Abstract
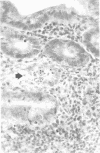
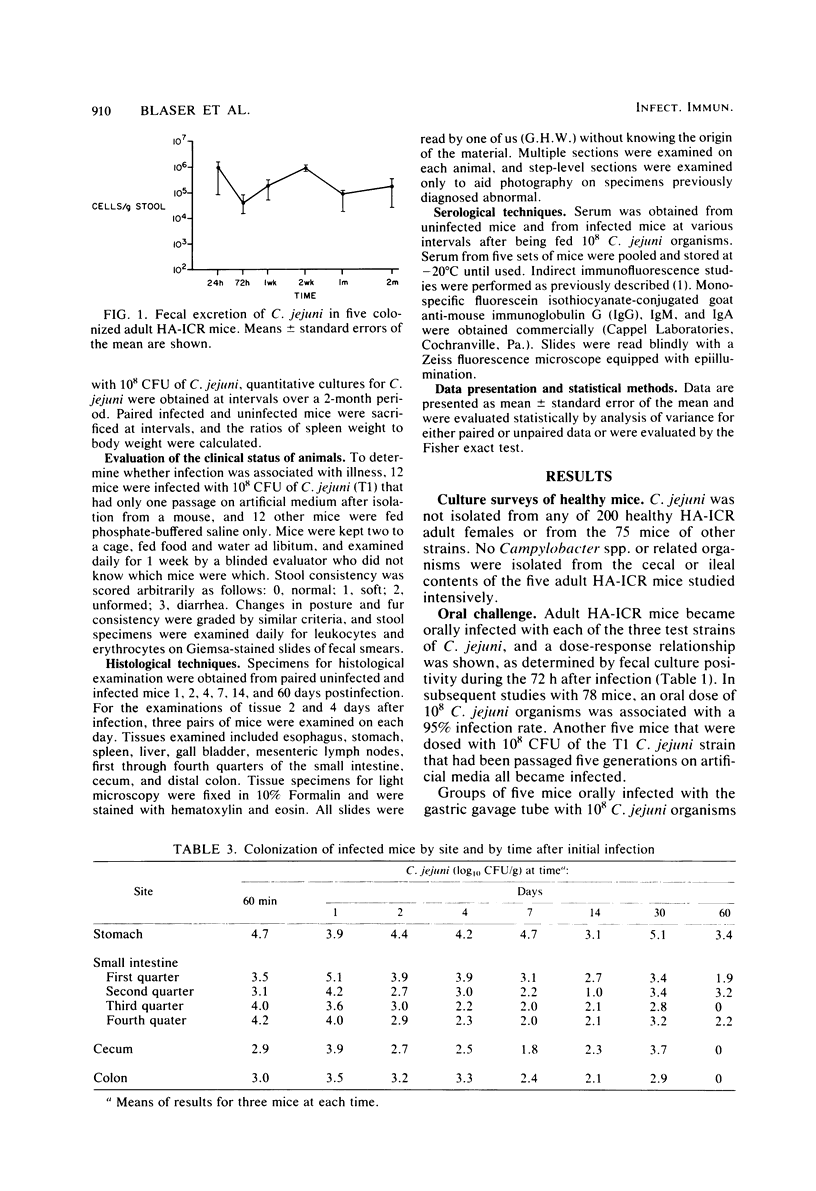
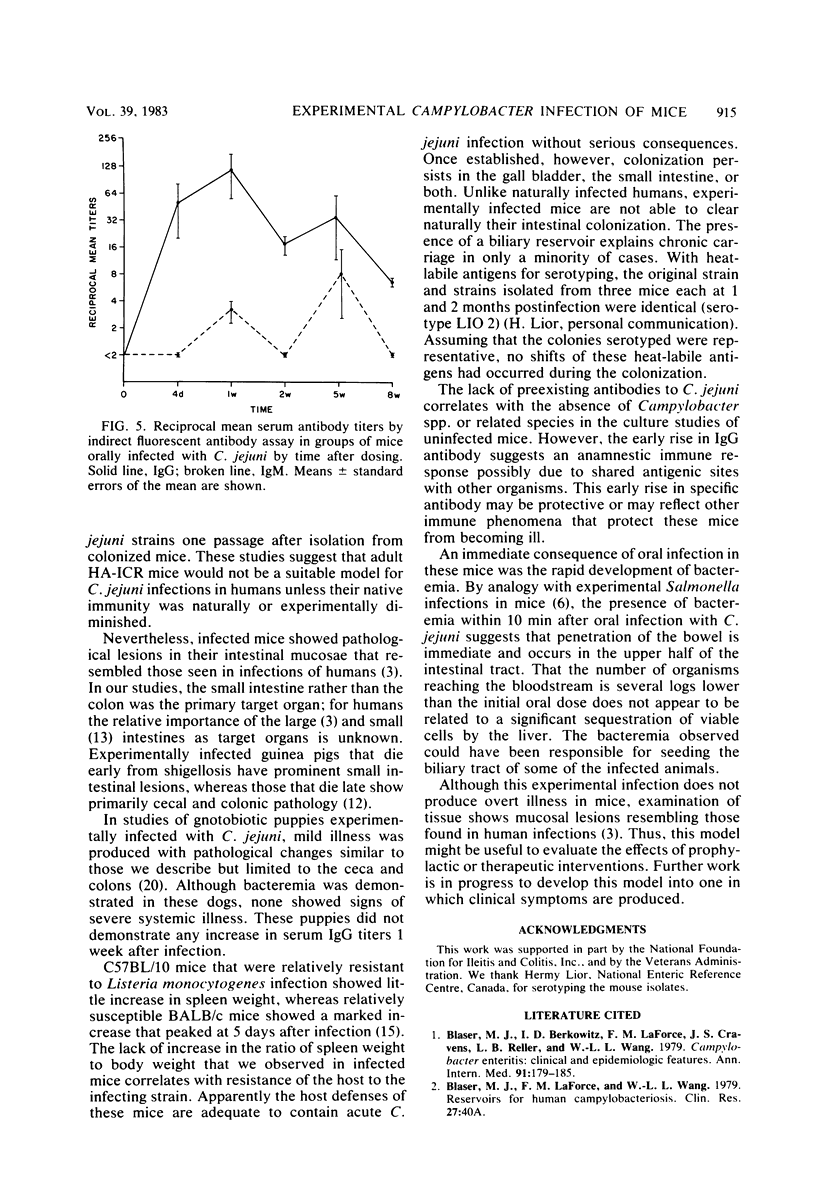
HA-ICR adult mice were studied to develop an animal model for Campylobacter jejuni enteritis in humans. Fecal and ileal cultures made by selective and nonselective methods showed that C. jejuni and related organisms are not bowel commensals. Intragastric feeding of 108 CFU of three different strains of C. jejuni produced infection in 100% of the animals, and infection rates were dose dependent. Pretreatment with antibiotics or opiates was not necessary to induce infection. Fresh isolates and strains passed on artificial media yielded similar infection rates. Infected mice did not show signs of illness, but transient bacteremia within 10 min of oral infection was observed in nearly 100%. The small intestine was the principal target organ, with epithelial inflammation seen 48 h after infection. Control mice of four species had undetectable serum immunoglobulin G antibody specific for the infecting strain, but infected mice showed peak titers at 1 week with rapid decline. Immunoglobulin M titers rose minimally, and immunoglobulin A titers did not rise. Infected mice uniformly became chronic asymptomatic excretors, shedding 104 to 106 CFU/g of feces; a minority were biliary carriers. Intestine carriage was most pronounced in the stomach and proximal small intestine. Because this experimental infection led to bacteremia, transient pathological changes, and immunoglobulin G titer rises, this model may be useful for evaluating the effects of prophylactic and therapeutic interventions.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaser M. J., Berkowitz I. D., LaForce F. M., Cravens J., Reller L. B., Wang W. L. Campylobacter enteritis: clinical and epidemiologic features. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Aug;91(2):179–185. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Parsons R. B., Wang W. L. Acute colitis caused by Campylobacter fetus ss. jejuni. Gastroenterology. 1980 Mar;78(3):448–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Reller L. B. Campylobacter enteritis. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1444–1452. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butzler J. P., Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis. Clin Gastroenterol. 1979 Sep;8(3):737–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Immunity to enteric infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1970 Mar;1(3):243–250. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.3.243-250.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbel M. J., Redwood D. W. Susceptibility of the bank vole Clethrionomys glariolus to infection with Campylobacter fetus. Br Vet J. 1978 May-Jun;134(3):212–213. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)33484-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. P., McAllister J. S., Savage D. C. Microbial colonization of the intestinal epithelium in suckling mice. Infect Immun. 1973 Apr;7(4):666–672. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.4.666-672.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORMAL S. B., DAMMIN G. J., SCHNEIDER H., LABREC E. H. Experimental Shigella infections. II. Characteristics of a fatal enteric infection in guinea pigs following the subcutaneous inoculation of carbon tetrachloride. J Bacteriol. 1959 Dec;78:800–804. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.6.800-804.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernie D. S., Park R. W. The isolation and nature of campylobacters (microaerophilic vibrios) from laboratory and wild rodents. J Med Microbiol. 1977 Aug;10(3):325–329. doi: 10.1099/00222615-10-3-325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field L. H., Underwood J. L., Pope L. M., Berry L. J. Intestinal colonization of neonatal animals by Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):884–892. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.884-892.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgeorge R. B., Baskerville A., Lander K. P. Experimental infection of Rhesus monkeys with a human strain of Campylobacter jejuni. J Hyg (Lond) 1981 Jun;86(3):343–351. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400069096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay D. J., Ganguli L. A. Campylobacter enteritis presenting as an acute abdomen. Postgrad Med J. 1980 Mar;56(653):205–206. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.56.653.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madge D. S. Campylobacter enteritis in young mice. Digestion. 1980;20(6):389–394. doi: 10.1159/000198479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel T. E., Cheers C. Resistance and susceptibility of mice to bacterial infection: histopathology of listeriosis in resistant and susceptible strains. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):851–861. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.851-861.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pejtschev P. Ein Fall von Vibrio Fetus bei Rattus norvegicus. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1969 Jul;16(5):480–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L., Hennessy J. N. Passive hemagglutination technique for serotyping Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni on the basis of soluble heat-stable antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Dec;12(6):732–737. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.6.732-737.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F., Barker I. K., Manninen K. I., Miniats O. P. Campylobacter jejuni colitis in gnotobiotic dogs. Can J Comp Med. 1981 Oct;45(4):377–383. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roach S., Tannock G. W. A note on the isolation of spiral-shaped bacteria from the caecum of mice. J Appl Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;47(3):521–525. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1979.tb01213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Palacios G. M., Escamilla E., Torres N. Experimental Campylobacter diarrhea in chickens. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):250–255. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.250-255.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]