Abstract
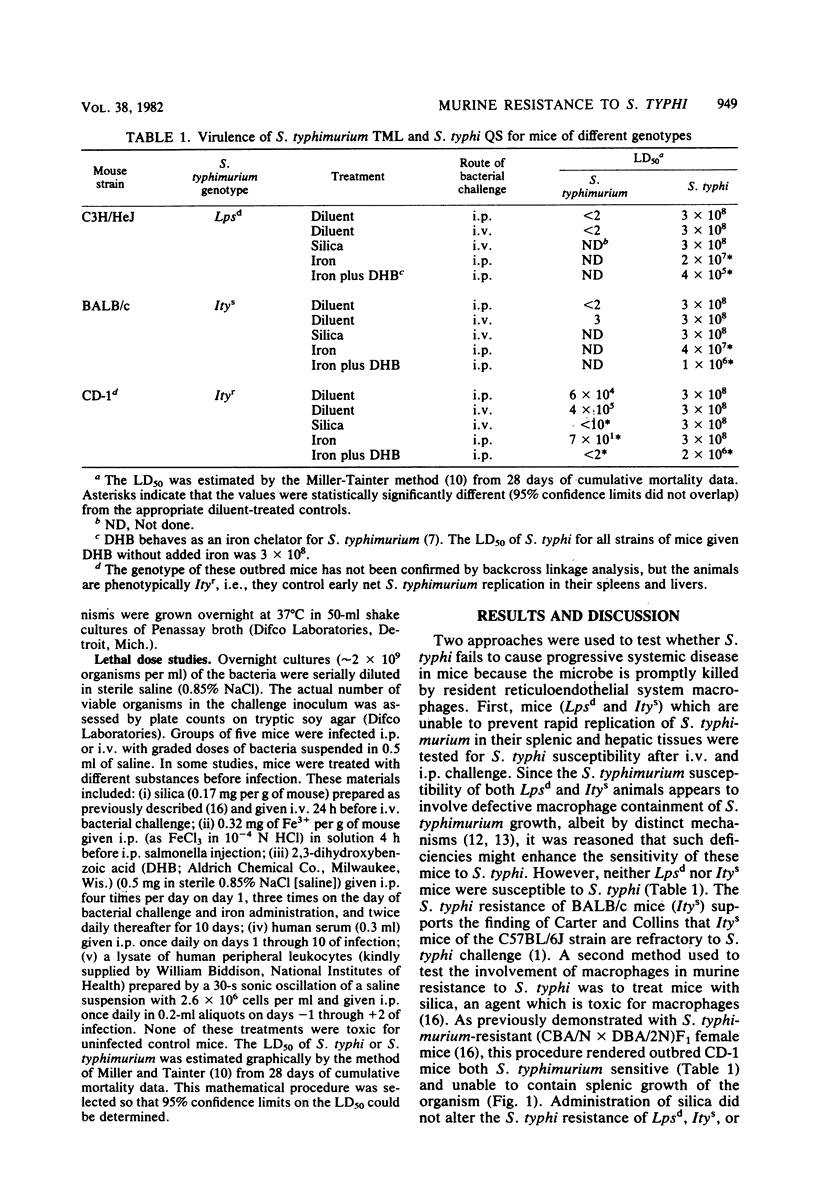
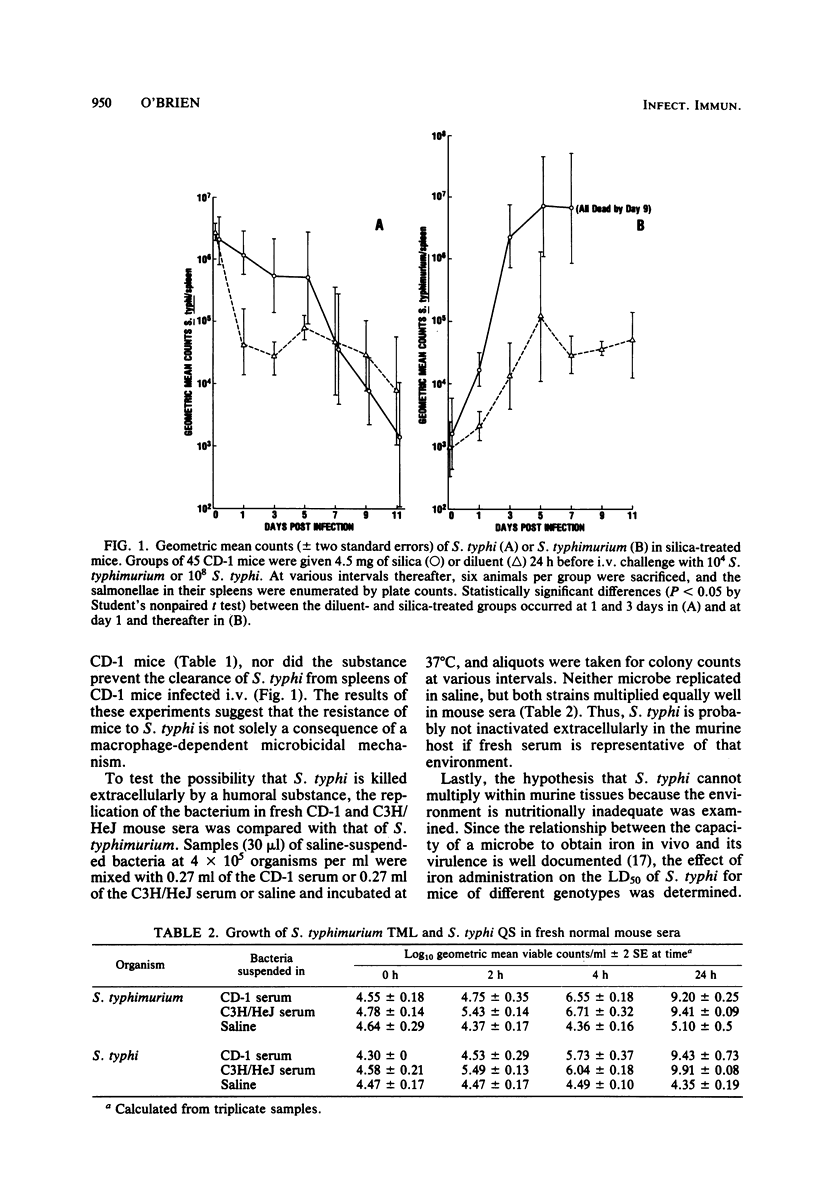
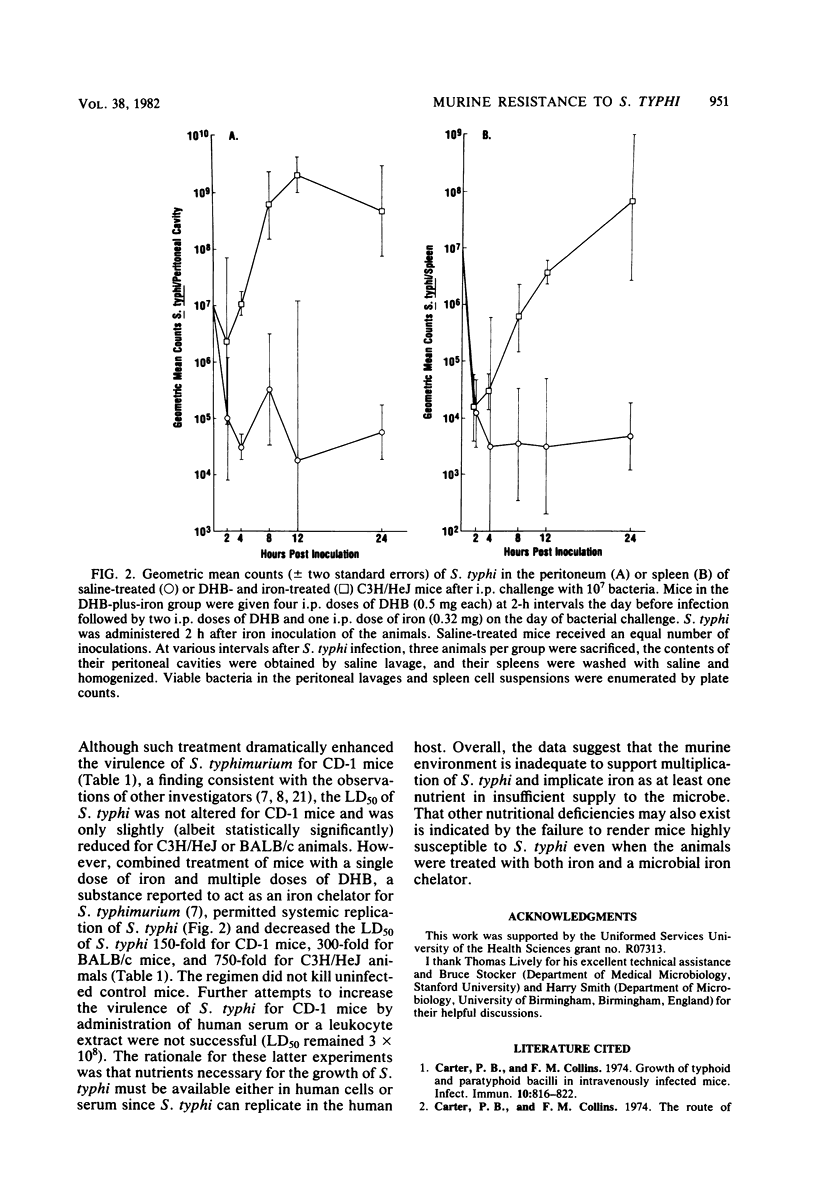
The basis for the natural resistance of mice to Salmonella typhi was examined. In contrast to Salmonella typhimurium, the virulence of S. typhi for mice was independent of the mouse strain and was not affected by inactivation of murine macrophages with silica. However, mice were more susceptible to S. typhi when given iron alone or iron and an iron chelator. The results suggest that the failure of S. typhi to undergo net growth in murine tissues reflects an inability of the bacterium to multiply rather than rapid killing by resident macrophages.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carter P. B., Collins F. M. Growth of typhoid and paratyphoid bacilli in intravenously infected mice. Infect Immun. 1974 Oct;10(4):816–822. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.4.816-822.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Carter P. B. Growth of salmonellae in orally infected germfree mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):41–47. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.41-47.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Salmonellosis in orally infected specific pathogen-free C57B1 mice. Infect Immun. 1972 Feb;5(2):191–198. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.2.191-198.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Broitman S. A., Zamcheck N. Salmonella enteritis. II. Fulminant diarrhea in and effects on the small intestine. Am J Dig Dis. 1971 Nov;16(11):1007–1013. doi: 10.1007/BF02235013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornick R. B., Greisman S. E., Woodward T. E., DuPont H. L., Dawkins A. T., Snyder M. J. Typhoid fever: pathogenesis and immunologic control. N Engl J Med. 1970 Sep 24;283(13):686–691. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197009242831306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. L., Peterson C. M., Grady R. W., Kumbaraci T., Cerami A., Graziano J. H. Effects of iron chelators and iron overload on Salmonella infection. Nature. 1977 May 5;267(5606):63–65. doi: 10.1038/267063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvach J. T., Wiles T. I., Mellencamp M. W., Kochan I. Use of transferrin-iron enterobactin complexes as the source of iron by serum-exposed bacteria. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):439–445. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.439-445.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B., Blanden R. V., Collins F. M. Host-parasite relations in mouse typhoid. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):573–583. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Rosenstreich D. L., Scher I., Campbell G. H., MacDermott R. P., Formal S. B. Genetic control of susceptibility to Salmonella typhimurium in mice: role of the LPS gene. J Immunol. 1980 Jan;124(1):20–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Rosenstreich D. L., Taylor B. A. Control of natural resistance to Salmonella typhimurium and Leishmania donovani in mice by closely linked but distinct genetic loci. Nature. 1980 Oct 2;287(5781):440–442. doi: 10.1038/287440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Scher I., Campbell G. H., MacDermott R. P., Formal S. B. Susceptibility of CBA/N mice to infection with Salmonella typhimurium: influence of the X-linked gene controlling B lymphocyte function. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):720–724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Scher I., Formal S. B. Effect of silica on the innate resistance of inbred mice to Salmonella typhimurium infection. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):513–520. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.513-520.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. M., Finkelstein R. A. The critical role of iron in host-bacterial interactions. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jun;61(6):1428–1440. doi: 10.1172/JCI109062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant J., Glynn A. A. Genetics of resistance to infection with Salmonella typhimurium in mice. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jan;133(1):72–78. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant J., Glynn A. A. Locating salmonella resistance gene on mouse chromosome 1. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Jul;37(1):1–6. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell C. J., Jr, DeSett C. R., Lowenthal J. P., Berman S. The effect of adding iron to mucin on the enhancement of virulence for mice of Salmonella typhi strain TY 2. J Biol Stand. 1980;8(1):79–85. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(80)80049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puschmann M., Ganzoni A. M. Increased resistance of iron-deficient mice to salmonella infection. Infect Immun. 1977 Sep;17(3):663–664. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.3.663-664.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPAUN J. STUDIES ON THE INFLUENCE OF THE ROUTE OF IMMUNIZATION IN THE ACTIVE MOUSE PROTECTION TEST WITH INTRAPERITONEAL CHALLENGE FOR POTENCY ASSAY OF TYPHOID VACCINES. Bull World Health Organ. 1964;31:793–798. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher I., Ahmed A., Strong D. M., Steinberg A. D., Paul W. E. X-linked B-lymphocyte immune defect in CBA/HN mice. I. Studies of the function and composition of spleen cells. J Exp Med. 1975 Apr 1;141(4):788–803. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J., Kelly K., Largen M., Taylor B. A. The genetic mapping of a defective LPS response gene in C3H/HeJ mice. J Immunol. 1978 Feb;120(2):422–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


