Abstract
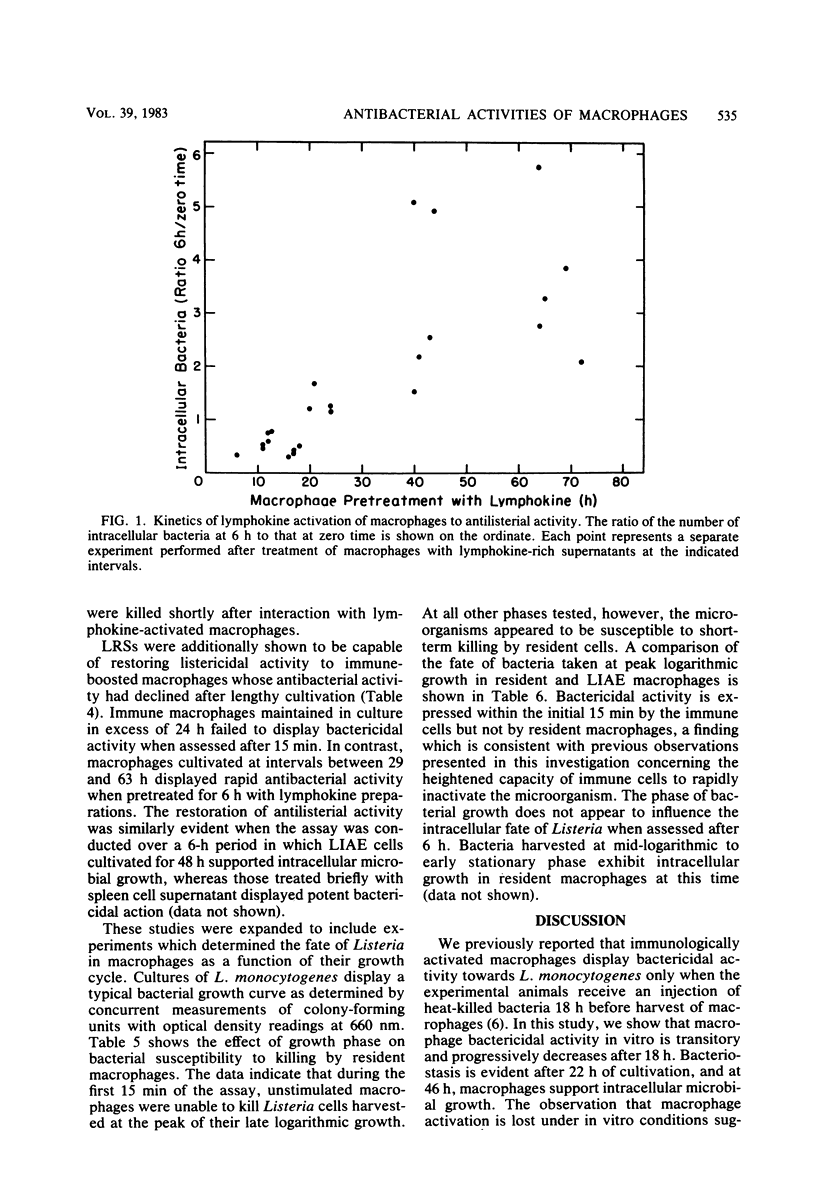
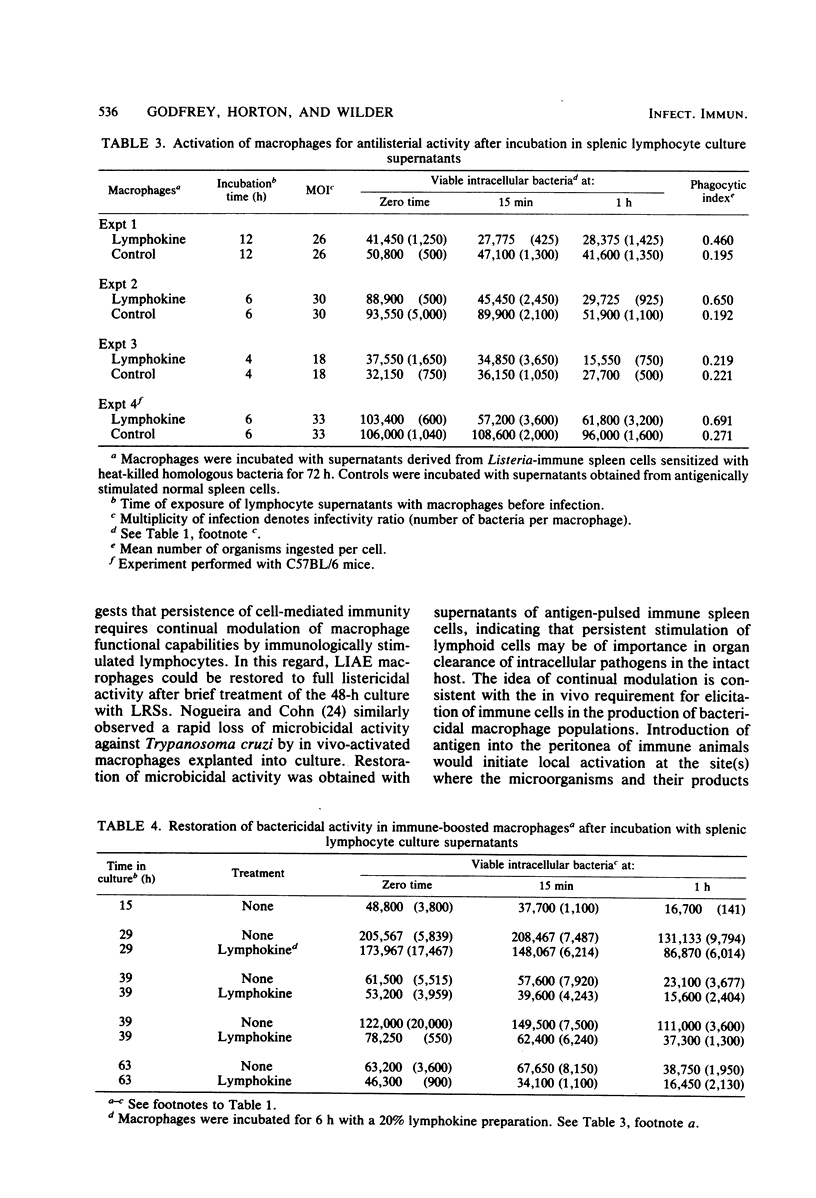
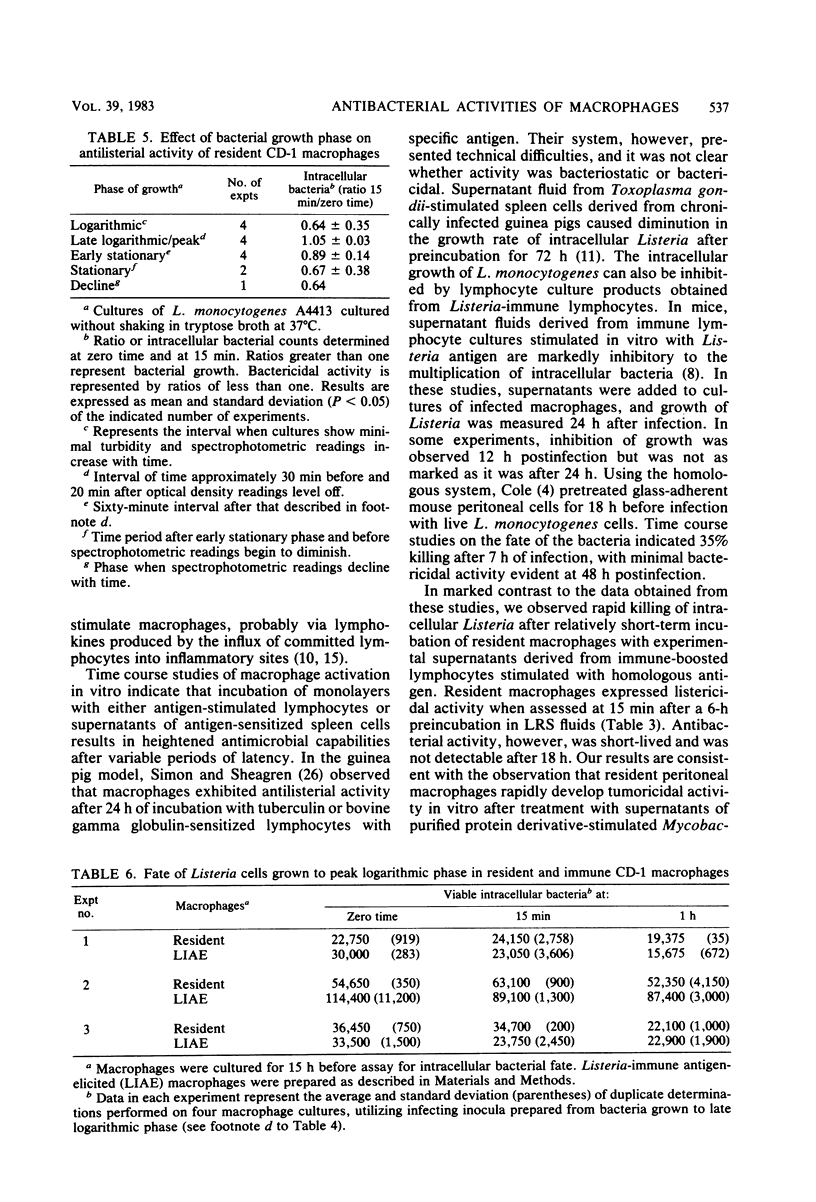
Murine peritoneal macrophages were rapidly rendered listericidal after exposure to lymphokine-rich supernatants (LRSs) derived from antigen-pulsed Listeria monocytogenes-immune spleen cells. A 6-h incubation period with LRSs was sufficient to induce microbicidal activity in resident macrophages. In vitro induction of macrophage listericidal activity by constant exposure to LRSs persisted for 18 h, after which time spleen cell factors were no longer capable of modifying intracellular inactivation of Listeria. Results obtained by utilizing a short assay indicated that the killing kinetics is extremely rapid, with large numbers of bacteria destroyed during the first 15 min of infection. Intracellular killing at this time appeared to be greatly dependent upon the stage of growth from which the microorganisms were harvested. Induction of bactericidal macrophages by infection of mice with a sublethal dose of virulent Listeria cells and subsequent intraperitoneal elicitation with heat-killed homologous bacteria was similarly a transient event. Macrophages harvested 18 h after antigenic challenge displayed dramatic antibacterial activity during the first 22 h in culture. After 22 h, activity was lost, and stasis was observed during the ensuing 23 h. At 68 h, macrophages were devoid of antilisterial action. Activity, however, could be recalled after incubation with LRSs.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baughin R. E., Bonventre P. F. Cell-mediated immune phenomena induced by lymphokines from splenic lymphocytes of mice with chronic staphylococcal infection. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):313–319. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.313-319.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baughn R., Bonventre P. F. Phagocytosis and intracellular killing of Staphylococcus aureus by normal mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):346–352. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.346-352.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole P. Activation of mouse peritoneal cells to kill Listeria monocytogenes by T-lymphocyte products. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):36–41. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.36-41.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowles R. E., Fajardo I. M., Leibowitch J. L., David J. R. The enhancement of macrophage bacteriostasis by products of activated lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Oct 1;138(4):952–964. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.4.952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington-Fowler L., Henson P. M., Wilder M. S. Fate of Listeria monocytogenes in resident and activated macrophages. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):11–16. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.11-16.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington-Fowler L., Wilder M. S. Fate of Listeria monocytogenes in murine peritoneal macrophage subpopulations. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):124–132. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.124-132.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T., Youmans G. P. The in vitro inhibition of growth of intracellular Listeria monocytogenes by lymphocyte products. Cell Immunol. 1973 Dec;9(3):353–362. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90050-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnovsky M. L., Lazdins J. K. Biochemical criteria for activated macrophages. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):809–813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koster F. T., McGregor D. D. The mediator of cellular immunity. 3. Lymphocyte traffic from the blood into the inflamed peritoneal cavity. J Exp Med. 1971 Apr 1;133(4):864–876. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.4.864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krahenbuhl J. L., Remington J. S. In vitro induction of nonspecific resistance in macrophages by specifically sensitized lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):337–343. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.337-343.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazdins J. K., Kühner A. L., David J. R., Karnovsky M. L. Alteration of some functional and metabolic characteristics of resident mouse peritoneal macrophages by lymphocyte mediators. J Exp Med. 1978 Sep 1;148(3):746–758. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.3.746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIKI K., MACKANESS G. B. THE PASSIVE TRANSFER OF ACQUIRED RESISTANCE TO LISTERIA MONOCYTOGENES. J Exp Med. 1964 Jul 1;120:93–103. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. The influence of immunologically committed lymphoid cells on macrophage activity in vivo. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):973–992. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor D. D., Logie P. S. The mediator of cellular immunity. VII. Localization of sensitized lymphocytes in inflammatory exudates. J Exp Med. 1974 Jun 1;139(6):1415–1430. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.6.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Cohn Z. A. Macrophage oxygen-dependent antimicrobial activity. III. Enhanced oxidative metabolism as an expression of macrophage activation. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1596–1609. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W. Susceptibility of Leishmania to oxygen intermediates and killing by normal macrophages. J Exp Med. 1981 May 1;153(5):1302–1315. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.5.1302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacy C. A., Leonard E. J., Meltzer M. S. Macrophages in resistance to rickettsial infections: characterization of lymphokines that induce rickettsiacidal activity in macrophages. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):204–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Karnovsky M. L., David J. R. Alterations of macrophage functions by mediators from lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1971 Jun 1;133(6):1356–1376. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.6.1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Remold H. G., David J. R. Characterization of a lymphocyte factor which alters macrophage functions. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):275–290. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Root R. K. Hydrogen peroxide release from mouse peritoneal macrophages: dependence on sequential activation and triggering. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1648–1662. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C., Nogueira N., Juangbhanich C., Ellis J., Cohn Z. Activation of macrophages in vivo and in vitro. Correlation between hydrogen peroxide release and killing of Trypanosoma cruzi. J Exp Med. 1979 May 1;149(5):1056–1068. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.5.1056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira N., Cohn Z. A. Trypanosoma cruzi: in vitro induction of macrophage microbicidal activity. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):288–300. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlager S. I., Meltzer M. S. Macrophage activation for tumor cytotoxicity: analysis of cellular lipid and fatty acid content during lymphokine activation. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1981 Mar;29(3):227–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon H. B., Sheagren J. N. Enhancement of macrophage bactericidal capacity by antigenically stimulated immune lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1972 Jun;4(2):163–174. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitalny G. L. Dissociation of bactericidal activity from other functions of activated macrophages in exudates induced by thioglycolate medium. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):274–284. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.274-284.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder M. S., Edberg J. C. Interaction of virulent and avirulent Listeria monocytogenes with cultured mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):409–415. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.409-415.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



