Abstract
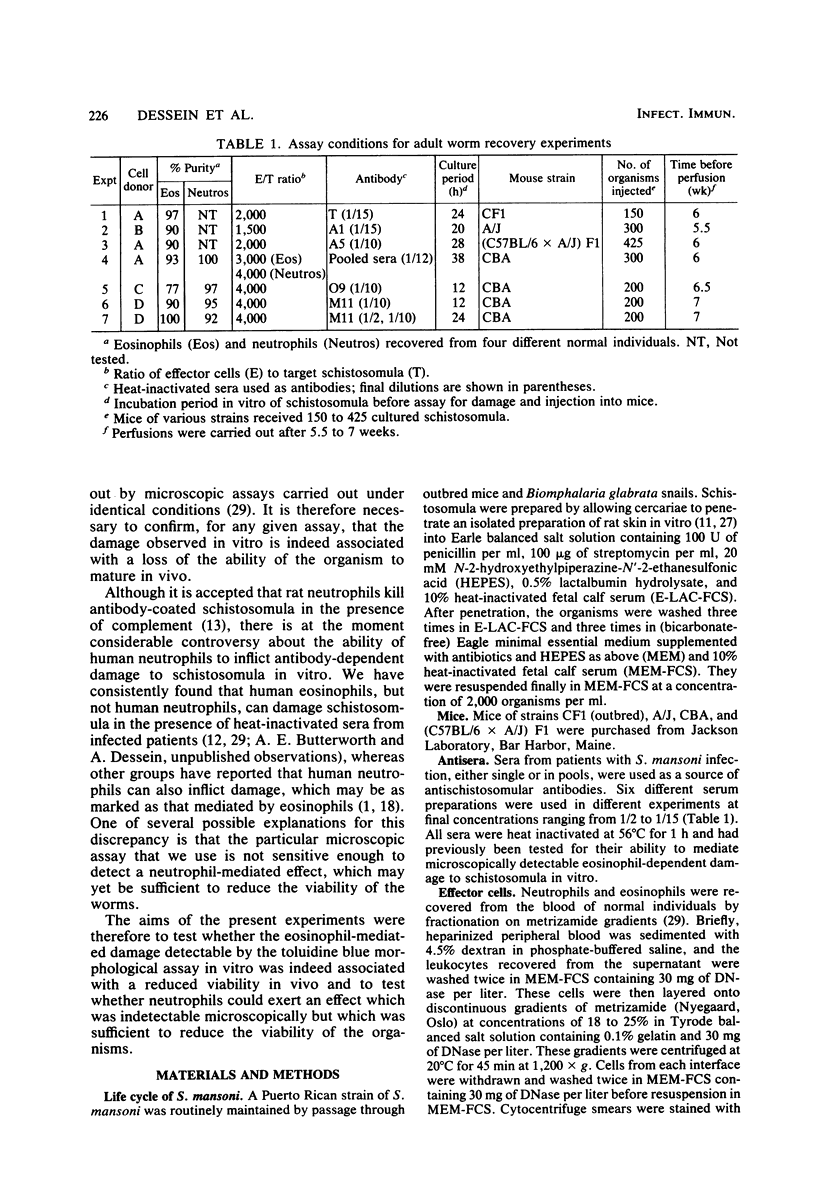
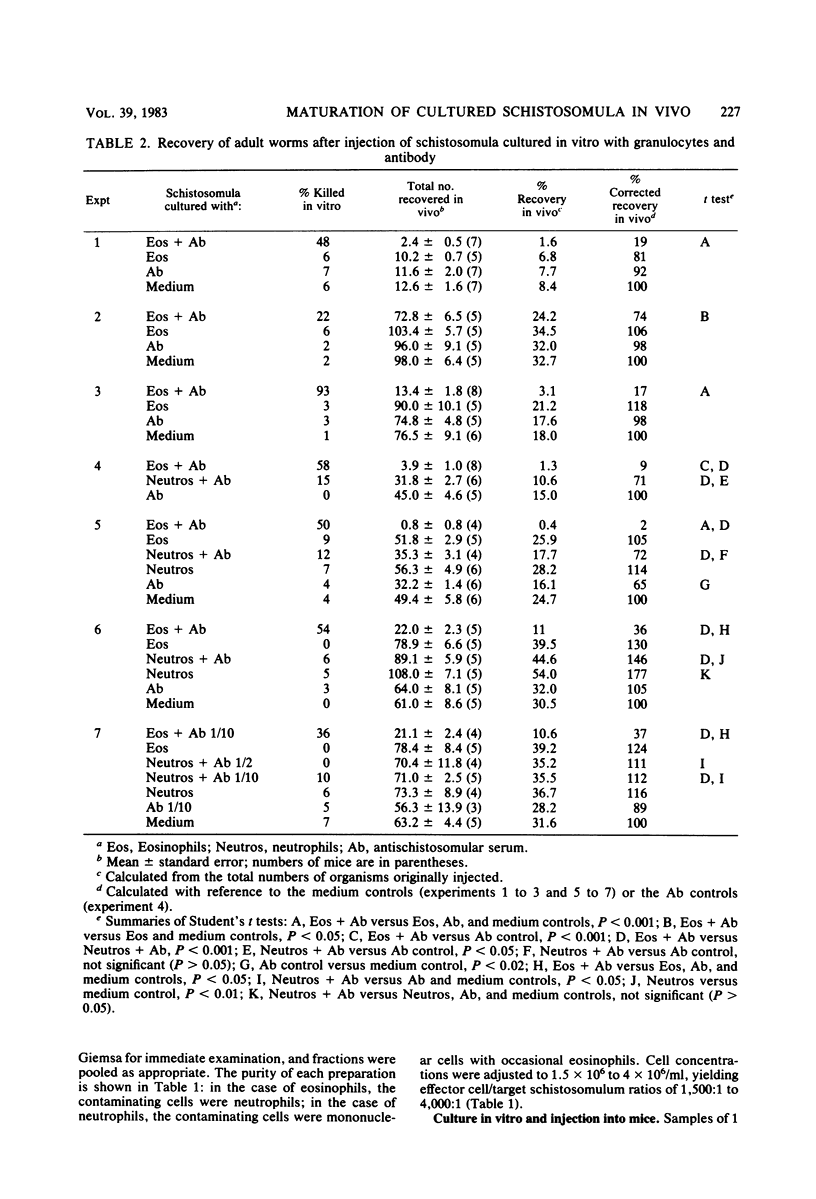
Seven experiments were carried out to test the relationship between the morphological assay for damage to schistosomula in vitro with toluidine blue and the loss of the ability of damaged organisms to mature in vivo. Schistosomula were prepared by penetration of rat skin and cultured for 12 to 38 h in the presence of various combinations of purified human eosinophils or neutrophils and heat-inactivated human antischistosomular serum. Samples were scored for microscopically detectable damage, and the remaining organisms were injected intravenously into normal mice. These mice were perfused after 5.5 to 7 weeks, and the recovery of adult worms was determined. After culture of schistosomula in medium alone, between 8.4 and 32.7% of injected organisms matured into adult worms. There was no significant difference in the capacity of freshly prepared and cultured schistosomula to mature in vivo. Schistosomula cultured with antibody alone showed no significant damage in vitro, and in only one of seven experiments was there a significant (35%) reduction compared with the medium controls in their capacity to mature in vivo. Schistosomula cultured with neutrophils alone or eosinophils alone showed no significant damage in vitro and no loss of viability in vivo. Schistosomula cultured with neutrophils and antibody showed a 28% reduction in recovery in one experiment but an increase in recovery (12 and 46%) in two other experiments. In contrast, schistosomula cultured with eosinophils and antibody showed evidence of both marked damage in vitro (22 to 93% dead organisms) and loss of viability in vivo (26 to 98% reduction in recovery) in all seven experiments. These findings justify the use of the toluidine blue morphological assay as an estimate of irreversible damage to schistosomula and confirm that human eosinophils and neutrophils differ markedly in their capacity to mediate antibody-dependent damage in vitro.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anwar A. R., Smithers S. R., Kay A. B. Killing of schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni coated with antibody and/or complement by human leukocytes in vitro: requirement for complement in preferential killing by eosinophils. J Immunol. 1979 Feb;122(2):628–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth A. E., David J. R., Franks D., Mahmoud A. A., David P. H., Sturrock R. F., Houba V. Antibody-dependent eosinophil-mediated damage to 51Cr-labeled schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni: damage by purieid eosinophils. J Exp Med. 1977 Jan 1;145(1):136–150. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.1.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth A. E., Sturrock R. F., Houba V., Rees P. H. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated damage to schistosomula in vitro. Nature. 1974 Dec 6;252(5483):503–505. doi: 10.1038/252503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth A. E., Vadas M. A., Wassom D. L., Dessein A., Hogan M., Sherry B., Gleich G. J., David J. R. Interactions between human eosinophils and schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. II. The mechanism of irreversible eosinophil adherence. J Exp Med. 1979 Dec 1;150(6):1456–1471. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.6.1456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth A. E., Wassom D. L., Gleich G. J., Loegering D. A., David J. R. Damage to schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni induced directly by eosinophil major basic protein. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):221–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron A., Capron M., Camus D., Vernes A. Les phénomènes d'hypersensibilité au cours des schistosamiases humaines à "Schistosoma mansoni" et "Schistosoma haematobium". II Etude in vitro de l'activité léthale des sérums de malades pour les schistosomules de Schistosoma mansoni. Rapports avec les tests d'hypersensibilité. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1973 Dec;21(10):1079–1084. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron A., Dessaint J. P., Joseph M., Rousseaux R., Capron M., Bazin H. Interaction between IgE complexes and macrophages in the rat: a new mechanism of macrophage activation. Eur J Immunol. 1977 May;7(5):315–322. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830070515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron M., Capron A., Torpier G., Bazin H., Bout D., Joseph M. Eosinophil-dependent cytotoxicity in rat schistosomiasis. Involvement of IgG2a antibody and role of mast cells. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Feb;8(2):127–133. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron M., Rousseaux J., Mazingue C., Bazin H., Capron A. Rat mast cell-eosinophil interaction in antibody-dependent eosinophil cytotoxicity to Schistosoma mansoni schistosomula. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2518–2525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caulfield J. P., Korman G., Butterworth A. E., Hogan M., David J. R. The adherence of human neutrophils and eosinophils to schistosomula: evidence for membrane fusion between cells and parasites. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jul;86(1):46–63. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. A., Smithers S. R. The effects of immune rhesus monkey serum on schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni during cultivation in vitro. Int J Parasitol. 1972 Mar;2(1):79–98. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(72)90036-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David J. R., Vadas M. A., Butterworth A. E., de Brito P. A., Carvalho E. M., David R. A., Bina J. C., Andrade Z. A. Enhanced helminthotoxic capacity of eosinophils from patients with eosinophilia. N Engl J Med. 1980 Nov 13;303(20):1147–1152. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198011133032004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean D. A., Wistar R., Murrell K. D. Combined in vitro effects of rat antibody and neutrophilic leukocytes on schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1974 May;23(3):420–428. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1974.23.420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glauert A. M., Butterworth A. E. Morphological evidence for the ability of eosinophils to damage antibody-coated schistosomula. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1977;71(5):392–395. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(77)90036-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glauert A. M., Butterworth A. E., Sturrock R. F., Houba V. The mechansim of antibody-dependent, eosinophil-mediated damage to schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni in vitro: a study by phase-contrast and electron microscopy. J Cell Sci. 1978 Dec;34:173–192. doi: 10.1242/jcs.34.1.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James E. R., Taylor M. G. Transformation of cercariae to schistosomula: a quantitative comparison of transformation techniques and of infectivity by different injection routes of the organisms produced. J Helminthol. 1976 Dec;50(4):223–233. doi: 10.1017/s0022149x0002664x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassis A. I., Aikawa M., Mahmoud A. F. Mouse antibody-dependent eosinophil and macrophage adherence and damage to schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. J Immunol. 1979 Feb;122(2):398–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazura J. W., Fanning M. M., Blumer J. L., Mahmoud A. A. Role of cell-generated hydrogen peroxide in granulocyte-mediated killing of schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jan;67(1):93–102. doi: 10.1172/JCI110037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis F. A., Sher A., Colley D. G. Failure of plasma from human schistosomiasis mansoni patients to protect mice from Schistosoma mansoni cercarial challenge. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 Jul;26(4):723–726. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1977.26.723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaren D. J., Ramalho-Pinto F. J. Eosinophil-mediated killing of schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni in vitro: synergistic effect of antibody and complement. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1431–1438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaren D. J., Ramalho-Pinto F. J., Smithers S. R. Ultrastructural evidence for complement and antibody-dependent damage to schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni by rat eosinophils in vitro. Parasitology. 1978 Dec;77(3):313–324. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000050277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips S. M., Colley D. G. Immunologic aspects of host responses to schistosomiasis: resistance, immunopathology, and eosinophil involvement. Prog Allergy. 1978;24:49–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramalho-Pinto F. J., McLaren D. J., Smithers S. R. Complement-mediated killing of schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni by rat eosinophils in vitro. J Exp Med. 1978 Jan 1;147(1):147–156. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithers S. R., Terry R. J., Hockley D. J. Host antigens in schistosomiasis. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1969 Feb 25;171(1025):483–494. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1969.0007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithers S. R., Terry R. J. The infection of laboratory hosts with cercariae of Schistosoma mansoni and the recovery of the adult worms. Parasitology. 1965 Nov;55(4):695–700. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000086248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas M. A., Butterworth A. E., Sherry B., Dessein A., Hogan M., Bout D., David J. R. Interactions between human eosinophils and schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. I. Stable and irreversible antibody-dependent adherence. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1441–1448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas M. A., David J. R., Butterworth A., Pisani N. T., Siongok T. A. A new method for the purification of human eosinophils and neutrophils, and a comparison of the ability of these cells to damage schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1228–1236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



