Abstract
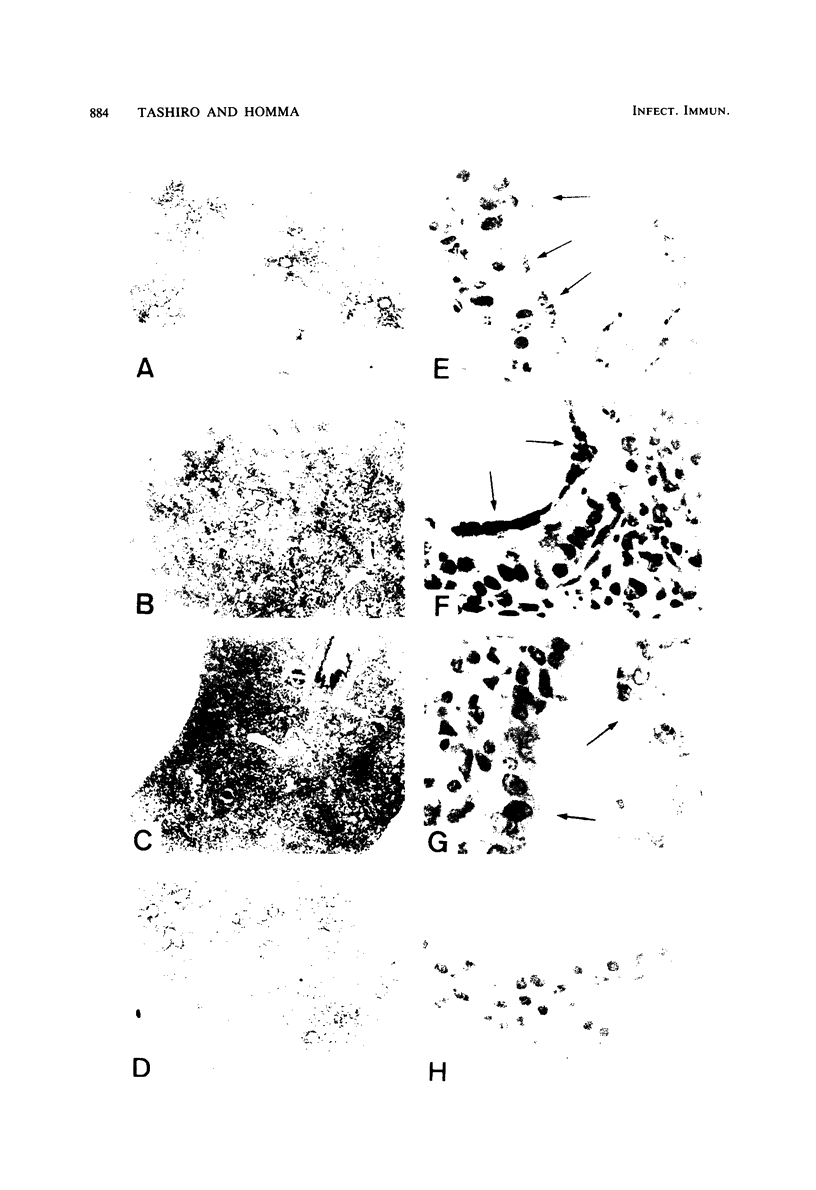
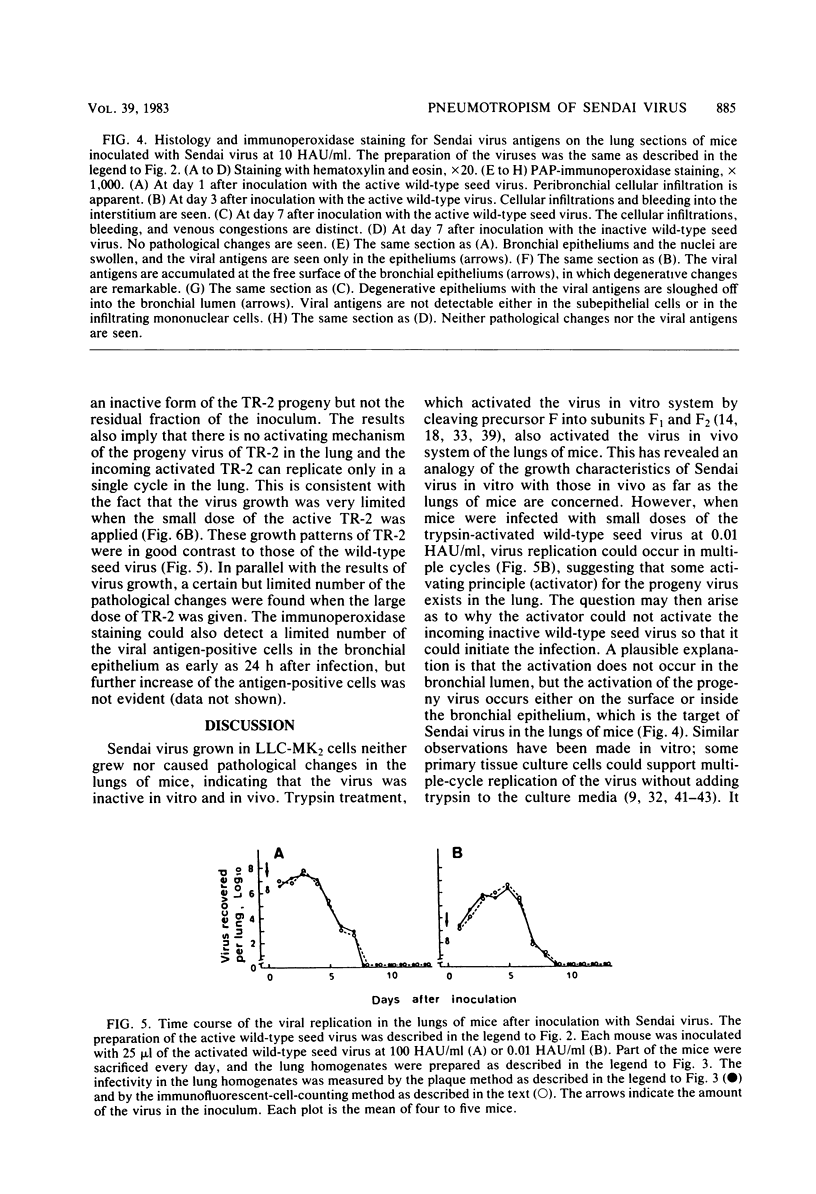
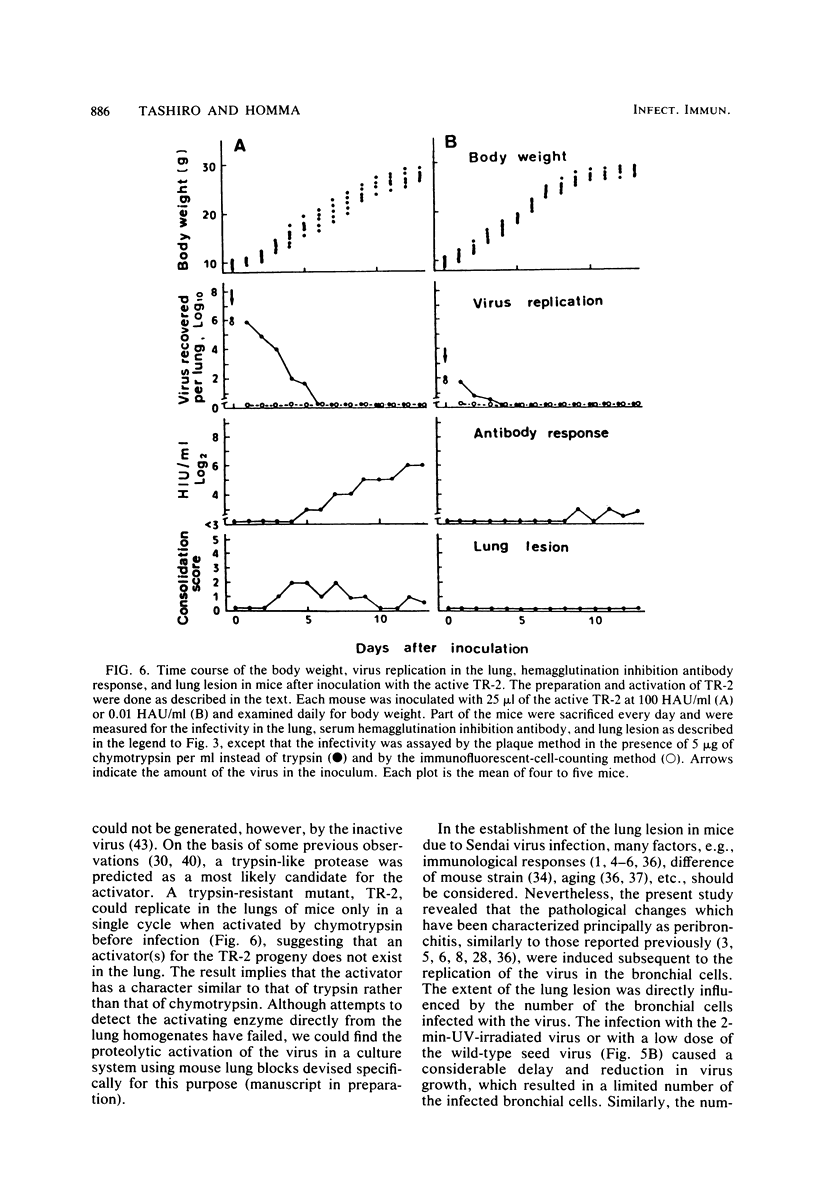
The pneumotropism of Sendai virus in mice was studied in relation to the activation and replication of the virus in the lung. Inactive Sendai virus grown in LLC-MK2 cells, which possessed an uncleaved precursor glycoprotein, F, and was noninfectious to tissue culture cells, neither grew nor caused pathological changes in the lung of mice. When trypsin treatment was made which cleaved F into F1 and F2 subunits, the virus became activated so that it could initiate replication in the bronchial epithelium of the lung. In this case, the progeny virus was produced in the activated form and multiple-cycle replication occurred successively. A parallel relationship was found between the degree of the viral replication and that of clinical signs of the respiratory disease, body weight loss, and histopathological changes in the lung. A protease mutant, TR-2, which was able to be activated only by chymotrypsin but not by trypsin, could also initiate replication in the bronchial epithelium, when activated by chymotrypsin before inoculation into mice. The progeny virus, however, remained inactive, and the replication was limited to a single cycle, which resulted in the limited lung lesion. The overall results suggest that some activating mechanism for the progeny virus of wild-type Sendai virus exists in the lung of mice and the principle (activator) responsible for this phenomenon has a character similar to trypsin. The possible location of the activator is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. J., Bainbridge D. R., Pattison J. R., Heath R. B. Cell-mediated immunity to Sendai virus infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):239–244. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.239-244.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. J., Pattison J. R., Cureton R. J., Argent S., Heath R. B. The role of host responses in the recovery of mice from Sendai virus infection. J Gen Virol. 1980 Feb;46(2):373–379. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-46-2-373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appell L. H., Kovatch R. M., Reddecliff J. M., Gerone P. J. Pathogenesis of Sendai virus infection in mice. Am J Vet Res. 1971 Nov;32(11):1835–1841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blandford G., Cureton R. J., Heath R. B. Studies of the immune respnse in Sendai virus infection of mice. J Med Microbiol. 1971 Aug;4(3):351–356. doi: 10.1099/00222615-4-3-351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blandford G., Heath R. B. Studies on the immune response and pathogenesis of Sendai virus infection of mice. I. The fate of viral antigens. Immunology. 1972 Apr;22(4):637–649. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blandford G. Studies on the immune response and pathogenesis of Sendai virus infection of mice. III. The effects of cyclophosphamide. Immunology. 1975 May;28(5):871–883. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew P., Sparrow S. A comparison in germ-free mice of the pathogenesis of Sendai virus and mouse pneumonia virus infections. J Pathol. 1980 Mar;130(3):153–158. doi: 10.1002/path.1711300303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlington R. W., Portner A., Kingsbury D. W. Sendai virus replication: an ultrastructural comparison of productive and abortive infections in avian cells. J Gen Virol. 1970 Dec;9(3):169–177. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-9-3-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINSBERG H. S., HORSFALL F. L., Jr Quantitative aspects of the multiplication of influenza A virus in the mouse lung; relation between the degree of viral multiplication and the extent of pneumonia. J Exp Med. 1952 Feb;95(2):135–145. doi: 10.1084/jem.95.2.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garten W., Berk W., Nagai Y., Rott R., Klenk H. D. Mutational changes of the protease susceptibility of glycoprotein F of Newcastle disease virus: effects on pathogenicity. J Gen Virol. 1980 Sep;50(1):135–147. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-1-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J., HOYER B. H. Early stages of enterovirus infection. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:101–112. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Ouchi M. Trypsin action on the growth of Sendai virus in tissue culture cells. 3. Structural difference of Sendai viruses grown in eggs and tissue culture cells. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1457–1465. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1457-1465.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Tamagawa S. Restoration of the fusion activity of L cell-borne Sendai virus by trypsin. J Gen Virol. 1973 Jun;19(3):423–426. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-19-3-423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Tozawa H., Shimizu K., Ishida N. A proposal for designation of Sendai virus proteins. Jpn J Microbiol. 1975 Dec;19(6):467–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1975.tb00967.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M. Trypsin action on the growth of Sendai virus in tissue culture cells. I. Restoration of the infectivity for L cells by direct action of tyrpsin on L cell-borne Sendai virus. J Virol. 1971 Nov;8(5):619–629. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.5.619-629.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M. Trypsin action on the growth of Sendai virus in tissue culture cells. II. Restoration of the hemolytic activity if L cell-borne Sendai virus by trypsin. J Virol. 1972 May;9(5):829–835. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.5.829-835.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M. [Host-induced modification of hemagglutinating virus of Japan (HVJ, Sendai virus) (author's transl)]. Uirusu. 1975 Sep;25(1-2):7–18. doi: 10.2222/jsv.25.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe C., Morgan C. Interactions between Sendai virus and human erythrocytes. J Virol. 1969 Jan;3(1):70–81. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.1.70-81.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISHIDA N., HOMMA M. A variant Sendai virus, infectious to egg embryos but not to L cells. III. Growth characteristics of myxoyiruses in tissue culture. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1960 Dec 25;73:56–69. doi: 10.1620/tjem.73.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISHIDA N., HOMMA M. Host-controlled variation observed with Sendai virus grown in mouse fibroblast (L) cells. Virology. 1961 Aug;14:486–488. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90342-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida N., Homma M. Sendai virus. Adv Virus Res. 1978;23:349–383. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mims C. A., Murphy F. A. Parainfluenza virus Sendai infection in macrophages, ependyma, choroid plexus, vascular endothelium and respiratory tract of mice. Am J Pathol. 1973 Mar;70(3):315–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan C., Howe C. Structure and development of viruses as observed in the electron microscope. IX. Entry of parainfluenza I (Sendai) virus. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):1122–1132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.1122-1132.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu M., Homma M. Trypsin action on the growth of Sendai virus in tissue culture cells. V. An activating enzyme for Sendai virus in the chorioallantoic fluid of the embryonated chicken egg. Microbiol Immunol. 1980;24(2):113–122. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1980.tb00569.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAGATA I., MAENO K., YOSHII S., MATSUMOTO T. PLAQUE FORMATION BY HVJ IN CALF KIDNEY CELLS. (BRIEF REPORT). Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1965;15:257–259. doi: 10.1007/BF01257738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai Y., Shimokata K., Yoshida T., Hamaguchi M., Iinuma M., Maeno K., Matsumoto T., Klenk H. D., Rott R. The spread of a pathogenic and an apathogenic strain of Newcastle disease virus in the chick embryo as depending on the protease sensitivity of the virus glycoproteins. J Gen Virol. 1979 Nov;45(2):263–272. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-45-2-263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohuchi M., Homma M. Trypsin action on the growth of Sendai virus in tissue culture cells. IV. Evidence for activation of sendai virus by cleavage of a glycoprotein. J Virol. 1976 Jun;18(3):1147–1150. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.3.1147-1150.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker J. C., Whiteman M. D., Richter C. B. Susceptibility of inbred and outbred mouse strains to Sendai virus and prevalence of infection in laboratory rodents. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):123–130. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.123-130.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson T. W., Cureton R. J., Heath R. B. The effect of cyclophosphamide on Sendai virus infection of mice. J Med Microbiol. 1969 May;2(2):137–145. doi: 10.1099/00222615-2-2-137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson T. W., Cureton R. J., Heath R. B. The pathogenesis of Sendai virus infection in the mouse lung. J Med Microbiol. 1968 Aug;1(1):89–95. doi: 10.1099/00222615-1-1-89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez Boulan E., Sabatini D. D. Asymmetric budding of viruses in epithelial monlayers: a model system for study of epithelial polarity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5071–5075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAWICKI L. Influence of age of mice on the recovery from experimental Sendal virus infection. Nature. 1961 Dec 30;192:1258–1259. doi: 10.1038/1921258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAWICKI L. Studies on experimental Sendai virus infection in laboratory mice. Acta Virol. 1962 Jul;6:347–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHIGETA S. PLAQUE FORMATION AND GROWTH CHARACTERISTICS OF SENDAI VIRUS IN CHICK KIDNEY CELL CULTURES. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1964 Jul 25;83:114–120. doi: 10.1620/tjem.83.114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Identification of biological activities of paramyxovirus glycoproteins. Activation of cell fusion, hemolysis, and infectivity of proteolytic cleavage of an inactive precursor protein of Sendai virus. Virology. 1974 Feb;57(2):475–490. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90187-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Protease activation mutants of sendai virus. Activation of biological properties by specific proteases. Virology. 1976 Jan;69(1):265–277. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90213-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuta H., Akami M., Matumoto M. Plaque formation by sendai virus of parainfluenza virus group, type 1 on monkey, calf kidney and chick embryo cell monolayers. Jpn J Microbiol. 1971 Mar;15(2):175–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1971.tb00567.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S. M., Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Loss on serial passage of rhesus monkey kidney cells of proteolytic activity required for Sendai virus activation. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):235–241. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.235-241.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita K., Maru M., Sato K. A sensitive plaque assay for Sendai virus in an established line of monkey kidney cells. Jpn J Microbiol. 1974 May;18(3):262–264. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1974.tb00955.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. R. The nature of Reed-Sternberg cells and other malignant "reticulum" cells. Lancet. 1974 Oct 5;2(7884):802–807. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Nunen M. C., van der Veen J. Experimental infection with Sendai virus in mice. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1967;22(3):388–397. doi: 10.1007/BF01242959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]