Abstract
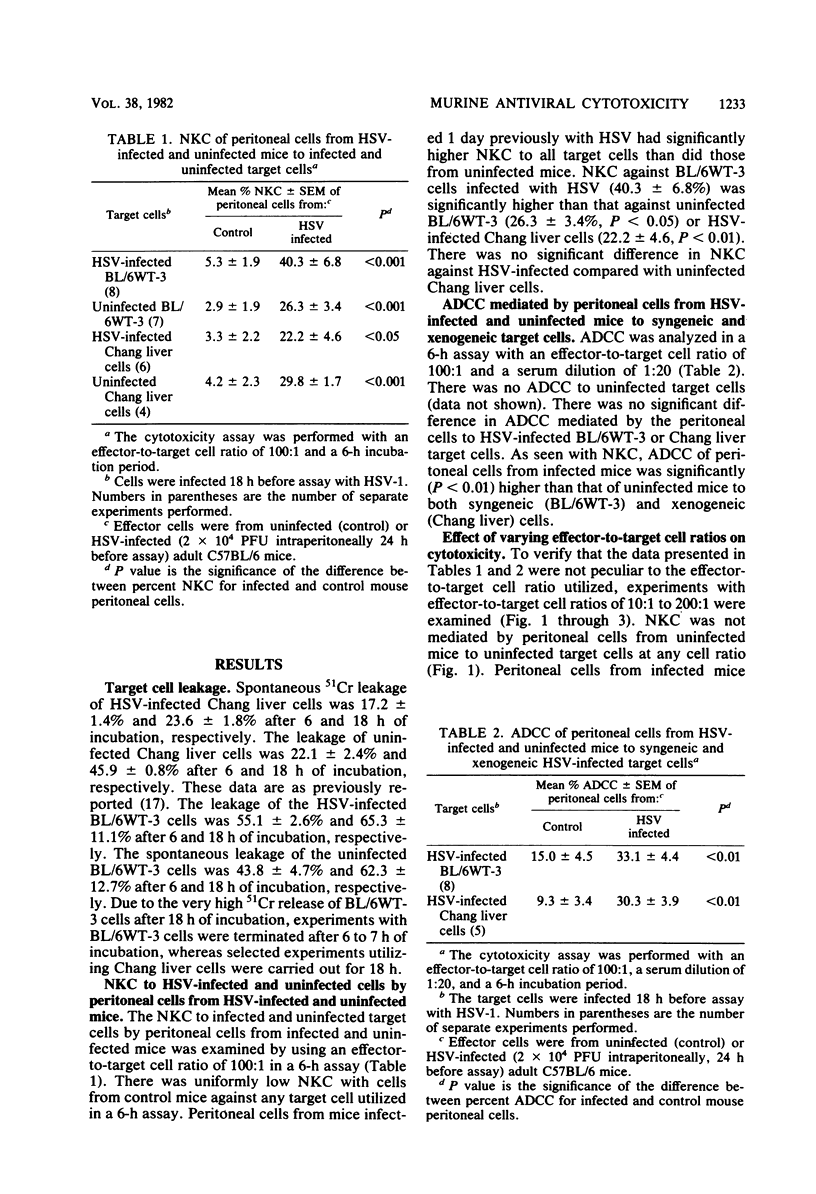
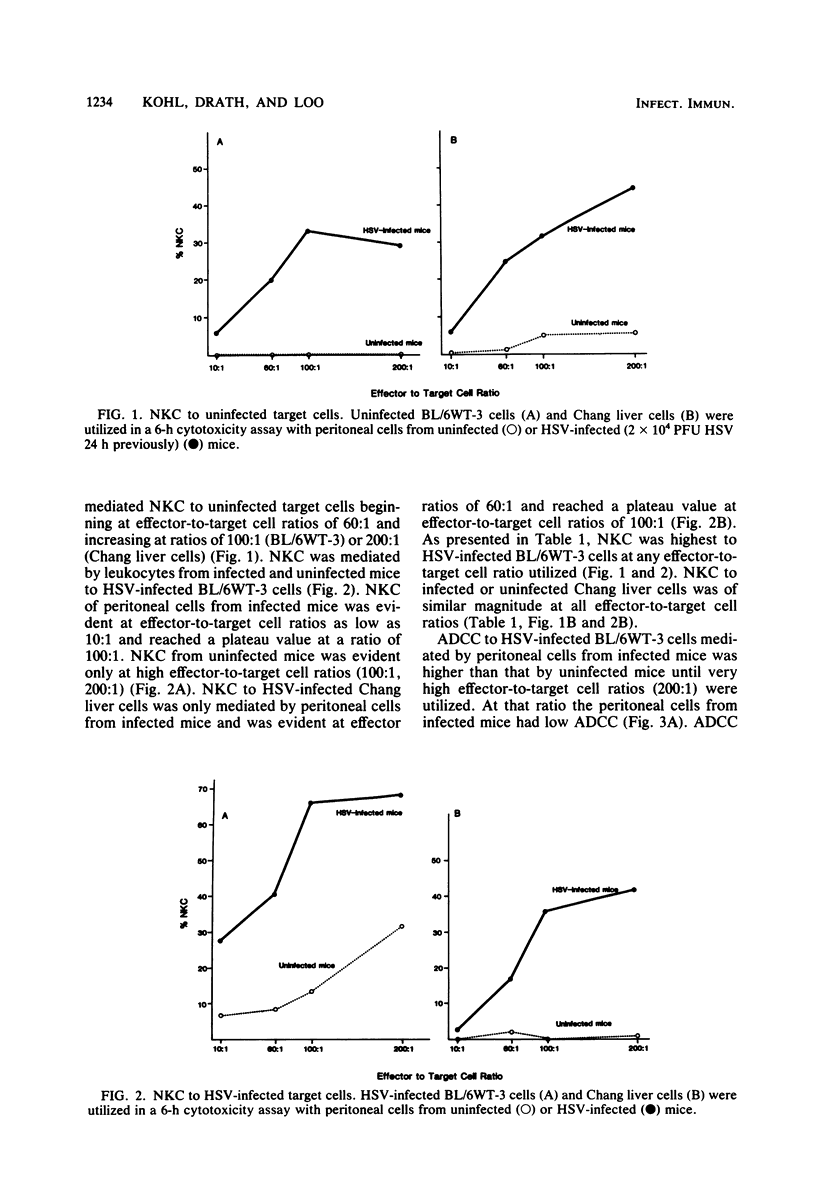
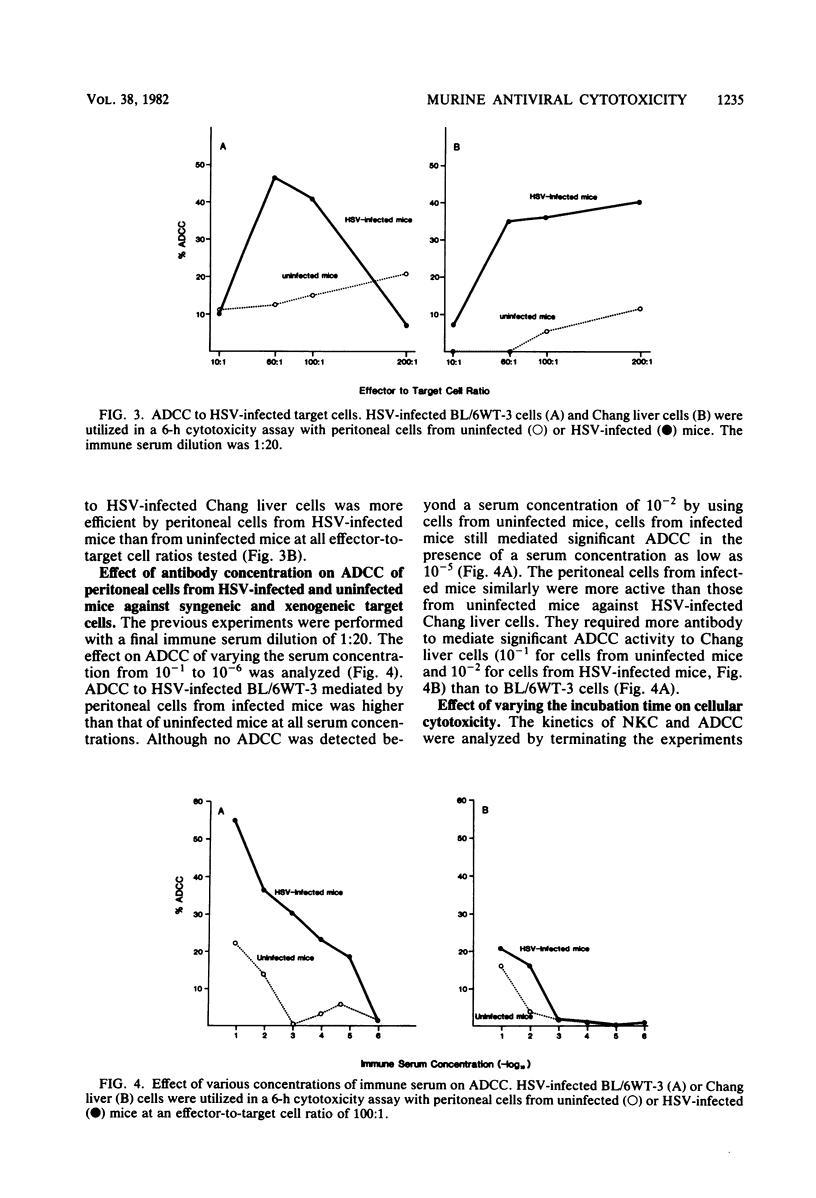
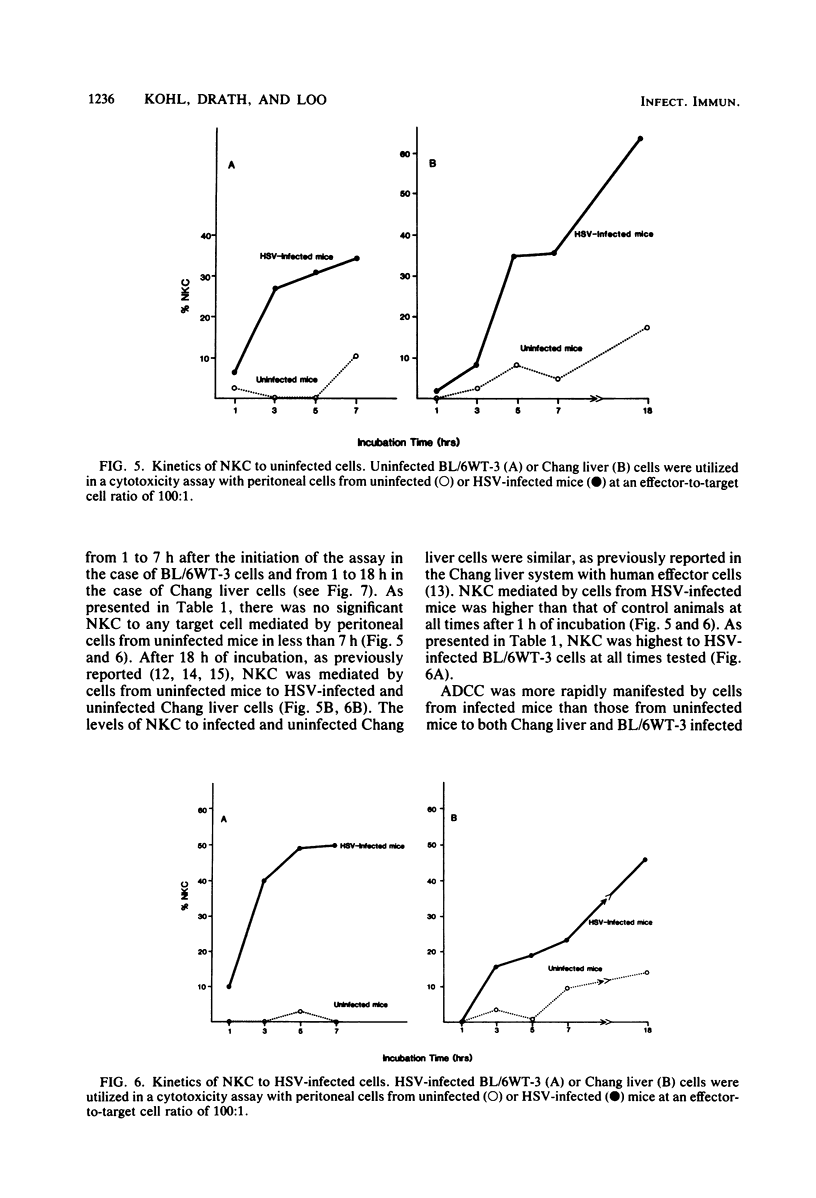
Cellular cytotoxicity of C57BL/6 adult mice peritoneal cells to xenogeneic (Chang liver) and syngeneic (BL/6-WT3) herpes simplex virus (HSV)-infected cells was analyzed in a 6-h 51Cr release assay. There was no difference in antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity to either target. There was no natural killer cytotoxicity to targets with cells from uninfected mice except at very high effector cell ratios. HSV-infected (2 X 10(4) PFU intraperitoneally 1 day previously) mice mediated significantly higher antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and required less antibody (10(-5) versus 10(-2) dilution), fewer cells, and less time to kill than cells from uninfected mice. HSV-infected mice mediated natural killer cytotoxicity but preferentially killed syngeneic HSV-infected cells. Stimulation of cytotoxicity was not virus specific since influenza-infected mice mediated similar levels of cytotoxicity to HSV-infected targets. There was no difference in morphology (95% macrophage) or in the percentage of FcR-positive cells, but infected mice had more peritoneal cells and generated higher levels of superoxide in response to opsonized zymosan or phorbolmyristate acetate. These data demonstrate nonspecific virus-stimulated metabolic and effector cell function which may enhance clearance of virus in an infected host.
Full text
PDF

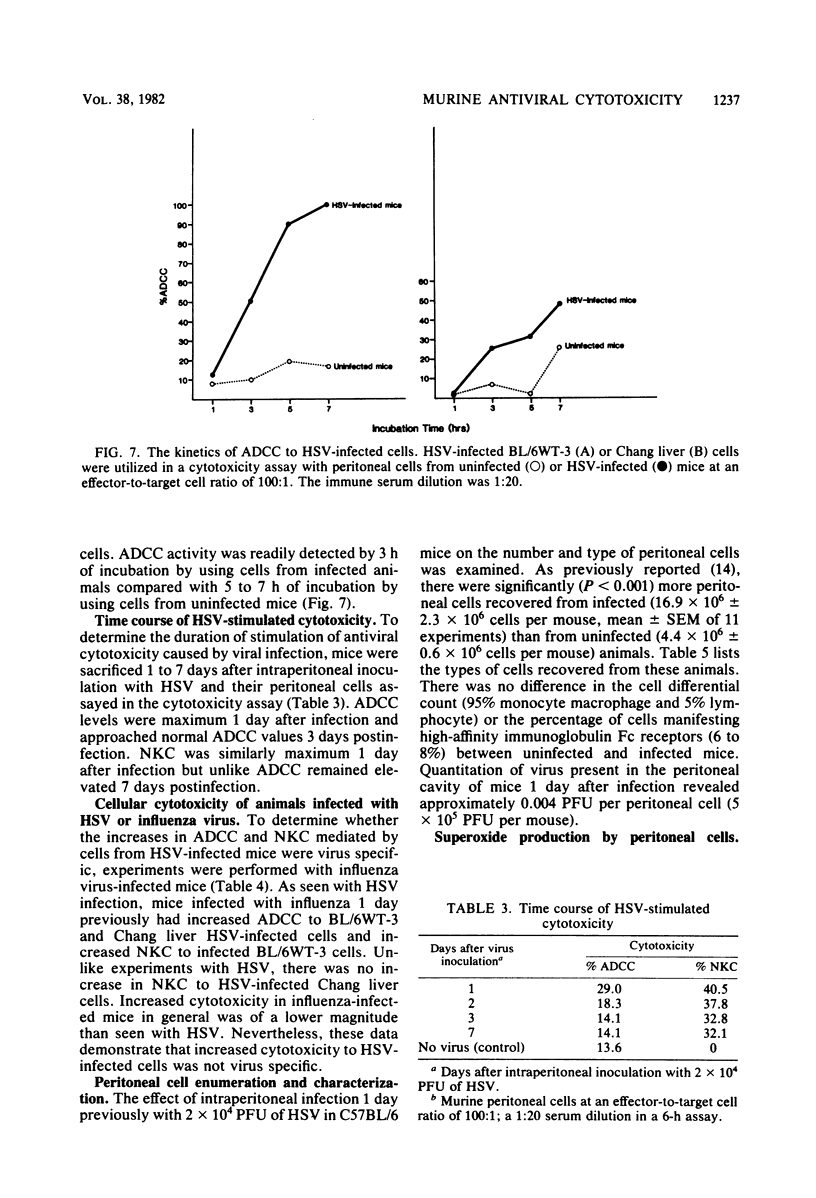
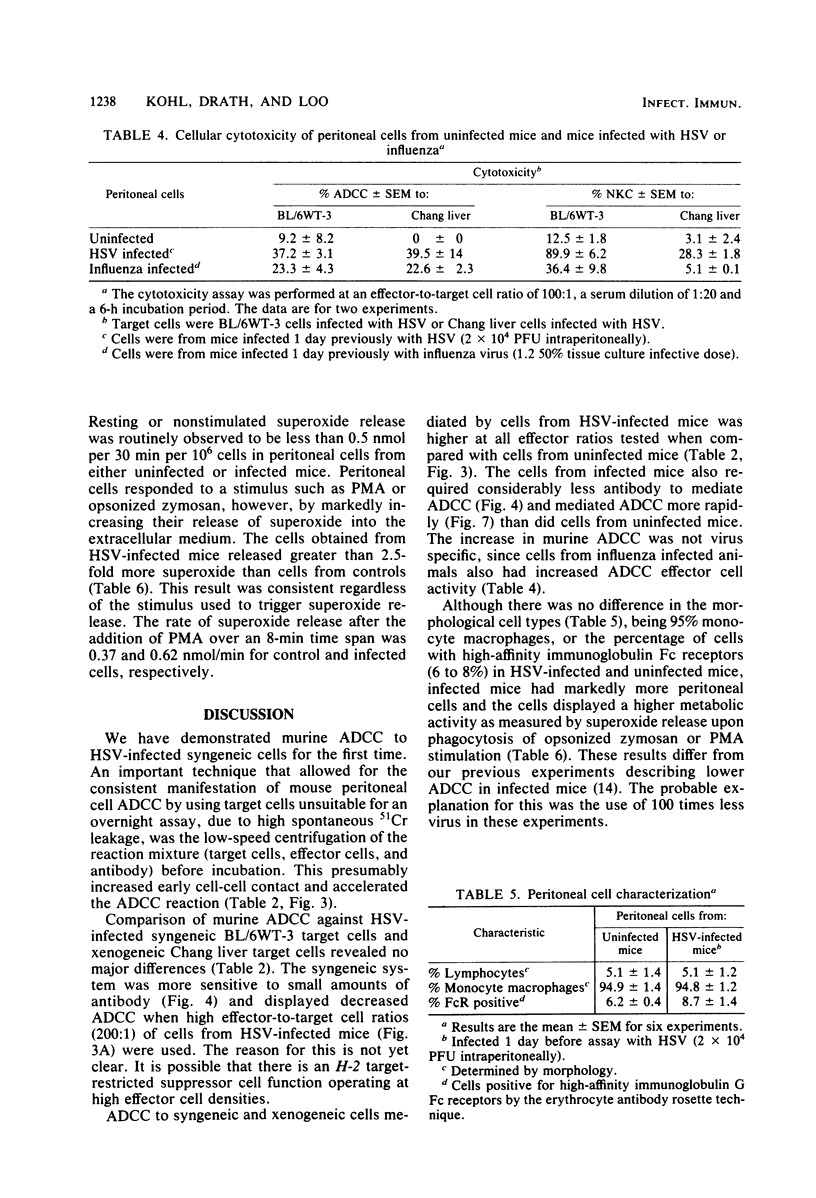



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armerding D., Mayer P., Scriba M., Hren A., Rossiter H. In-vivo modulation of macrophage functions by herpes simplex virus type 2 in resistant and sensitive inbred mouse strains. Immunobiology. 1981;160(2):217–227. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(81)80049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armerding D., Rossiter H. Induction of natural killer cells by herpes-simplex virus type 2 in resistant and sensitive inbred mouse strains. Immunobiology. 1981;158(4):369–379. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(81)80007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armerding D., Simon M. M., Hämmerling U., Hämmerling G. J., Rossiter H. Function, target-cell preference and cell-surface characteristics of herpes-simplex virus type-2-induced non-antigen-specific killer cells. Immunobiology. 1981;158(4):347–368. doi: 10.1016/s0171-2985(81)80006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter V. C., Schaffer P. A., Tevethia S. S. The involvement of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins in cell-mediated immunity. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1655–1660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ching C., Lopez C. Natural killing of herpes simplex virus type 1-infected target cells: normal human responses and influence of antiviral antibody. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):49–56. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.49-56.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drath D. B., Karnovsky M. L. Superoxide production by phagocytic leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1975 Jan 1;141(1):257–262. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.1.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Droller M. J., Perlmann P., Schneider M. U. Enhancement of natural and antibody-dependent lymphocyte cytotoxicity by drugs which inhibit prostaglandin production by tumor target cells. Cell Immunol. 1978 Aug;39(1):154–164. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90090-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grewal A. S., Rouse B. T., Babiuk L. A. Mechanisms of resistant of herpesviruses: comparison of the effectiveness of different cell types in mediating antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):698–703. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.698-703.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heron I., Moller-Larsen A., Berg K. Effector cell involved in cell-mediated cytotoxicity to cells infected with herpes simplex virus type 1. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):48–53. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.48-53.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klassen D. K., Sagone A. L., Jr Evidence for both oxygen and non-oxygen dependent mechanisms of antibody sensitized target cell lysis by human monocytes. Blood. 1980 Dec;56(6):985–992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S., Cahall D. L., Walters D. L., Schaffner V. E. Murine antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity to herpes simplex virus-infected target cells. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):25–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S., Frazier J. J., Greenberg S. B., Pickering L. K., Loo L. S. Interferon induction of natural killer cytotoxicity in human neonates. J Pediatr. 1981 Mar;98(3):379–384. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80699-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S., Lawman M. J., Rouse B. T., Cahall D. L. Effect of herpes simplex virus infection on murine antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and natural killer cytotoxicity. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):704–711. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.704-711.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S., Loo L. S. Ontogeny of murine cellular cytotoxicity to herpes simplex virus-infected cells. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):847–850. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.847-850.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S., Pickering L. K., Cleary T. G., Steinmetz K. D., Loo L. S. Human colostral cytotoxicity. II. Relative defects in colostral leukocyte cytotoxicity and inhibition of peripheral blood leukocyte cytotoxicity by colostrum. J Infect Dis. 1980 Dec;142(6):884–891. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.6.884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S., Starr S. E., oleske J. M., Shore S. L., Ashman R. B., Nahmias A. J. Human monocyte-macrophage-mediated antibody-dependent cytotoxicity to herpes simplex virus-infected cells. J Immunol. 1977 Mar;118(3):729–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller C. A., LoBuglio A. F. Monocyte-mediated antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity: the role of the metabolic burst. Blood. 1981 Aug;58(2):293–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawman M. J., Rouse B. T., Courtney R. J., Walker R. D. Cell-mediated immunity against herpes simplex induction of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):133–139. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.133-139.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melewicz F. M., Shore S. L., Ades E. W., Phillips D. J. The mononuclear cell in human blood which mediates antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity to virus-infected target cells. II. Identification as a K cell. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):567–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H., Pancake S. J., Noseworthy J., Karnovsky M. L. Measurement of rates of phagocytosis: the use of cellular monolayers. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jan;40(1):216–224. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.1.216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moller-Larsen A., Heron I., Haahr S. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity to herpes-infected cells in humans: dependence on antibodies. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):43–47. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.43-47.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash A. A., Phelan J., Wildy P. Cell-mediated immunity in herpes simplex virus-infected mice: H-2 mapping of the delayed-type hypersensitivity response and the antiviral T cell response. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1260–1262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C., Cohn Z. Role of oxygen-dependent mechanisms in antibody-induced lysis of tumor cells by activated macrophages. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):198–208. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oleske J. M., Ashman R. B., Kohl S., Shore S. L., Starr S. E., Wood P., Nahmias A. J. Human polymorphonuclear leucocytes as mediators of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity to herpes simplex virus-infected cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Mar;27(3):446–453. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfizenmaier K., Jung H., Starzinski-Powitz A., Röllinghoff M., Wagner H. The role of T cells in anti-herpes simplex virus immunity. I. Induction of antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):939–944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piontek G. E., Weltzin R., Tompkins W. A. Enhanced cytotoxicity of mouse natural killer cells for vaccinia and herpes virus-infected targets. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1980 Feb;27(2):175–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rager-Zisman B., Bloom B. R. Immunological destruction of herpes simplex virus I infected cells. Nature. 1974 Oct 11;251(5475):542–543. doi: 10.1038/251542a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramshaw I. A. Lysis of herpesvirus-infected cells by immune spleen cells. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):767–769. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.767-769.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichman R. C., Dolin R., Vincent M. M., Fauci A. S. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity in recurrent herpes simplex virus infections in man. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Sep;155(4):571–576. doi: 10.3181/00379727-155-39853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodda S. J., White D. O. Cytotoxic macrophages: a rapid nonspecific response to viral infection. J Immunol. 1976 Dec;117(6):2067–2072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rola-Pleszczynski M. In vitro induction of human cell-mediated cytotoxicity directed against herpes simplex virus-infected cells. Kinetics in normal donors and patients with recurrent herpes labialis. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1981 Jul;6(1):39–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Lawman M. J. Induction of cytotoxic T lymphocytes against herpes simplex virus type i: role of accessory cells and amplifying factor. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2341–2346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Wardley R. C., Babiuk L. A. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in cows: comparison of effector cell activity against heterologous erthrocyte and herpesvirus-infected bovine target cells. Infect Immun. 1976 May;13(5):1433–1441. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.5.1433-1441.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell A. S., Percy J. S., Kovithavongs T. Cell-mediated immunity to Herpes simplex in humans: lymphocyte cytotoxicity measured by 51-Cr release from infected cells. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):355–359. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.355-359.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleupner C. J., Olsen A., Glasgow L. A. Activation of reticuloendothelial cells following infection with murine cytomegalovirus. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jun;139(6):641–652. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.6.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethi K. K., Brandis H. Interferon enhances T cell mediated cytotoxicity of H-2 compatible target cells infected with UV-inactivated herpes simplex virus. Arch Virol. 1978;57(2):177–183. doi: 10.1007/BF01315679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethi K. K., Stroehmann I., Brandis H. Human T-cell cultures from virus-sensitized donors can mediate virus-specific and HLA-restricted cell lysis. Nature. 1980 Aug 14;286(5774):718–720. doi: 10.1038/286718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethi K. K., Wolff M. H. The nature of host-cell herpes-simplex virus interactions(s) that renders cells susceptible to virus-specific cytotoxic T cells. Immunobiology. 1980 Dec;157(4-5):365–378. doi: 10.1016/s0171-2985(80)80006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore S. L., Black C. M., Melewicz F. M., Wood P. A., Nahmias A. J. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity to target cells infected with type 1 and type 2 herpes simplex virus. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):194–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebens H., Tevethia S. S., Babior B. M. Neutrophil-mediated antibody-dependent killing of herpes-simplex-virus-infected cells. Blood. 1979 Jul;54(1):88–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanwick T. L., Campbell D. E., Nahmias A. J. Spontaneous cytotoxicity mediated by human monocyte-macrophages against human fibroblasts infected with herpes simplex virsu--augmentation by interferon. Cell Immunol. 1980 Aug 1;53(2):413–416. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90342-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trofatter K. F., Jr, Daniels C. A. Interaction of human cells with prostaglandins and cyclic AMP modulators. I. Effects on complement-mediated lysis and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytolysis of herpes simplex virus-infected human fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1363–1370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson P. C. Leukocyte locomotion and chemotaxis: effects of bacteria and viruses. Rev Infect Dis. 1980 Mar-Apr;2(2):293–318. doi: 10.1093/clinids/2.2.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


