Abstract
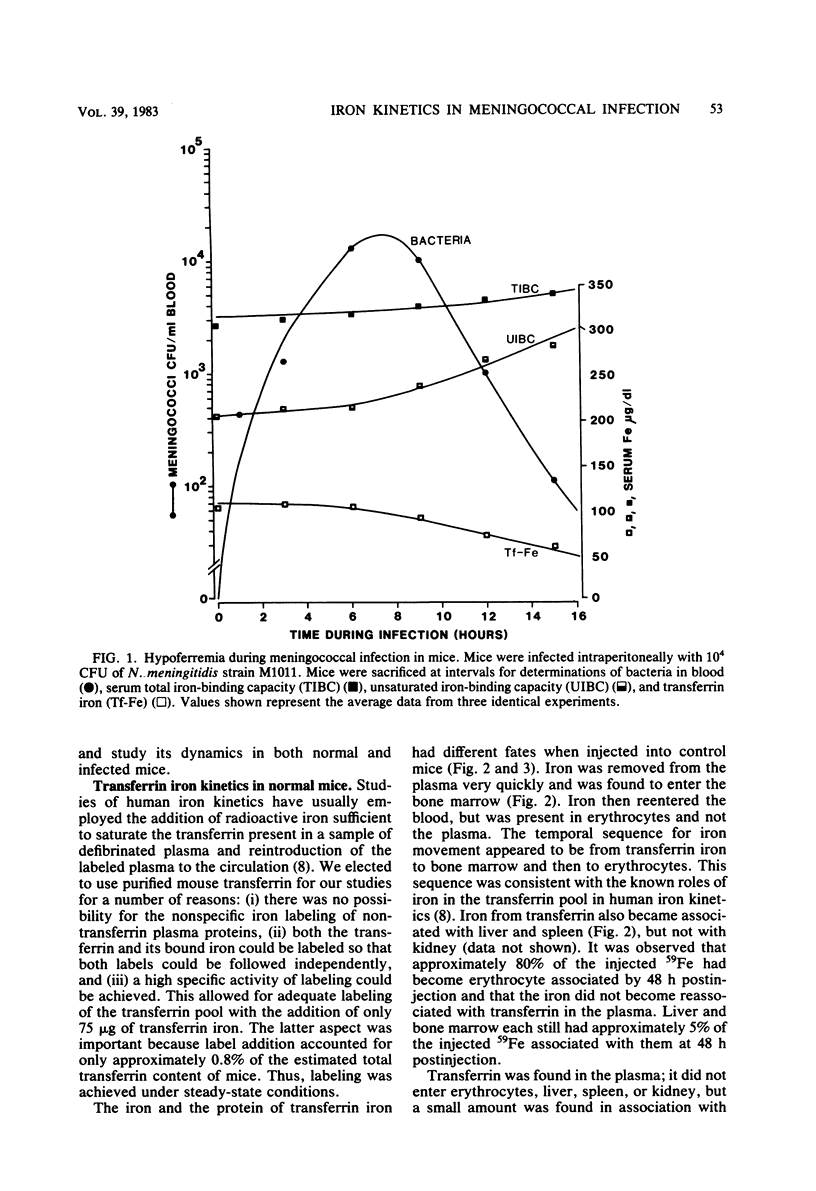
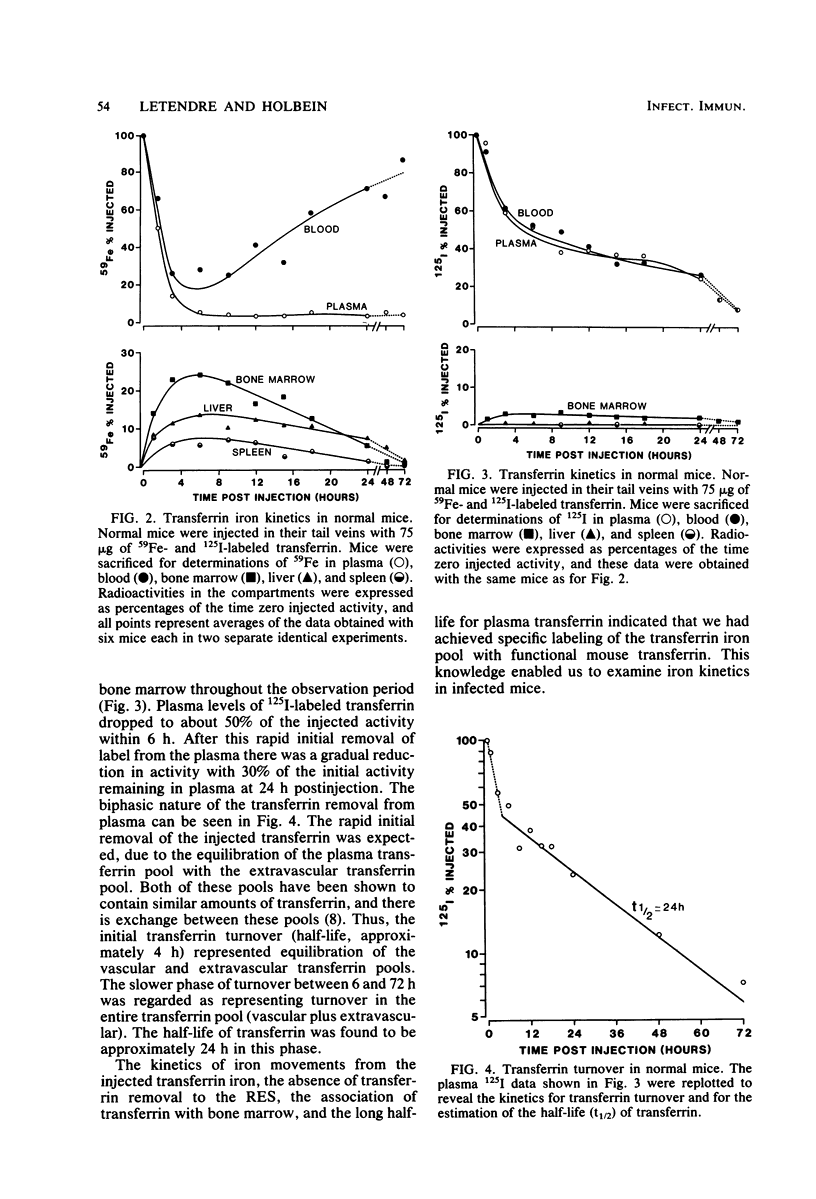
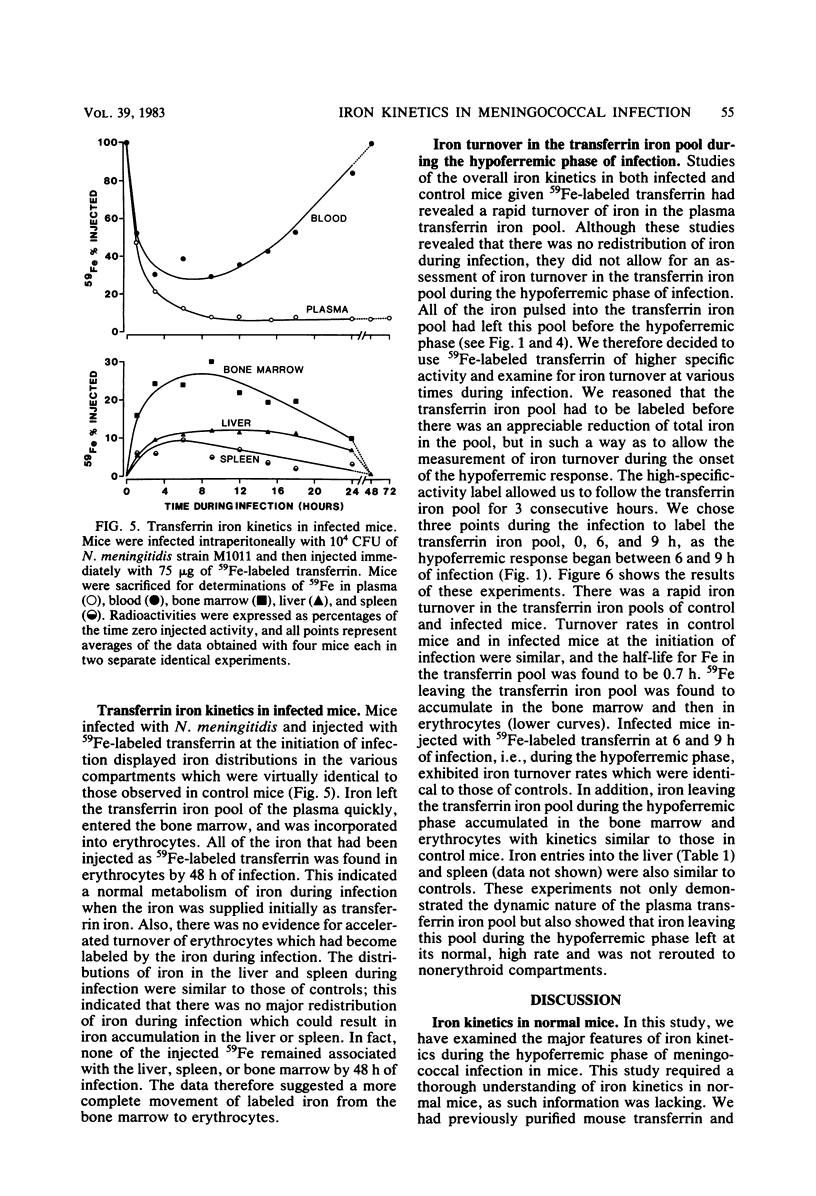
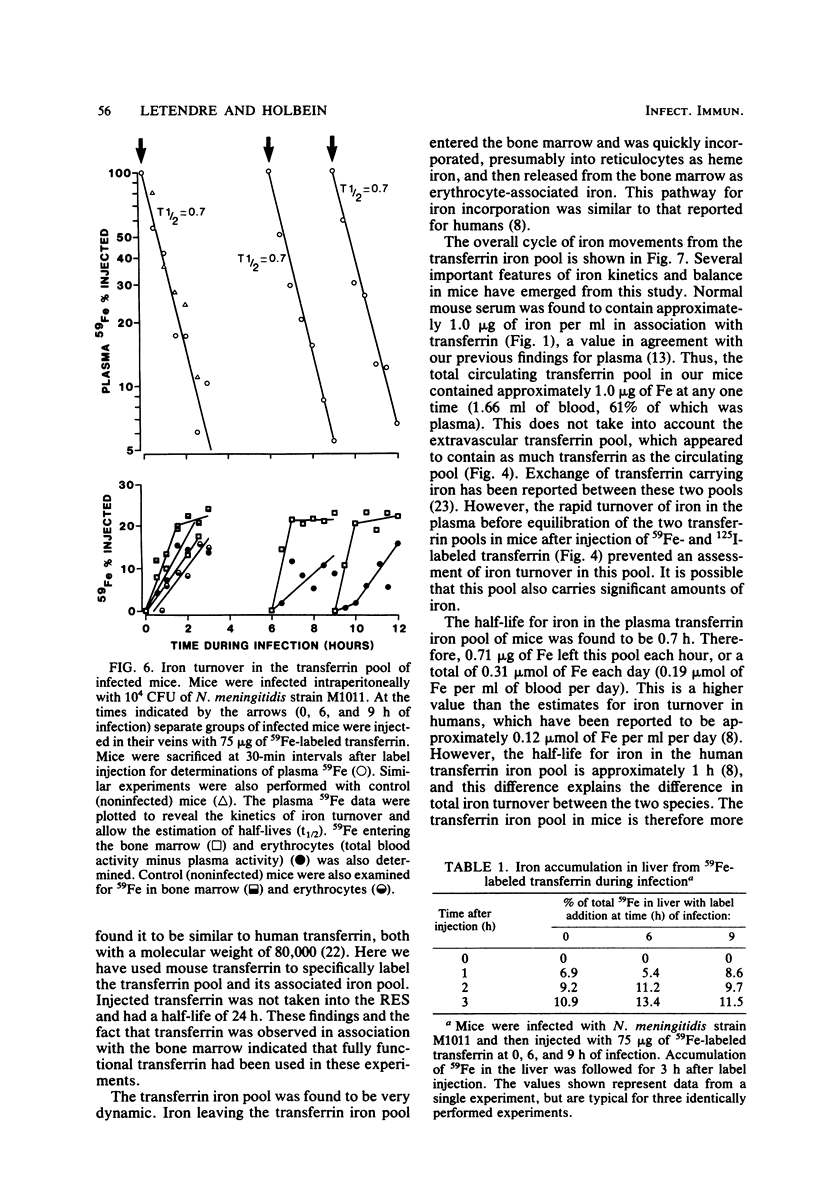
Mouse transferrin was used to specifically label the plasma transferrin iron pool for studies of iron kinetics in normal mice and infected mice during the hypoferremic phase of experimental meningococcal infection. The plasma transferrin iron pool of normal mice was found to be very dynamic, with a half-life of iron in the pool of 0.7 h. Iron left the plasma pool, entered the bone marrow, and was released into the blood in erythrocytes. Iron from the transferrin pool also entered the liver and spleen and was presumably in the reticuloendothelial system components of these organs. Most of the iron that had been supplied as transferrin iron was found in erythrocytes by 48 h after injection. Studies with mice infected with Neisseria meningitidis strain M1011 revealed similar kinetics for transferrin iron. There was no redistribution of iron within the various iron pools as a result of infection. Iron turnover in the plasma transferrin pool during the hypoferremic phase was similar to control rates, and iron leaving the pool entered its normal erythroid compartments. The lack of accelerated turnover of plasma iron and the finding that plasma iron was not rerouted to storage compartments during the hypoferremic phase provided good evidence that lactoferrin and leukocytic endogenous mediator were not directly involved in redirecting transferrin iron. Our evidence has implicated an impaired return of reticuloendothelial system-processed iron to the transferrin pool during the hypoferremic response. This appears to be a logical point in the erythroid iron cycle for host-mediated iron sequestration, as the reticuloendothelial system is involved in iron storage and may regulate iron levels in the plasma transferrin pool under normal conditions.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aisen P., Leibman A., Zweier J. Stoichiometric and site characteristics of the binding of iron to human transferrin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):1930–1937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aisen P., Listowsky I. Iron transport and storage proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:357–393. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archibald F. S., DeVoe I. W. Iron acquisition by Neisseria meningitidis in vitro. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):322–334. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.322-334.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisel W. R. Trace element in infectious processes. Med Clin North Am. 1976 Jul;60(4):831–849. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31864-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brener D., DeVoe I. W., Holbein B. E. Increased virulence of Neisseria meningitidis after in vitro iron-limited growth at low pH. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):59–66. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.59-66.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen J. J., Rogers H. J., Griffiths E. Role of iron in bacterial infection. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;80:1–35. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66956-9_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREIREICH E. J., MILLER A., EMERSON C. P., ROSS J. F. The effect of inflammation on the utilization of erythrocyte and transferrin bound radioiron for red cell production. Blood. 1957 Nov;12(11):972–983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths E., Humphreys J. Isolation of enterochelin from the peritoneal washings of guinea pigs lethally infected with Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):286–289. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.286-289.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAURANI F. I., BURKE W., MARTINEZ E. J. DEFECTIVE REUTILIZATION OF IRON IN THE ANEMIA OF INFLAMMATION. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Apr;65:560–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbein B. E. Differences in virulence for mice between disease and carrier strains of Neisseria meningitidis. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Jul;27(7):738–741. doi: 10.1139/m81-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbein B. E. Enhancement of Neisseria meningitidis infection in mice by addition of iron bound to transferrin. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):120–125. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.120-125.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbein B. E. Iron-controlled infection with Neisseria meningitidis in mice. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):886–891. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.886-891.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbein B. E., Jericho K. W., Likes G. C. Neisseria meningitidis infection in mice: influence of iron, variations in virulence among strains, and pathology. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):545–551. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.545-551.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kampschmidt R. F., Pulliam L. A., Upchurch H. F. The activity of partially purified leukocytic endogenous mediator in endotoxin-resistant C3H/HeJ mice. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Apr;95(4):616–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochan I., Kvach J. T., Wiles T. I. Virulence-associated acquisition of iron in mammalian serum by Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1977 Apr;135(4):623–632. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.4.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letendre E. D., Holbein B. E. A sensitive and convenient assay procedure for transferrin and its application to the purification of mouse transferrin. Can J Biochem. 1981 Nov-Dec;59(11-12):906–910. doi: 10.1139/o81-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan E. H., Marsaglia G., Giblett E. R., Finch C. A. A method of investigating internal iron exchange utilizing two types of transferrin. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Mar;69(3):370–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOYES W. D., BOTHWELL T. H., FINCH C. A. The role of the reticulo-endothelial cell in iron metabolism. Br J Haematol. 1960 Jan;6:43–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1960.tb06216.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Microbial iron compounds. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:715–731. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J. L., Masson P. L., Heremans J. F. The involvement of lactoferrin in the hyposideremia of acute inflammation. J Exp Med. 1974 Oct 1;140(4):1068–1084. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.4.1068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannemacher R. W., Jr, Pekarek R. S., Klainer A. S., Bartelloni P. J., Dupont H. L., Hornick R. B., Beisel W. R. Detection of a leukocytic endogenous mediator-like mediator of serum amino acid and zinc depression during various infectious illnesses. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):873–875. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.873-875.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron and infection. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):45–66. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.45-66.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins M., Williams P., Cavill I. Transferrin iron uptake by human synovium. Ann Rheum Dis. 1977 Oct;36(5):474–475. doi: 10.1136/ard.36.5.474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancey R. J., Breeding S. A., Lankford C. E. Enterochelin (enterobactin): virulence factor for Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):174–180. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.174-180.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



