Abstract
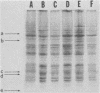
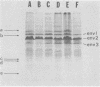
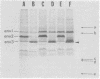
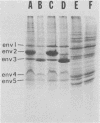
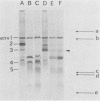
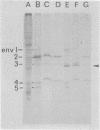
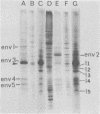
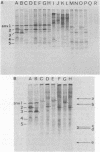
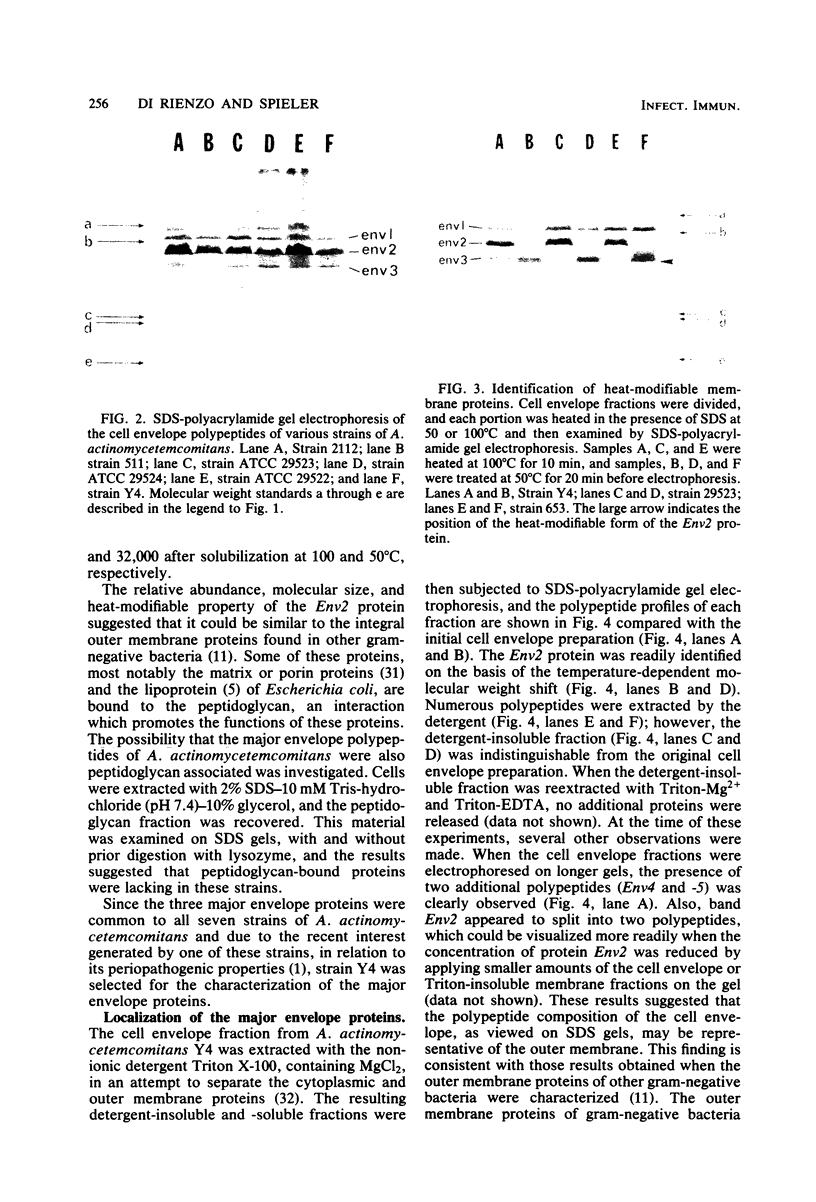
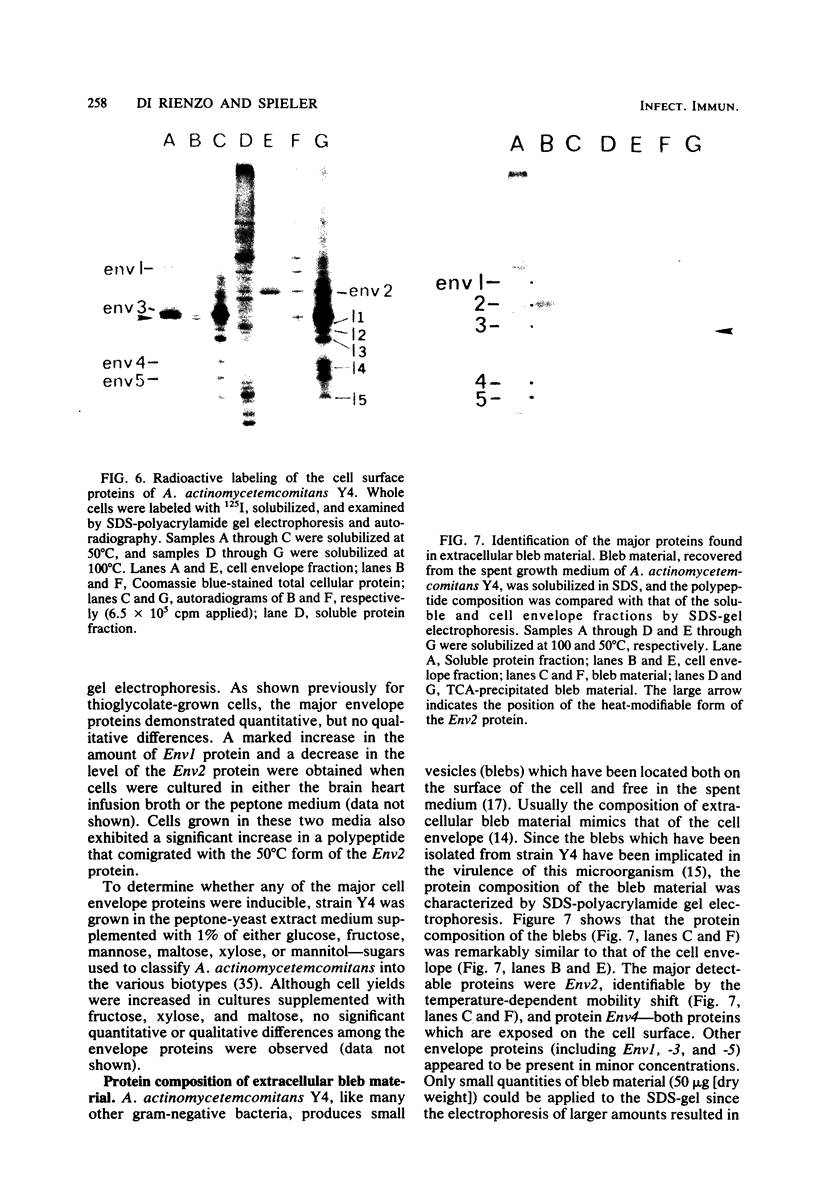
The major cell envelope protein compositions of seven Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans strains of human origin were compared by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The major envelope polypeptides were homogeneous, in relation to molecular weight, in all of the strains that were examined. The characterization of the five major proteins, designated Env1 through Env5, in the leukotoxic strain Y4 revealed that proteins Env2 to -5 may reside in the outer membrane as suggested by differential detergent extractions and 125I-labeling experiments. The proteins did not demonstrate covalent or ionic interactions with the peptidoglycan; however, one protein, Env2, displayed heat-modifiable properties, having apparent molecular weights of 32,000 and 45,000 when heated in sodium dodecyl sulfate at 50 and 100 degrees C, respectively. The protein composition of the extracellular "bleb" material, normally released by strain Y4, was determined, and proteins Env1 to -4 were the predominant protein species found. A comparison of the cell envelope proteins of strain Y4 with those of other members of the human oral flora, including species within the genera Capnocytophaga, Bacteroides, and Fusobacterium, revealed distinct differences on the basis of molecular size and heat-modifiable properties. However, the membrane proteins of Haemophilus aphrophilus showed a remarkable degree of homology with those of A. actinomycetemcomitans.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baehni P., Tsai C. C., McArthur W. P., Hammond B. F., Taichman N. S. Interaction of inflammatory cells and oral microorganisms. VIII. Detection of leukotoxic activity of a plaque-derived gram-negative microorganism. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):233–243. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.233-243.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J., Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Outer membrane protein and biotype analysis of pathogenic nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):535–540. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.535-540.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beher M. G., Schnaitman C. A., Pugsley A. P. Major heat-modifiable outer membrane protein in gram-negative bacteria: comparison with the ompA protein of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):906–913. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.906-913.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björck L., Kronvall G. Analysis of bacterial cell wall proteins and human serum proteins bound to bacterial cell surfaces. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1981 Feb;89(1):1–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1981.tb00144_89b.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Sieglin U. The covalent murein-lipoprotein structure of the Escherichia coli cell wall. The attachment site of the lipoprotein on the murein. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Apr;13(2):336–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00936.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgher L. W., Loomis G. W., Ware F. Systemic infection due to Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Am J Clin Pathol. 1973 Sep;60(3):412–415. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/60.3.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. H., Hancock R. E., Mishell R. I. Mitogenic effects of purified outer membrane proteins from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):178–184. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.178-184.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dankert J., Hofstra H. Antibodies against outer membrane proteins in rabbit antisera prepared against Escherichia coli O26 K60. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Feb;104(2):311–320. doi: 10.1099/00221287-104-2-311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiRienzo J. M., Inouye M. Lipid fluidity-dependent biosynthesis and assembly of the outer membrane proteins of E. coli. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):155–161. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90303-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiRienzo J. M., Nakamura K., Inouye M. The outer membrane proteins of Gram-negative bacteria: biosynthesis, assembly, and functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:481–532. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.002405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellner J. J., Rosenthal M. S., Lerner P. I., McHenry M. C. Infective endocarditis caused by slow-growing, fastidious, Gram-negative bacteria. Medicine (Baltimore) 1979 Mar;58(2):145–158. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197903000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., McNelis R. M., Gotschlich E. C. Strain-specific variation in the protein and lipopolysaccharide composition of the group B meningococcal outer membrane. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):973–981. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.973-981.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gankema H., Wensink J., Guinée P. A., Jansen W. H., Witholt B. Some characteristics of the outer membrane material released by growing enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):704–713. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.704-713.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C., Tanner A. C., Socransky S. S. Morphology and ultrastructure of oral strains of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and Haemophilus aphrophilus. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):588–600. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.588-600.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving J. T., Newman M. G., Socransky S. S., Heely J. D. Histological changes in experimental periodontal disease in rats mono-infected with a gram-negative organism. Arch Oral Biol. 1975 Mar;20(3):219–220. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(75)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston K. H., Holmes K. K., Gotschlich E. C. The serological classification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. I. Isolation of the outer membrane complex responsible for serotypic specificity. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):741–758. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiley P., Holt S. C. Characterization of the lipopolysaccharide from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans Y4 and N27. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):862–873. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.862-873.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb M. R., Smith D. H. Outer membrane protein composition in disease isolates of Haemophilus influenzae: pathogenic and epidemiological implications. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):709–717. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.709-717.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL R. G., GILLESPIE W. A. BACTERIAL ENDOCARDITIS DUE TO AN ACTINOBACILLUS. J Clin Pathol. 1964 Sep;17:511–512. doi: 10.1136/jcp.17.5.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B. F., Derby B. M., Budzilovich G. N., Ransohoff J. Brain abscess due to Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Neurology. 1967 Sep;17(9):833–837. doi: 10.1212/wnl.17.9.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchers F., Braun V., Galanos C. The lipoprotein of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli: a B-lymphocyte mitogen. J Exp Med. 1975 Aug 1;142(2):473–482. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.2.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muhle I., Rau J., Ruskin J. Vertebral osteomyelitis due to Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. JAMA. 1979 Apr 27;241(17):1824–1825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman M. G., Socransky S. S. Predominant cultivable microbiota in periodontosis. J Periodontal Res. 1977 Mar;12(2):120–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1977.tb00114.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman M. G., Socransky S. S., Savitt E. D., Propas D. A., Crawford A. Studies of the microbiology of periodontosis. J Periodontol. 1976 Jul;47(7):373–379. doi: 10.1902/jop.1976.47.7.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbeeke N., Lugtenberg B. Major outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli strains of human origin. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Dec;121(2):373–380. doi: 10.1099/00221287-121-2-373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reithmeier R. A., Bragg P. D. Purification and characterization of heat-modifiable protein from the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1974 May 1;41(2):195–198. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)81210-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbusch J. P. Characterization of the major envelope protein from Escherichia coli. Regular arrangement on the peptidoglycan and unusual dodecyl sulfate binding. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):8019–8029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Solubilization of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli by Triton X-100. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):545–552. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.545-552.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenker B. J., McArthur W. P., Tsai C. C. Immune suppression induced by Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. I. Effects on human peripheral blood lymphocyte responses to mitogens and antigens. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):148–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J., Reynolds H. S., Genco R. J. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in human periodontal disease: a cross-sectional microbiological investigation. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1013–1020. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1013-1020.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J. The predominant cultivable organisms in juvenile periodontitis. Scand J Dent Res. 1976 Jan;84(1):1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1976.tb00454.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taichman N. S., Dean R. T., Sanderson C. J. Biochemical and morphological characterization of the killing of human monocytes by a leukotoxin derived from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):258–268. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.258-268.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner A. C., Haffer C., Bratthall G. T., Visconti R. A., Socransky S. S. A study of the bacteria associated with advancing periodontitis in man. J Clin Periodontol. 1979 Oct;6(5):278–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1979.tb01931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend T. R., Gillenwater J. Y. Urinary tract infection due to Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. JAMA. 1969 Oct 20;210(3):558–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]