Abstract
Previous studies indicated that the teichoic acid isolated from strains of Streptococcus sanguis was group specific and defined the Lancefield group H streptococci. To determine the specific antigenic determinants, the antigen was extracted from a group H streptococcus (ATCC 903) by the phenol-water method and purified by column chromatography. The isolated antigen had a glycerol/phosphate/glucose molar ratio of 1:0.9:0.3; the lipid concentration was 7.6% of its dry weight. No nucleic acids were detected, and amino acids constituted approximately 2% of the dry weight. The minimum concentration of antigen required to sensitize erythrocytes for hemagglutination with a 1:1,000 dilution of either group H antiserum or antiteichoic acid serum was 0.02 microgram/ml. Hemagglutination inhibition studies suggested that the major antigenic determinant consisted of an alpha-glucose linked to the glycerol phosphate backbone.
Full text
PDF

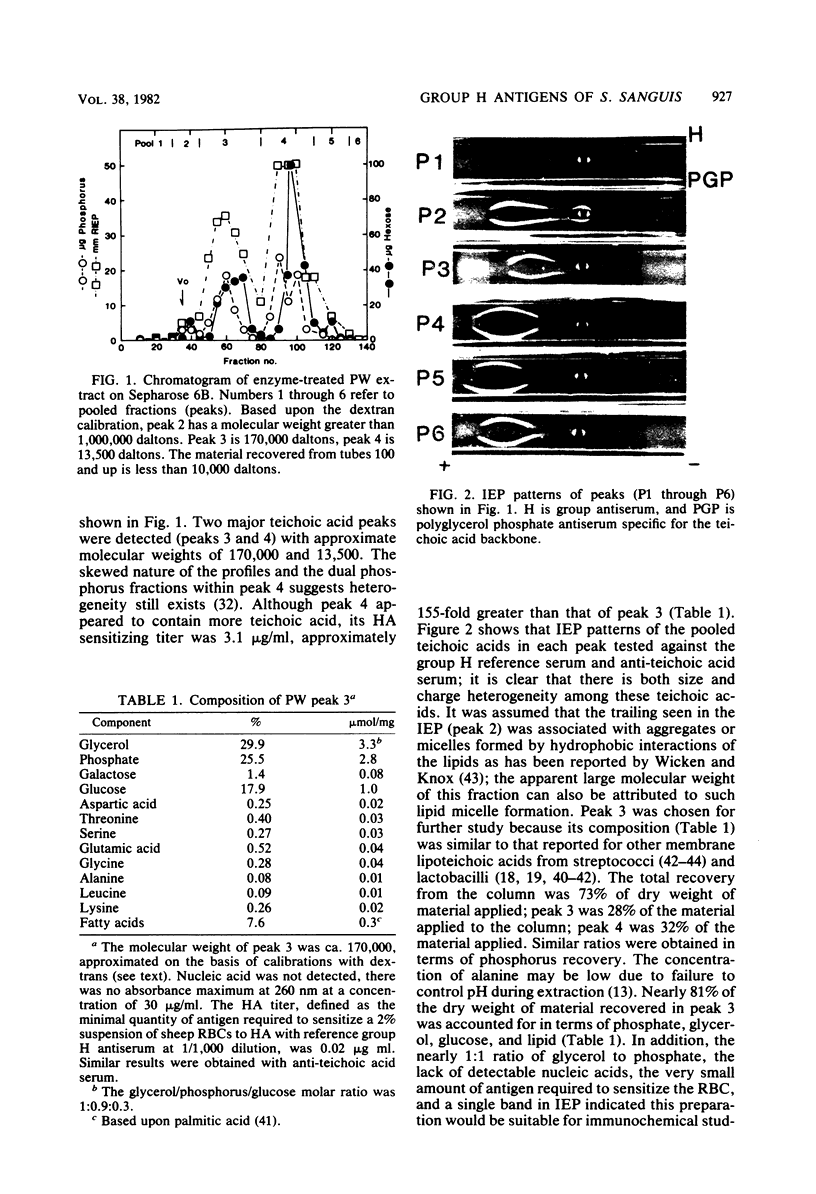
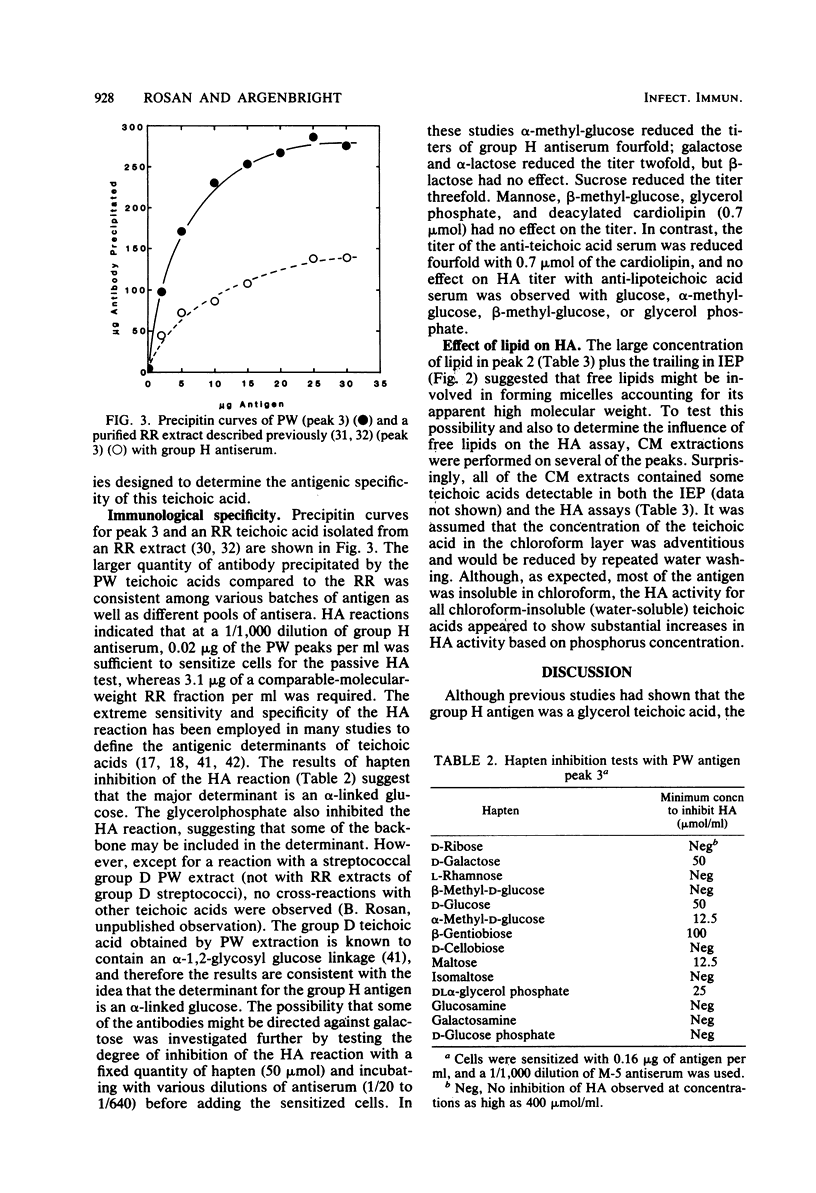



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appelbaum B., Golub E., Holt S. C., Rosan B. In vitro studies of dental plaque formation: adsorption of oral streptococci to hydroxyaptite. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):717–728. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.717-728.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelbaum B., Rosan B. Antigens of Streptococcus sanguis: purification and characterization of the b antigen. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):896–904. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.896-904.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. A., Bleiweis A. S. Chemical, immunochemical, and structural studies of the cross-reactive antigens of Streptococcus mutans AHT and B13. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):326–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.326-336.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J. A numerical taxonomic study of human oral streptococci. Odontol Revy. 1968;19(2):137–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper H. R., Chorpenning F. W., Roses S. Lipid-free glycerol teichoic acids with potent membrane-binding activity. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):462–469. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.462-469.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coykendall A. L., Specht P. A. DNA base sequence homologies among strains of Streptococcus sanguis. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Nov;91(1):92–98. doi: 10.1099/00221287-91-1-92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARMER E. D. Serological subdivisions among the Lancefield group H streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Oct;11(2):131–138. doi: 10.1099/00221287-11-2-131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R. Physiological differentiation of viridans streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Feb;5(2):184–201. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.2.184-201.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer W., Koch H. U., Rösel P., Fiedler F. Alanine ester-containing native lipoteichoic acids do not act as lipoteichoic acid carrier. Isolation, structural and functional characterization. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4557–4562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., van Houte J. On the formation of dental plaques. J Periodontol. 1973 Jun;44(6):347–360. doi: 10.1902/jop.1973.44.6.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewett M. J., Knox K. W., Wicken A. J. Studies on the group F antigen of lactobacilli: detection of antibodies by haemagglutination. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Mar;60(3):315–322. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-3-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. W., Hewett M. J., Wicken A. J. Studies on the group F antigen of lactobacilli: antigenicity and serological specificity of teichoic acid preparations. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Mar;60(3):303–313. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-3-303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. W., Wicken A. J. Serological properties of the wall and membrane teichoic acids from Lactobacillus helveticus NCIB 8025. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Oct;63(2):237–248. doi: 10.1099/00221287-63-2-237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C., PERLMANN G. E. Preparation and properties of type-specific M antigen isolated from a group A, type 1 hemolytic streptococcus. J Exp Med. 1952 Jul;96(1):71–82. doi: 10.1084/jem.96.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao M., Rosen S. Serotypes of Streptococcus sanguis from six-year-old children. J Dent Res. 1978 Jan;57(1):54–54. doi: 10.1177/00220345780570012101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxted W. R., Fraser C. A. Sensitivity to acid of the type antigens of Streptococcus faecalis. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Apr;43(1):145–150. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-1-145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANTZ L. A., RANDALL E. Use of autoclaved extracts of hemolytic streptococci for serological grouping. Stanford Med Bull. 1955 May;13(2):290–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosan B. A comparison of the phenol water and Rantz and Randall teichoic acid antigens in group H streptococci. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1978;107:791–802. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3369-2_89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosan B. Absence of glycerol teichoic acids in certain oral streptococci. Science. 1978 Sep 8;201(4359):918–920. doi: 10.1126/science.684416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosan B. Antigens of Streptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun. 1973 Feb;7(2):205–211. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.2.205-211.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosan B. Determination of muramic acid in automated amino acid analysis. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):624–628. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosan B. Relationship of the cell wall composition of group H streptococci and Streptococcus sanguis to their serological properties. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1144–1153. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1144-1153.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvestri L. J., Craig R. A., Ingram L. O., Hoffmann E. M., Bleiweis A. S. Purification of lipoteichoic acids by using phosphatidyl choline vesicles. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):107–118. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.107-118.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WICKEN A. J., ELLIOTT S. D., BADDILEY J. The identity of streptococcal group D antigen with teichoic acid. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 May;31:231–239. doi: 10.1099/00221287-31-2-231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washburn M. R., White J. C., Niven C. F., Jr Streptococcus S.B.E.: Immunological Characteristics. J Bacteriol. 1946 Jun;51(6):723–729. doi: 10.1128/jb.51.6.723-729.1946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. C., Niven C. F., Jr Streptococcus S.B.E.: A Streptococcus Associated with Subacute Bacterial Endocarditis. J Bacteriol. 1946 Jun;51(6):717–722. doi: 10.1128/jb.51.6.717-722.1946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Gibbens J. W., Knox K. W. Comparative studies on the isolation of membrane lipoteichoic acid from Lactobacillus fermenti. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jan;113(1):365–372. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.1.365-372.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Knox K. W. Characterization of group N streptococcus lipoteichoic acid. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):973–981. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.973-981.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Knox K. W. Lipoteichoic acids: a new class of bacterial antigen. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1161–1167. doi: 10.1126/science.46620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Knox K. W. Studies on the group F antigen of lactobacilli: isolation of a teichoic acid-lipid complex from Lactobacillus fermenti NCTC 6991. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Mar;60(3):293–301. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-3-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]