lundkvist U. A new and simple radioimmunoassay method for the determination of IgE. Immunochemistry. 1972 Oct;9(10):1021–1030. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90112-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller M., Geller M., Flaherty D. K., Capanema de Sourza A. P. Serum IgE levels in toxoplasmosis. Ann Allergy. 1980 Oct;45(4):251–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyneman D. Immunology of leishmaniasis. Bull World Health Organ. 1971;44(4):499–514. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman D. R. Comparison of methods of performing the radioallergosorbent test: Phadebas, Fadal-Nalebuff and Hoffman protocols. Ann Allergy. 1980 Dec;45(6):343–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussain R., Hamilton R. G., Kumaraswami V., Adkinson N. F., Jr, Ottesen E. A. IgE responses in human filariasis. I. Quantitation of filaria-specific IgE. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1623–1629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson S. G., Mellbin T., Vahlquist B. Immunoglobulin levels in Ethiopian preschool children with special reference to high concentrations of immunoglobulin E (IgND). Lancet. 1968 May 25;1(7552):1118–1121. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90187-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch N. R., Dunand P., Newcomb R. W., Chai H., Bigley J. Influence of IgG antibody and glycopeptide allergens on the correlation between the radioallergosorbent test (RAST) and skin testing or bronchial challenge with alternaria. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Oct;22(1):35–46. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch N. R., Turner K. J. Application of in vitro and in vivo assay techniques in the isolation of rye grass (Lolium perenne) pollen allergens. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1974;47(6):818–828. doi: 10.1159/000231273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddison S. E., Kagan I. G., Elsdon-Dew R. Comparison of intradermal and serologic tests for the diagnosis of amebiasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1968 Jul;17(4):540–547. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1968.17.540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D. G., Meyers D. A., Bias W. B. The epidemiology and genetics of atopic allergy. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 24;305(26):1551–1559. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112243052603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matossian-Rogers A., Lumsden W. H., Dumonde D. C. Numerical immunotaxonomy of Leishmania. I. Differentiation of four strains of Leishmania by serological tests. Immunology. 1976 Jul;31(1):1–19. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen K., Sheppard J., Holmes W., Tizard I. Experimental bovine trypanosomiasis. Changes in serum immunoglobulins, complement and complement components in infected animals. Immunology. 1978 Nov;35(5):817–826. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr T. S., Blair A. M. Potentiated reagin response to egg albumin and conalbumin in Nippostrongylus brasiliensis infected rats. Life Sci. 1969 Oct 15;8(20):1073–1077. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(69)90459-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orren A., Dowdle E. B. The effects of sex and age on serum IgE concentrations in three ethnic groups. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1975;48(6):824–835. doi: 10.1159/000231370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez H., Labrador F., Torrealba J. W. Variations in the response of five strains of mice to Leishmania mexicana. Int J Parasitol. 1979 Feb;9(1):27–32. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(79)90062-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revoltella R., Jayakar S. D., Tinelli M., Scaglia M., Peracino A., Desmarais J. C., Siccardi A. G. Parasite-reactive serum IgE antibodies in African populations. Relation to intestinal parasite load. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1980;62(1):23–33. doi: 10.1159/000232480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma B. K., Talwar K. K., Bhatnagar V., Kumar L., Ganguly N. K., Mahajan R. C. Recurrent anaphylaxis due to Plasmodium vivax infection. Lancet. 1979 Jun 23;1(8130):1340–1341. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91965-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiger R. F., Steiger E. Cultivation of Leishmania donovani and Leishmania braziliensis in defined media: nutritional requirements. J Protozool. 1977 Aug;24(3):437–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1977.tb04771.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner K. J. The conflicting role of parasitic infections in modulating the prevalence of asthma. P N G Med J. 1978 Mar;21(1):86–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


