Abstract
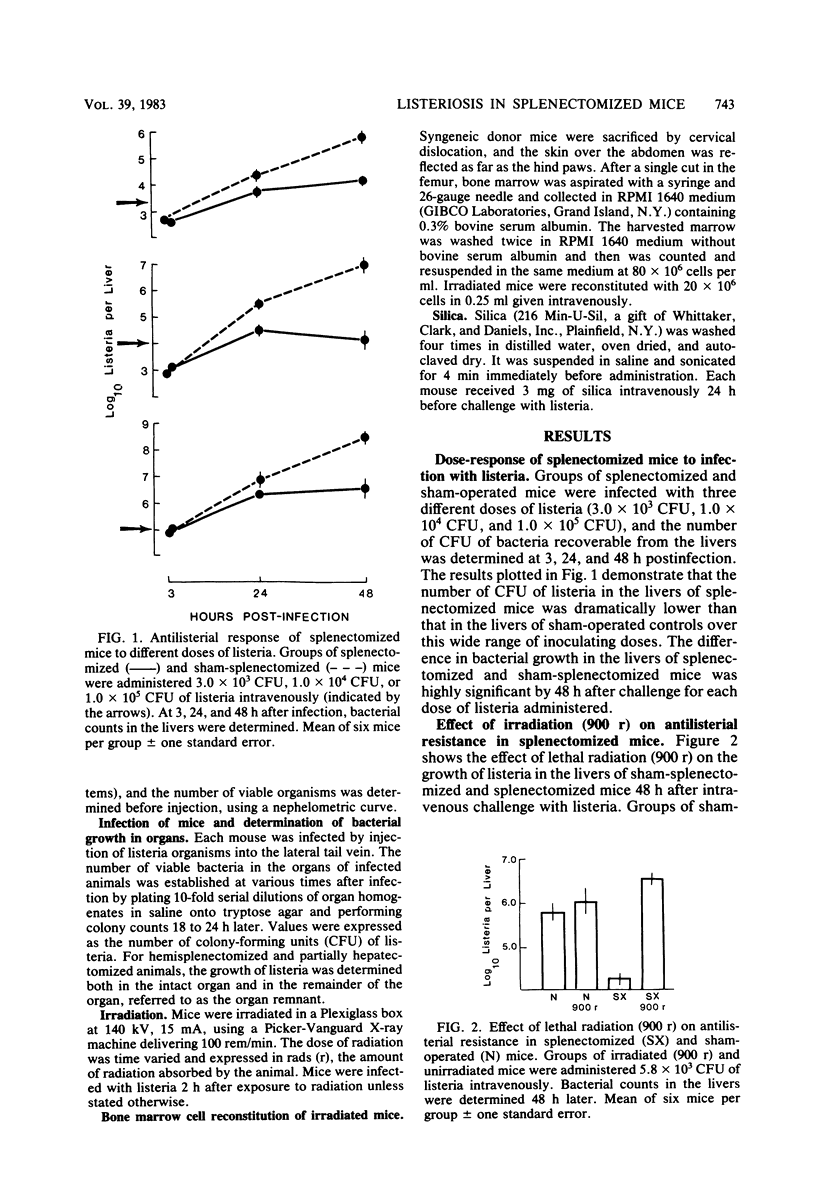
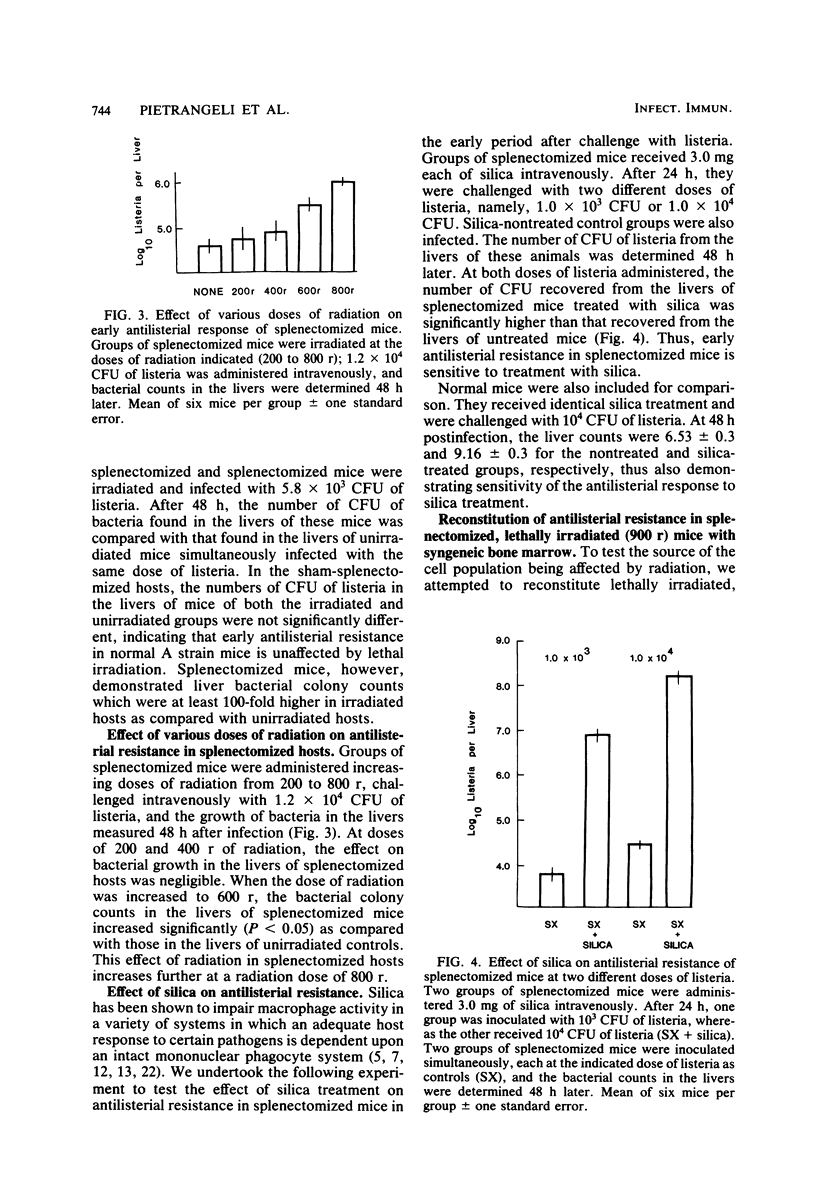
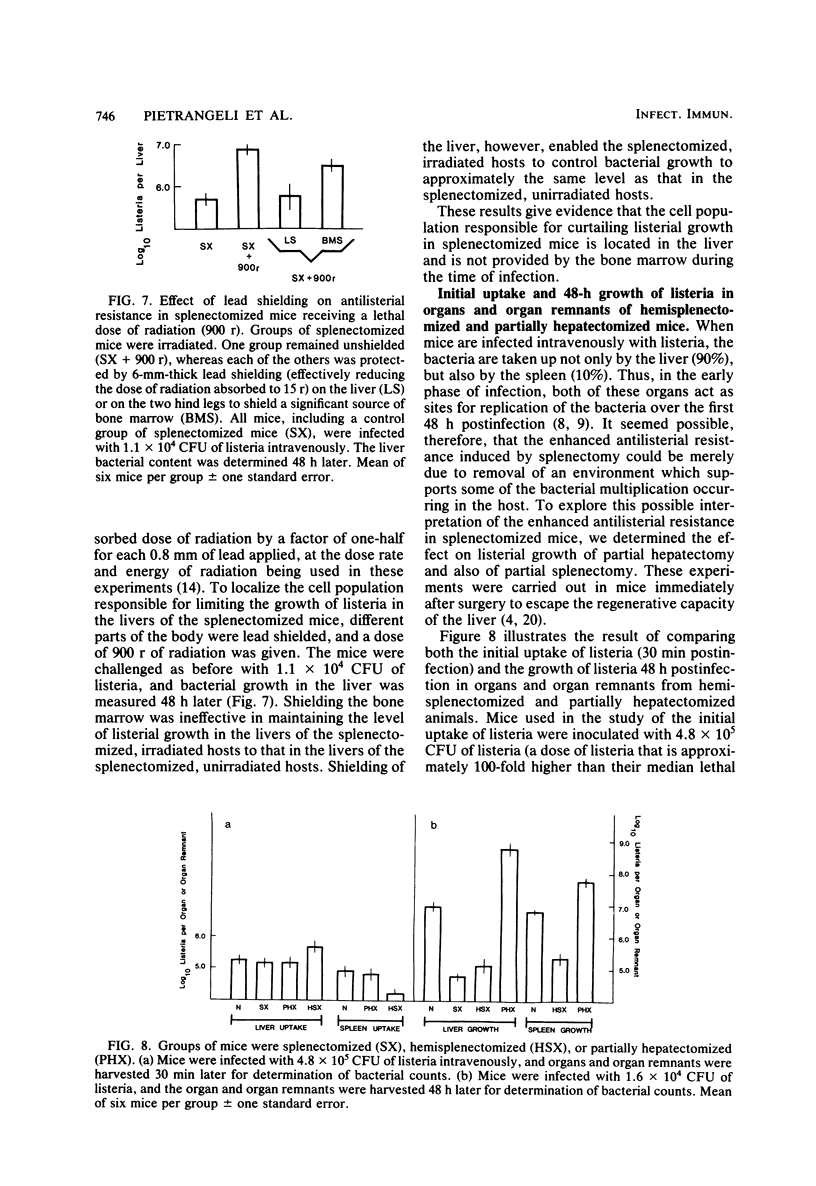
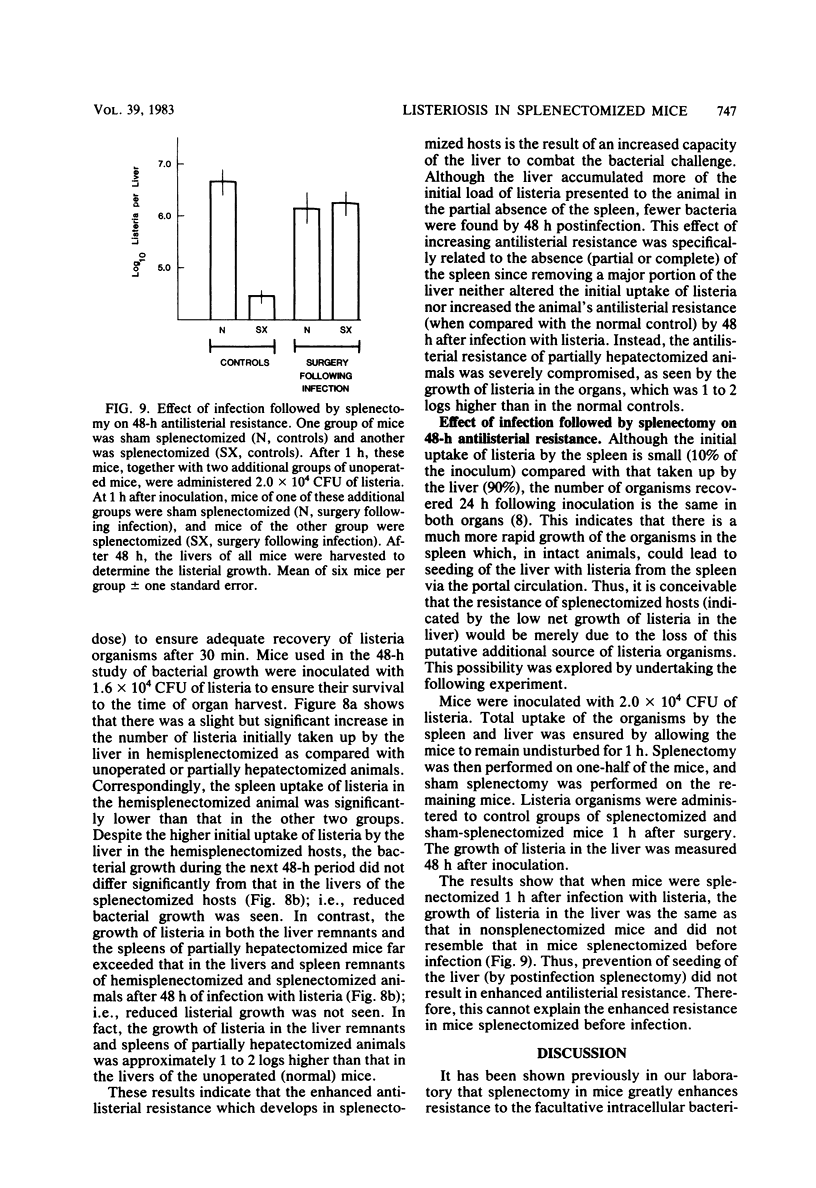
The characteristics of mononuclear phagocytes mediating resistance to infection with Listeria monocytogenes during the early phase (up to 48 h) of the response were investigated in mice of the A strain that had undergone splenectomy. Although irradiation in the sham-operated host had no effect on its antilisterial response when administered immediately before infection, it markedly reduced the ability of the splenectomized host to resist listerial challenge. This effect of radiation was demonstrable in the high-dose range (600 r) and could not be reversed immediately by repopulation with 20 × 106 syngeneic nucleated bone marrow cells. Administration of silica 24 h before infection profoundly enhanced the growth of L. monocytogenes in the liver of splenectomized mice. Shielding of the liver, but not the bone marrow, protected the splenectomized host against the effects of radiation, indicating that the cell population responsible for mediating the enhanced antilisterial resistance resides in the liver. The enhanced antilisterial resistance of splenectomized mice was specifically because of the absence of the spleen and not merely because of the removal of a favorable replicating environment for listeria organisms.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chan C., Kongshavn P. A., Skamene E. Enhanced primary resistance to Listeria monocytogenes in T cell-deprived mice. Immunology. 1977 Apr;32(4):529–537. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheers C., Waller R. Activated macrophages in congenitally athymic "nude mice" and in lethally irradiate mice. J Immunol. 1975 Sep;115(3):844–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmerling P., Finger H., Bockemühl J. Listeria monocytogenes infection in nude mice. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):437–439. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.437-439.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KESSEL R. W., MONACO L., MARCHISIO M. A. THE SPECIFICITY OF THE CYTOTOXIC ACTION OF SILICA--A STUDY IN VITRO. Br J Exp Pathol. 1963 Aug;44:351–364. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane F. C., Unanue E. R. Requirement of thymus (T) lymphocytes for resistance to listeriosis. J Exp Med. 1972 May 1;135(5):1104–1112. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.5.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy M. H., Wheelock E. F. Effects of intravenous silica on immune and non-immune functions of the murine host. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):41–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. The influence of immunologically committed lymphoid cells on macrophage activity in vivo. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):973–992. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. Cellular mediators of anti-Listeria immunity as an enlarged population of short lived, replicating T cells. Kinetics of their production. J Exp Med. 1973 Aug 1;138(2):342–355. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.2.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. The relative importance of blood monocytes and fixed macrophages to the expression of cell-mediated immunity to infection. J Exp Med. 1970 Sep 1;132(3):521–534. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.3.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Scher I., Formal S. B. Effect of silica on the innate resistance of inbred mice to Salmonella typhimurium infection. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):513–520. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.513-520.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearsall N. N., Weiser R. S. The macrophage in allograft immunity. I. Effects of silica as a specific macrophage toxin. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1968 Apr;5(2):107–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadarangani C., Skamene E., Kongshavn P. A. Cellular basis for genetically determined enhanced resistance of certain mouse strains to listeriosis. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):381–386. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.381-386.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skamene E., Chayasirisobhon W. Enhanced resistance to Listeria monocytogenes in splenectomized mice. Immunology. 1977 Dec;33(6):851–858. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skamene E., Chayasirisobhon W., Konshavn P. A. Increased phagocytic activity of splenectomized mice challenged with Listeria monocytogenes. Immunology. 1978 May;34(5):901–907. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya K., Shimotori S., Taniguchi T., Nomoto K. Cellular mechanisms in the protection against infection by Listeria monocytogenes in mice. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Jun;100(2):373–379. doi: 10.1099/00221287-100-2-373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkman A., Collins F. M. Recovery of delayed-type hypersensitivity in mice following suppressive doses of X-radiation. J Immunol. 1968 Nov;101(5):846–859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON M. E., STOWELL R. E., YOKOYAMA H. O., TSUBOI K. K. Cytological changes in regenerating mouse liver. Cancer Res. 1953 Jan;13(1):86–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Blanden R. V., Langman R. E. Early appearance of sensitized lymphocytes in mice infected with Listeria monocytogenes. J Immunol. 1974 Feb;112(2):496–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zisman B., Wheelock E. F., Allison A. C. Role of macrophages and antibody in resistance of mice against yellow fever virus. J Immunol. 1971 Jul;107(1):236–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



