Abstract
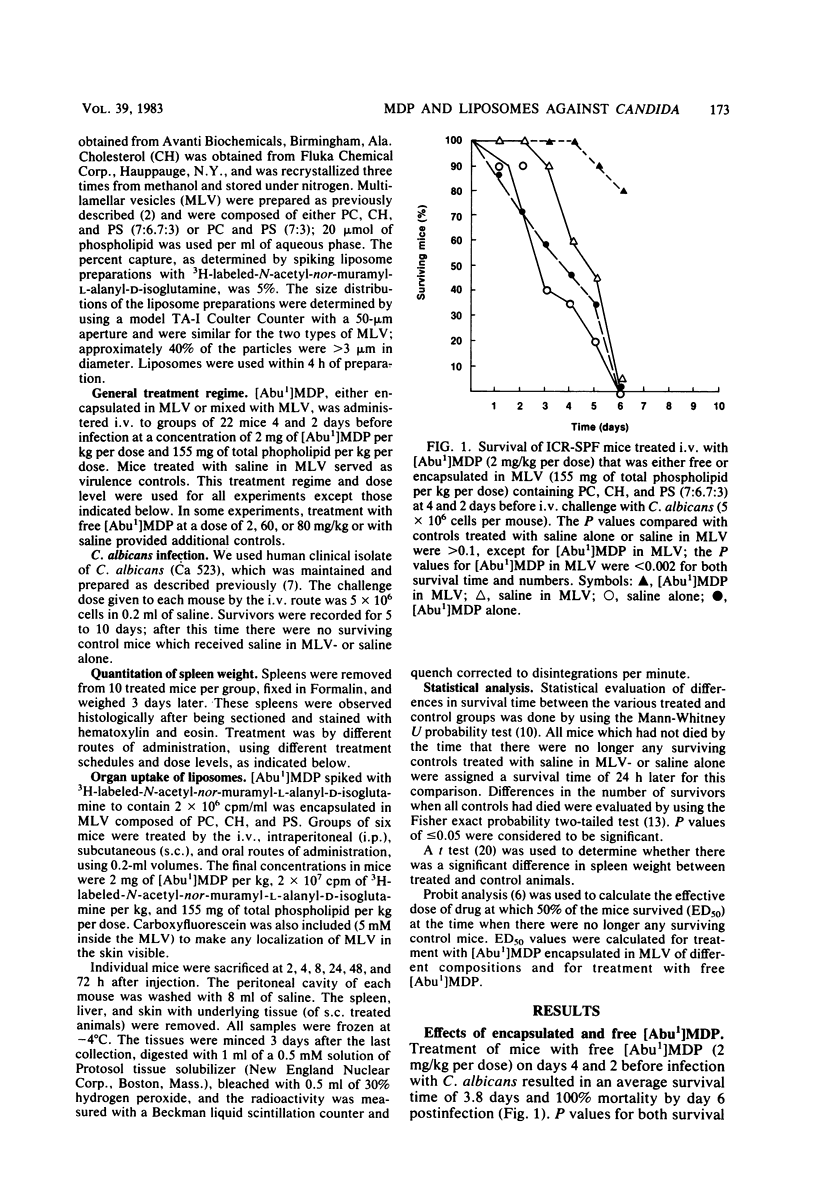
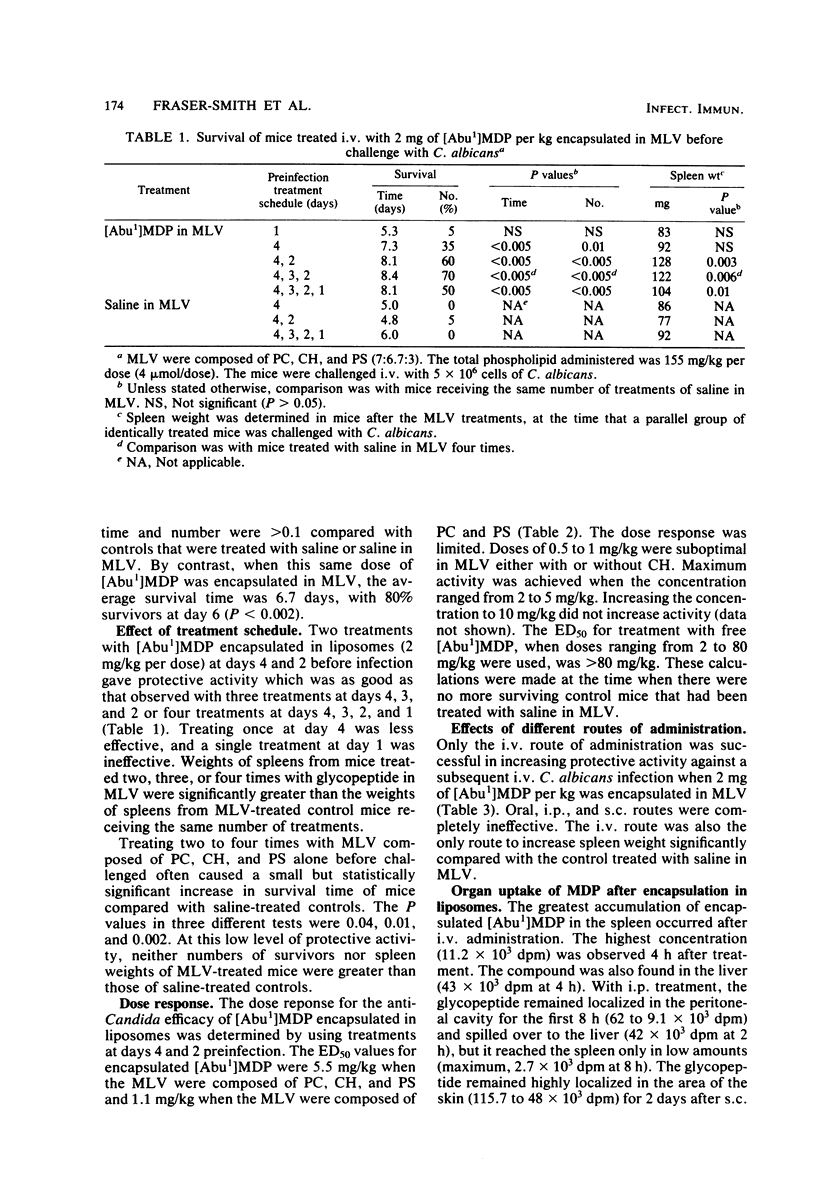
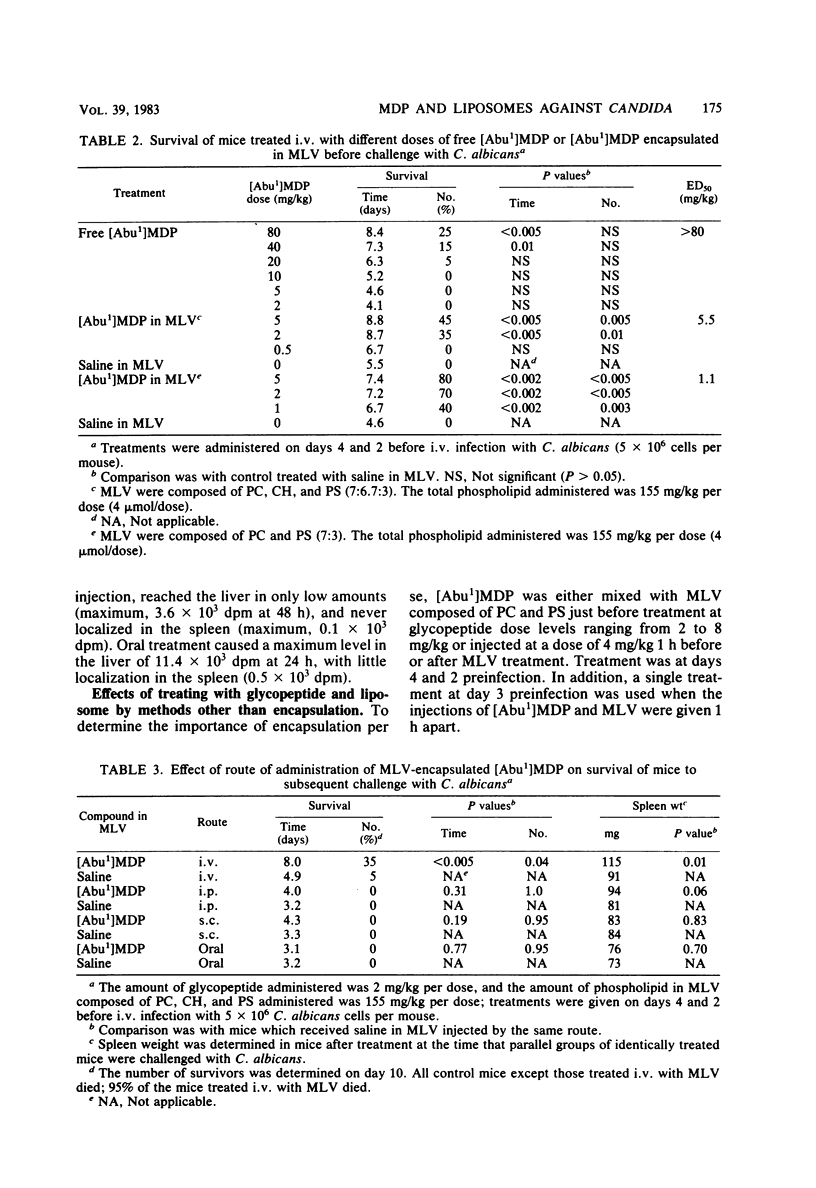
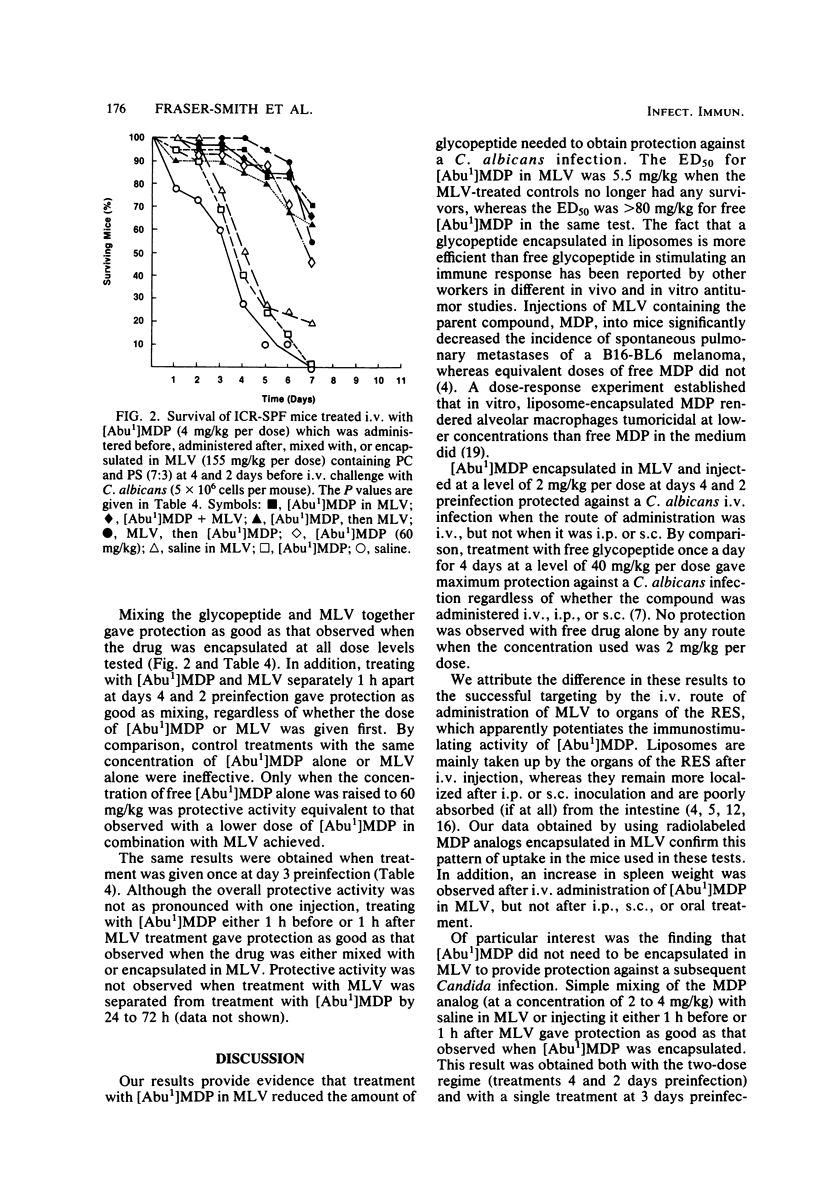
Encapsulation of N-acetylmuramyl-L-alpha-aminobutyryl-D-isoglutamine in multilamellar vesicles composed of phosphatidylcholine, cholesterol, and phosphatidylserine (7:6.7:3) or phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylserine (7:3) reduced the amount of drug needed to protect against a Candida albicans intravenous infection. The 50% effective doses for encapsulated and free drug were 5.5 and greater than 80 mg/kg, respectively. The optimum treatment was twice (at days 4 and 2 preinfection) by the intravenous route. Intraperitoneal, subcutaneous, and oral routes of administration were ineffective. The same potentiation of anti-Candida activity was observed whether the lower dose of drug was encapsulated in multilamellar vesicles, mixed with multilamellar vesicles, or given either 1 h before or 1 h after multilamellar vesicles. It was postulated that the mechanism of action involved the retention of the liposomes by organs of the reticuloendothelial system, resulting in an enhanced response of the macrophages to the immunostimulating activity of the N-acetylmuramyl-L-alpha-aminobutyryl-D-isoglutamine given in conjunction with the vesicles.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cummings N. P., Pabst M. J., Johnston R. B., Jr Activation of macrophages for enhanced release of superoxide anion and greater killing of Candida albicans by injection of muramyl dipeptide. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1659–1669. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eppstein D. A., Stewart W. E., 2nd Altered pharmacological properties of liposome-associated human interferon-alpha. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):575–582. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.575-582.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J., Barnes Z., Fogler W. E., Kirsh R., Bugelski P., Poste G. Involvement of macrophages in the eradication of established metastases following intravenous injection of liposomes containing macrophage activators. Cancer Res. 1982 Feb;42(2):496–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J., Sone S., Fogler W. E., Barnes Z. L. Eradication of spontaneous metastases and activation of alveolar macrophages by intravenous injection of liposomes containing muramyl dipeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1680–1684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein M., Weissmann G. The introduction of enzymes into cells by means of liposomes. J Lipid Res. 1978 Mar;19(3):289–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser-Smith E. B., Matthews T. R. Protective effect of muramyl dipeptide analogs against infections of Pseudomonas aeruginosa or Candida albicans in mice. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):676–683. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.676-683.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser-Smith E. B., Waters R. V., Matthews T. R. Correlation between in vivo anti-Pseudomonas and anti-Candida activities and clearance of carbon by the reticuloendothelial system for various muramyl dipeptide analogs, using normal and immunosuppressed mice. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):105–110. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.105-110.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadden J. W., Englard A., Sadlik J. R., Hadden E. M. The comparative effects of isoprinosine, levamisole, muramyl dipeptide and SM1213 on lymphocyte and macrophage proliferation and activation in vitro. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1979;1(1):17–27. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(79)90026-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juy D., Chedid L. Comparison between macrophage activation and enhancement of nonspecific resistance to tumors by mycobacterial immunoadjuvants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4105–4109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim J. J., Togawa A., Chedid L., Mizel S. Components of mycobacteria and muramyl dipeptide with adjuvant activity induce lymphocyte activating factor. Cell Immunol. 1980 Mar 1;50(1):71–81. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabst M. J., Johnston R. B., Jr Increased production of superoxide anion by macrophages exposed in vitro to muramyl dipeptide or lipopolysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1980 Jan 1;151(1):101–114. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano R. E., Weinstein J. N. Interactions of liposomes with mammalian cells. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:435–468. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.002251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parant M., Parant F., Chedid L., Yapo A., Petit J. F., Lederer E. Fate of the synthetic immunoadjuvant, muramyl dipeptide (14C-labelled) in the mouse. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1979;1(1):35–41. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(79)90028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritter C., Rutman R. J. Relative enhancement by various liposomes of BCNU effectiveness against L-1210 leukemia in vivo. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1980 Oct;30(1):123–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sone S., Fidler I. J. In vitro activation of tumoricidal properties in rat alveolar macrophages by synthetic muramyl dipeptide encapsulated in liposomes. Cell Immunol. 1981 Jan 1;57(1):42–50. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90118-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada H., Tsujimoto M., Kato K., Kotani S., Kusumoto S., Inage M., Shiba T., Yano I., Kawata S., Yokogawa K. Macrophage activation by bacterial cell walls and related synthetic compounds. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):48–53. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.48-53.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka A., Nagao S., Nagao R., Kotani S., Shiba T., Kusumoto S. Stimulation of the reticuloendothelial system of mice by muramyl dipeptide. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):302–307. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.302-307.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniyama T., Holden H. T. Direct augmentation of cytolytic activity of tumor-derived macrophages and macrophage cell lines by muramyl dipeptide. Cell Immunol. 1979 Dec;48(2):369–374. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90131-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., Wahl L. M., McCarthy J. B., Chedid L., Mergenhagen S. E. Macrophage activation by mycobacterial water soluble compounds and synthetic muramyl dipeptide. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2226–2231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters R. V., Ferraresi R. W. Muramyl dipeptide stimulation of particle clearance in several animal species. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1980 Nov;28(5):457–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto Y., Nagao S., Tanaka A., Koga T., Onoue K. Inhibition of macrophage migration by synthetic muramyl dipeptide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):923–928. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


