Abstract
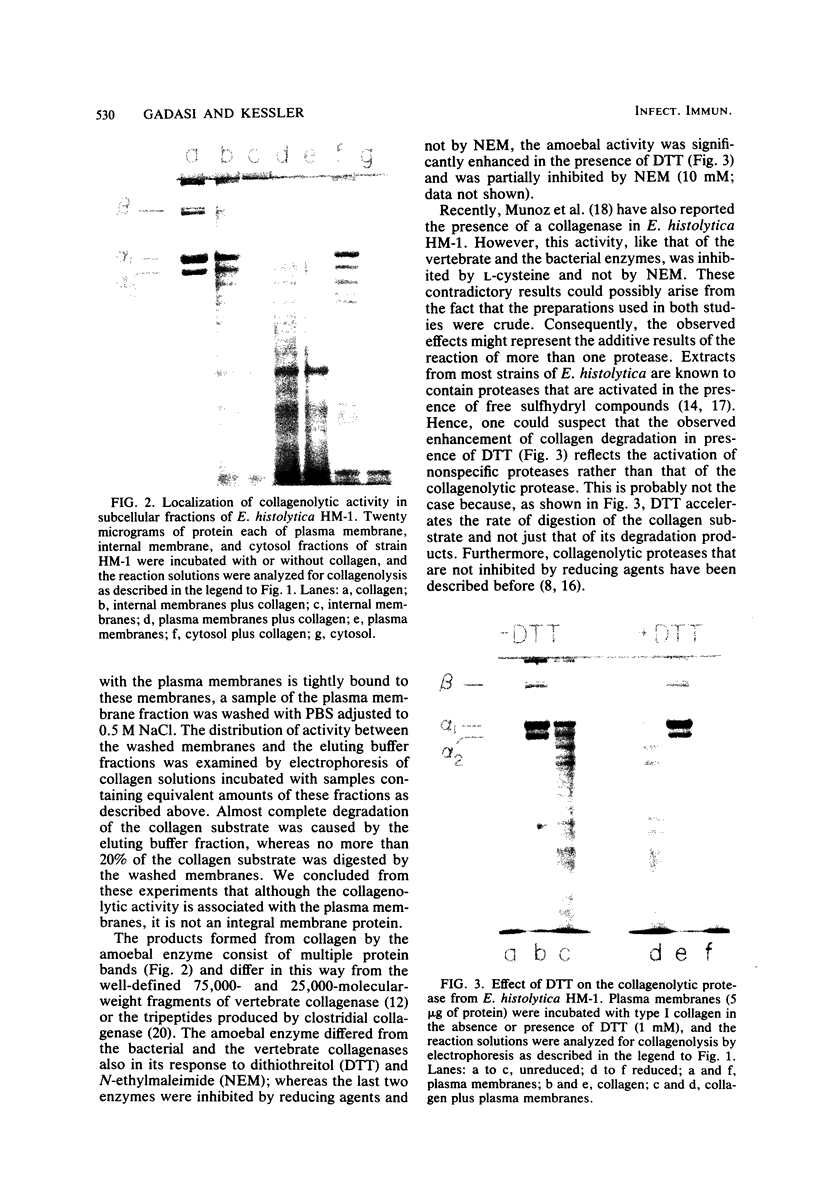
The levels of collagenolytic activity of strains HM-1:1 MSS (HM-1), (HM-1), 200-NIH, and HK-9 of Entamoeba histolytica were compared. Collagen degradation was evaluated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Conditioned media as well as extracts of the highly virulent strain HM-1 effectively degraded native type I collagen. Significantly lower activity was found in the analogous fractions of strains 200-NIH and HK-9, which are not as virulent. The collagenolytic activity of strain HM-1 was associated with the isolated plasma membrane fraction and could be eluted from the membranes by buffers of high ionic strength, indicating that it is not an integral membrane protein. Unlike the vertebrate and the clostridial collagenases, the collagenolytic activity of E. histolytica HM-1 was enhanced in presence of dithiothreitol and was inhibited by N-ethylmaleimide. The correlation between virulence of the individual strains and their collagenolytic activity suggests that collagenase might play a role in pathogenesis of amoebiasis. The localization of the enzyme on the plasma membrane and its presence in the extracellular medium favor this view.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aley S. B., Scott W. A., Cohn Z. A. Plasma membrane of Entamoeba histolytica. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):391–404. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos H. J. Entamoeba histolytica: cytopathogenicity of intact amebae and cell-free extracts; isolation and characterization of an intracellular toxin. Exp Parasitol. 1979 Jun;47(3):369–377. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(79)90089-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos H. J., Leijendekker W. J., van den Eijk A. A. Entamoeba histolytica: cytopathogenicity, including serum effects on contact-dependent and toxin-induced lysis of hamster kidney cell monolayers. Exp Parasitol. 1980 Dec;50(3):342–357. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(80)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S., Harlow D. R., Cunnick C. C. A new medium for the axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(4):431–432. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S., Phillips B. P., Bartgis I. L. A comparison of the virulence of nine strains of axenically cultivated E. histolytica in hamster liver. Arch Invest Med (Mex) 1974;5(Suppl 2):423–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton R. D., Meerovitch E., Costerton J. W. The functional morphology of pathogenicity in Entamoeba histolytica. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1970 Sep;64(3):299–304. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1970.11686695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen A. Z., Henderson K. O., Jeffrey J. J., Bradshaw R. A. A collagenolytic protease from the hepatopancreas of the fiddler crab, Uca pugilator. Purification and properties. Biochemistry. 1973 Apr 24;12(9):1814–1822. doi: 10.1021/bi00733a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadirian E., Meerovitch E. Behavior of axenic IP-106 strain of Entamoeba histolytica in the golden hamster. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1978 Mar;27(2 Pt 1):241–247. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1978.27.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillin F. D., Diamond L. S. Attachment and short-term maintenance of motility and viability of Entamoeba histolytica in a defined medium. J Protozool. 1980 May;27(2):220–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1980.tb04685.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. S., Cleary E. G. The determination of collagen and elastin. Methods Biochem Anal. 1967;15:25–76. doi: 10.1002/9780470110331.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarumilinta R., Maegraith B. G. Enzymes of entamoeba histolytica. Bull World Health Organ. 1969;41(2):269–273. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecroisey A., Boulard C., Keil B. Chemical and enzymatic characterization of the collagenase from the insect Hypoderma lineatum. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Nov;101(2):385–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb19730.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin J., Faubert G. Partial purification and some properties of a neutral sulfhydryl and an acid proteinase from Entamoeba histolytica. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Apr;23(4):420–425. doi: 10.1139/m77-062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., Croft B. Y., Guerrant R. L. Cytopathogenic mechanisms of Entamoeba histolytica. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):377–390. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trissl D., Martínez-Palomo A., Argüello C., de la Torre M., de la Hoz R. Surface properties related to concanavalin A-induced agglutination. A comparative study of several Entamoeba strains. J Exp Med. 1977 Mar 1;145(3):652–665. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.3.652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trissl D., Martínez-Palomo A., de la Torre M., de la Hoz R., Pérez de Suárez E. Surface properties of Entamoeba: increased rates of human erythrocyte phagocytosis in pathogenic strains. J Exp Med. 1978 Nov 1;148(5):1137–1143. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.5.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]