Abstract
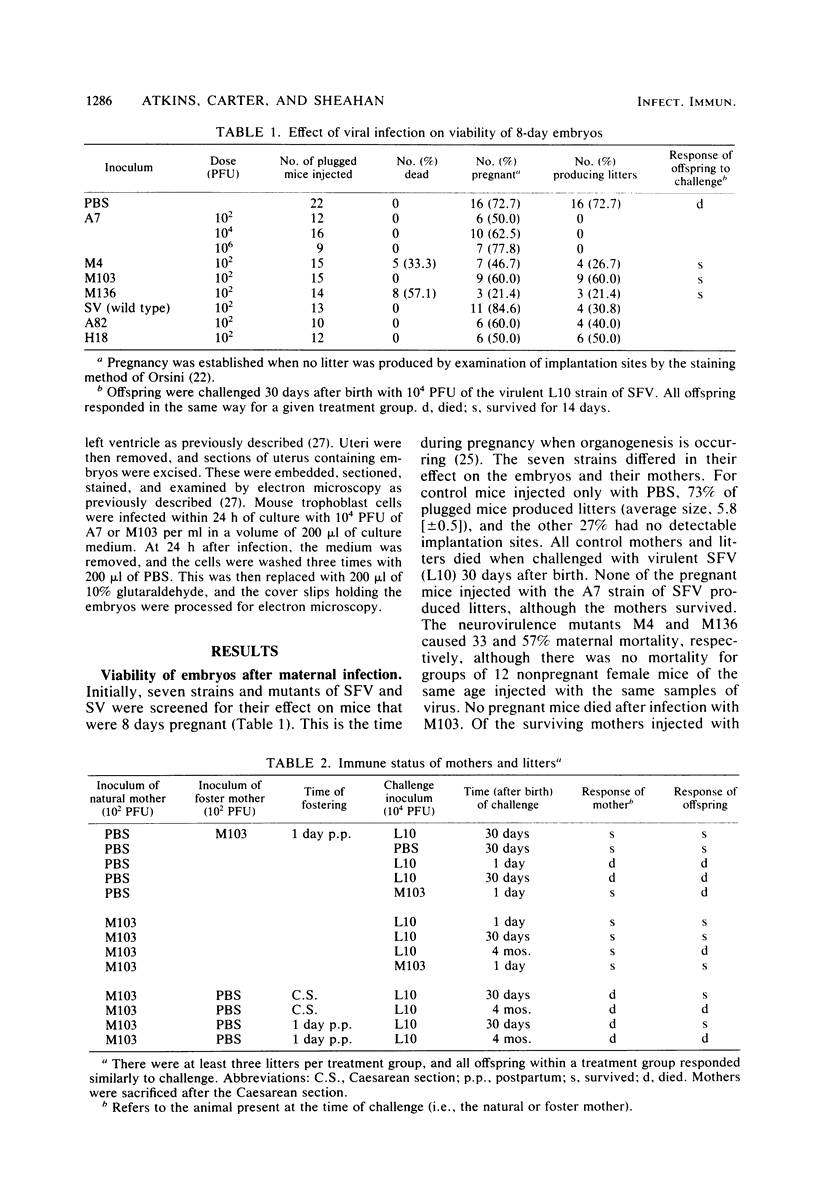
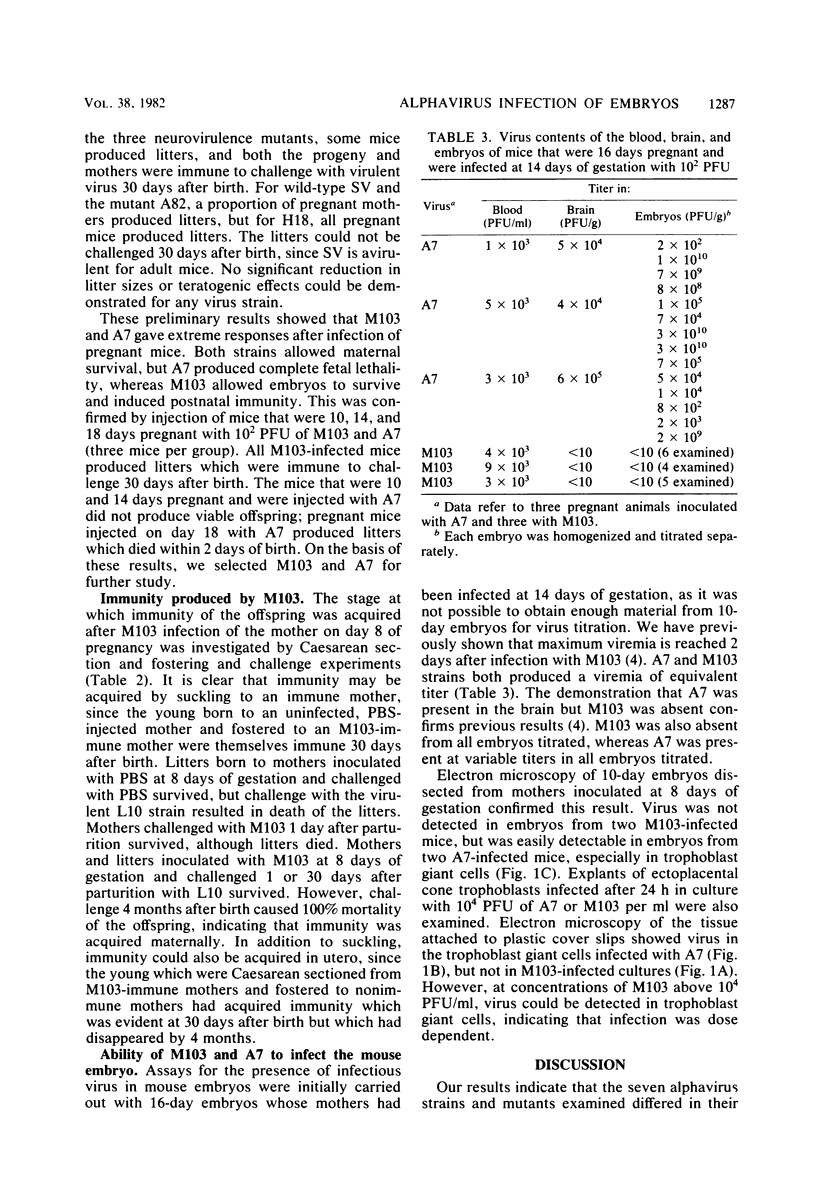
Seven strains and mutants of the alphaviruses, Semliki Forest virus and Sindbis virus, differed in their lethality for mouse embryos and their mothers. The A7 strain and the neurovirulence mutant M103 of Semliki Forest virus were selected for detailed comparison. A7 produced 100% lethality of mouse embryos but was avirulent for their mothers. M103 did not kill embryos or their mothers but did induce postnatal immunity. This immunity could be induced in utero or by suckling to an immune mother. Infectious virus could be recovered from the brain, blood, and embryos of mice infected with A7. Mice infected with M103 developed a viremia of similar titer, but virus could not be recovered from brain or embryos. Electron microscopy showed multiplying virus in trophoblast and fetal tissue after infection with A7, but no virus could be detected in such tissue after infection with M103. Cultures of ectoplacental cone trophoblast cells incubated in the presence of A7 or M103 showed multiplying A7 in the giant cells, but no M103. It is concluded that A7 can traverse both the blood-brain barrier and the placenta, whereas M103 can traverse neither.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkins G. J., Samuels J., Kennedy S. I. Isolation and preliminary characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of Sindbis virus strain AR339. J Gen Virol. 1974 Dec;25(3):371–380. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-25-3-371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins G. J., Sheahan B. J. Semliki forest virus neurovirulence mutants have altered cytopathogenicity for central nervous system cells. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):333–341. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.333-341.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett P. N., Atkins G. J. Virulence of temperature-sensitive mutants of Sindbis virus in neonatal mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):848–852. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.848-852.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett P. N., Sheahan B. J., Atkins G. J. Isolation and preliminary characterization of Semliki Forest virus mutants with altered virulence. J Gen Virol. 1980 Jul;49(1):141–147. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-49-1-141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger M. L. Humoral and cell-mediated immune mechanisms in the production of pathology in avirulent Semliki Forest virus encephalitis. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):244–253. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.244-253.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradish C. J., Allner K., Maber H. B. Infection, interaction and the expression of virulence by defined strains of Semliki forest virus. J Gen Virol. 1972 Sep;16(3):359–372. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-16-3-359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradish C. J., Allner K., Maber H. B. The virulence of original and derived strains of Semliki forest virus for mice, guinea-pigs and rabbits. J Gen Virol. 1971 Aug;12(2):141–160. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-12-2-141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradish C. J., Allner K. The early responses of mice to respiratory or intraperitoneal infection by defined virulent and avirulent strains of Semliki forest virus. J Gen Virol. 1972 Jun;15(3):205–218. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-15-3-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carretti N., Ovary Z. Transmission of gamma G antibodies from maternal to fetal circulation in the mouse. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Feb;130(2):509–512. doi: 10.3181/00379727-130-33592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter J. The expression of surface antigens on three trophoblastic tissues in the mouse. J Reprod Fertil. 1978 Nov;54(2):433–439. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0540433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Tamayo J., Esparza J., Martínez A. J. Placental and fetal alterations due to Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus in rats. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):813–821. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.813-821.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. W., Porter G. P. Fetal-maternal plasma calcium relationships in the rabbit. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1971 Jul;56(3):160–168. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1971.sp002115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill P. M., Young M. Net placental transfer of free amino acids against varying concentrations. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(2):409–422. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagelman S., Suckling A. J., Webb H. E., Bowen F. T. The pathogenesis of avirulent Semliki Forest virus infections in athymic nude mice. J Gen Virol. 1978 Dec;41(3):599–607. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-41-3-599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRBY D. R., BILLINGTON W. D., BRADBURY S., GOLDSTEIN D. J. ANTIGEN BARRIER OF THE MOUSE PLACENTA. Nature. 1964 Nov 7;204:548–549. doi: 10.1038/204548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOGOTHETOPOULOS J., SCOTT R. F. Active iodide transport across the placenta of the guinea-pig, rabbit and rat. J Physiol. 1956 May 28;132(2):365–371. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathur A., Arora K. L., Chaturvedi U. C. Congenital infection of mice with Japanese encephalitis virus. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):26–29. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.26-29.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morphis L. G., Gitlin D. Maturation of the maternofoetal transport system for human gamma-globulin in the mouse. Nature. 1970 Nov 7;228(5271):573–573. doi: 10.1038/228573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORSINI M. W. Technique of preparation, study and photography of benzyl-benzoate cleared material for embryological studies. J Reprod Fertil. 1962 Apr;3:283–287. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0030283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattyn S. R., De Vleesschauwer L., van der Groen G. Replication of arboviruses in mouse organ cultures. II. Multiplication of virulent and avirulent Semliki Forest and western equine encephalitis viruses in mouse organ cultures. Arch Virol. 1975;49(1):33–37. doi: 10.1007/BF02175593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusztai R., Gould E. A., Smith H. Infection patterns in mice of an avirulent and virulent strain of Semliki Forest virus. Br J Exp Pathol. 1971 Dec;52(6):669–677. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheahan B. J., Barrett P. N., Atkins G. J. Demyelination in mice resulting from infection with a mutant of Semliki Forest virus. Acta Neuropathol. 1981;53(2):129–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00689993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIDDAS W. F. Transport mechanisms in the foetus. Br Med Bull. 1961 May;17:107–111. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a069882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward C. G., Marshall I. D., Smith H. Investigations of reasons for the avirulence of the A7 strain of Semliki Forest virus in adult mice. Br J Exp Pathol. 1977 Dec;58(6):616–624. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




