Abstract
Background
Interleukin 4 (IL-4) is an anti-inflammatory cytokine, which regulates balance between TH1 and TH2 immune response, immunoglobulin class switching and humoral immunity. Polymorphisms in this gene have been reported to affect the risk of infectious and autoimmune diseases.
Methods
We have analyzed three regulatory IL-4 polymorphisms; -590C>T, -34C>T and 70 bp intron-3 VNTR, in 4216 individuals; including: (1) 430 ethnically matched case-control groups (173 severe malaria, 101 mild malaria and 156 asymptomatic); (2) 3452 individuals from 76 linguistically and geographically distinct endogamous populations of India, and (3) 334 individuals with different ancestry from outside India (84 Brazilian, 104 Syrian, and 146 Vietnamese).
Results
The -590T, -34T and intron-3 VNTR R2 alleles were found to be associated with reduced malaria risk (P<0.001 for -590C>T and -34C>T, and P = 0.003 for VNTR). These three alleles were in strong LD (r2>0.75) and the TTR2 (-590T, -34T and intron-3 VNTR R2) haplotype appeared to be a susceptibility factor for malaria (P = 0.009, OR = 0.552, 95% CI = 0.356 –0.854). Allele and genotype frequencies differ significantly between caste, nomadic, tribe and ancestral tribal populations (ATP). The distribution of protective haplotype TTR2 was found to be significant (χ2 3 = 182.95, p-value <0.001), which is highest in ATP (40.5%); intermediate in tribes (33%); and lowest in caste (17.8%) and nomadic (21.6%).
Conclusions
Our study suggests that the IL-4 polymorphisms regulate host susceptibility to malaria and disease progression. TTR2 haplotype, which gives protection against malaria, is high among ATPs. Since they inhabited in isolation and mainly practice hunter-gatherer lifestyles and exposed to various parasites, IL-4 TTR2 haplotype might be under positive selection.
Introduction
Plasmodium falciparum malaria is one of the major causes of morbidity and mortality in tropical and sub-tropical areas [1]. Despite the significant advances in disease control, Plasmodium falciparum malaria accounts for 1–3 million deaths annually [2]. The variation in the severity of Plasmodium falciparum infections include different phenotypes such as hyper or asymptomatic parasitaemia, mild malaria, severe malaria and cerebral malaria [3], [4] and the host genetic architecture contribute to these malarial phenotypes [5]. Increasing epidemiological and experimental evidences suggest that the host genetic variations play an essential role to thwart actively or passively the parasite invasion. [4]. The fundamental attribute of the innate immune system is to recognize pathogen and react swiftly to contain the early infection while signaling to specific adaptive immune response. Studies have investigated role of innate immune genes such as Toll-like receptors (TLR2, 4, 9), chemokines and cytokines role in Plasmodium falciparum malaria [6]. In addition, plethora of studies have documented that genetic heterogeneity in many immune genes is associated with malaria susceptibility [3].
Malarial infection is characterized by pro-inflammatory responses during early stages of infection followed by anti-inflammatory responses during disease progression [7]. The human Interleukin 4 (IL-4) located in the chromosome 5 (5q31-33), is an anti-inflammatory cytokine produced by CD4+ Th2 cells, basophils and mast cells. IL-4 regulates variety of cell types [8] and play an essential role in differentiation of Th2 effector cells, suppression of Th1 signaling, promoting humoral immunity and Ig class switching and a dominant role in immunopathology [9], [10], [11]. Studies have revealed that INF-γ levels were significantly elevated during early stages of malaria, whereas the IL-4 levels were elevated during intermediate and late stages indicating a switch towards Th2 response [12]. A significant inverse correlation between IL-4 to INF-γ ratio and peripheral parasitaemia in malaria patients has been documented [13].
Human IL-4 gene promoter contains six conserved binding sites of NFAT (nuclear factor of activated T-cells), a transcription factor; along with activator protein 1 (AP1) regulates IL-4 transcription [14]. Studies have shown that the -590C/T transition creates a seventh NFAT binding site and synergistically up regulates IL-4 transcription rate up to 3 fold [15]. Studies have documented that elevated antibody IgG and IgE levels against malaria antigens, parasitaemia and malaria susceptibility has been associated with IL-4 -590T allele in several African populations [8], [16], [17], [18], [19]. The -590T allele is believed to be under positive selection in various populations and indicates local adaptation to diverse pathogenic challenges [20]. Further, -34T promoter polymorphism association with elevated total serum IgE levels has been demonstrated [8]. Also the presence of H3K27Ac mark was observed near active regulatory element of intron-3 VNTR region in different cell lines (www.ucsc.edu). Studies have established that IL-4 as a key regulator in malaria and three regulatory IL-4 polymorphisms (-590C/T, -34C/T and in intron-3 VNTR) have been shown to regulate serum IL-4 levels, IgG, IgE, disease progression and survival [16], [17], [18], [19], [21], [22], [23], [24], [25]. Also the three regulatory polymorphisms in the IL-4 loci were associated with end stage renal disease, multiple sclerosis, autoimmune Grave’s disease, chronic polyarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, rhinitis and atopic dermatitis [21], [26], [27], [28], [29].
Although several studies have documented on functional significance of IL-4 polymorphisms in different ethnicities, to the best of our knowledge no studies have investigated the contribution of IL-4 variants in Indian population. Indian populations remain isolated from rest of the world for thousands of years and are unique in their origin and have accumulated unique set of mutations and the variants influencing disease susceptibility among Indian populations remain different compared to other ethnicities [30]–[31]. In this study, we aim to investigate the contribution of three functional IL-4 polymorphisms rs2243250 (-590 C>T, promoter), rs2070874 (-34 C>T, 5′UTR) and rs79071878 (intron-3, 70 bp VNTR) with P. falciparum malaria infection in well-defined malaria cases and in ethnically matched controls. Since the entire Indian subcontinent represents a malaria endemic region, we extended our investigation of the three functional IL-4 polymorphisms to different linguistically and geographically isolated Indian populations and compared the observed differences to that of different ethnicities representing world populations.
Materials and Methods
Study Subjects
A total of 4216 individuals were investigated for IL-4 gene polymorphisms (-590C/T, -34C/T and in intron-3 VNTR). Of which 173 individuals were clinically characterized with Plasmodium falciparum severe malaria and 101 with mild malaria and 156 with asymptomatic individuals from P. falciparum endemic states, Orissa and Chhattisgarh (Table 1). We also utilized 3452 individuals from 76 distinct populations representing caste (n = 1568), nomadic (n = 114), tribes (n = 517) and ancestral tribal populations [(ATP) (n = 1253)] of India. Also three world populations representing tropical regions such as Brazil (n = 84), Syria (n = 104) and Vietnam (n = 146) were included in this study (Table 2).
Table 1. Characteristics of studied subjects segregated according to clinical classification.
| Sample Size | Mean Age (year)± SD | Male: Female | |
| Asymptomatic | 156 | 29.87±19.57 | 92∶64 |
| Mild Malaria | 101 | 30.24±15.71 | 67∶34 |
| Severe Malaria | 173 | 26.11±12.38 | 103∶70 |
Table 2. Characteristics of studied subjects of various world populations.
| Ethnicity | Population | No. of individuals |
| India | Caste | 1568 |
| Nomadic | 114 | |
| Tribe | 517 | |
| Ancestral tribes | 1253 | |
| Brazil | Brazil | 84 |
| Syria | Syria | 104 |
| Vietnam | Vietnam | 146 |
Sampling
All individuals representing the malaria cohort were clinically classified. Classification of malaria was carried out on WHO guidelines; severe malaria (n = 173) is defined as severe anemia (hemoglobin <50 g/l) and/or hyper-parasitemia (>250,000 parasites/µl, corresponding to >10% infected erythrocytes), a Blantyre coma score ≤2 and other facultative signs of severe malaria such as cerebral malaria, convulsions, hypoglycemia, and respiratory distress. All individuals were hospitalized for treatment. Mild malaria (n = 101) is defined as parasitemia 1000–50,000/µl on admission, no schizontaemia, circulating leukocytes containing malarial pigment <50/µl, not homozygous for hemoglobin S, hemoglobin >80 g/l, platelets >50/nl, leukocytes <12/nl, lactate <3 mmol/l, and blood glucose >50 mg/dl. Asymptomatic individuals (n = 156) were characterized as individuals harboring parasites without clinical signs during sample collection. Intra-venous blood sample (∼5 ml) was collected from each individual admitted at Ispat General Hospital, Rourkela, India; and Pt. Jawaharlal Nehru Memorial Medical College, Raipur, India.
Ethical Committee Approval
An informed written consent was obtained from every individual. The study was approved by the Institutional Ethical Committee (IEC) of Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology, Hyderabad, India; Ispat General Hospital, Rourkela, Orissa, India; and Pt. Jawaharlal Nehru Memorial Medical College, Raipur, Chhattisgarh, India.
Genotyping of SNP and VNTR Variants
Genomic DNA was extracted from whole blood using the protocol as previously described [32]. To re-sequence 800 bp of IL-4 promoter region, we utilized the reference sequence from the ENSEMBL (ID: ENSG00000113520; www.ensembl.org). The sequence specific primer pairs were designed using the Primer-BLAST (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/tools/primer-blast), MacVector (MacVector, Inc. USA) and the Amplify 3X (http://engels.genetics.wisc.edu/amplify) software platforms.
DNA was amplified using a primer pair spanning the promoter regions to detect polymorphisms at -590C/T and -34C/T variants. The primer pairs employed were IL-4_promo_F: 5′-TATGGACCTGCTGGGACCCAAACTA-3′, and IL-4_promo_R: 5′-CACCTTCTGCTCTGTGAGGCTGTTC-3′ (Eurofiins mwg operon). In brief: 5 ng of genomic DNA was amplified in a 10 µl reaction volume using Qiagen long-range PCR kit following manufacturers instructions (Qiagen, Germany) on a GeneAmp 9700 Thermal cycler (ABI, USA). Thermal cycling parameters for amplification were: initial denaturation at 94°C for 3 min, followed by 35 cycles of 30 sec at 93°C denaturation, 25 sec at 66°C annealing, 1 min 30 sec at 68°C extension, followed by a final extension of 5 min at 68°C. PCR products were cleaned up using Exo-SAP-IT (USB, Affymetrix, USA) and 1 µl of the purified product were directly used as templates for sequencing, using the BigDye terminator v. 3.1 cycle sequencing kit Applied Biosystems, USA) on an ABI 3730XL DNA sequencer, according to the manufacturer’s instructions. DNA polymorphisms were identified when assembled with the reference sequence using AutoAssembler software (Applied Biosystems).
The variable nucleotide repeat regions (VNTR) in the intron-3 were amplified using primer pairs IL-4_del_70_F: 5′-GCCTTTAGATTCCACCACGAGTATG-3′ and IL-4_del_70_R: 5′-GGTCATCTTTTCCTCCCCTGTATCTTA-3′. PCR products were size fractionated on 2% agarose gel to detect the repeat polymorphisms. PCR amplicons of 389 bp (two repeats each of 70 bp) were designated as R2 whereas amplicons of 459 bp (three repeats, each of 70 bp) as R3. A subset of samples were reconfirmed and validated for their R2 and R3 polymorphisms by direct sequencing.
Statistical Analysis
The allele and genotype frequencies were analyzed by simple gene counting and expectation-maximum (EM) algorithm and the significance of deviations from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium was tested using the random-permutation procedure as implemented in the Arlequin v.3.5.1.2 software (http://cmpg.unibe.ch/software/arlequin3/) [33]. Pairwise Fst values and co-ancestry coefficient were calculated using Arlequin using un-phased data Linkage disequilibrium (LD) analysis was performed using Haploview v4.2 software [34]. The allele and genotype distribution were calculated by chi square test in different sample sets using the SPSS (ver. 20). In all analysis, a two tailed p-value less than 0.05 were considered significant. Chi square contingency-table test results were interpreted by standardized residual method of post hoc analysis [35]. Probable effect of sex stratification and sample size were verified by bootstrap (10000 random sampling events) with bias-corrected and accelerated (BCa) method, using SPSS (ver. 20).
Results
Role of IL-4 Variants in Malaria
The distributions of IL-4 genotype and allele frequencies are summarized in Table 3 and Figure 1. Mainly two copies and three copies of 70 bp repeat (intron-3 VNTR) has been observed in humans and are designated as R2 and R3 respectively, whereas only a single copy of 70 bp repeat has been observed in other primates (Figure S1, www.ensembl.org). The genotype frequencies of intron-3 VNTR polymorphism differed significantly among ethnically matched asymptomatic controls, individuals with mild and severe malaria (χ2 4 = 42.2; p<0.001). Promoter polymorphisms -590 C>T and -34 C>T also differed significantly among the studied malarial sub groups (χ2 4 = 19.5; p<0.001 and χ2 4 = 25.3; p<0.001). Similarly, allele distributions also differed significantly among these groups (intron-3 VNTR: χ2 2 = 30.3; p<0.001, -590 C>T χ2 2 = 13.6; p<0.001 and -34 C>T χ2 2 = 11.3; p = 0.003). All three studied loci were in HW equilibrium and were in strong LD (r2>0.75) (Figure 2) with two major haplotypes, CCR3 and TTR2 identified (Table S2). Therefore, analysis has been performed only with VNTR polymorphism or the resulting haplotypes. Significant difference has been observed in the distribution of these haplotypes between cases and asymptomatic control (OR = 0.552, 95% CI = 0.356−0.854, p = 0.009) (Table S2) with TTR2 as protective haplotype.
Table 3. Distribution of IL4 genotypes and alleles in patients with malaria and in asymptomatic controls.
| SNP ID and Polymorphism | Genotype (%) | Genotype Comparison | Allele (%) | Allele Comparison | |||||
| ?2 4 | P-value | ?2 2 | P-value | ||||||
| rs79071878, R2/R3 | R2R2 | R2R3 | R3R3 | R2 | R3 | ||||
| Asymptomatic | 19 (12.2) | 89 (57.1) | 48 (30.8) | 127 (40.7) | 185 (59.3) | ||||
| Mild Malaria | 4 (4.0) | 31 (30.7) | 66 (65.3) | 39 (19.3) | 163 (80.7) | ||||
| Severe Malaria | 20 (11.6) | 51 (29.5) | 102 (59.0) | 42.2 | <0.001 | 91 (26.3) | 255 (73.7) | 30.3 | <0.001 |
| rs2070874, -34C/T | TT | TC | CC | T | C | ||||
| Asymptomatic | 15 (9.6) | 83 (53.2) | 58 (37.2) | 113 (36.2) | 199 (63.8) | ||||
| Mild Malaria | 2 (2.0) | 39 (38.6) | 60 (59.4) | 43 (21.2) | 159 (78.7) | ||||
| Severe Malaria | 19 (11.0) | 54 (31.2) | 100 (57.8) | 25.3 | <0.001 | 92 (26.6) | 254 (73.4) | 13.6 | <0.001 |
| rs2243250, -590 C/T | TT | TC | CC | T | C | ||||
| Asymptomatic | 15 (9.6) | 80 (51.3) | 61 (39.1) | 110 (35.3) | 202 (64.7) | ||||
| Mild Malaria | 4 (4.0) | 37 (36.6) | 60 (59.4) | 45 (22.3) | 157 (77.7) | ||||
| Severe Malaria | 19 (11) | 54 (31.2) | 100 (57.8) | 19.5 | <0.001 | 92 (26.6) | 254 (73.4) | 11.3 | 0.003 |
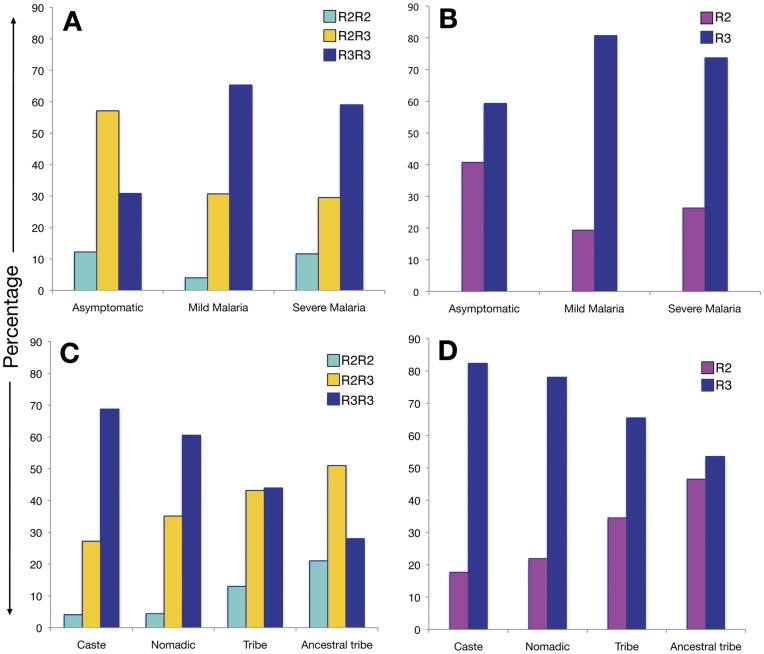
Figure 1. Distribution of IL-4 intron-3 VNTR polymorphism.
A and B: genotype and allelic distribution between malaria case control groups, respectively; C and D: genotype and allelic distribution among caste, nomadic, tribe and ancestral tribe, respectively.
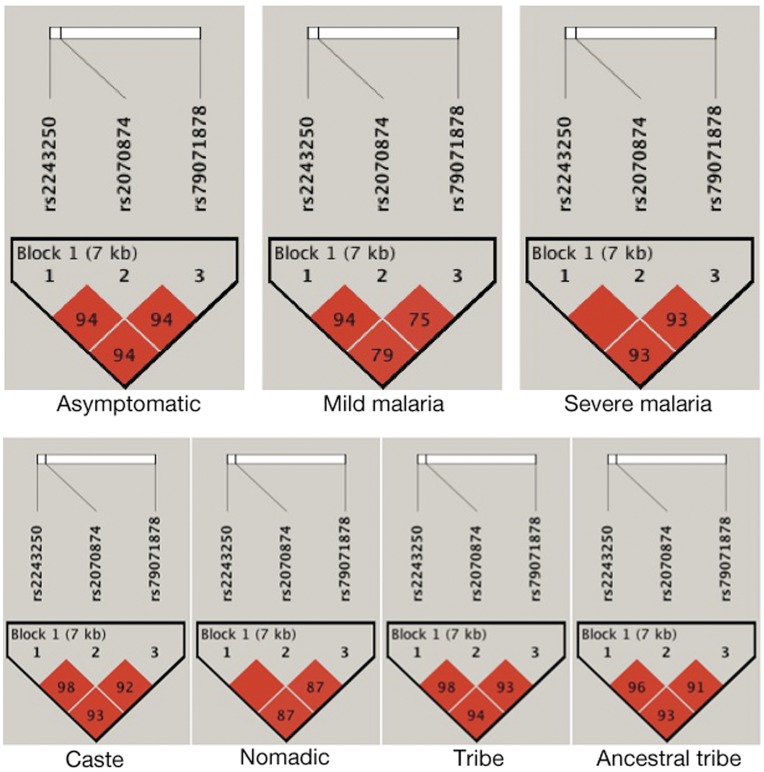
Figure 2. Linkage Disequilibrium (LD) of studied IL-4 loci (-590 C/T, -34 C/T and intron-3 VNTR) in malaria case control and Indian population groups.
The three studied SNPs are in strong LD (r2>0.75, malaria case control groups; r2>0.87, population groups).
Post-hoc analysis of chi-square contingency-table test showed over representation of genotype R3R2 (57.1%; z score = 5.5) and under representation of R3R3 (30.8%; z score = −6.1) genotypes in asymptomatic control; while over representation of R3R3 [(mild, 65.3%; z score = 3.5), (severe, 59.0%; z score = 3.0)] and under representation of R2R3 [(mild, 30.7%; z score = −2.1), (severe, 29.5%; z score = −3.6)] and R2R2 [(mild, 4%; z score = −2.3) (severe, 59.0%; z score = 0.9)] in mild and severe malaria group and mainly contributes to the Chi-square [(Figure 1), (Table S1)]. Comparison of mild and severe malaria genotype distribution shows non-significant difference between these two groups χ2 2 = 4.6; p = 0.097; while significant difference was observed between asymptomatic vs. mild (χ2 2 = 30.2; p<0.001) and asymptomatic vs. severe malaria (χ2 2 = 28.9; p<0.001) (Table 4). Since it has been reported that TT homozygous and CT heterozygous at position -590 and -34, R2R2 and R2R3 genotype leads to higher serum IL-4 level [22], we pooled R2R2 and R2R3 for further analysis. Again, comparison of R2R2+R2R3 vs. R3R3 between various groups show statistically significant difference, except between mild and severe malaria χ2 1 = 1.1 p = 0.293 (Table 4). Therefore, we pooled mild and severe group together and compared with asymptomatic control, which came out to be highly significant [χ2 1 = 35.8; OR = 3.566, 95% CI = 2.348–5.416 p<0.001] (Table 4).
Table 4. Genotype comparison among various groups of malaria case control and population study in multiple stages.
| Group 1 Vs. Group 2 | R2R2, R2R3, R3R3 | (R2R2+R2R3) Vs. R3R3 | |||
| ?2 2 | p-value | ?2 1 | p-value | ||
| Malaria case-control groups | |||||
| Asymptomatic | Mild Malaria | 30.2 | <0.001 | 28.3 | <0.001 |
| Asymptomatic | Severe Malaria | 28.9 | <0.001 | 25.1 | <0.001 |
| Mild Malaria | Severe Malaria | 4.6 | 0.097 | 1.1 | 0.293 |
| Asymptomatic | Pooled Cases | 38.0 | <0.001 | 35.8 | <0.001* |
| Population groups | |||||
| Caste | Nomadic | 3.48 | 0.175 | 2.9 | 0.08 |
| Caste | Tribe | 118.9 | <0.001 | 101.4 | <0.001 |
| Caste | ATP | 482.5 | <0.001 | 437.9 | <0.001 |
| Tribe | ATP | 44.32 | <0.001 | 40.0 | <0.001 |
OR = 3.566, 95% CI = 2.348–5.416;
As the proportion of male sample were higher in asymptomatic as well as in case groups, we further analyzed the distribution of R2/R3 in these groups for the possible effect of sex stratification. The frequency of protective allele R2 was found significantly lower in both the male and female groups of mild and severe malaria compared to asymptomatic control and rule out the possibility of sex stratification (Table S3).
Association of Haplotype TTR2 with Ancestral and Tribal Indian Population
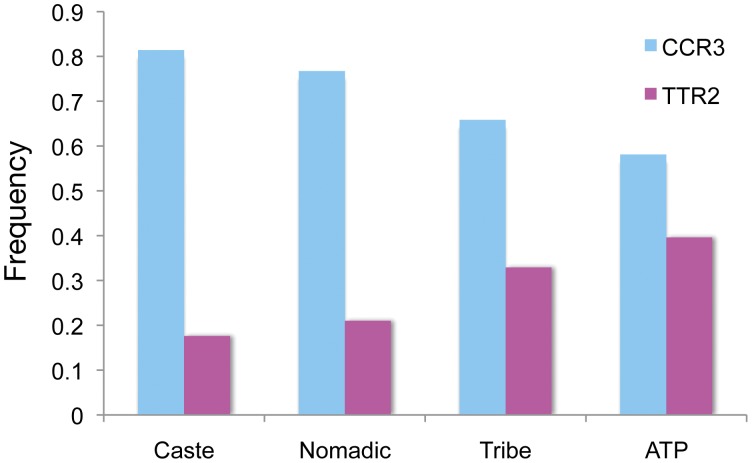
Among 3613 individuals from a total of 76 endogamous Indian ethnic populations investigated, we found striking pattern of genotype prevalence based on their social status and inhabitation. Most of the studied populations were in HW equilibrium (Table 5) and those, which were not in HW, were excluded for further analysis. Based on their social status, inhabitation, co-ancestry coefficient and pairwise Fst (Figure S2), we initially grouped these populations into three groups; namely, caste, nomadic and tribal populations. Caste is further grouped in to traditionally upper, middle and lower caste populations to see if there is any difference between these groups. Our study did not find any significant difference in genotype distribution among these groups (Figure S3). Further, tribal group has been divided into two groups the tribe (started agriculture recently) and the ancestral tribal population [(ATP), which includes all hunter-gatherer tribal populations]. The genotype distribution of these three loci (-590C/T, -34C/T and the intron-3 VNTR) differed significantly among the four classified sub groups (χ2 6 = 501.1; p<0.001, χ2 6 = 326.9; p<0.001 and χ2 6 = 323.2; p<0.001) respectively (Table 6). In addition, allelic distributions differed also significantly (Table 6). We found these markers in strong LD having r2>0.87 (Figure 2) with significant difference in haplotype distribution among these four subgroups (χ2 3 = 182.95, p-value <0.001) (Table S2). The protective haplotype TTR2 has been found to be highest in ATP (40.5%); intermediate in tribes (33%); and lowest in caste (17.8%) and nomadic (21.6%) (Figure 3).
Table 5. Social status, geographical origin, ethnicity, linguistic affiliation and HW equilibrium of Indian populations included in present study.
| S. No. | Population | SocialDesignation | LanguageFamily | State | SampleSize | R2R2(%) | R2R3(%) | R3R3(%) | Obs.Het. | Exp.Het. | P-value |
| 1 | Kapu | Caste | Dravidian | Andhra Pradesh | 57 | 2(3.51) | 17(29.82) | 38(66.67) | 0.298 | 0.303 | 1 |
| 2 | Reddy | Caste | Dravidian | Andhra Pradesh | 56 | 1(1.79) | 14(25) | 41(73.21) | 0.25 | 0.247 | 1 |
| 3 | Vysya | Caste | Dravidian | Andhra Pradesh | 48 | 0(0) | 8(16.67) | 40(83.33) | 0.167 | 0.154 | 1 |
| 4 | Yadav | Caste | Dravidian | Pudduchery | 48 | 1(2.08) | 7(14.58) | 40(83.33) | 0.146 | 0.171 | 0.3365 |
| 5 | Achari | Caste | Dravidian | Tamil Nadu | 71 | 3(4.23) | 17(23.94) | 51(71.83) | 0.239 | 0.273 | 0.3714 |
| 6 | Gugavellar | Caste | Dravidian | Tamil Nadu | 68 | 1(1.47) | 11(16.18) | 56(82.35) | 0.161 | 0.174 | 0.4696 |
| 7 | Lingayat | Caste | Dravidian | Tamil Nadu | 47 | 1(2.13) | 12(25.53) | 34(72.34) | 0.255 | 0.256 | 1 |
| 8 | Muppanar | Caste | Dravidian | Tamil Nadu | 15 | 1(6.67) | 4(26.67) | 10(66.67) | 0.267 | 0.331 | 0.4612 |
| 9 | Muthaliar | Caste | Dravidian | Tamil Nadu | 43 | 3(6.98) | 11(25.58) | 29(67.44) | 0.256 | 0.319 | 0.0855 |
| 10 | Pillai | Caste | Dravidian | Tamil Nadu | 79 | 4(5.1) | 17(21.52) | 58(73.42) | 0.215 | 0.266 | 0.2676 |
| 11 | Sonakar | Caste | Indo-European | Chhattisgarh | 41 | 0(0) | 11(26.83) | 30(73.17) | 0.268 | 0.235 | 1 |
| 12 | Lohana | Caste | Indo-European | Gujarat | 46 | 1(2.17) | 11(23.91) | 34(73.91) | 0.239 | 0.245 | 1 |
| 13 | Tadavi | Caste | Indo-European | Gujarat | 22 | 0(0) | 8(36.36) | 14(63.64) | 0.363 | 0.301 | 0.3141 |
| 14 | Bania | Caste | Indo-European | Hariyana | 34 | 1(2.94) | 10(29.41) | 23(67.65) | 0.294 | 0.295 | 1 |
| 15 | Pandit | Caste | Indo-European | Hariyana | 15 | 1(6.67) | 3(20) | 11(73.33) | 0.2 | 0.287 | 0.3250 |
| 16 | SC | Caste | Indo-European | Hariyana | 40 | 2(5) | 11(27.5) | 27(67.5) | 0.275 | 0.308 | 0.5995 |
| 17 | Kamboj | Caste | Indo-European | Haryana | 100 | 0(0) | 30(30) | 70(70) | 0.3 | 0.256 | 0.1169 |
| 18 | KashGujjar | Caste | Indo-European | Kashmir | 44 | 3(6.81) | 12(27.27) | 29(65.91) | 0.273 | 0.315 | 0.6439 |
| 19 | KashMushlim | Caste | Indo-European | Kashmir | 57 | 2(3.51) | 21(36.84) | 34(59.65) | 0.368 | 0.345 | 1 |
| 20 | KashPandit | Caste | Indo-European | Kashmir | 47 | 2(4.26) | 14(29.79) | 31(65.96) | 0.298 | 0.312 | 0.6604 |
| 21 | Baghel | Caste | Indo-European | Madhya Pradesh | 35 | 0(0) | 13(37.14) | 22(62.86) | 0.371 | 0.307 | 0.5678 |
| 22 | Silawat | Caste | Indo-European | Madhya Pradesh | 90 | 6(6.67) | 31(34.44) | 53(58.89) | 0.344 | 0.383 | 0.8623 |
| 23 | Jatav | Caste | Indo-European | Rajasthan | 36 | 3(8.33) | 10(27.78) | 23(63.89) | 0.2778 | 0.351 | 0.3241 |
| 24 | Kurmi | Caste | Indo-European | Rajasthan | 56 | 3(5.36) | 14(25) | 39(69.64) | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.3502 |
| 25 | Meena | Caste | Indo-European | Rajasthan | 41 | 1(2.44) | 9(21.95) | 31(75.61) | 0.219 | 0.235 | 0.5384 |
| 26 | Brahmins | Caste | Indo-European | Uttar Pradesh | 59 | 2(3.39) | 14(23.73) | 43(72.88) | 0.237 | 0.261 | 0.6056 |
| 27 | Kshatriya | Caste | Indo-European | Uttar Pradesh | 40 | 1(2.5) | 8(20) | 31(77.5) | 0.2 | 0.221 | 0.4732 |
| 28 | Khatri | Caste | Indo-European | Punjab | 30 | 2(6.67) | 8(26.67) | 20(66.67) | 0.267 | 0.325 | 0.3060 |
| 29 | Bisht | Caste | Indo-European | Uttarakhand | 45 | 1(2.22) | 9(20) | 35(77.78) | 0.2 | 0.217 | 0.5007 |
| 30 | Rawat | Caste | Indo-European | Uttarakhand | 87 | 10(11.49) | 34(39.08) | 43(49.43) | 0.391 | 0.430 | 0.4571 |
| 31 | Darj_caste | Caste | Indo-European | West Bengal | 32 | 3(9.3) | 14(43.75) | 15(46.88) | 0.437 | 0.448 | 0.6923 |
| 32 | Thapa | Caste | Tibeto-Burman | Nepal | 39 | 3(7.69) | 13(33.33) | 23(58.97) | 0.333 | 0.373 | 0.6607 |
| 33 | Banjara | Nomadic | Indo-European | Rajasthan | 42 | 1(2.38) | 14(33.33) | 27(64.29) | 0.333 | 0.312 | 1 |
| 34 | NariKuruwar | Nomadic | Indo-European | Tamil Nadu | 72 | 4(5.56) | 26(36.11) | 42(58.33) | 0.361 | 0.363 | 1 |
| 35 | BodoGadaba | ATP | Austro-Asiatic | Andhra Pradesh | 39 | 4(10.26) | 26(66.67) | 9(23.08) | 0.667 | 0.498 | 0.0501 |
| 36 | Chenchu | ATP | Austro-Asiatic | Andhra Pradesh | 45 | 7(15.56) | 17(37.78) | 21(46.67) | 0.378 | 0.457 | 0.3213 |
| 37 | Asur | ATP | Austro-Asiatic | Jharkhand | 45 | 6(13.33) | 23(51.11) | 16(35.56) | 0.511 | 0.481 | 0.7568 |
| 38 | Bhumij | ATP | Austro-Asiatic | Jharkhand | 91 | 14(15.38) | 42(46.15) | 35(38.46) | 0.461 | 0.476 | 0.8257 |
| 39 | Birhor | ATP | Austro-Asiatic | Jharkhand | 59 | 10(16.95) | 27(45.76) | 22(37.29) | 0.457 | 0.483 | 0.7860 |
| 40 | Kharia | ATP | Austro-Asiatic | Jharkhand | 41 | 4(9.76) | 22(53.66) | 15(36.59) | 0.536 | 0.470 | 0.5009 |
| 41 | Parharia | ATP | Austro-Asiatic | Jharkhand | 19 | 7(36.84) | 11(57.89) | 1(5.26) | 0.579 | 0.462 | 0.3436 |
| 42 | Saharia | ATP | Austro-Asiatic | Madhya Pradesh | 30 | 3(10) | 17(56.67) | 10(33.33) | 0.567 | 0.481 | 0.4446 |
| 43 | Bondo | ATP | Austro-Asiatic | Orissa | 40 | 8(20) | 24(60) | 8(20) | 0.6 | 0.506 | 0.3411 |
| 44 | Didayi | ATP | Austro-Asiatic | Orissa | 30 | 8(26.67) | 11(36.67) | 11(36.67) | 0.366 | 0.503 | 0.1575 |
| 45 | Andamani | ATP | Andamanese | Andaman | 18 | 1(5.56) | 9(50) | 8(44.44) | 0.5 | 0.436 | 1 |
| 46 | KondaReddy | ATP | Dravidian | Andhra Pradesh | 15 | 4(26.67) | 7(46.67) | 4(26.67) | 0.466 | 0.517 | 1 |
| 47 | KondaSavara | ATP | Dravidian | Andhra Pradesh | 93 | 37(39.78) | 52(55.91) | 4(4.3) | 0.559 | 0.439 | 0.0890 |
| 48 | Porja | ATP | Dravidian | Andhra Pradesh | 69 | 23(33.33) | 32(46.38) | 14(20.29) | 0.463 | 0.495 | 0.6314 |
| 49 | Kattunayakan | ATP | Dravidian | Kerala | 47 | 4(8.51) | 22(46.81) | 21(44.68) | 0.468 | 0.439 | 0.7444 |
| 50 | Paniyas | ATP | Dravidian | Kerala | 33 | 7(21.21) | 20(60.61) | 6(18.18) | 0.606 | 0.507 | 0.3072 |
| 51 | Kuruman | ATP | Dravidian | Kerela | 25 | 7(28) | 12(48) | 6(24) | 0.48 | 0.509 | 1 |
| 52 | Kurumba | ATP | Dravidian | Tamil Nadu | 43 | 3(6.98) | 21(48.84) | 19(44.19) | 0.488 | 0.436 | 0.4959 |
| 53 | Kathodi | ATP | Indo-European | Gujarat | 10 | 2(20) | 4(40) | 4(40) | 0.4 | 0.505 | 0.5729 |
| 54 | Kotwali | ATP | Indo-European | Gujarat | 100 | 10(10) | 52(52) | 38(38) | 0.52 | 0.463 | 0.2806 |
| 55 | Katkari | ATP | Indo-European | Maharashtra | 16 | 6(37.5) | 6(37.5) | 4(25) | 0.375 | 0.508 | 0.3476 |
| 56 | Baiga | ATP | Indo-European | Madhya Pradesh | 60 | 9(15) | 40(66.67) | 11(18.33) | 0.666 | 0.503 | 0.0188 |
| 57 | Buxa | ATP | Indo-European | Uttar Pradesh | 46 | 13(28.26) | 26(56.52) | 7(15.22) | 0.565 | 0.497 | 0.3806 |
| 58 | Onge | ATP | Jarwa-Onge | Andaman_nikobar | 11 | 3(27.27) | 7(63.64) | 1(9.09) | 0.636 | 0.506 | 0.5532 |
| 59 | Mizo | ATP | Tibeto-Burman | Mizoram | 15 | 8(53.33) | 6(40) | 1(6.67) | 0.4 | 0.404 | 1 |
| 60 | AoNaga | ATP | Tibeto-Burman | Nagaland | 34 | 17(50) | 12(35.29) | 5(14.71) | 0.352 | 0.425 | 0.2575 |
| 61 | Juang | ATP | Tibeto-Burman | Orissa | 69 | 15(21.74) | 35(50.72) | 19(27.54) | 0.507 | 0.502 | 1 |
| 62 | Korku | Tribe | Austro-Asiatic | Madhya Pradesh | 42 | 6(14.29) | 19(45.24) | 17(40.48) | 0.452 | 0.471 | 1 |
| 63 | Koia | Tribe | Dravidian | Andhra Pradesh | 86 | 6(6.97) | 40(46.51) | 40(46.51) | 0.465 | 0.422 | 0.6098 |
| 64 | Kotiya | Tribe | Dravidian | Andhra Pradesh | 23 | 7(30.43) | 11(47.83) | 5(21.74) | 0.478 | 0.507 | 1 |
| 65 | Oddari | Tribe | Dravidian | Andhra Pradesh | 19 | 2(10.53) | 6(31.58) | 11(57.89) | 0.316 | 0.398 | 0.5492 |
| 66 | Halaki | Tribe | Dravidian | Karnataka | 36 | 1(2.78) | 14(38.89) | 21(58.33) | 0.389 | 0.350 | 0.6563 |
| 67 | Malayan | Tribe | Dravidian | Kerala | 41 | 5(12.2) | 21(51.22) | 15(36.59) | 0.512 | 0.476 | 0.7435 |
| 68 | Muthan | Tribe | Dravidian | Kerala | 61 | 7(11.47) | 24(39.34) | 30(49.18) | 0.393 | 0.429 | 0.2782 |
| 69 | Kolcha | Tribe | Indo-European | Gujarat | 59 | 2(3.39) | 30(50.85) | 27(45.76) | 0.508 | 0.413 | 0.1119 |
| 70 | MahadeoKoli | Tribe | Indo-European | Maharashtra | 51 | 8(15.69) | 23(45.1) | 20(39.22) | 0.451 | 0.476 | 0.7695 |
| 71 | Tharu | Tribe | Indo-European | Uttarakhand | 48 | 11(22.92) | 20(41.67) | 17(35.42) | 0.417 | 0.497 | 0.3758 |
| 72 | Nyshi | Tribe | Tibeto-Burman | Arunachal Pradesh | 10 | 8(80) | 2(20) | 0(0) | 0.2 | 0.189 | 1 |
| 73 | Darj_tribe | Tribe | Tibeto-Burman | West Bengal | 11 | 3(27.27) | 5(45.45) | 3(27.27) | 0.455 | 0.523 | 1 |
| 74 | Malaikuruwar | ATP | Dravidian | Tamil Nadu | 62 | 4(6.45) | 5(8.06) | 53(85.48) | 0.081 | 0.189 | 0.0006 |
| 75 | Toda | ATP | Dravidian | Tamil Nadu | 48 | 3(6.25) | 3(6.25) | 42(87.50) | 0.062 | 0.171 | 0.0014 |
| 76 | Ulladan | Tribe | Dravidian | Kerala | 30 | 1(3.3) | 8(26.66) | 21(70.00) | 0.266 | 0.278 | 0.1613 |
R2: Two Repeat of IL-4 intro-3 VNTR, R3: Three repeat, ATP: Ancestral Tribal Population, Obs.Het : Observed heterozygocity, Exp.Het : Expected heterozygocity, P-value in bold shows departure from HW equilibrium at 0.05 level.
Table 6. Genotype and allele distribution of IL-4 intron-3 VNTR polymorphism, -34CT and -590CT in various groups of Indian population.
| Genotype (%) | Genotypic Comparison | Allele (%) | |||||||
| ?2 6 | p-value | ?2 3 | p-value | ||||||
| rs79071878, R2/R3 | R2R2 | R2R3 | R3R3 | R2 | R3 | ||||
| Caste | 64 (4.1) | 426 (27.2) | 1078 (68.8) | 554 (17.7) | 2582 (82.3) | ||||
| Nomadic | 5 (4.4) | 40 (35.1) | 69 (60.5) | 50 (21.9) | 178 (78.1) | ||||
| Tribe | 67 (13.0) | 223 (43.1) | 227 (43.9) | 357 (34.5) | 677 (65.5) | ||||
| ATP | 240 (21.0) | 583 (51.0) | 320 (28.0) | 501.1 | <0.001 | 1063 (46.5) | 1223 (53.5) | 537.6 | <0.001 |
| rs2070874, -34 C/T | TT | TC | CC | T | C | ||||
| Caste | 67 (4.4) | 443 (28.2) | 1058 (67.4) | 577 (18.4) | 2559 (81.6) | ||||
| Nomadic | 6 (5.3) | 39 (34.2) | 69 (60.5) | 51 (22.4) | 177 (77.6) | ||||
| Tribe | 63 (12.2) | 239 (46.2) | 215 (41.6) | 365 (35.3) | 669 (64.7) | ||||
| ATP | 205 (17.9) | 519 (45.4) | 419 (36.7) | 323.2 | <0.001 | 929 (40.6) | 1357 (59.4) | 347.9 | <0.001 |
| rs2243250, -590 C/T | TT | TC | CC | T | C | ||||
| Caste | 71 (4.5) | 439 (28.0) | 1058 (67.5) | 581 (18.5) | 2555 (81.5) | ||||
| Nomadic | 6 (5.3) | 39 (34.2) | 69 (60.5) | 51 (22.4) | 177 (77.6) | ||||
| Tribe | 63 (12.2) | 236 (45.6) | 218 (42.2) | 362 (35.0) | 672 (65.0) | ||||
| ATP | 212 (18.5) | 514 (45.0) | 417 (36.5) | 326.9 | <0.001 | 938 (41.0) | 1348 (59.0) | 351.4 | <0.001 |
ATP: ancestral tribal population.
Figure 3. Haplotype distribution among various Indian social groups.
The prevalence of protective haplotype TTR2 is significantly higher in ancestral tribal populations.
The genotype proportions between caste and nomadic did not differ significantly χ2 2 = 3.48; p = 0.175, however, it differ significantly between caste vs. tribe; caste vs. ATP; and tribe vs. ATP with χ2 2 = 118.9; p<0.001, χ2 2 = 482.5; p<0.001 and χ2 2 = 44.32; p<0.001, respectively (Table 4). We have also pooled R2R2 and R2R3 genotype together in agreement with higher IL-4 serum level [27] and compared with R3R3 genotype and found significant difference in genotype distribution between caste vs. tribe; caste vs. ATP; and tribe vs. ATP pairs with χ2 1 = 101.4; p<0.001, χ2 1 = 437.9; p<0.001 and χ2 1 = 40.0; p<0.001, respectively (Table 4). Post-hoc analysis of chi-square contingency-table test result show over representation of genotype R3R3 (68.8%; z score = 19.6) and under representation of genotype R2R3 (27.2%; z score = −12.2) and R2R2 (4.1%; z score = −12.3) in caste while ancestral population ATP showed over representation of R2R3 (51.0%; z score = 11.1) and R2R2 (21.0%; z score = 12.9) and under representation of R3R3 (28.0%; z score = −18.9) genotype. Tribal group showed intermediate of caste and ATP [(R2R2, 13%; z score = 1.3), (R2R3, 43.1%; z score = 2.6), (R2R2, 43.9%; z score = −3.4)] (Figure 1) (Table S1).
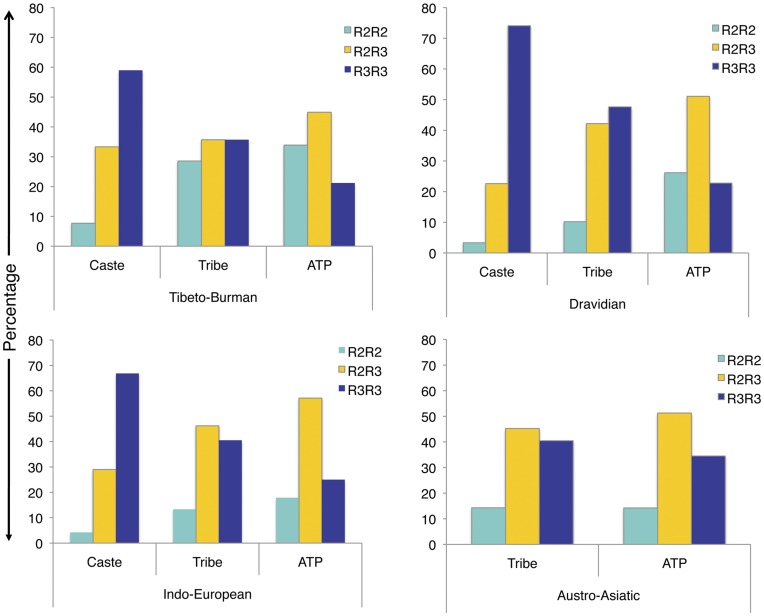
Since there are four major linguistic families in India, we classified the samples in to four groups, namely; Indo-European (IE), Dravidian (DV), Austro-Asiatic (AA) and Tibeto-Burman (TB). Each linguistic family has been further classified in to caste, tribe and ATP. Interestingly, the difference in genotype distribution among caste, tribe and ATP follow the same pattern as of TTR2 haplotype distribution in ATP (highest), tribe and caste (lowest) populations (Figure 4).
Figure 4. Genotype distribution of IL-4 intron-3 VNTR polymorphism in four linguistic families of Indian populations.
Geographical Distribution of IL-4 Variants
Comparison of all three studied variants to other world populations (Syria, Brazilian and Vietnamese) revealed diverse geographical patterns. We retrieved earlier reported data and compared with Indian population. We found Vietnamese has very high R2R2 (65.7%) genotype frequency, similar to other Southeast Asian countries. However, R2R2 genotype frequency in Syrian and Brazilian were only 4.8% and 6%, respectively (Figure S4).
Discussion
We have screened the regulatory polymorphisms of IL-4 promoter region (rs2243250, -590CT and rs2070874, -34 CT) and intron-3 repeat region (rs79071878, 70 bp VNTR) to investigate their possible role in survival against disease and pathogen or infection employing three different approaches: (1) case-control malaria cohort from Orissa and Chhattisgarh, the malaria endemic regions of India; (2) a comprehensive assessment in seventy-six ethnically, linguistically and geographically diverse populations inhabited across India; and (3) evaluation of samples from Brazil, Syria and Vietnam and comparison of results with Indian populations.
We observed significant difference in genotype and allele frequency distribution along with haplotype carriage between three groups of malaria case-control study. However, mild and severe groups do not differ among themselves; they differ significantly when compared to asymptomatic control. We also found these regulatory markers are in strong LD (r2>0.75) and carriage of the resultant haplotype TTR2 with asymptomatic and CCR3 with malaria cases (OR = 0.552, 95%CI = 0.356–0.854, p = 0.009) (Table S2). Malaria outcome is the result of complex interaction of a large number of factors and the pathogenesis might be regulated by various mechanisms. However, our findings show that the high IL-4 producing haplotype TTR2 protects or increases survival against Plasmodium falciparum malaria. It has been reported that the carriers of TT with cerebral malaria had elevated total IgE compared to non-carriers and suggested that the IL-4 play a regulatory role in the pathogenesis of malaria in Ghanaian children [8]. Further, association between IL-4 -590T allele and lower prevalence of Plasmodium falciparum infection in asymptomatic Fulani population of Mali has been documented [36]. Several findings have shown association of -590T, -34T and intron-3 VNTR polymorphism R2 with high level of serum IL-4 and consequent high level of total IgG, IgE, anti-plasmodium IgG and IgE, and severity of infection in several populations of malaria endemic region across the globe [16], [17], [18], [19], [21], [22], [23], [24], [25], [37].
It has been established that the high level of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IFN-γ) produced during malaria infection leads to severe pathogenesis [38], [39], [40], [41], [42], [43]. These cytokine up-regulates expressions of endothelial adhesion molecules (ICAM-1) in brain and kidney, which facilitates increased sequestration of parasitized RBC within the microvasculature of these organs [38], [39]. This increased sequestration of parasitized RBC leads to cerebral malaria and renal failure. Further, inhibitory effect of TNF-α on erythropoiesis and subsequent severe malarial pathogenesis has been demonstrated in human and mouse model of experimental cerebral malaria (ECM) [41], [42], [43]. In ECM mouse model, treatment with anti-inflammatory cytokine IFN-α and IFN-ß inhibited cerebral malaria and reduced the parasite burden [39], [40]. IFN-ß treatment down regulate pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-α, IFN-γ, ICAM-1, CXCL9 and CXCR3 [40]. These studies indicate, a check on pro-inflammatory cytokine by anti-inflammatory cytokine can lead to enhanced survival against Plasmodium falciparum malaria. This supports our finding that shows high IL-4 producing haplotype, TTR2, provide decreased susceptibility to Plasmodium infection.
In contrast to the general accepted view that IL-4 secreting CD4+ T cells are anti-inflammatory mediators and suppress pro-inflammatory response, CD4+ T cells has been found to be crucial to the development of pro-inflammatory CD8+ T cell response against Plasmodium sporozoite infected hepatocytes [44], [45], [46]. It has been observed that early development of protective circumsporozoite protein (CSP) specific CD8+ T cell originates in cutaneous lymphoid tissue of infected site and then migrate to other sites including liver [47], [48]. Development of this immunity requires IL-4 mediated cross talk of CD4/CD8 cells [44]. The CSP specific CD8+ T cells, which get primed in presence of IL-4 signals, differentiate into effector memory CD8+ T cells, whereas in absence of IL-4 the response fails to develop further after few days and reduced by more than 90% compared to that in presence of CD4+ T cells. These recent reports further support our findings [44].
In this study, among Indian populations, we found over-representation of R2R2 and R2R3 genotype in ATP while under-representation in caste and vice-versa. No significant difference in genotype or allele distribution has been found between caste and nomadic populations. Our Y-chromosomal markers based population study explains that this deviation from general perception is due to recent admixture and gene flow between the caste and nomadic populations (our unpublished data). However, significant difference has been found between all other groups. Every single Indian population maintain its unique genetic architecture; mainly due to endogamy marriage practice over the last thousands of year. This has been well supported by our earlier studies using mtDNA, Y chromosome and autosomal genetic markers [30], [31]. We found that these three markers are in strong LD (r2>0.87) with two main haplotypes TTR2 and CCR3. Distribution of protective haplotype TTR2 has been found significantly higher in ATP than tribe and caste while at intermediary in tribe. The ATPs are inhabited in isolated forest and they mainly practice hunter-gatherer lifestyle, hence, they are under constant exposure to helminthes and various other parasites. Therefore, positive selection [20] might be operating on IL-4 locus of the ATPs compared to caste populations, who practice modern lifestyle and expose to modern medicine.
This is the first study of its kind, where we studied the IL-4 variations in such a depth in diverse Indian populations. We also observed that a few populations (Bodo, Gadaba, Baiga, Toda, Malai Kuruwar) are significantly departs from HW equilibrium, which might be the result of positive selection or founder effect as their population size are very small and follow very strict endogamy practice.
Apart from its role in controlling malaria and other pathogenic disease, the IL-4 polymorphisms (-590T, -34T and intron-3 VNTR R2) have been found to be associated with end stage renal disease, multiple sclerosis, autoimmune Grave’s disease, polyarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, rhinitis and atopic dermatitis [21], [26], [27], [28], [29]. This Th2 response also mediates inflammatory response to helminth infection [49]. This indicates ATP and tribal populations not only have more survival potential against autoimmune and allergic disease but also against extracellular helminthic infection then the caste populations.
In conclusion, IL-4 -590T, -34T and intron-3 VNTR R2 allele is associated with enhanced survival against malaria and other extracellular pathogens in Indian populations. However, their role needs to be assessed further for other infectious, inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. This observation may assist in finding individuals at high risk and hence, disease management. These linked marker along with other markers being in LD can cause balance shift of cytokine profile and hence TH1 and TH2 response in an individual up to an extent, where it can be deleterious also. Thus, a delicate balance of various cytokine is more important than the specific one. Hence, for detailed understanding, other regulators need to be studied among Indian populations. Our study also emphasize the importance of host genetics in resistance/susceptibility to infectious disease.
Supporting Information
Multiple sequence alignment of IL4 intron-3 VNTR (70 bp repeat) region of six primates. Mostly two and three copies of repeats has been observed in humans, whereas only a single copy of 70 bp repeat has been observed in other primates (www.ensembl.org).
(TIF)
Pairwise Fst matrix of 76 studied ethnically, geographically and linguistically different Indian populations.
(TIF)
Comparison of IL-4 intron-3 VNTR R2/R3 genotype distribution among various caste populations (upper, middle and lower caste).
(TIF)
Frequency of three studied loci (-590 C/T, -34 C/T and intron-3 VNTR) in the present study and various world populations. *Present study
(TIF)
Post-hoc analysis of chi-square contingency-table test showing adjusted residual (z-score) value in malaria case control and population groups.
(DOC)
Haplotype frequency distribution among various groups of malaria case control and population study.
(DOC)
Comparison of IL4 intron-3 VNTR polymorphism R2/R3 between patient and asymptomatic group, stratified by sex
(DOC)
Acknowledgments
We thank all individuals who provided their blood sample and consent for genetic analysis. We would also like to thank Mr. A. G. Reddy and Mr. Rakesh Tamang, Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology, Hyderabad for their help and support.
Funding Statement
This work was supported by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, New Delhi(www.csir.res.in) [Senior research fellowship to ANJ, Bhatanagar Fellowship OLP0011 to LS] and UK-India Education and Research Initiative (www.ukieri.org) RG-4772 to KT. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1. Eid NA, Hussein AA, Elzein AM, Mohamed HS, Rockett KA, et al. (2010) Candidate malaria susceptibility/protective SNPs in hospital and population-based studies: the effect of sub-structuring. Malaria journal 9: 119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bairwa M, Rajput M, Khanna P, Rohilla R, Verma R, et al.. (2012) Malaria vaccine: A bright prospect for elimination of malaria. Human vaccines & immunotherapeutics 8. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 3. Driss A, Hibbert JM, Wilson NO, Iqbal SA, Adamkiewicz TV, et al. (2011) Genetic polymorphisms linked to susceptibility to malaria. Malaria journal 10: 271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Stevenson MM, Riley EM (2004) Innate immunity to malaria. Nature reviews Immunology 4: 169–180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Hill AV (1999) The immunogenetics of resistance to malaria. Proceedings of the Association of American Physicians 111: 272–277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Fell AH, Currier J, Good MF (1994) Inhibition of Plasmodium falciparum growth in vitro by CD4+ and CD8+ T cells from non-exposed donors. Parasite immunology 16: 579–586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Gowda NM, Wu X, Gowda DC (2012) TLR9 and MyD88 are crucial for the development of protective immunity to malaria. Journal of immunology 188: 5073–5085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Gyan BA, Goka B, Cvetkovic JT, Kurtzhals JL, Adabayeri V, et al. (2004) Allelic polymorphisms in the repeat and promoter regions of the interleukin-4 gene and malaria severity in Ghanaian children. Clinical and experimental immunology 138: 145–150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Murphy KM, Reiner SL (2002) The lineage decisions of helper T cells. Nature reviews Immunology 2: 933–944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Guo L, Hu-Li J, Zhu J, Watson CJ, Difilippantonio MJ, et al. (2002) In TH2 cells the Il4 gene has a series of accessibility states associated with distinctive probabilities of IL-4 production. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 99: 10623–10628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Banchereau J, Briere F, Galizzi JP, Miossec P, Rousset F (1994) Human interleukin 4. Journal of lipid mediators and cell signalling 9: 43–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Cabantous S, Poudiougou B, Oumar AA, Traore A, Barry A, et al. (2009) Genetic evidence for the aggravation of Plasmodium falciparum malaria by interleukin 4. The Journal of infectious diseases 200: 1530–1539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Tangteerawatana P, Pichyangkul S, Hayano M, Kalambaheti T, Looareesuwan S, et al. (2007) Relative levels of IL4 and IFN-gamma in complicated malaria: association with IL4 polymorphism and peripheral parasitemia. Acta tropica 101: 258–265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Burke TF, Casolaro V, Georas SN (2000) Characterization of P5, a novel NFAT/AP-1 site in the human IL-4 promoter. Biochemical and biophysical research communications 270: 1016–1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Rosenwasser LJ, Borish L (1997) Genetics of atopy and asthma: the rationale behind promoter-based candidate gene studies (IL-4 and IL-10). American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine 156: S152–155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Farouk SE, Dolo A, Bereczky S, Kouriba B, Maiga B, et al. (2005) Different antibody- and cytokine-mediated responses to Plasmodium falciparum parasite in two sympatric ethnic tribes living in Mali. Microbes and infection/Institut Pasteur 7: 110–117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Luoni G, Verra F, Arca B, Sirima BS, Troye-Blomberg M, et al. (2001) Antimalarial antibody levels and IL4 polymorphism in the Fulani of West Africa. Genes and immunity 2: 411–414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Verra F, Luoni G, Calissano C, Troye-Blomberg M, Perlmann P, et al. (2004) IL4–589C/T polymorphism and IgE levels in severe malaria. Acta tropica 90: 205–209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Marsh DG, Neely JD, Breazeale DR, Ghosh B, Friedhoff LR, et al.. (1995) Total serum IgE levels and chromosome 5q. Clinical and experimental allergy : journal of the British Society for Allergy and Clinical Immunology 25 Suppl 2: 79–83; discussion 95–76. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 20. Rockman MV, Hahn MW, Soranzo N, Goldstein DB, Wray GA (2003) Positive selection on a human-specific transcription factor binding site regulating IL4 expression. Current biology : CB 13: 2118–2123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Hunt PJ, Marshall SE, Weetman AP, Bell JI, Wass JA, et al. (2000) Cytokine gene polymorphisms in autoimmune thyroid disease. The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism 85: 1984–1988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Nakashima H, Miyake K, Inoue Y, Shimizu S, Akahoshi M, et al. (2002) Association between IL-4 genotype and IL-4 production in the Japanese population. Genes and immunity 3: 107–109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Perlmann H, Helmby H, Hagstedt M, Carlson J, Larsson PH, et al. (1994) IgE elevation and IgE anti-malarial antibodies in Plasmodium falciparum malaria: association of high IgE levels with cerebral malaria. Clinical and experimental immunology 97: 284–292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Perlmann P, Perlmann H, Flyg BW, Hagstedt M, Elghazali G, et al. (1997) Immunoglobulin E, a pathogenic factor in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Infection and immunity 65: 116–121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Perlmann P, Perlmann H, Looareesuwan S, Krudsood S, Kano S, et al. (2000) Contrasting functions of IgG and IgE antimalarial antibodies in uncomplicated and severe Plasmodium falciparum malaria. The American journal of tropical medicine and hygiene 62: 373–377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Kantarci OH, Schaefer-Klein JL, Hebrink DD, Achenbach SJ, Atkinson EJ, et al. (2003) A population-based study of IL4 polymorphisms in multiple sclerosis. Journal of neuroimmunology 137: 134–139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Mittal RD, Manchanda PK (2007) Association of interleukin (IL)-4 intron-3 and IL-6–174 G/C gene polymorphism with susceptibility to end-stage renal disease. Immunogenetics 59: 159–165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Buchs N, Silvestri T, di Giovine FS, Chabaud M, Vannier E, et al. (2000) IL-4 VNTR gene polymorphism in chronic polyarthritis. The rare allele is associated with protection against destruction. Rheumatology 39: 1126–1131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Vasudevan R, Norhasniza MN, Patimah I (2011) Association of variable number of tandem repeats polymorphism in the IL-4 gene with end-stage renal disease in Malaysian patients. Genetics and molecular research : GMR 10: 943–947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Reich D, Thangaraj K, Patterson N, Price AL, Singh L (2009) Reconstructing Indian population history. Nature 461: 489–494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Dhandapany PS, Sadayappan S, Xue Y, Powell GT, Rani DS, et al. (2009) A common MYBPC3 (cardiac myosin binding protein C) variant associated with cardiomyopathies in South Asia. Nature genetics 41: 187–191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Thangaraj K, Joshi MB, Reddy AG, Gupta NJ, Chakravarty B, et al. (2002) CAG repeat expansion in the androgen receptor gene is not associated with male infertility in Indian populations. Journal of andrology 23: 815–818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Excoffier L, Laval G, Schneider S (2005) Arlequin (version 3.0): an integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evolutionary bioinformatics online 1: 47–50. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ (2005) Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 21: 263–265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Beasley TM, Schumacker RE (1995) Multiple Regression Approach to Analyzing Contingency Tables: Post Hoc and Planned Comparison Procedures. The Journal of Experimental Education 64: 79–93. [Google Scholar]
- 36. Vafa M, Maiga B, Berzins K, Hayano M, Bereczky S, et al. (2007) Associations between the IL-4–590 T allele and Plasmodium falciparum infection prevalence in asymptomatic Fulani of Mali. Microbes and infection/Institut Pasteur 9: 1043–1048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Perlmann P, Perlmann H, ElGhazali G, Blomberg MT (1999) IgE and tumor necrosis factor in malaria infection. Immunology letters 65: 29–33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. van der Heyde HC, Nolan J, Combes V, Gramaglia I, Grau GE (2006) A unified hypothesis for the genesis of cerebral malaria: sequestration, inflammation and hemostasis leading to microcirculatory dysfunction. Trends in parasitology 22: 503–508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Vigario AM, Belnoue E, Gruner AC, Mauduit M, Kayibanda M, et al. (2007) Recombinant human IFN-alpha inhibits cerebral malaria and reduces parasite burden in mice. Journal of immunology 178: 6416–6425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Morrell CN, Srivastava K, Swaim A, Lee MT, Chen J, et al. (2011) Beta interferon suppresses the development of experimental cerebral malaria. Infection and immunity 79: 1750–1758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Chang KH, Stevenson MM (2004) Malarial anaemia: mechanisms and implications of insufficient erythropoiesis during blood-stage malaria. International journal for parasitology 34: 1501–1516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. McGuire W, Knight JC, Hill AV, Allsopp CE, Greenwood BM, et al. (1999) Severe malarial anemia and cerebral malaria are associated with different tumor necrosis factor promoter alleles. The Journal of infectious diseases 179: 287–290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Othoro C, Lal AA, Nahlen B, Koech D, Orago AS, et al. (1999) A low interleukin-10 tumor necrosis factor-alpha ratio is associated with malaria anemia in children residing in a holoendemic malaria region in western Kenya. The Journal of infectious diseases 179: 279–282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Carvalho LH, Sano G, Hafalla JC, Morrot A, Curotto de Lafaille MA, et al. (2002) IL-4-secreting CD4+ T cells are crucial to the development of CD8+ T-cell responses against malaria liver stages. Nature medicine 8: 166–170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Protzer U, Maini MK, Knolle PA (2012) Living in the liver: hepatic infections. Nature reviews Immunology 12: 201–213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Overstreet MG, Cockburn IA, Chen YC, Zavala F (2008) Protective CD8 T cells against Plasmodium liver stages: immunobiology of an ‘unnatural’ immune response. Immunological reviews 225: 272–283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Chakravarty S, Cockburn IA, Kuk S, Overstreet MG, Sacci JB, et al. (2007) CD8+ T lymphocytes protective against malaria liver stages are primed in skin-draining lymph nodes. Nature medicine 13: 1035–1041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Schmidt NW, Podyminogin RL, Butler NS, Badovinac VP, Tucker BJ, et al. (2008) Memory CD8 T cell responses exceeding a large but definable threshold provide long-term immunity to malaria. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 105: 14017–14022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Huber JP, Ramos HJ, Gill MA, Farrar JD (2010) Cutting edge: Type I IFN reverses human Th2 commitment and stability by suppressing GATA3. Journal of immunology 185: 813–817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Multiple sequence alignment of IL4 intron-3 VNTR (70 bp repeat) region of six primates. Mostly two and three copies of repeats has been observed in humans, whereas only a single copy of 70 bp repeat has been observed in other primates (www.ensembl.org).
(TIF)
Pairwise Fst matrix of 76 studied ethnically, geographically and linguistically different Indian populations.
(TIF)
Comparison of IL-4 intron-3 VNTR R2/R3 genotype distribution among various caste populations (upper, middle and lower caste).
(TIF)
Frequency of three studied loci (-590 C/T, -34 C/T and intron-3 VNTR) in the present study and various world populations. *Present study
(TIF)
Post-hoc analysis of chi-square contingency-table test showing adjusted residual (z-score) value in malaria case control and population groups.
(DOC)
Haplotype frequency distribution among various groups of malaria case control and population study.
(DOC)
Comparison of IL4 intron-3 VNTR polymorphism R2/R3 between patient and asymptomatic group, stratified by sex
(DOC)