Abstract
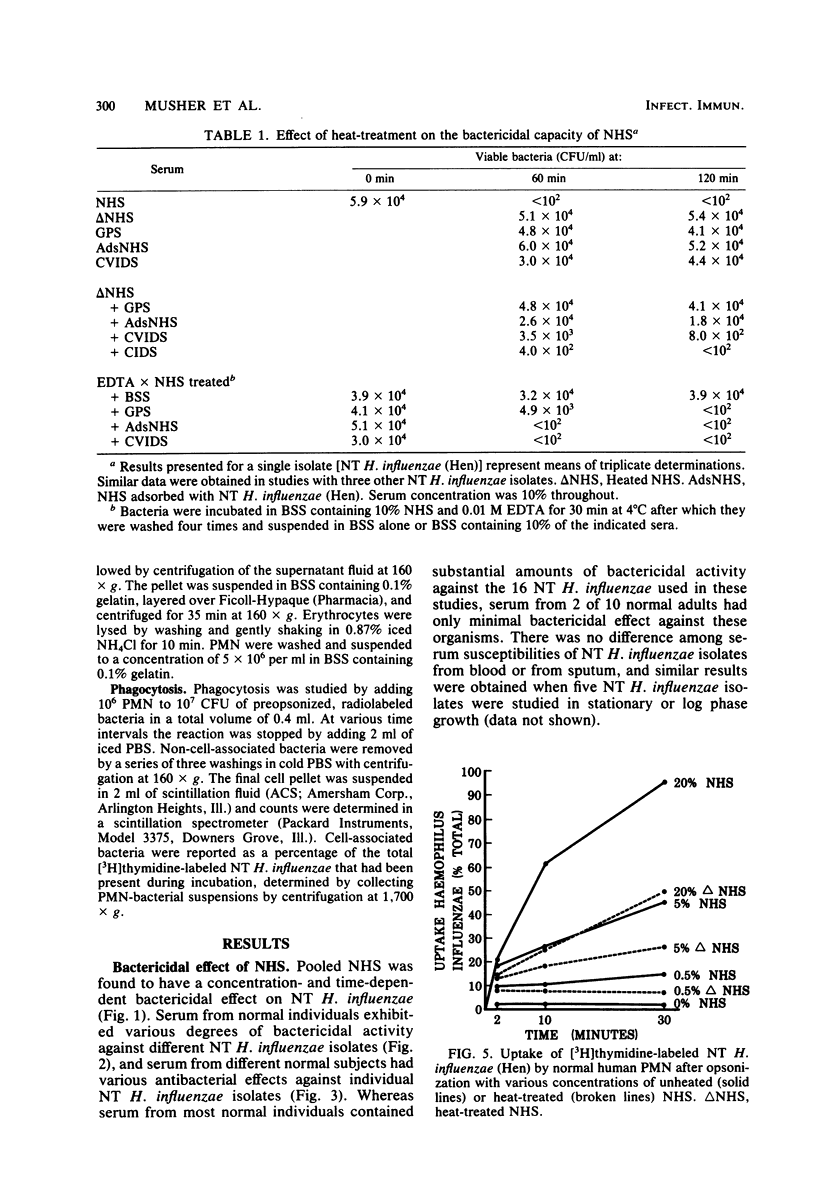
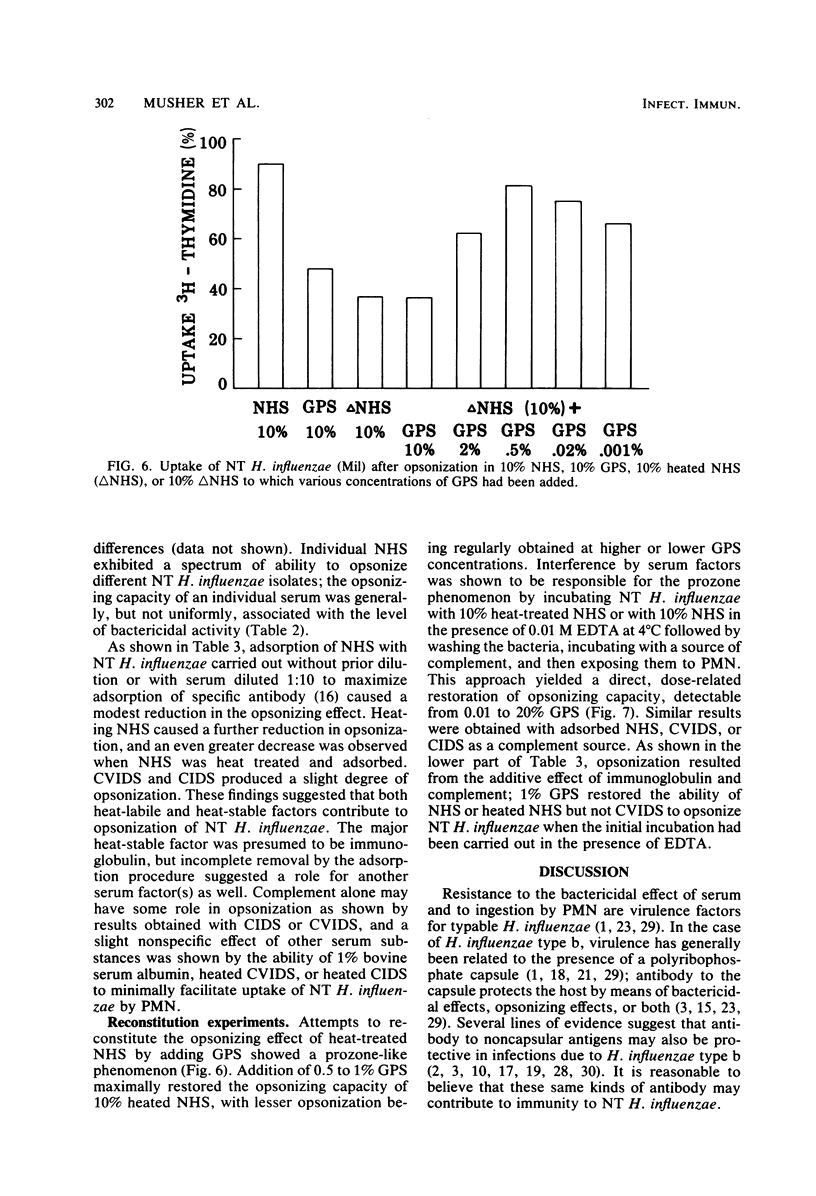
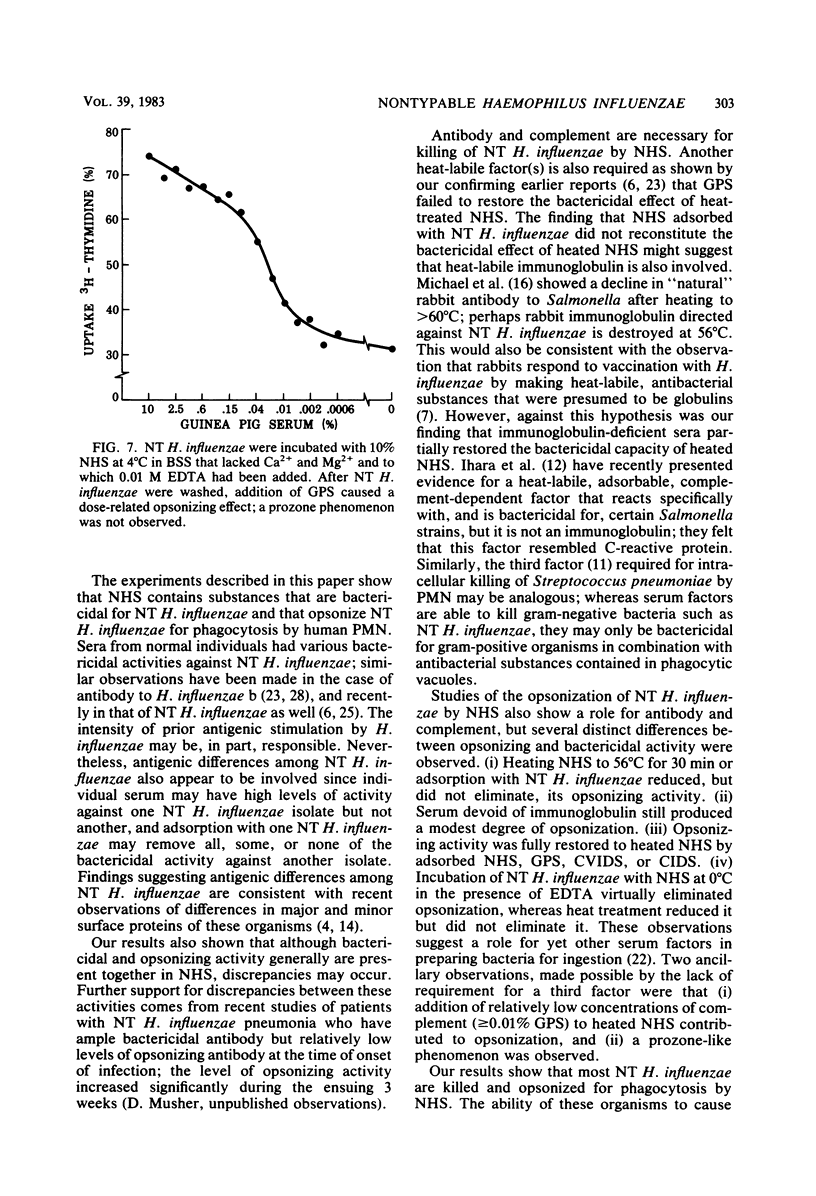
The observation that nontypable (NT) Haemophilus influenzae causes serious infection in adults has stimulated interest in mechanisms that may protect the human host against NT H. influenzae infection. Incubating NT H. influenzae with normal human serum (NHS) caused dose- and time-dependent killing that varied with the individual NHS and NT H. influenzae. Adsorption of NHS with NT H. influenzae removed bactericidal activity against the adsorbing isolate but not necessarily that against others, suggesting antigenic diversity and supporting recent studies that show different outer membrane protein profiles among NT H. influenzae. Heating NHS to 56 degrees C for 30 min abolished bactericidal activity; this activity was not restored by complement-rich guinea pig serum or NT H. influenzae-adsorbed NHS. This is analogous to the "third factor" needed for intraleukocytic killing of pneumococci. Optimal opsonization of NT H. influenzae for phagocytosis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes required antibody and complement, but other serum factors also played a role. Bactericidal activity generally, but not uniformly, correlated with opsonizing activity of individual NHS. Humoral factors may be important in host defenses against NT H. influenzae infection; their emergence during convalescence warrants further study.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson P., Flesher A., Shaw S., Harding A. L., Smith D. H. Phenotypic and genetic variation in the susceptibility of Haemophilus influenzae type b to antibodies to somatic antigens. J Clin Invest. 1980 Apr;65(4):885–891. doi: 10.1172/JCI109741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Peter G., Johnston R. B., Jr, Wetterlow L. H., Smith D. H. Immunization of humans with polyribophosphate, the capsular antigen of Hemophilus influenzae, type b. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jan;51(1):39–44. doi: 10.1172/JCI106794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J., Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Outer membrane protein and biotype analysis of pathogenic nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):535–540. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.535-540.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk S. L., Holtsclaw S. A., Wiener S. L., Smith J. K. Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae in the elderly. Arch Intern Med. 1982 Mar;142(3):537–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branefors P., Dahlberg T. Serum bactericidal effect on capsulated and non-capsulated Haemophilus influenzae. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1980 Feb;88(1):47–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb00071.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg T., Branefors P. Characterization of the bactericidal antibody response against Haemophilus influenzae. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1980 Jun;88(3):115–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb00082.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigin R. D., Richmond D., Hosler D. W., Shackelford P. G. Reassessment of the role of bactericidal antibody in Hemophilus influenzae infection. Am J Med Sci. 1971 Dec;262(6):338–346. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197112000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granoff D. M., Rockwell R. Experimental Haemophilus influenzae type b meningitis: immunological investigation of the infant rat model. Infect Immun. 1978 Jun;20(3):705–713. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.3.705-713.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guckian J. C., Cavallo T., Fine D. P. Opsonization of pneumococci. II. Metabolic effects of a "third" human serum activity that mediates intracellular killing. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1666–1670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihara I., Harada Y., Ihara S., Kawakami M. A new complement-dependent bactericidal factor found in nonimmune mouse sera: specific binding to polysaccharide of Ra chemotype Salmonella. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1256–1260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram D. L., Collier A. M., Pendergrass E., King S. H. Methods for serotyping nasopharyngeal isolates of Haemophilus influenzae: slide agglutination, Quellung reaction, countercurrent immunoelectrophoresis, latex agglutination, and antiserum agar. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 May;9(5):570–574. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.5.570-574.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb M. R., Smith D. H. Outer membrane protein composition in disease isolates of Haemophilus influenzae: pathogenic and epidemiological implications. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):709–717. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.709-717.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MICHAEL J. G., WHITBY J. L., LANDY M. Studies on natural antibodies to gram-negative bacteria. J Exp Med. 1962 Jan 1;115:131–146. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Anderson P. Meningitis caused by Haemophilus influenzae in infant rats: protective immunity and antibody priming by gastrointestinal colonization with Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1979 Oct;140(4):471–478. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.4.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Vaughn K. A. The type b capsular polysaccharide as a virulence determinant of Haemophilus influenzae: studies using clinical isolates and laboratory transformants. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):517–524. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R. L., Norden C. W., Demchak T. A. Significance of noncapsular antigens in protection against experimental Haemophilus influenzae type b disease: cross-reactivity. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):619–626. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.619-626.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myhre E. B. Typing of Haemophilus influenzae by counterimmunoelectrophoresis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Apr;82(2):164–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb02308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä P. H., Peltola H., Käyhty H., Jousimies H., Pettay O., Ruoslahti E., Sivonen A., Renkonen O. V. Polysaccharide vaccines of group A Neisseria meningtitidis and Haemophilus influenzae type b: a field trial in Finland. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S43–S50. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M., Stull T. L., Smith A. L. Comparative virulence of Haemophilus influenzae with a type b or type d capsule. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):518–524. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.518-524.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saba T. M., Jaffe E. Plasma fibronectin (opsonic glycoprotein): its synthesis by vascular endothelial cells and role in cardiopulmonary integrity after trauma as related to reticuloendothelial function. Am J Med. 1980 Apr;68(4):577–594. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90310-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw S., Smith A. L., Anderson P., Smith D. H. The paradox of Hemophilus infuenzae type B bacteremia in the presence of serum bactericidal activity. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):1019–1029. doi: 10.1172/JCI108525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shurin P. A., Pelton S. I., Tager I. B., Kasper D. L. Bactericidal antibody and susceptibility to otitis media caused by nontypable strains of Haemophilus influenzae. J Pediatr. 1980 Sep;97(3):364–369. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80182-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon H. B., Southwick F. S., Moellering R. C., Jr, Sherman E. Hemophilus influenzae in hospitalized adults: current perspectives. Am J Med. 1980 Aug;69(2):219–226. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90381-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solotorovsky M., Lynn M. Haemophilus influenzae: immunology and immunoprotection. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1978 Sep;6(1):1–32. doi: 10.3109/10408417809090618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari R. P., Lynn M., Birnbaum A. J., Solotorovsky M. Characterization of the immunoprotective antigen of ribosomal preparations from Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):58–65. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.58-65.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. J., Jr, Musher D. M., Septimus E. J., McGowan J. E., Jr, Quinones F. J., Wiss K., Vance P. H., Trier P. A. Haemophilus influenzae infections in adults: characterization of strains by serotypes, biotypes, and beta-lactamase production. J Infect Dis. 1981 Aug;144(2):101–106. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.2.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



