Abstract
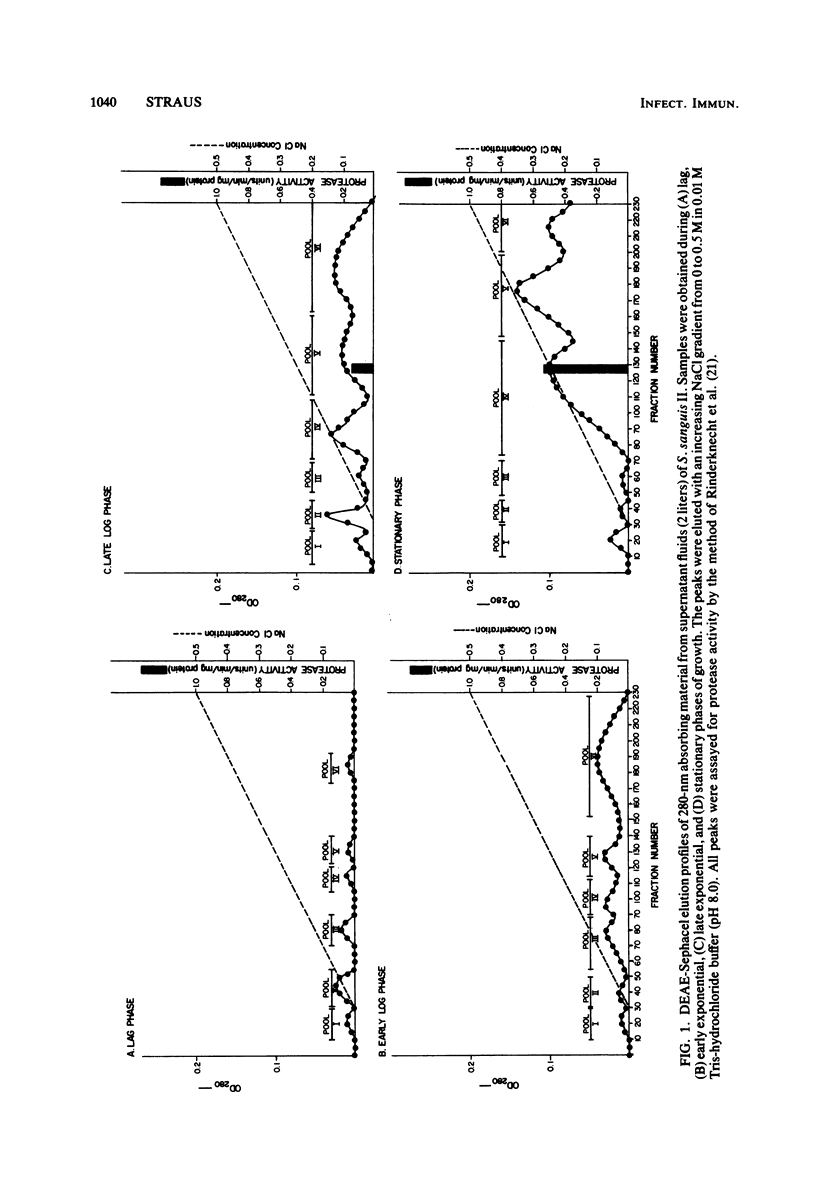
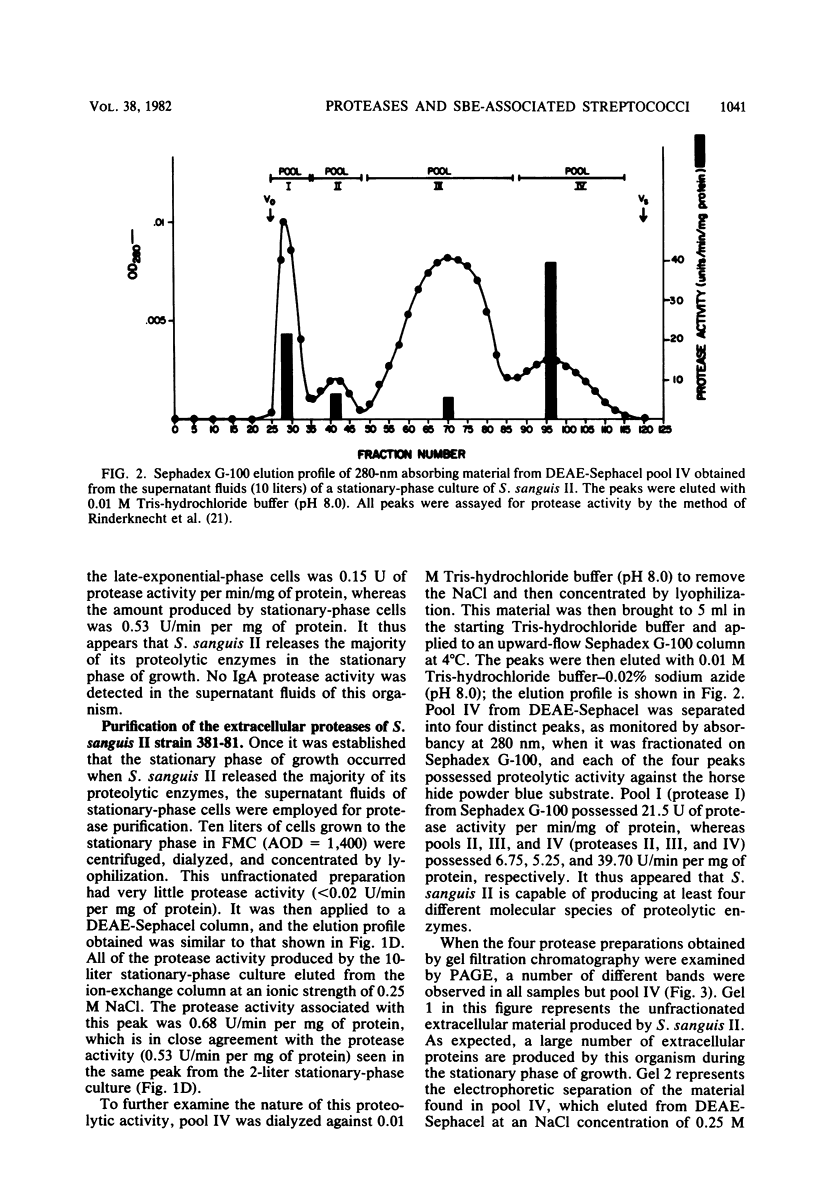
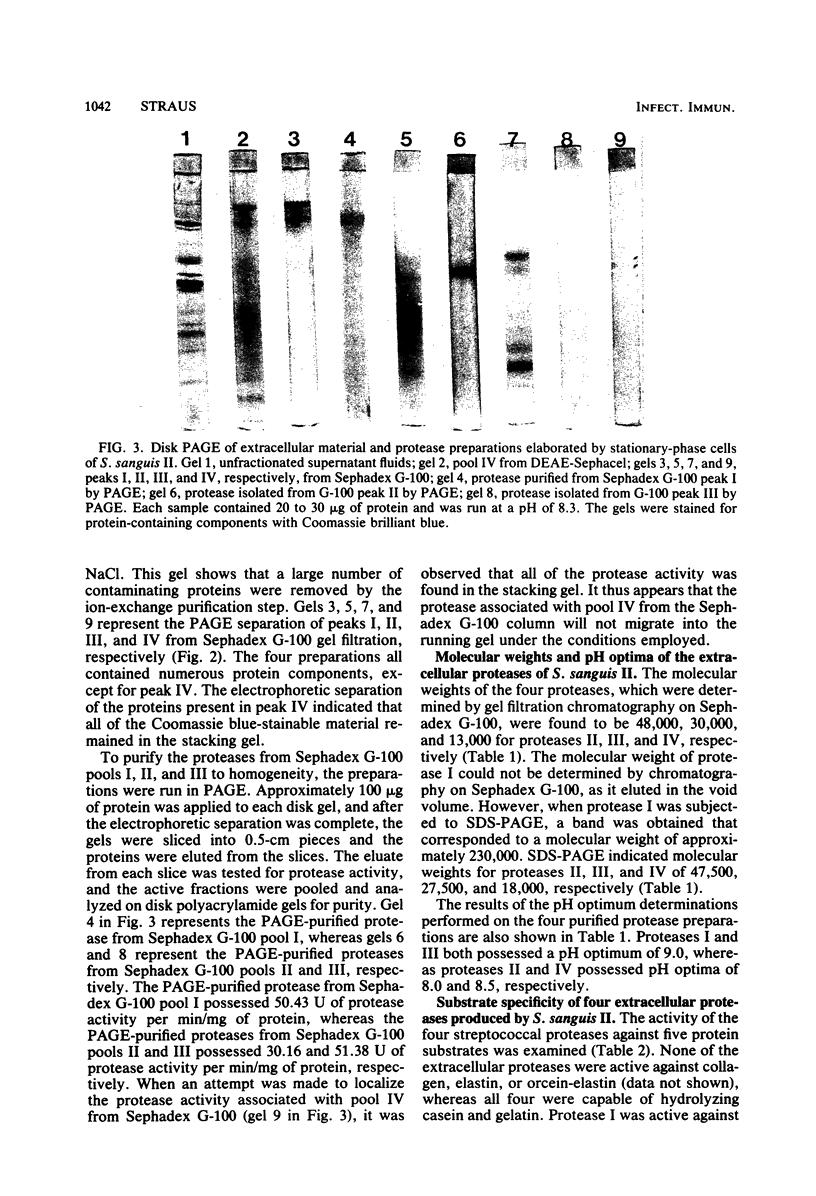
A viridans streptococcus (Streptococcus sanguis biotype II) isolated from the blood of a patient with subacute bacterial endocarditis was examined for protease production. In broth culture, extracellular proteolytic enzymes were not produced by this organism until after the early exponential phase of growth, with maximal protease production occurring during the stationary phase. Four distinct proteases were isolated and purified from the supernatant fluids of stationary-phase cultures, employing a combination of ion-exchange column chromatography, gel filtration column chromatography, and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. All four proteases could be eluted from a diethylaminoethyl cellulose column at a sodium chloride gradient concentration of 0.25 M but were separable by gel filtration chromatography on a Sephadex G-100 column. They varied in molecular weights as determined by gel filtration and sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis from approximately 13,000 to 230,000. All four proteases had pH optima of between 8.0 and 9.0, and two of the proteases were active against casein, human serum albumin, and gelatin but were not active against elastin and collagen. The remaining two proteases were able to degrade only casein and gelatin. These results show that S. sanguis is able to excrete maximal levels of potentially destructive enzymes when the organisms are not actively multiplying. This finding may explain some of the damage caused in heart tissue by these organisms during subacute bacterial endocarditis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durack D. T., Beeson P. B. Experimental bacterial endocarditis. I. Colonization of a sterile vegetation. Br J Exp Pathol. 1972 Feb;53(1):44–49. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durack D. T., Beeson P. B. Experimental bacterial endocarditis. II. Survival of a bacteria in endocardial vegetations. Br J Exp Pathol. 1972 Feb;53(1):50–53. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durack D. T. Experimental bacterial endocarditis. IV. Structure and evolution of very early lesions. J Pathol. 1975 Feb;115(2):81–89. doi: 10.1002/path.1711150204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genco R. J., Plaut A. G., Moellering R. C., Jr Evaluation of human oral organisms and pathogenic Streptococcus for production of IgA protease. J Infect Dis. 1975 May;131 (Suppl):S17–S21. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.supplement.s17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnosspelius G. Purification and properties of an extracellular protease from Myxococcus virescens. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):17–25. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.17-25.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K., Ramirez-Ronda C. H., Holmes R. K., Sanford J. P. Adherence of bacteria to heart valves in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1364–1370. doi: 10.1172/JCI108216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutschik E., Møller S., Christensen N. Experimental endocarditis in rabbits. 3. Significance of the proteolytic capacity of the infecting strains of Streptococcus faecalis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1979 Dec;87(6):353–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook E. W., 3rd, Sande M. A. Role of the vegetation in experimental Streptococcus viridans endocarditis. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1433–1438. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1433-1438.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. G., Morris J. M., Berk R. S. The extracellular protease from Pseudomonas aeruginosa exhibiting elastase activity. Can J Microbiol. 1967 Jun;13(6):711–719. doi: 10.1139/m67-093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labib R. S., Calvanico N. J., Tomasi T. B., Jr Studies on extracellular proteases of Streptococcus sanguis. Purification and characterization of a human IgA1 specific protease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 12;526(2):547–559. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90145-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y., Means G. E., Feeney R. E. The action of proteolytic enzymes on N,N-dimethyl proteins. Basis for a microassay for proteolytic enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 10;244(3):789–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht H., Geokas M. C., Silverman P., Haverback B. J. A new ultrasensitive method for the determination of proteolytic activity. Clin Chim Acta. 1968 Aug;21(2):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(68)90127-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SACHAR L. A., WINTER K. K., SICHER N., FRANKEL S. Photometric method for estimation of elastase activity. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Nov;90(2):323–326. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-22022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D. C., Mattingly S. J., Milligan T. W., Doran T. I., Nealon T. J. Protease production by clinical isolates of type III group B streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):421–423. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.421-423.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D. C., Mattingly S. J., Milligan T. W. Production of extracellular material by streptococci associated with subacute bacterial endocarditis. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):148–156. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.148-156.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terleckyj B., Willett N. P., Shockman G. D. Growth of several cariogenic strains of oral streptococci in a chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):649–655. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.649-655.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Houte J., Jordan H. V., Bellack S. Proportions of Streptococcus sanguis, an organism associated with subacute bacterial endocarditis, in human feces and dental plaque. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):658–659. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.658-659.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein L., Schlesinger J. J. Pathoanatomic, pathophysiologic and clinical correlations in endocarditis (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1974 Oct 17;291(16):832–837. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197410172911609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



