Abstract
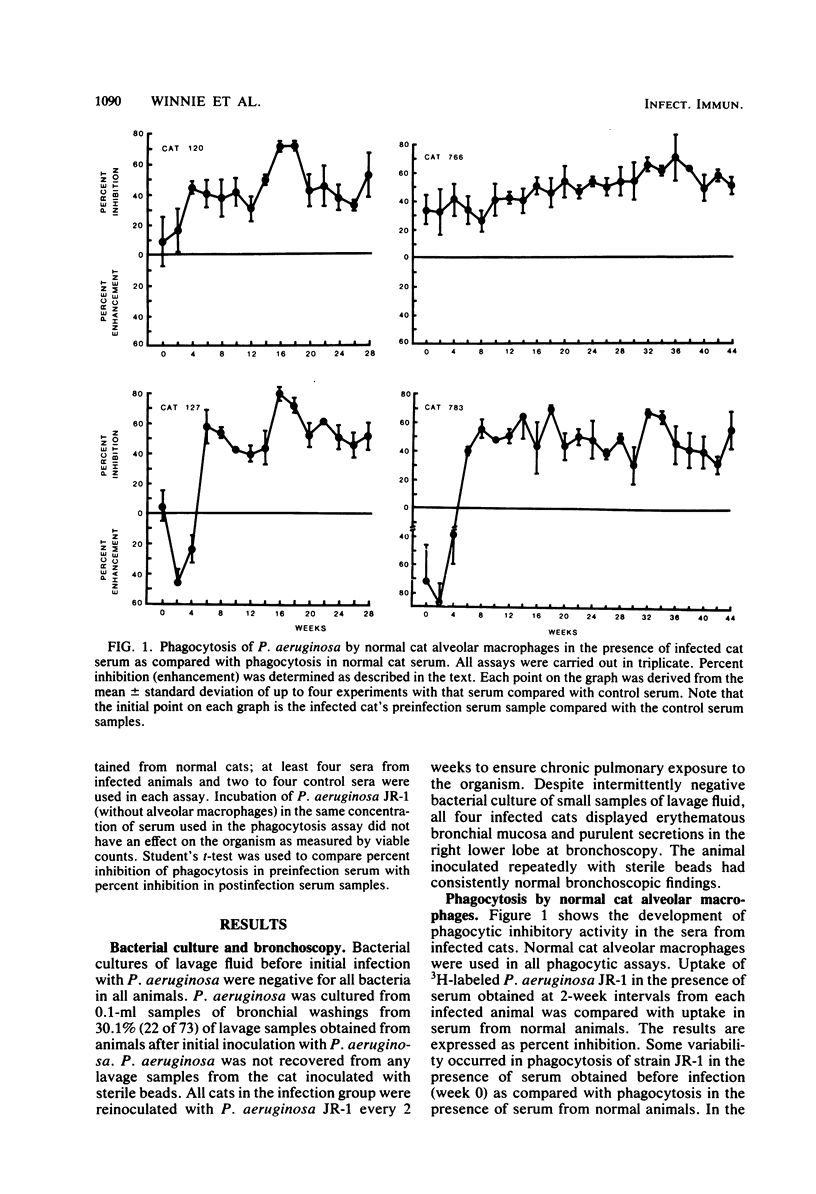
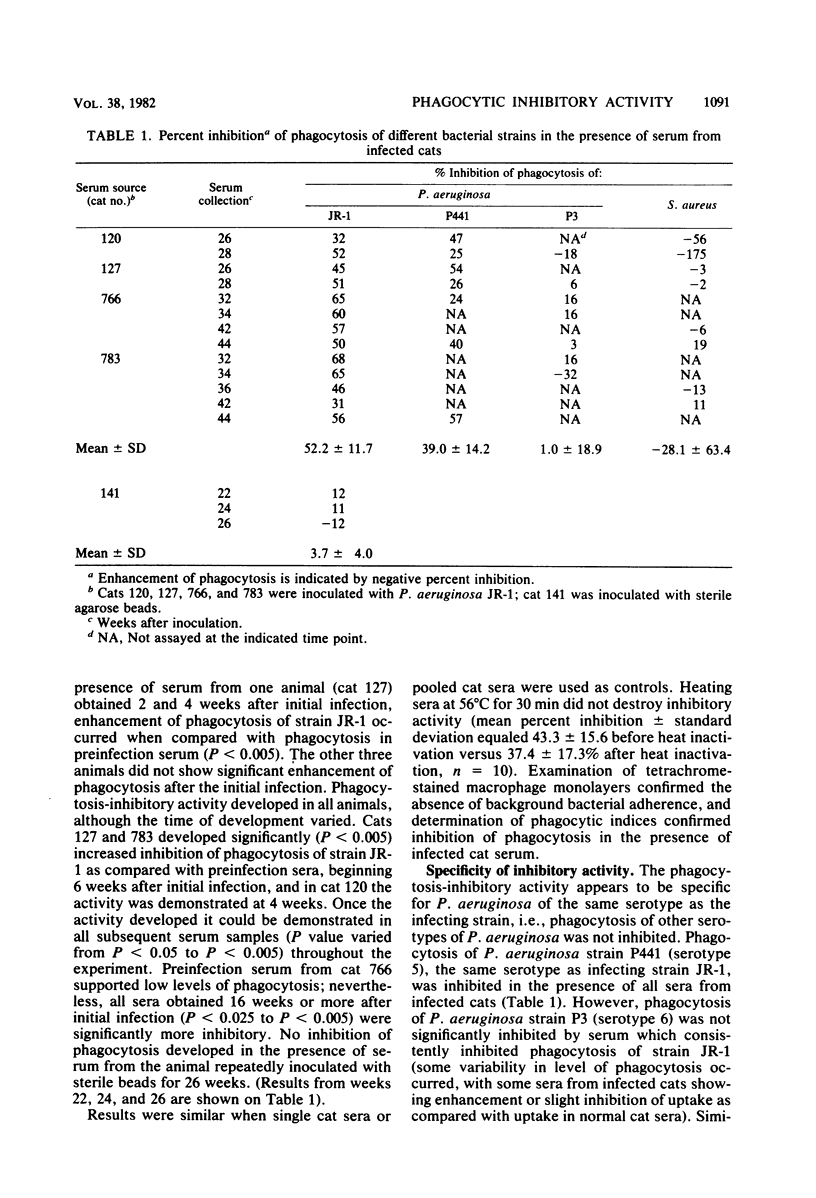
Chronic pulmonary infection has been established in cats by repeated intrapulmonary inoculation of viable Pseudomonas aeruginosa enmeshed in agarose beads. In the serum of all chronically infected animals, a substance(s) developed which inhibited phagocytosis of P. aeruginosa by normal cat alveolar macrophages. Phagocytosis was measured by incubating macrophage monolayers (5 X 10(5) alveolar macrophages) for 20 min in the presence of 3H-labeled bacteria and 5% serum from control or infected animals. Inhibitory activity developed 4 to 16 weeks after initial infection, and inhibition of phagocytosis of P. aeruginosa in the presence of infected cat serum ranged from 30 to 79%. After inhibitory activity developed, it persisted throughout the remainder of the experiment in each animal. The activity was specific for P. aeruginosa of the infecting serotype and did not affect phagocytosis of gram-positive organisms. Inhibitory activity was unchanged by heating serum at 56 degrees C for 30 min. We have previously described a P. aeruginosa-specific, heat-stable, phagocytosis-inhibitory activity in the serum of patients with cystic fibrosis. Since inhibitory activity also develops in cats with chronic P. aeruginosa pulmonary infection, such activity may not be a primary intrinsic abnormality in patients with cystic fibrosis. The animal model described here offers a system for following the development of and for characterization of the P. aeruginosa-specific phagocytosis-inhibitory activity.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cash H. A., Woods D. E., McCullough B., Johanson W. G., Jr, Bass J. A. A rat model of chronic respiratory infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Mar;119(3):453–459. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.3.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fick R. B., Jr, Naegel G. P., Matthay R. A., Reynolds H. Y. Cystic fibrosis pseudomonas opsonins. Inhibitory nature in an in vitro phagocytic assay. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):899–914. doi: 10.1172/JCI110345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MYRVIK Q., LEAKE E. S., FARISS B. Studies on pulmonary alveolar macrophages from the normal rabbit: a technique to procure them in a high state of purity. J Immunol. 1961 Feb;86:128–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y., Thompson R. E. Pulmonary host defenses. I. Analysis of protein and lipids in bronchial secretions and antibody responses after vaccination with pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Immunol. 1973 Aug;111(2):358–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomassen M. J., Boxerbaum B., Demko C. A., Kuchenbrod P. J., Dearborn D. G., Wood R. E. Inhibitory effect of cystic fibrosis serum on pseudomonas phagocytosis by rabbit and human alveolar macrophages. Pediatr Res. 1979 Sep;13(9):1085–1088. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197909000-00030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomassen M. J., Demko C. A., Boxerbaum B., Stern R. C., Kuchenbrod P. J. Multiple of isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa with differing antimicrobial susceptibility patterns from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Infect Dis. 1979 Dec;140(6):873–880. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.6.873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. E., Boat T. F., Doershuk C. F. Cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Jun;113(6):833–878. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.113.6.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. E. Pseudomonas: the compromised host. Hosp Pract. 1976 Aug;11(8):91–100. doi: 10.1080/21548331.1976.11706983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Sant'Agnese P. A., Davis P. B. Research in cystic fibrosis (third of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Sep 9;295(11):597–602. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197609092951105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


